The Influence of Mattress Stiffness on Spinal Curvature and Intervertebral Disc Stress—An Experimental and Computational Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
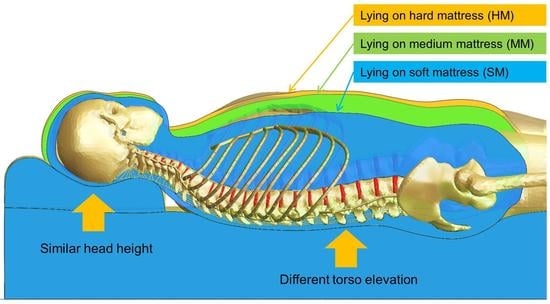
- Measurement of spinal curvature while lying in a supine position on different-stiffness mattresses.
- Computational simulation of contact pressure distribution.
- Investigating the internal stress of IVDs.
- Investigating the relationship between spinal curvature and musculoskeletal health.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Physical Experiment
2.1.1. Participants
2.1.2. Materials
2.1.3. Equipment
2.1.4. Experimental Procedures
2.2. Computational Simulation
2.2.1. Participant Information
2.2.2. Geometry Reconstruction
2.2.3. Ligaments
2.2.4. Sleeping Support System
2.2.5. Mesh
2.2.6. Material Property
2.2.7. Boundary and Loading Conditions
2.2.8. Model Validation
3. Results
3.1. Spinal Curvature
3.2. FE Predicted Pressure Distribution
3.3. IVD Peak Loading
4. Discussion
4.1. Findings
4.1.1. Changes in the Craniocervical Region
4.1.2. Changes in Lumbar Lordosis
4.1.3. Soft Tissue Deformation
4.1.4. Insufficient Upper Back Support
4.2. Limitations
4.3. Future Works
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, D.W.C.; Chen, T.L.W.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, M. Sleeping mattress determinants and evaluation: A biomechanical review and critique. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, A.; Fess, P.; James, D.; Murphy, J.; Myers, J.; Rooney, M.; Taylor, J.; Torii, A. Effect of different mattress designs on promoting sleep quality, pain reduction, and spinal alignment in adults with or without back pain; systematic review of controlled trials. Sleep Health 2015, 1, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaert, V.; Haex, B.; de Wilde, T.; Berckmans, D.; Verbraecken, J.; de Valck, E.; Vander Sloten, J. Ergonomics in bed design: The effect of spinal alignment on sleep parameters. Ergonomics 2011, 54, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanpied, P.R.; Gross, A.R.; Elliott, J.M.; Devaney, L.L.; Clewley, D.; Walton, D.M.; Sparks, C.; Robertson, E.K. Neck Pain: Revision 2017. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2017, 47, A1–A83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genebra, C.; Maciel, N.M.; Bento, T.P.F.; Simeao, S.; Vitta, A. Prevalence and factors associated with neck pain: A population-based study. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2017, 21, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chohan, A.; Ramli, K.; Cook, A.; May, K.; Selfe, J.; Richards, J. “Spinal alignment” cushion in the management of low back pain—A randomized controlled study. PRM 2019, 2, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, W.-K.; Chen, B.; Liu, R.-T.; Cheung, J.C.-W.; Wong, D.W.-C. Spine Posture, Mobility, and Stability of Top Mobile Esports Athletes: A Case Series. Biology 2022, 11, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaert, V.; Druyts, H.; van Deun, D.; Exadaktylos, V.; Verbraecken, J.; Vandekerckhove, M.; Haex, B.; Vander Sloten, J. Estimating spine shape in lateral sleep positions using silhouette-derived body shape models. Int. J. Ind. Ergonom. 2012, 42, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiba, Y.; Kamijo, M.; Inui, S.; Yoshida, H.; Shuimizu, Y. Study on relation between sleeping comfort and sleeping posture. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Kansei Engineering and Emotion Research, Paris, France, 2–4 March 2010; pp. 1656–1659. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, K.; Okamoto, M.; Hatsushikano, S.; Caseiro, G.; Watanabe, K. Difference in whole spinal alignment between supine and standing positions in patients with adult spinal deformity using a new comparison method with slot-scanning three-dimensional X-ray imager and computed tomography through digital reconstructed radiography. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 437. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Yang, J.H.; Chang, D.G.; Suk, S.I.; Suh, S.W.; Song, K.S.; Park, J.B.; Cho, W. Adult Spinal Deformity: Current Concepts and Decision-Making Strategies for Management. Asian Spine J. 2020, 14, 886–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haex, B. Back and Bed: Ergonomic Aspects of Sleeping; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-Y.; Wang, M.-J. Better combination of thickness and hardness of mattress topper for supine sleeping posture: A physiological measurements evaluation. Int. J. Ind. Ergonom 2020, 78, 102979. [Google Scholar]
