Depression and Obesity: Analysis of Common Biomarkers
Abstract
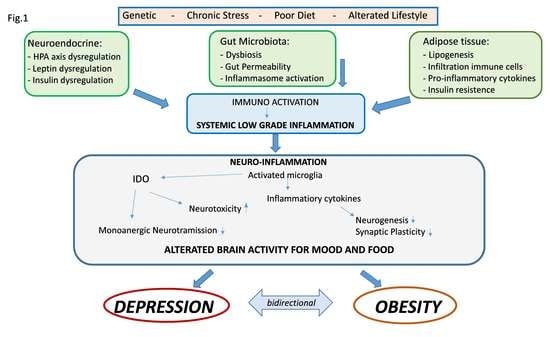
:1. Introduction
2. Psychological and Behavioral Aspects
3. Immuno-Inflammatory Aspects
4. Alterations of Neuroendocrine Function
5. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis (HPA)
6. Leptin
7. Insulin
8. Microbiota
9. Genetic Aspects
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milaneschi, Y.; Lamers, F.; Peyrot, W.J.; Baune, B.T.; Breen, G.; Dehghan, A.; Forstner, A.J.; Grabe, H.J.; Homuth, G.; Kan, C.; et al. Genetic Association of Major Depression With Atypical Features and Obesity-Related Immunometabolic Dysregulations. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppino, F.S.; De Wit, L.M.; Bouvy, P.F.; Stijnen, T.; Cuijpers, P.; Penninx, B.W.; Zitman, F.G. Overweight, Obesity, and Depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuron, L.; Lasselin, J.; Castanon, N. Role of Adiposity-Driven Inflammation in Depressive Morbidity. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 42, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moore, M.E.; Stunkard, A.; Srole, L. Obesity, Social Class, and Mental Illness. JAMA 1962, 181, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, A.; Maggard-Gibbons, M.; Maher, A.R.; Booth, M.J.; Miake-Lye, I.; Beroes, J.M.; Shekelle, P.G. Mental Health Conditions Among Patients Seeking and Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. JAMA 2016, 315, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasselin, J.; Capuron, L. Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation in Metabolic Disorders: Relevance for Behavioral Symptoms. Neuroimmunomodulation 2014, 21, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, L.; Luppino, F.; Van Straten, A.; Penninx, B.; Zitman, F.; Cuijpers, P. Depression and obesity: A meta-analysis of community-based studies. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2010, 178, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xiao, L. Obesity and Depression in US Women: Results From the 2005–2006 National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey. Obesity 2009, 18, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, G.E.; Ludman, E.J.; A Linde, J.; Operskalski, B.H.; Ichikawa, L.; Rohde, P.; Finch, E.A.; Jeffery, R.W. Association between obesity and depression in middle-aged women. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2008, 30, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milaneschi, Y.; Simmons, W.; Van Rossum, E.F.C.; Penninx, B.W. Depression and obesity: Evidence of shared biological mechanisms. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 24, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldofski, S.; Mauche, N.; Dogan-Sander, E.; Bot, M.; Brouwer, I.A.; Paans, N.P.G.; Cabout, M.; Gili, M.; Van Grootheest, G.; Hegerl, U.; et al. Depressive Symptom Clusters in Relation to Body Weight Status: Results From Two Large European Multicenter Studies. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, S.J.; Woo, H.-T.; Cho, S.; Park, K.; Jeong, S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kang, D.; Shin, A. Association between body size, weight change and depression: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Psychiatry 2017, 211, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quek, Y.; Tam, W.W.; Melvyn, Z.; Ho, R.C.M. Exploring the association between childhood and adolescent obesity and depression: A meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, L.A.; Salameh, P.; Nasser, W.; Nasser, Z.; Godin, I. Obesity and symptoms of depression among adults in selected countries of the Middle East: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Obes. 2014, 5, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannan, M.; Al Mamun, A.; Doi, S.; Clavarino, A.M. Prospective Associations between Depression and Obesity for Adolescent Males and Females- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, A.E.; The LifeLines Cohort Study; Kahali, B.; Berndt, S.I.; Justice, A.E.; Pers, T.H.; Day, F.R.; Powell, C.; Vedantam, S.; Buchkovich, M.L.; et al. Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature 2015, 518, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marmorstein, N.; Iacono, W.G.; Legrand, L. Obesity and depression in adolescence and beyond: Reciprocal risks. