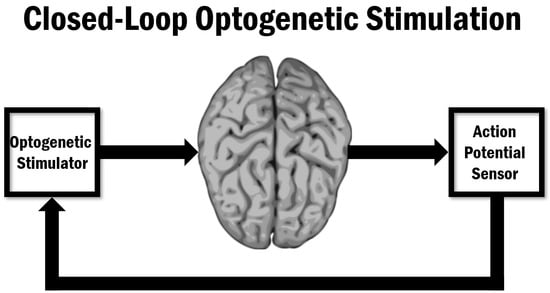
A Closed-Loop Optogenetic Stimulation Device
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Closed-Loop Optogenetic Stimulation System
3. Hardware Component
3.1. Hybrid Electrode
3.2. Action Potential Detector
3.2.1. Pre-Amplifier
3.2.2. Band Pass Filter
3.2.3. Post-Amplifier
3.3. Optogenetic Deep Brain Stimulator (ODBS)
3.4. Power Source
3.5. Integration of the CLOS Device
4. Software Component
4.1. Feature Extractor
4.2. Control Algorithm
4.3. Pulse Generator
5. Experimental Setup
5.1. Evaluation of Hybrid Electrode
5.2. Evaluation of Action Potential Detector
5.2.1. Bench-Testing Setup
5.2.2. In Vitro Test Setup
5.3. Evaluation of CLOS Device
6. Experimental Results
6.1. Evaluation Results of Hybrid Electrode
6.2. Evaluation Results of Action Potential Detector
6.2.1. Bench-Testing Results
6.2.2. In Vitro Test Results
6.3. Evaluation Results of CLOS Device
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parastarfeizabadi, M.; Kouzani, A.Z. Advances in closed-loop deep brain stimulation devices. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2017, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montagni, E.; Resta, F.; Mascaro, A.L.A.; Pavone, F.S. Optogenetics in brain research: From a strategy to investigate physiological function to a therapeutic tool. Photonics 2019, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardoso-Cruz, H.; Paiva, P.; Monteiro, C.; Galhardo, V. Bidirectional optogenetic modulation of prefrontal-hippocampal connectivity in pain-related working memory deficits. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deisseroth, K. Optogenetics. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edward, E.S.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Tye, S.J. Towards miniaturized closed-loop optogenetic stimulation devices. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ghekiere, H.; Beeckmans, D.; Tambuyzer, T.; Van Kuyck, K.; Aerts, J.M.; Nuttin, B. Conceptualization and validation of an open-source closed-loop deep brain stimulation system in rat. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grosenick, L.; Marshel, J.H.; Deisseroth, K. Closed-loop and activity-guided optogenetic control. Neuron 2015, 86, 106–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krook-Magnuson, E.; Armstrong, C.; Oijala, M.; Soltesz, I. On-demand optogenetic control of spontaneous seizures in temporal lobe epilepsy. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laxpati, N.G.; Mahmoudi, B.; Gutekunst, C.A.; Newman, J.P.; Zeller-Townson, R.; Gross, R.E. Real-time in vivo optogenetic neuromodulation and multielectrode electrophysiologic recording with NeuroRighter. Front. Neuroeng. 2014, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NeuroRighter. Available online: https://sites.google.com/site/neurorighter/ (accessed on 22 December 2019).
- Nguyen, T.K.; Navratilova, Z.; Cabral, H.; Wang, L.; Gielen, G.; Battaglia, F.P.; Bartic, C. Closed-loop optical neural stimulation based on a 32-channel low-noise recording system with online spike sorting. J. Neural Eng. 2014, 11, 046005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, J.P.; Fong, M.F.; Millard, D.C.; Whitmire, C.J.; Stanley, G.B.; Potter, S.M. Optogenetic feedback control of neural activity. Elife 2015, 4, e07192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pashaie, R.; Baumgartner, R.; Richner, T.J.; Brodnick, S.K.; Azimipour, M.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Williams, J.C. Closed-loop optogenetic brain interface. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 2327–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, K.Y.; Sirowatka, B.; Weber, A.; Wen, L. Opto-micro ECoG array: A hybrid neural interface with transparent micro ECoG electrode array and integrated LEDs for optogenetics. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2013, 7, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.T.; Williams, P.A.; Braine, C.E.; Lin, D.T.; John, S.W.; Irazoqui, P.P. A miniature, fiber-coupled, wireless, deep-brain optogenetic stimulator. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2015, 23, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cree Direct Attach DA2432 LEDs CxxxDA2432-Sxx00-x Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.cree.com/led-chips/media/documents/CPR3FM.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2019).
