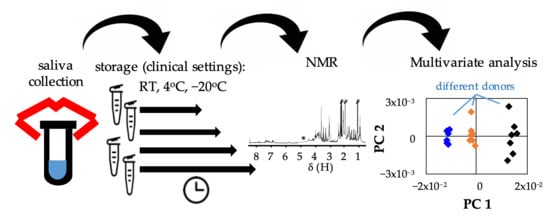
Evaluation of Saliva Stability for NMR Metabolomics: Collection and Handling Protocols
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Saliva Stability after Collection, at 22 °C, 4 °C and −20 °C
2.2. Stability of Saliva after Preparation for NMR Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Inter-Individual Variability in Salivary Metabolic Profile
3.2. Saliva Stability Post-Collection
3.3. Saliva Stability Post-Preparation for NMR Analysis
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Sample Preparation for NMR Analysis
4.3. NMR Spectroscopy
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics–the link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. ‘Metabonomics’: Understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica 1999, 29, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallares-Mendez, R.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; Cruz-Bautista, I.; Del Bosque-Plata, L. Metabolomics in diabetes, a review. Ann. Med. 2016, 48, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordalewska, M.; Maskiszewski, M. Metabolomics in cardiovascular diseases. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 113, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, E.G.; Ciborowski, M. Applications of Metabolomics in Cancer Studies. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 965, 209–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trygg, J.; Holmes, E.; Lundstedt, T. Chemometrics in Metabonomics. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, A.; Parkes, H.G.; Carpenter, G.H.; So, P.-W. Developing and Standardizing a Protocol for Quantitative Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR) Spectroscopy of Saliva. J. Proteome. Res. 2018, 17, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardner, A.; Carpenter, G.; So, P.-W. Salivary Metabolomics: From Diagnostic Biomarker Discovery to Investigating Biological Function. Metabolites 2020, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aimetti, M.; Cacciatore, S.; Graziano, A.; Tenori, L. Metabonomic analysis of saliva reveals generalized chronic periodontitis signature. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidalgo, T.K.S.; Freitas-Fernandes, L.B.; Angeli, R.; Muniz, A.M.S.; Gonsalves, E.; Santos, R.; Nadal, J.; Almeida, F.C.L.; Valente, A.P.; Souza, I.P.R. Salivary metabolite signatures of children with and without dental caries lesions. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkonen, J.J.W.; Singh, S.P.; Herrala, M.; Lappalainen, R.; Myllymaa, S.; Kulla, A.M. Salivary metabolomics in the diagnosis of oral cancer and periodontal diseases. J. Periodontal Res. 2016, 51, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.L.S.; Duarte, D.; Carneiro, T.J.; Ferreira, S.; Cunha, B.; Soares, D.; Costa, A.L.; Gil, A.M. Saliva NMR metabolomics: Analytical issues in pediatric oral health research. Oral Diaseases 2019, 25, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, L.R.; Martins, C.; Fidalgo, T.K.; Freitas-Fernandes, L.B.; Torres, R.O.; Soares, A.L.; Almeida, F.C.; Valente, A.P.; de Souza, I.P. Salivary Metabolite Fingerprint of Type 1 Diabetes in Young Children. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 2491–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueira, J.; Jonsson, P.; Adolfsson, A.N.; Nyberg, L.; Ohman, A. NMR analysis of the human saliva metabolome distinguishes dementia patients from matched controls. Mol. BioSyst. 2016, 12, 2562–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, A.; Geddes, T.; Han, B.; Bahado-Singh, R.O.; Wilson, G.D.; Imam, K.; Maddens, M.; Graham, S.F. Diagnostic Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease as Identified in Saliva using 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 58, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dona, A.C.; Jimenez, B.; Schaefer, H.; Humpfer, E.; Spraul, M.; Lewis, M.R.; Pearce, J.T.M.; Holmes, E.; Lindom, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Precision high throughput proton NMR spectroscopy of human urine, serum and plasma for large-scale metabolic phenotyping. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9887–9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Galhano, E.; Pita, C.; Almeida, M.C.; Carreira, I.M.; Gil, A.M. Human Plasma Stability during Handling and Storage: Impact on NMR Metabolomics. Analyst 2014, 139, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.H.; Luchinat, C.; Turano, P.; Tenori, L.; Roy, R.; Salek, R.M.; Ryan, D.; Merzaban, J.S.; Kadduraj-Daouk, R.; Zeri, A.C.; et al. Standardizing the Experimental Conditions for Using Urine in NMR-Based Metabolomic Studies with a Particular Focus on Diagnostic Studies: A Review. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 872–894. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, V.L.; Hoover, E.; Wang, Y.; Zanetti, K.A. Pre-Analytical Factors that Affect Metabolite Stability in Human Urine, Plasma, and Serum: A Review. Metabolites 2019, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirwan, J.A.; Brennan, L.; Broadhurst, D.; Fiehn, O.; Cascante, M.; Dunn, W.B.; Schmidt, M.A.; Velagapudi, V. Preanalytical Processing and Biobanking Procedures of Biological Samples for Metabolomics Research: A White Paper, Community Perspective (for “Precision Medicine and Pharmacometabolomics Task Group”—The Metabolomics Society Initiative). Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toone, R.J.; Peacock, O.J.; Smith, A.A.; Thompson, D.; Drawer, S.; Cook, C.; Stokes, K.A. Measurement of steroid hormones in saliva: Effects of sample storage condition. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2013, 73, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalla, A.A.; Thomsen, G.; Knudsen, G.M.; Frokjaer, V.G. The effect of storage conditions on salivary cortisol concentrations using an enzyme immunoassay. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2015, 75, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, S.; Gettler, L.T.; McDade, T.W.; Belarmino, N.M.; Kuzawa, C.W. The effects of collection and storage conditions in the field on salivary testosterone, cortisol, and sIgA values. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2018, 45, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presser, E.; Simunyandi, M.; Brown, J. The effects of storage time and temperature on recovery of salivary secretory immunoglobulin A. Hum. Biol. 2014, 26, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomadaki, K.; Helmerhorst, E.J.; Tian, N.; Sun, X.; Siqueira, W.L.; Walt, D.R.; Oppenheim, F.G. Whole-saliva proteolysis and its impact on salivary diagnostics. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qing, Z.; Ling-Ling, E.; Dong-Sheng, W.; Hong-Chen, L. Relationship of advanced oxidative protein products in human saliva and plasma: Age- and gender-related changes and stability during storage. Free Radic. Res. 2012, 46, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, R.; Thompson, H.; Kistler, J.O.; Wade, W.G.; Galloway, J.; Peakman, T.; Proctor, G.B. Effects of the UK Biobank collection protocol on potential biomarkers in saliva. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 1786–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasim, N.A.; Ariffin, S.H.Z.; Shahidan, M.A.; Abidin, I.Z.Z.; Senafi, S.; Jemain, A.A.; Wahab, R.M.A. Stability of lactate dehydrogenase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase and tartrate resistant acid phosphatase in human saliva and gingival crevicular fluid in the presence of protease inhibitor. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2013, 65, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmerhorst, E.J.; Dawes, C.; Oppenheim, F.G. The complexity of Oral Physiology and its impact on salivary diagnostics. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, N.; Marques, J.; Esteves, M.; Fernandes, M.; Mendes, V.M.; Afonso, A.; Dias, S.; Pereira, J.P.; Manadas, B.; Correira, M.J.; et al. Protein Quality Assessment on Saliva Samples for Biobanking Purposes. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2014, 14, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, D.R.; Souza, R.O.; Dias, L.B.; Ribas, T.B.; de Oliveira, L.C.F.; Sumida, D.H.; Dornelles, R.C.M.; Nakamune, A.C.M.S.; Chaves-Neto, A.H. The effects of storage time and temperature on the stability of salivary phosphatases, transaminases and dehydrogenase. Arch. Oral Biol. 2018, 85, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barranco, T.; Rubio, C.P.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Rubio, M.; Damia, E.; Lamy, E.; Cugat, R.; Cerón, J.J.; Tecles, F.; Escribano, D. Changes of salivary biomarkers under different storage conditions: Effects of temperature and length of storage. Biochem. Med. 2019, 29, 010706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emekli-Alturfan, E.; Yarat, A.; Çaliskan-Ak, E.; Pisiriciler, R. Determination of Storage Time of Saliva Samples Obtained from Patients with and without Chronic Periodontitis for the Comparison of Some Biochemical and Cytological Parameters. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2013, 27, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Dixon, R.A.; Li, L. Development of Isotope Labeling LC-MS for Human Salivary Metabolomics and Application to Profiling Metabolome Changes Associated with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Anal. Chem. 2012, 18, 10802–10811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Gao, P.; Wang, X.; Duan, Y. Investigation and identification of potential biomarkers in human saliva for the early diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 427, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, A.; Mori, M.; Hiwatari, K.; Yamaguchi, E.; Itoi, T.; Sunamura, M.; Soga, T.; Tomita, M.; Sugimoto, M. Effect of storage conditions on salivary polyamines quantified via liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmerhorst, E.J.; Oppenheim, F.G. Saliva: A Dynamic Proteome. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silwood, C.J.L.; Lynch, E.; Claxson, A.W.D.; Grootveld, M.C. 1H and 13C NMR Spectroscopic Analysis of Human Saliva. J. Dent. Res. 2002, 81, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, I.; Stretch, C.; Barnaby, P.; Bhatnager, K.; Rankin, K.; Fu, H.; Weljie, A.; Jha, N.; Slupsky, C. Understanding the human salivary metabolome. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 577–584. [Google Scholar]
- Dame, Z.T.; Aziat, F.; Mandal, R.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Bouatra, S.; Bourzouie, S.; Guo, A.C.; Sajed, T.; Deng, L.; Lin, H.; et al. The human saliva metabolome. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1864–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.P.; Saxena, M.; Saimbi, C.S.; Arif, J.M.; Roy, R. Metabolic profiling by 1H NMR spectroscopy of saliva shows clear distinction between control and diseased case of periodontitis. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, A.; Parkes, H.G.; So, P.-W.; Carpenter, G.H. Determining bacterial and host contributions to the human salivary metabolome. J. Oral Microbiol. 2019, 11, 1617014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, N. Microbial ecosystem in the oral cavity: Metabolic diversity in an ecological niche and its relationship with oral diseases. Int. Congr. 2005, 1284, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N. Oral Microbiome Metabolism: From “Who Are They? ” to “What Are They Doing?” J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 1628–1637. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, P.D.; Do, T.; Beighton, D.; Devine, D.A. Influence of saliva on the oral microbiota. Periodontology 2000 2016, 70, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanishi, N.; Hoshi, N.; Masahiro, S.; Enomotod, A.; Otad, S.; Kanekod, M.; Tomita, M.; Kimoto, K. Effects of inter-day and intra-day variation on salivary metabolomic profiles. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 489, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Slupsky, C.M. Metabolic Fingerprint of Dimethyl Sulfone (DMSO2) in Microbial-Mammalian Co-metabolism. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 5281–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, C.K.; Zeisel, S.H. Formation of trimethylamine from dietary choline by Streptococcus sanguis I, which colonizes the mouth. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1990, 1, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fothergill, J.C.; Guest, J.R. Catabolism of l-lysine by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Microbiol. 1977, 99, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neyraud, E.; Schwartz, C.; Brignot, H.; Jouanin, I.; Tremblay-Franco, M.; Canlet, C.; Tournier, C. Longitudinal analysis of the salivary metabolome of breast-fed and formula-fed infants over the first year of life. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecles, F.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; De Torre, C.; Carrillo, J.M.; Rubio, M.; García, M.; Cugat, R.; Cerón, J.J. Total esterase activity in human saliva: Validation of an automated assay, characterization and behaviour after physical stress. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2016, 76, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apatzidou, D.A.; Iskas, A.; Konstantinidis, A.; Alghamdi, A.M.; Tumelty, M.; Lappin, D.F.; Nile, C.J. Clinical associations between acetylcholine levels and cholinesterase activity in saliva and gingival crevicular fluid and periodontal diseases. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Craciun, S.; Balskus, E.P. Microbial conversion of choline to trimethylamine requires a glycyl radical enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21307–21312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Disler, W.; Kröncke, A. The lactate metabolism of the oral bacterium Veillonella from human saliva. Arch. Oral Biol. 1981, 26, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.D.; Jang, J.H.; Oh, Y.J.; Kwon, H.J. Analyses of organic acids and inorganic anions and their relationship in human saliva before and after glucose intake. Arch. Oral Biol. 2014, 59, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, V.M.; Teles, R.; Trivedi, H.M.; Devizio, W.; Xu, T.; Mitchell, M.W.; Milburn, M.V.; Guo, L. Acceleration of purine degradation by periodontal diseases. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkness, R.A. Hypoxanthine, xanthine and uridine in body fluids, indicators of ATP depletion. J. Chromatog. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1988, 429, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radak, Z.; Chung, H.Y.; Goto, S. Systemic adaptation to oxidative challenge induced by regular exercise. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterer, J. Biomarkers of peripheral muscle fatigue during exercise. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2012, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lichstein, H.C.; Soule, M.H. Studies of the Effect of Sodium Azide on Microbic Growth and Respiration: I. The Action of Sodium Azide on Microbic Growth. J. Bacteriol. 1943, 47, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navazesh, M.; Kumar, S.K. Measuring salivary flow: Challenges and opportunities. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2008, 139, 35S–40S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vaázquez- Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0 -The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veselkov, K.A.; Lindon, J.C.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Crockford, D.; Volynkin, V.V.; Holmes, E.; Davies, D.B.; Nicholson, J.K. Recursive Segment-Wise Peak Alignment of Biological 1H NMR Spectra for Improved Metabolic Biomarker Recovery. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berben, L.; Sereika, S.M.; Engberg, S. Effect Size Estimation: Methods and Examples. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2012, 49, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| T (°C) | Metabolite (δ H/ppm, Multiplicity) | 6 h vs. 0 h | 8 h vs. 0 h | 12 h vs. 0 h | 24 h vs. 0 h | 48 h vs. 0 h | Correlation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect Size | p-Value | Effect Size | p-Value | Effect Size | p-Value | Effect Size | p-Value | Effect Size | p-Value | r2 | p-Value | ||