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carey, M.; Small, H.; Yoong, S.L.; Boyes, A.; Bisquera, A.; Sanson-Fisher, R. Prevalence of comorbid depression and obesity in general practice: A cross-sectional survey. Br. J. Gen. Pr. 2014, 64, e122–e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Macedo, T.T.S.; Portela, P.P.; Palamira, C.S.; Mussi, F.C. Obese people’s perception of their own bodies. Esc. Anna Nery 2015, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarevich, I.; Zepeda, M.Z.; Irigoyen-Camacho, M.E.; Velázquez-Alva, M.D.C. Relationship among obesity, depression, and emotional eating in young adults. Appetite 2016, 107, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ansari, W.; Adetunji, H.; Oskrochi, R. Food and Mental Health: Relationship between Food and Perceived Stress and Depressive Symptoms among University Students in the United Kingdom. Central Eur. J. Public Heal. 2014, 22, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ventura, T.; Santander, J.; Torres, R.; Contreras, A.M. Neurobiologic basis of craving for carbohydrates. Nutrition 2014, 30, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.B.; Monteze, N.M.; Calarge, C.; Ferreira, A.V.M.; Teixeira, A.L. Pathways linking obesity to neuropsychiatric disorders. Nutrition 2019, 66, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beccuti, G.; Pannain, S. Sleep and obesity. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2011, 14, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ambrósio, G.; Kaufmann, F.N.; Manosso, L.; Platt, N.; Ghisleni, G.; Rodrigues, A.L.S.; Rieger, D.K.; Kaster, M.P. Depression and peripheral inflammatory profile of patients with obesity. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 91, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanon, N.; Lasselin, J.; Capuron, L. Neuropsychiatric Comorbidity in Obesity: Role of Inflammatory Processes. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dantzer, R.; O’Connor, J.C.; Freund, G.G.; Johnson, R.; Kelley, K.W. From inflammation to sickness and depression: When the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castanon, N.; Luheshi, G.; Layé, S. Role of neuroinflammation in the emotional and cognitive alterations displayed by animal models of obesity. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penninx, B.W.; Milaneschi, Y.; Lamers, F.; Vogelzangs, N. Understanding the somatic consequences of depression: Biological mechanisms and the role of depression symptom profile. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Lowe, G.; Pepys, M.B.; Thompson, S.G.; Collins, R.; Danesh, J. C-reactive protein concentration and risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and mortality: An individual participant meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cesari, M. Inflammatory Markers and Onset of Cardiovascular Events: Results From the Health ABC Study. Circulation 2003, 108, 2317–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jantaratnotai, N.; Mosikanon, K.; Lee, Y.; McIntyre, R.S. The interface of depression and obesity. Obes. Res. Clin. Pr. 2017, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.H.; Maletic, V.; Raison, C.L. Inflammation and Its Discontents: The Role of Cytokines in the Pathophysiology of Major Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berk, M.; Williams, L.J.; Jacka, F.N.; O’Neil, A.; Pasco, J.; Moylan, S.; Allen, N.B.; Stuart, A.L.; Hayley, A.C.; Byrne, M.L.; et al. So depression is an inflammatory disease, but where does the inflammation come from? BMC Med. 2013, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, K.L.; Cathomas, F.; Russo, S.J. Central and Peripheral Inflammation Link Metabolic Syndrome and Major Depressive Disorder. Physiology 2019, 34, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Valles, A.; Inoue, W.; Rummel, C.; Luheshi, G.N. Obesity, adipokines and neuroinflammation. Neuropharmacology 2015, 96, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, V.D. Impact of immune-metabolic interactions on age-related thymic demise and T cell senescence. Semin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, R.; Syrjänen, J.; Syrj, J. Obesity and the risk and outcome of infection. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 37, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menon, V.; Rajan, T. Psychiatric disorders and obesity: A review of association studies. J. Postgrad. Med. 2017, 63, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, O.; Olefsky, J.M. The cellular and signaling networks linking the immune system and metabolism in disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory Mechanisms in Obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Anderson, D.; Lurie-Beck, J. The relationship between abdominal obesity and depression in the general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Res. Clin. Pr. 2011, 5, e267–e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belza, A.; Toubro, S.; Stender, S.; Astrup, A. Effect of diet-induced energy deficit and body fat reduction on high-sensitive CRP and other inflammatory markers in obese subjects. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rao, S.R. Inflammatory markers and bariatric surgery: A meta-analysis. Inflamm. Res. 2012, 61, 789–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuron, L.; Miller, A.H. Immune system to brain signaling: Neuropsychopharmacological implications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 130, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, K.L.; Pillon, N.J.; Sivaloganathan, D.M.; Costford, S.R.; Liu, Z.; Theret, M.; Chazaud, B.; Klip, A. Palmitoleate Reverses High Fat-induced Proinflammatory Macrophage Polarization via AMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK)*. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 16979–16988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rui, L.; Aguirre, V.; Kim, J.K.; Shulman, G.I.; Lee, A.; Corbould, A.; Dunaif, A.; White, M.F. Insulin/IGF-1 and TNF-α stimulate phosphorylation of IRS-1 at inhibitory Ser307 via distinct pathways. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.-J.; Higashimori, T.; Park, S.-Y.; Choi, H.; Dong, J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Noh, H.-L.; Cho, Y.-R.; Cline, G.; Kim, Y.-B.; et al. Differential effects of interleukin-6 and -10 on skeletal muscle and liver insulin action in vivo. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, F.O.; Gordon, S. The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, C.; Pamer, E.G. Monocyte recruitment during infection and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryder, E.; Diez-Ewald, M.; Mosquera, J.; Fernández, E.; Pedreanez, A.; Vargas, R.; Peña, C.; Fernandez, N. Association of obesity with leukocyte count in obese individuals without metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2014, 8, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Barnes, G.T.; Yang, Q.; Tan, G.; Yang, D.; Chou, C.J.; Sole, J.; Nichols, A.; Ross, J.S.; Tartaglia, L.A.; et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, S.; Hunter, D.; Huber, R.; Lemieux, J.; Slaymaker, S.; Vaddi, K.; Charo, I.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W. CCR2 modulates inflammatory and metabolic effects of high-fat feeding. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 116, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, A.H. Beyond depression: The expanding role of inflammation in psychiatric disorders. World Psychiatry 2020, 19, 108–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capuron, L.; Gumnick, J.F.; Musselman, D.L.; Lawson, D.H.; Reemsnyder, A.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Miller, A.H. Neurobehavioral Effects of Interferon-? in Cancer Patients Phenomenology and Paroxetine Responsiveness of Symptom Dimensions. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002, 26, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dowlati, Y.; Herrmann, N.; Swardfager, W.; Liu, H.; Sham, L.; Reim, E.K.; Lanctôt, K.L. A Meta-Analysis of Cytokines in Major Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiepers, O.J.; Wichers, M.; Maes, M. Cytokines and major depression. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacology Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 29, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raison, C.L.; Rutherford, R.E.; Woolwine, B.; Shuo, C.; Schettler, P.; Drake, D.F.; Haroon, E.; Miller, A.H. A randomized controlled trial of the tumor necrosis factor antagonist infliximab for treatment-resistant depression: The role of baseline inflammatory biomarkers. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiles, S.A.; Baker, A.L.; De Malmanche, T.; Attia, J. Interleukin-6, C-reactive protein and interleukin-10 after antidepressant treatment in people with depression: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2012, 42, 2015–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ho, R.C.M.; Mak, A. Interleukin (IL)-6, tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and soluble interleukin-2 receptors (sIL-2R) are elevated in patients with major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 139, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A.; Keum, N.; Okereke, O.I.; Sun, Q.; Kivimaki, M.; Rubin, R.R.; Hu, F.B. Bidirectional Association Between Depression and Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Köhler, C.A.; Freitas, T.H.; Maes, M.; De Andrade, N.Q.; Liu, C.S.; Fernandes, B.S.; Stubbs, B.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Herrmann, N.; et al. Peripheral cytokine and chemokine alterations in depression: A meta-analysis of 82 studies. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2017, 135, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Network and Pathway Analysis Subgroup of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium; Network and Pathway Analysis Subgroup of Psychiatric Genomics Consortium; O’Dushlaine, C.; Rossin, L.; Lee, P.H.; Duncan, L.; Parikshak, N.N.; Newhouse, S.; Ripke, S.; Neale, B.M.; et al. Psychiatric genome-wide association study analyses implicate neuronal, immune and histone pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menard, C.; Pfau, M.L.; Hodes, G.; Kana, V.; Wang, V.X.; Bouchard, S.; Takahashi, A.; Flanigan, M.E.; Aleyasin, H.; LeClair, K.B.; et al. Social stress induces neurovascular pathology promoting depression. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1752–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shelton, R.; Miller, A.H. Eating ourselves to death (and despair): The contribution of adiposity and inflammation to depression. Prog. Neurobiol. 2010, 91, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eisenberger, N.I.; Moieni, M. Inflammation affects social experience: Implications for mental health. World Psychiatry 2020, 19, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibney, S.M.; McGuinness, B.; Prendergast, C.; Harkin, A.; Connor, T.J. Poly I:C-induced activation of the immune response is accompanied by depression and anxiety-like behaviours, kynurenine pathway activation and reduced BDNF expression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 28, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrini, L.; Di Minno, G.; Amadio, P.; Ieraci, A.; Tremoli, E.; Barbieri, S.S. Association between Obesity and Circulating Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels: Systematic Review of Literature and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewitus, G.M.; Konefal, S.C.; Greenhalgh, A.D.; Pribiag, H.; Augereau, K.; Stellwagen, D. Microglial TNF-α Suppresses Cocaine-Induced Plasticity and Behavioral Sensitization. Neuron 2016, 90, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vezzani, A.; Maroso, M.; Balosso, S.; Sanchez, M.-A.; Bartfai, T. IL-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signaling in infection, inflammation, stress and neurodegeneration couples hyperexcitability and seizures. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, Z.; Deng, T.; Peterson, L.; Yu, R.; Lin, J.; Hamilton, D.J.; Reardon, P.R.; Sherman, V.; Winnier, G.E.; Zhan, M.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of human adipocytes implicates the NOD-like receptor pathway in obesity-induced adipose inflammation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 394, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stienstra, R.; Joosten, L.A.; Koenen, T.; Van Tits, B.; Van Diepen, J.A.; Berg, S.V.D.; Rensen, P.C.; Voshol, P.J.; Fantuzzi, G.; Hijmans, A.; et al. The Inflammasome-Mediated Caspase-1 Activation Controls Adipocyte Differentiation and Insulin Sensitivity. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alcocer-Gómez, E.; De-Miguel, M.; Barquero, N.C.; Núñez-Vasco, J.; Sánchez-Alcázar, J.A.; Fernández-Rodríguez, A.; Cordero, M.D. NLRP3 inflammasome is activated in mononuclear blood cells from patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 36, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlShehri, T.; Boone, S.; De Mutsert, R.; Penninx, B.; Rosendaal, F.; Le Cessie, S.; Milaneschi, Y.; Kanamori, D.M. The association between overall and abdominal adiposity and depressive mood: A cross-sectional analysis in 6459 participants. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 110, 104429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zunszain, P.; Anacker, C.; Cattaneo, A.; Carvalho, L.; Pariante, C.M. Glucocorticoids, cytokines and brain abnormalities in depression. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacology Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 35, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niraula, A.; Wang, Y.; Godbout, J.P.; Sheridan, J.F. Corticosterone Production during Repeated Social Defeat Causes Monocyte Mobilization from the Bone Marrow, Glucocorticoid Resistance, and Neurovascular Adhesion Molecule Expression. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 2328–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariante, C.M.; Lightman, S.L. The HPA axis in major depression: Classical theories and new developments. Trends Neurosci. 