- Cao, H.; Gu, L.; Mohanty, S.K.; Chiao, J.J. An integrated micro-LED optrode for optogenetic stimulation and electrical recording. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AD8293. Available online: https://www.mouser.com/datasheet/2/609/AD8293G80_160-877846.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2019).
- AD8237. Available online: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/AD8237.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2019).
- ATtiny44A. Available online: http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/devicedoc/8183s.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2019).
- CAT4104. Available online: https://www.onsemi.com/pub/Collateral/CAT4104-D.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2019).
- Qian, X.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Y.; Ma, B.; Hao, H.; Li, L. A method for removal of deep brain stimulation artifact from local field potentials. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 2217–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.A.; Go, V.; Murphy, T.; Fu, Q.; Morizio, J.; Yin, H.H. A wirelessly controlled implantable LED system for deep brain optogenetic stimulation. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, J.M.; Rieth, L.; Normann, R.A.; Tathireddy, P.; Solzbacher, F. Encapsulation of an integrated neural interface device with Parylene C. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 56, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusami, S.; Oskouei, R.H. Parylene coatings in medical devices and implants: A review. Univers. J. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 3, 9–14. [Google Scholar]


















| Ref | Detection Electrode | Stimulation Electrode | Detector Circuit | Stimulator Circuit | Software | Size/Weight | Power Supply | Fixation Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [8] | Plastics One electrode | Fiber-coupled diode laser | Analogue Brownlee 410 amplifier | NI USB-6221BNC digitizer, optical patch cords | MATLAB | Bench-top | _ | Screws and dental cement |
| [9] | 16-channel tungsten MEA, NeuroNexus array | Plexon Fiber-coupled LED | Triangle Biosystems recording head-stage | Plexon V-I controller | Neuro-Righter platform | Bench-top | _ | Flexible cable, skull screws |
| [11] | 32-channel electrodes | Fiber-coupled LED | RHA2132 amplifier, AD7980 digitizer | LED driver | MATLAB and LabVIEW | Bench-top setup PCB—29.5 mm × 43.3 mm | Battery +3 V and +5 V | Flat cable, micro-drive and screw |
| [12] | MEA | Fiber-coupled LED | Multichannel systems MEA60 analog amplifier, RZ2 multichannel bio acquisition | Custom LED driver | Neuro-Righter platform | Bench-top | _ | _ |
| [13] | 4 × 4 µECoG array | Laser source and arc lamp | Tucker–Davis high impedance amplifier | Digital micromirror device | Computer based system | Bench-top Implant—400 mg | _ | _ |
| This work | Hybrid electrode with implantable LED | Amplifier and filter | LED driver and micro-controller | Embedded C program | Head-mountable Size: 6 mm diameter; Weight: 0.44 g | LiPo Battery +3.7 V | No tether | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Edward, E.S.; Kouzani, A.Z. A Closed-Loop Optogenetic Stimulation Device. Electronics 2020, 9, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010096
Edward ES, Kouzani AZ. A Closed-Loop Optogenetic Stimulation Device. Electronics. 2020; 9(1):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010096
Chicago/Turabian StyleEdward, Epsy S., and Abbas Z. Kouzani. 2020. "A Closed-Loop Optogenetic Stimulation Device" Electronics 9, no. 1: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010096
APA StyleEdward, E. S., & Kouzani, A. Z. (2020). A Closed-Loop Optogenetic Stimulation Device. Electronics, 9(1), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010096