- Leilnahari, K.; Fatouraee, N.; Khodalotfi, M.; Sadeghein, M.A.; Kashani, Y.A. Spine alignment in men during lateral sleep position: Experimental study and modeling. Biomed. Eng. Online 2011, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Radwan, A.; Ashton, N.; Gates, T.; Kilmer, A.; VanFleet, M. Effect of different pillow designs on promoting sleep comfort, quality, & spinal alignment: A systematic review. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 42, 101269. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.F.; Lee, Y.L.; Liang, J.C. Shape design of an optimal comfortable pillow based on the analytic hierarchy process method. J. Chiropr. Med. 2011, 10, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, S.; Wong, D.W.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, M. Effect of pillow height on the biomechanics of the head-neck complex: Investigation of the cranio-cervical pressure and cervical spine alignment. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, M.Y.; Jeong, H.; Lee, S.; Choi, W.; Park, J.H.; Tak, S.J.; Choi, D.H.; Yim, J. Improving the quality of sleep with an optimal pillow: A randomized, comparative study. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2014, 233, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barker, J.B.; Cronin, D. Multi-level Validation of a Male Neck Finite Element Model with Active Musculature. J. Biomech. Eng. 2020, 143, 011004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.D.; Saravana Kumar, G.; Yoganandan, N. Cervical spine morphology and ligament property variations: A finite element study of their influence on sagittal bending characteristics. J. Biomech. 2019, 85, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkhoo, M.; Cheng, C.H.; Wang, J.L.; Khoz, Z.; El-Rich, M.; Hebela, N.; Khalaf, K. Development and validation of a geometrically personalized finite element model of the lower ligamentous cervical spine for clinical applications. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 109, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafarparandeh, I.; Erbulut, D.U.; Lazoglu, I.; Ozer, A.F. Development of a finite element model of the human cervical spine. Turk. Neurosurg. 2014, 24, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chon, T.; Zhang, Y.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis subjected to different loads. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Bojairami, I.; El-Monajjed, K.; Driscoll, M. Development and validation of a timely and representative finite element human spine model for biomechanical simulations. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Kamijo, M.; Shimizu, Y. A study to investigate the sleeping comfort of mattress using finite element method. Kansei Eng. Int. J. 2012, 11, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.; Won, B.H.; Cho, S.W. Finite element modeling for predicting the contact pressure between a foam mattress and the human body in a supine position. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 20, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.B.; Kim, H.T.; Her, N.Y.; Lee, J.M. Variation of Mechanical Characteristics of Polyurethane Foam: Effect of Test Method. Materials 2019, 12, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, T.T.-H.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, G.; Wong, D.W.-C.; Zhang, M. Measurement of covered curvature based on a tape of integrated accelerometers. Measurement 2022, 193, 110959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, J.M.; Cawley, D.T. Spinal Anatomy: Modern Concepts; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gilroy, A.M.; MacPherson, B.R.; Wikenheiser, J.C.; Schuenke, M.; Schulte, E.; Schumacher, U. Atlas of Anatomy, 4th ed.; Thieme Stuttgart: New Youk, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Drake, R.; Vogl, A.W.; Mitchell, A.W.; Tibbitts, R.; Richardson, P. Gray’s Atlas of Anatomy E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, H.; Talischi, C.; Lopez-Pamies, O.; Paulino, G.H. Polygonal finite elements for finite elasticity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2015, 101, 305–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agnew, A.M.; Moorhouse, K.; Kang, Y.-S.; Donnelly, B.R.; Pfefferle, K.; Manning, A.X.; Litsky, A.S.; Herriott, R.; Abdel-Rasoul, M.; Bolte, J.H. The response of pediatric ribs to quasi-static loading: Mechanical properties and microstructure. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 2501–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizee, E.; Robin, S.; Song, E.; Bertholon, N.; le Coz, J.-Y.; Besnault, B.; Lavaste, F. Development of a 3D finite element model of the human body. SAE Trans. 1998, 107, 2760–2782. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.C.; Wilcox, R.K. Finite element analysis of the spine: Towards a framework of verification, validation and sensitivity analysis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2008, 30, 1287–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaresan, S.; Yoganandan, N.; Pintar, F.A. Finite element analysis of the cervical spine: A material property sensitivity study. Clin. Biomech. 1999, 14, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxenbaum, J.A.; Reddy, V.; Futterman, B. Anatomy, Back, Intervertebral Discs; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nouri, A.; Tetreault, L.; Singh, A.; Karadimas, S.K.; Fehlings, M.G. Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy: Epidemiology, Genetics, and Pathogenesis. Spine 2015, 40, E675–E693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.L.; Wong, D.W.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, M. Foot arch deformation and plantar fascia loading during running with rearfoot strike and forefoot strike: A dynamic finite element analysis. J. Biomech. 2019, 83, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratner, B. The correlation coefficient: Its values range between +1/−1, or do they? J. Target. Meas. Anal. Mark. 2009, 17, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Gao, D.; Chen, Q.; Hu, Z.; Guo, J. Effects of interface pressure distribution on human sleep quality. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.-D.; Lee, J.-U.; Park, J.; Kim, J. Analysis of the body pressure-related sensory changes in the static supine position for healthy science research: A randomized controlled pilot trial. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2015, 7, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wong, D.W.-C.; Chen, T.L.-W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yan, F.; Zhang, M. Influence of arch support heights on the internal foot mechanics of flatfoot during walking: A muscle-driven finite element analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 132, 104355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, N.; Little, J.P.; Christou, A.; Adams, M.A.; Adam, C.J.; Masouros, S.D. Biomechanics of the human intervertebral disc: A review of testing techniques and results. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 69, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, V.; Heraud, J. The effects of pressure and shear on skin microcirculation in elderly stroke patients lying in supine or semi-recumbent positions. Age Ageing 1994, 23, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadepalli, S.C.; Erdemir, A.; Cavanagh, P.R. Comparison of hexahedral and tetrahedral elements in finite element analysis of the foot and footwear. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 2337–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Part | Material Property | References |
|---|---|---|
| Bone | E = 12 GPa, v = 0.3 | [32] |
| Rib cage | E = 4.86 GPa, v = 0.3 | [33] |
| Encapsulated soft tissue | E = 15 kPa, v = 0.49 | [34] |
| Ligaments | [21,35,36] | |
| Anterior longitudinal ligament | E = 11.9 kPa, v = 0.39 | |
| Capsular ligament | E = 7.7 kPa, v = 0.39 | |
| Flava ligament | E = 2.4 kPa, v = 0.39 | |
| Interspinous ligament | E = 3.4 kPa, v = 0.39 | |
| Intertransverse ligament | E = 10 kPa, v = 0.39 | |
| Posterior longitudinal ligament | E = 12.5 kPa, v = 0.39 | |
| Foam materials | ||
| Soft mattress | ||
| Medium mattress | Figure 1b, v = 0.01 | |
| Hard mattress | ||
| Pillow | ||
| Ground plate | Rigid part |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, T.T.-H.; Wang, Y.; Wong, D.W.-C.; Zhang, G.; Tan, Q.; Chen, T.L.-W.; Zhang, M. The Influence of Mattress Stiffness on Spinal Curvature and Intervertebral Disc Stress—An Experimental and Computational Study. Biology 2022, 11, 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11071030
Hong TT-H, Wang Y, Wong DW-C, Zhang G, Tan Q, Chen TL-W, Zhang M. The Influence of Mattress Stiffness on Spinal Curvature and Intervertebral Disc Stress—An Experimental and Computational Study. Biology. 2022; 11(7):1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11071030
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Tommy Tung-Ho, Yan Wang, Duo Wai-Chi Wong, Guoxin Zhang, Qitao Tan, Tony Lin-Wei Chen, and Ming Zhang. 2022. "The Influence of Mattress Stiffness on Spinal Curvature and Intervertebral Disc Stress—An Experimental and Computational Study" Biology 11, no. 7: 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11071030
APA StyleHong, T. T. -H., Wang, Y., Wong, D. W. -C., Zhang, G., Tan, Q., Chen, T. L. -W., & Zhang, M. (2022). The Influence of Mattress Stiffness on Spinal Curvature and Intervertebral Disc Stress—An Experimental and Computational Study. Biology, 11(7), 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11071030