2008, 31, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Hao, S.; Erion, J.R.; Wosiski-Kuhn, M.; Stranahan, A.M. Glucocorticoid sensitization of microglia in a genetic mouse model of obesity and diabetes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 269, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonino, N.; Fava, G.A. Psychiatric Disorders Associated with Cushing??s Syndrome. CNS Drugs 2001, 15, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardet, L.; Fève, B. Systemic Glucocorticoid Therapy: A Review of its Metabolic and Cardiovascular Adverse Events. Drugs 2014, 74, 1731–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stimson, R.; Walker, B.R. The role and regulation of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2013, 15, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouad-Mansour, M.; Pelletier, M.; Tchernof, A. Characterization of 5α-reductase activity and isoenzymes in human abdominal adipose tissues. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 161, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Klaauw, A.; Farooqi, I.S. The Hunger Genes: Pathways to Obesity. Cell 2015, 161, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, M.; Huang, T.-Y.; Garza, J.C.; Chua, S.C.; Lu, X.-Y. Selective deletion of leptin receptors in adult hippocampus induces depression-related behaviours. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farr, O.M.; Tsoukas, M.; Mantzoros, C.S. Leptin and the brain: Influences on brain development, cognitive functioning and psychiatric disorders. Metabolism 2015, 64, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; López, M.; Rahmouni, K. The cellular and molecular bases of leptin and ghrelin resistance in obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, F.; Ghasemi, R.; Ibrahim, N.M.; Dargahi, L.; Mohamed, Z.; Raymond, A.A.; Ahmadiani, A. Crosstalk Between Insulin and Toll-like Receptor Signaling Pathways in the Central Nervous system. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 50, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, C.T.; Araujo, E.P.; Bordin, S.A.; Ashimine, R.; Zollner, R.D.L.; Boschero, A.C.; Saad, M.; A Velloso, L. Consumption of a Fat-Rich Diet Activates a Proinflammatory Response and Induces Insulin Resistance in the Hypothalamus. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 4192–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, K.; Kondo, T.; Kahn, C.R. Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1 (SOCS-1) and SOCS-3 Cause Insulin Resistance through Inhibition of Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Insulin Receptor Substrate Proteins by Discrete Mechanisms. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 5434–5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donath, M.Y.; Shoelson, S.E. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasgon, N.L.; Kenna, H.A.; Wroolie, T.E.; Williams, K.E.; DeMuth, B.N.; Silverman, D.H. Insulin resistance and medial prefrontal gyrus metabolism in women receiving hormone therapy. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2014, 223, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, C.; Silva, N.; Golden, S.H.; Rajala, U.; Timonen, M.; Stahl, D.; Ismail, K. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the Association Between Depression and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knol, M.J.; Twisk, J.W.R.; Beekman, A.T.F.; Heine, R.J.; Snoek, F.J.; Pouwer, F. Depression as a risk factor for the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus. A meta-analysis. Diabetology 2006, 49, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rotella, F.; Mannucci, E. Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for depression. A meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2013, 99, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres-Fuentes, C.; Schellekens, H.; Dinan, T.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiota–gut–brain axis in obesity. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Gut microbiota: A missing link in psychiatry. World Psychiatry 2020, 19, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota–Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A. Gut permeability, obesity, and metabolic disorders: Who is the chicken and who is the egg? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 105, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baothman, O.A.; Zamzami, M.; Taher, I.; Abubaker, J.; Abu-Farha, M. The role of Gut Microbiota in the development of obesity and Diabetes. Lipids Heal. Dis. 2016, 15, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cani, P.D.; Bibiloni, R.; Knauf, C.; Waget, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.; Burcelin, R. Changes in Gut Microbiota Control Metabolic Endotoxemia-Induced Inflammation in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Diabetes in Mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Institutes of Health Office of Strategic Coordination—The Common Fund. Available online: https://commonfund.nih.gov/hmp/index (accessed on 15 July 2019).