| 22 °C | Amino acids | ||||||||||||
| alanine (1.48, d) | - | - | - | - | −1.62 ± 1.33 | 7.92 × 10−3 | −1.90 ± 1.39 | 1.6 × 10−2 | −1.82 ± 1.38 | 3.2 × 10−2 | −0.66 | 4.2 × 10−6 | |
| betaine (3.26, s) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −1.51 ± 1.30 | 3.3 × 10−2 | −0.58 | 9.5 × 10−5 | |
| sarcosine a (2.74, s) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −1.67 ± 1.34 | 7.9 × 10−3 | −0.56 | 1.8 × 10−4 | |
| SCFA | |||||||||||||
| acetate (1.92, s) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.57 ± 1.31 | 2.6 × 10−2 | 0.52 | 5.9 × 10−4 | |
| Organic acids | |||||||||||||
| lactate (4.11, q) | - | - | −1.33 ± 1.26 | 3.22 × 10−2 | −1.75 ± 1.36 | 3.3 × 10−2 | −2.07 ± 1.44 | 7.9 × 10−3 | −2.53 ± 1.56 | 7.9 × 10−3 | −0.64 | 8.1 × 10−6 | |
| pyruvate a (2.38, s) | - | - | - | - | - | - | −1.41 ± 1.28 | 3.2 × 10−2 | −1.70 ± 1.35 | 1.6 × 10−2 | −0.58 | 8.7 × 10−5 | |
| Carbohydrates | |||||||||||||
| galactose (5.27, d) | - | - | - | - | - | - | −1.67 ± 1.34 | 3.2 × 10−2 | −2.05 ± 1.44 | 7.9 × 10−3 | −0.50 | 1.0 × 10−3 | |
| Other compounds | |||||||||||||
| choline (3.20, s) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −2.04 ± 1.43 | 3.2 × 10−2 | −0.49 | 1.5 × 10−3 | |
| hypoxanthine (8.19, s) | - | - | - | - | - | - | −1.44 ± 1.43 | 3.2 × 10−2 | - | −0.47 | 2.2 × 10−3 | ||
| NAG a (2.06, s) | - | -- | - | - | - | - | - | −1.85 ± 1.38 | 3.2 × 10−2 | −0.55 | 2.0 × 10−4 | ||
| Unassigned resonances | |||||||||||||
| U1 (0.75, br) | −1.62 ± 1.33 | 3.2 × 10−2 | −1.73 ± 1.35 | 3.2 × 10−2 | −1.41 ± 1.28 | 3.2 × 10−2 | −2.50 ± 1.57 | 7.9 × 10−3 | −2.80 ± 1.66 | 7.9 × 10−3 | −0.66 | 3.5 × 10−6 | |
| U3 (3.22, s) | - | - | - | - | - | - | −1.60 ± 1.32 | 1.6 × 10−2 | −0.50 | 9.0 × 10−4 | |||
| 4 °C | Amino acids | ||||||||||||
| glycine (3.56, s) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.33 ± 1.14 | 3.5 × 10−2 | 0.46 | 5.1 × 10−4 | |
| tyrosine (6.90, d) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.79 ± 1.23 | 1.4 × 10−2 | 1.97 ± 1.27 | 4.7 × 10−3 | 0.57 | 7.3 × 10−6 | |
| SCFA | |||||||||||||
| butyrate (1.55, q) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −1.23 ± 1.12 | 4.8 × 10−2 | −0.43 | 1.3 × 10−3 | |
| Carbohydrates | |||||||||||||
| galactose b (5.27, d) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.99 ± 1.27 | 8.2 × 10−3 | 0.46 | 5.9 × 10−4 | |
| xylose (5.21, d) | 1.26 ± 1.16 | 4.1 × 10−2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.48 ± 1.16 | 2.2 × 10−2 | 0.45 | 6.7 × 10−4 | |
| Other compounds | |||||||||||||
| hypoxanthine b (8.19, s) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.13 ± 1.10 | 3.5 × 10−2 | 0.34 | 1.4 × 10−2 | ||
| Unassigned resonances | |||||||||||||
| U1 b (0.75, br) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −2.18 ± 1.32 | 4.7 × 10−3 | −0.57 | 8.3 × 10−6 | |
| U2 (0.84, s) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −1.54 ± 1.17 | 2.2 × 10−2 | −0.40 | 2.7 × 10−3 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duarte, D.; Castro, B.; Pereira, J.L.; Marques, J.F.; Costa, A.L.; Gil, A.M. Evaluation of Saliva Stability for NMR Metabolomics: Collection and Handling Protocols. Metabolites 2020, 10, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10120515
Duarte D, Castro B, Pereira JL, Marques JF, Costa AL, Gil AM. Evaluation of Saliva Stability for NMR Metabolomics: Collection and Handling Protocols. Metabolites. 2020; 10(12):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10120515
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuarte, Daniela, Beatriz Castro, Joana Leonor Pereira, Joana Faria Marques, Ana Luísa Costa, and Ana M. Gil. 2020. "Evaluation of Saliva Stability for NMR Metabolomics: Collection and Handling Protocols" Metabolites 10, no. 12: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10120515
APA StyleDuarte, D., Castro, B., Pereira, J. L., Marques, J. F., Costa, A. L., & Gil, A. M. (2020). Evaluation of Saliva Stability for NMR Metabolomics: Collection and Handling Protocols. Metabolites, 10(12), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10120515