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Young Koh, G.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Chatelier, E.; MetaHIT Consortium; Nielsen, T.; Qin, J.; Prifti, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Falony, G.; Almeida, M.; Arumugam, M.; Batto, J.-M.; et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Cai, Y. Gut microbiota and obesity: Implications for fecal microbiota transplantation therapy. Hormones 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Salbaum, J.M.; Luo, M.; Blanchard, E.; Taylor, C.M.; Welsh, D.A.; Berthoud, H.-R. Obese-type gut microbiota induce neurobehavioral changes in the absence of obesity. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 77, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, R.; Wang, K.; Hu, J. Effect of Probiotics on Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrition 2016, 8, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, M.M.; El Aidy, S.; Crispie, F.; O’Sullivan, O.; Cotter, P.; Stanton, C.; Kelly, P.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T. N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs) Reverse the Impact of Early-Life Stress on the Gut Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, R.P.; Layé, S. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and their metabolites in brain function and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, G.; A Hart, R.; Charlesworth, R.P.; Sharpley, C.F. Gut microbiome and depression: What we know and what we need to know. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 29, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Ding, B.; Feng, C.; Yin, S.; Zhang, T.; Qi, X.; Lv, H.; Guo, X.; Dong, K.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Prevotella and Klebsiella proportions in fecal microbial communities are potential characteristic parameters for patients with major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 207, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.R.; Borre, Y.; Brien, C.O.; Patterson, E.; El Aidy, S.; Deane, J.; Kennedy, P.J.; Beers, S.; Scott, K.A.; Moloney, G.; et al. Transferring the blues: Depression-associated gut microbiota induces neurobehavioural changes in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 82, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Zeng, B.; Zhou, C.; Liu, M.; Fang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zeng, L.; Chen, J.-J.; Fan, S.-H.; Du, X.; et al. Gut microbiome remodeling induces depressive-like behaviors through a pathway mediated by the host’s metabolism. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, G.B.; Keating, D.J.; Young, R.; Wong, M.-L.; Licinio, J.; Wesselingh, S. From gut dysbiosis to altered brain function and mental illness: Mechanisms and pathways. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maes, M.; Kubera, M.; Leunis, J.-C. The gut–brain barrier in major depression: Intestinal mucosal dysfunction with an increased translocation of LPS from gram negative enterobacteria (leaky gut) plays a role in the inflammatory pathophysiology of depression. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2008, 29, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.-J.; Lee, W.-J.; Tseng, P.; Lee, P.-H.; Lin, M.-T.; Yang, W.-S. Bariatric surgery decreased the serum level of an endotoxin-associated marker: Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2014, 10, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-altering microorganisms: The impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoud, H.-R.; Neuhuber, W.L. Functional and chemical anatomy of the afferent vagal system. Auton. Neurosci. 2000, 85, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Debs, L.H.; Patel, A.P.; Nguyen, D.; Patel, K.; O’Connor, G.; Grati, M.; Mittal, J.; Yan, D.; Eshraghi, A.A.; et al. Neurotransmitters: The Critical Modulators Regulating Gut–Brain Axis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 2359–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lach, G.; Schellekens, H.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Anxiety, Depression, and the Microbiome: A Role for Gut Peptides. Neurotherapy 2017, 15, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mulugeta, A.; Zhou, A.; Vimaleswaran, K.S.; Dickson, C.; Hyppönen, E. Depression increases the genetic susceptibility to high body mass index: Evidence from UK Biobank. Depression Anxiety 2019, 36, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speed, M.S.; Jefsen, O.; Børglum, A.D.; Speed, U.; Østergaard, S.D. Investigating the association between body fat and depression via Mendelian randomization. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tyrrell, J.N.; Mulugeta, A.; Wood, A.R.; Zhou, A.; Beaumont, R.N.; A Tuke, M.; Jones, S.E.; Ruth, K.S.; Yaghootkar, H.; Sharp, S.; et al. Using genetics to understand the causal influence of higher BMI on depression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawbridge, R.; Arnone, D.; Danese, A.; Papadopoulos, A.; Herane-Vives, A.; Cleare, A.; Herane, A. Inflammation and clinical response to treatment in depression: A meta-analysis. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 1532–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMatteo, M.R.; Lepper, H.S.; Croghan, T.W. Depression Is a Risk Factor for Noncompliance With Medical Treatment. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Marlicz, W.; Misera, A.; Koulaouzidis, A.; Łoniewski, I. Microbiome—The Missing Link in the Gut–Brain Axis: Focus on Its Role in Gastrointestinal and Mental Health. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cizza, G.; Ronsaville, D.S.; Kleitz, H.; Eskandari, F.; Mistry, S.; Torvik, S.; Sonbolian, N.; Reynolds, J.C.; Blackman, M.R.; Gold, P.W.; et al. Clinical Subtypes of Depression Are Associated with Specific Metabolic Parameters and Circadian Endocrine Profiles in Women: The Power Study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e28912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogelzangs, N.; Comijs, H.C.; Voshaar, R.O.; Stek, M.L.; Penninx, B.W. Late-life depression symptom profiles are differentially associated with immunometabolic functioning. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 41, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasserre, A.M.; Glaus, J.; Vandeleur, C.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Vaucher, J.; Bastardot, F.; Waeber, G.; Vollenweider, P.; Preisig, M. Depression With Atypical Features and Increase in Obesity, Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, and Fat Mass. JAMA Psychiatry 2014, 71, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lasserre, A.M.; Strippoli, M.F.; Glaus, J.; Gholam-Rezaee, M.; Vandeleur, C.L.; Castelao, E.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Waeber, G.; Vollenweider, P.; Preisig, M. Prospective associations of depression subtypes with cardio-metabolic risk factors in the general population. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 22, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ouakinin, S.; Barreira, D.P.; Gois, C.J. Depression and Obesity: Integrating the Role of Stress, Neuroendocrine Dysfunction and Inflammatory Pathways. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasgon, N.L.; McEwen, B.S. Insulin resistance—a missing link no more. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1648–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milaneschi, Y.; Lamers, F.; Berk, M.; Penninx, B.W. Depression Heterogeneity and Its Biological Underpinnings: Toward Immunometabolic Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, J.C.; Guo, M.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X.-Y. Leptin restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis in a chronic unpredictable stress model of depression and reverses glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 17, 790–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milano, W.; Ambrosio, P.; Carizzone, F.; De Biasio, V.; Di Munzio, W.; Foia, M.G.; Capasso, A. Depression and Obesity: Analysis of Common Biomarkers. Diseases 2020, 8, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases8020023
Milano W, Ambrosio P, Carizzone F, De Biasio V, Di Munzio W, Foia MG, Capasso A. Depression and Obesity: Analysis of Common Biomarkers. Diseases. 2020; 8(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases8020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilano, Walter, Paola Ambrosio, Francesca Carizzone, Valeria De Biasio, Walter Di Munzio, Maria Gabriella Foia, and Anna Capasso. 2020. "Depression and Obesity: Analysis of Common Biomarkers" Diseases 8, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases8020023
APA StyleMilano, W., Ambrosio, P., Carizzone, F., De Biasio, V., Di Munzio, W., Foia, M. G., & Capasso, A. (2020). Depression and Obesity: Analysis of Common Biomarkers. Diseases, 8(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases8020023