Exploring the Characteristic Aroma of Beef from Japanese Black Cattle (Japanese Wagyu) via Sensory Evaluation and Gas Chromatography-Olfactometry
Abstract
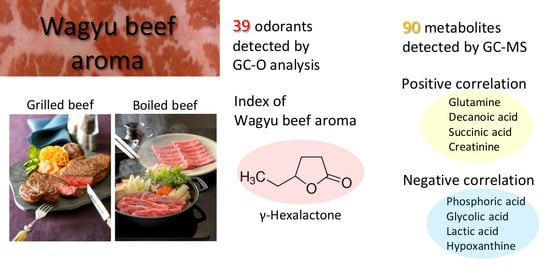
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Sensory Evaluation of Beef Aroma
2.2. Establishment of Analysis Method for Beef Aroma
2.3. Relationship between Sensory Evaluation and Odorant
2.4. Identification of Metabolites Associated with Rich and Sweet Aromas
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection
3.2. Sensory Evaluation
3.3. Concentration of Odorants from Boiled Beef
3.4. GC–O Analysis
3.5. Quantification of Odorants
3.6. Metabolomics Analysis
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Motoyama, M.; Sasaki, K.; Watanabe, A. Wagyu and the factors contributing to its beef quality: A Japanese industry overview. Meat Sci. 2016, 120, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhu, B.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H.; Liu, G.E.; et al. Genome-Wide Assessment of Runs of Homozygosity in Chinese Wagyu Beef Cattle. Animals 2020, 10, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scraggs, E.; Zanella, R.; Wojtowicz, A.; Taylor, J.F.; Gaskins, C.T.; Reeves, J.J.; de Avila, J.M.; Neibergs, H.L. Estimation of inbreeding and effective population size of full-blood Wagyu cattle registered with the American Wagyu Cattle Association. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2014, 131, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.; Ball, A.; Hughes, J.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Piyasiri, U.; Stark, J.; Watkins, P.; Warner, R. Sensory and Flavor Chemistry Characteristics of Australian Beef: Influence of Intramuscular Fat, Feed, and Breed. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4299–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotoh, T.; Nishimura, T.; Kuchida, K.; Mannen, H. The Japanese Wagyu beef industry: Current situation and future prospects-A review. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 933–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, G.; Motoyama, M.; Orita, K.; Takita, K.; Aonuma, T.; Nakajima, I.; Tajima, A.; Abe, A.; Sasaki, K. Assessment of the dynamics of sensory perception of Wagyu beef strip loin prepared with different cooking methods and fattening periods using the temporal dominance of sensations. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 3538–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corbin, C.H.; O’Quinn, T.G.; Garmyn, A.J.; Legako, J.F.; Hunt, M.R.; Dinh, T.T.N.; Rathmann, R.J.; Brooks, J.C.; Miller, M.F. Sensory evaluation of tender beef strip loin steaks of varying marbling levels and quality treatments. Meat Sci. 2015, 100, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrai, N.N.; Babji, A.S.; Maskat, M.Y.; Razali, A.F.; Yusop, S.M. Effects of marbling on physical and sensory characteristics of ribeye steaks from four different cattle breeds. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuishi, M.; Fujimori, M.; Okitani, A. Wagyu Beef Aroma in Wagyu (Japanese Black Cattle) Beef Preferred by the Japanese over Imported Beef. Anim. Sci. J. 2001, 72, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruri, J.L.; Larick, D.K. Volatile Concentration and Flavor of Beef as Influenced by Diet. J. Food Sci. 1992, 57, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuishi, M.; Kume, J.; Itou, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Arai, M.; Nagatomi, H.; Watanabe, K.; Hayase, F.; Okitani, A. Aroma Components of Wagyu Beef and Imported Beef. Nihon Chikusan Gakkaiho 2004, 75, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A.; Ueda, Y.; Higuchi, M.; Shiba, N. Analysis of Volatile Compounds in Beef Fat by Dynamic-Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction Combined with Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, C420–C425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, A.; Kamada, G.; Imanari, M.; Shiba, N.; Yonai, M.; Muramoto, T. Effect of aging on volatile compounds in cooked beef. Meat Sci. 2015, 107, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, S.; Amano, Y.; Kumazawa, K. Identification and Characterization of Volatile Components Causing the Characteristic Flavor of Wagyu Beef (Japanese Black Cattle). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8691–8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaga, K.; Tago, A.; Yoshinaga-Kiriake, A.; Gotoh, N. Characterization of lactones in Wagyu (Japanese beef) and imported beef by combining solvent extraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. LWT 2021, 135, 110015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahunty, C.M.; Eyres, G.; Dufour, J.P. Gas chromatography-olfactometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 2107–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Acampora Zellner, B.; Dugo, P.; Dugo, G.; Mondello, L. Gas chromatography–olfactometry in food flavour analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1186, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brattoli, M.; Cisternino, E.; Dambruoso, P.R.; de Gennaro, G.; Giungato, P.; Mazzone, A.; Palmisani, J.; Tutino, M. Gas chromatography analysis with olfactometric detection (GC-O) as a useful methodology for chemical characterization of odorous compounds. Sensors 2013, 13, 16759–16800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diez-Simon, C.; Mumm, R.; Hall, R.D. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics of volatiles as a new tool for understanding aroma and flavour chemistry in processed food products. Metab. Off. J. Metab. Soc. 2019, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueda, S.; Iwamoto, E.; Kato, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Shirai, Y.; Yamanoue, M. Comparative metabolomics of Japanese Black cattle beef and other meats using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldansaz, S.A.; Guo, A.C.; Sajed, T.; Steele, M.A.; Plastow, G.S.; Wishart, D.S. Livestock metabolomics and the livestock metabolome: A systematic review. PloS ONE 2017, 12, e0177675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muroya, S.; Ueda, S.; Komatsu, T.; Miyakawa, T.; Ertbjerg, P. MEATabolomics: Muscle and Meat Metabolomics in Domestic Animals. Metabolites 2020, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerth, C. Determination of volatile aroma compounds in beef using differences in steak thickness and cook surface temperature. Meat Sci. 2016, 117, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Olivero, S.J.; Pérez-Pont, M.L.; Conde, J.E.; Pérez-Trujillo, J.P. Determination of lactones in wines by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2014, 2014, 863019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.I.; Jo, C.; Tariq, M.R. Meat flavor precursors and factors influencing flavor precursors—A systematic review. Meat Sci. 2015, 110, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroya, S.; Oe, M.; Ojima, K.; Watanabe, A. Metabolomic approach to key metabolites characterizing postmortem aged loin muscle of Japanese Black (Wagyu) cattle. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 1172–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.H.B.; Kemp, R.; Samuelsson, L.M. Effects of dry-aging on meat quality attributes and metabolite profiles of beef loins. Meat Sci. 2016, 111, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelo, D.S.; Cônsolo, N.R.B.; Gómez, J.F.M.; Beline, M.; Goulart, R.S.; Corte, R.R.P.S.; Colnago, L.A.; Schilling, M.W.; Gerrard, D.E.; Silva, S.L. Metabolite profile and consumer sensory acceptability of meat from lean Nellore and Angus × Nellore crossbreed cattle fed soybean oil. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Gao, X.; Ma, F.; Wu, X. Comparison of umami taste peptides in water-soluble extractions of Jinhua and Parma hams. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, P.M.; Young, J.F. Creatine Monohydrate and Glucose Supplementation to Slow- and Fast-Growing Chickens Changes the Postmortem pH in Pectoralis Major. Poult. Sci. 2006, 85, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Kawakami, S.I.; Nakanishi, N. Expression of adipogenic transcription factors in adipose tissue of fattening Wagyu and Holstein steers. Meat Sci. 2009, 81, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichimura, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Hattori, A. Hypoxanthine enhances the cured meat taste. Anim. Sci. J. Nihon Chikusan Gakkaiho 2017, 88, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oyama, K. Genetic variability of Wagyu cattle estimated by statistical approaches. Anim. Sci. J. Nihon Chikusan Gakkaiho 2011, 82, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, A.; Maruo, Y.; Miki, T.; Yamasaki, T.; Saito, T. Influence of vitamin A on the quality of beef from the Tajima strain of Japanese Black cattle. Meat Sci. 1998, 48, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobe Beef Marketing & Distribution Promotion Association. Kobe Beef. 2020. Available online: http://www.kobe-niku.jp/top.html (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Iida, F.; Miyazaki, Y.; Tsuyuki, R.; Kato, K.; Egusa, A.; Ogoshi, H.; Nishimura, T. Changes in taste compounds, breaking properties, and sensory attributes during dry aging of beef from Japanese black cattle. Meat Sci. 2016, 112, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, W.; Bahr, W.; Schieberle, P. Solvent assisted flavour evaporation–A new and versatile technique for the careful and direct isolation of aroma compounds from complex food matrices. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 1999, 209, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, T.; Wanikawa, A.; Kono, K.; Shibata, K. Comparison of the Odor-Active Compounds in Unhopped Beer and Beers Hopped with Different Hop Varieties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8855–8861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, T.; Noba, S.; Yako, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Watanabe, T. Simulation of Pilsner-type beer aroma using 76 odor-active compounds. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 126, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, T.; Wanikawa, A.; Kagami, N.; Kawatsura, K. Analysis of hop-derived terpenoids in beer and evaluation of their behavior using the stir bar-sorptive extraction method with GC-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4701–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Group | Pedigree | Number of Cattle | Production Area | Slaughtered Age (month) | Carcass Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type A | Kedaka, Fujiyoshi, Yasufuku | 6 | Kagoshima prefecture | 29.5 ± 0.9 | 483.4 ± 40.1 |
| Type B | Tajima | 6 | Hyogo prefecture | 32.3 ± 1.3 | 406.6 ± 18.5 |
| Holstein | Holstein | 6 | Tochigi Prefecture | 21.3 ± 2.4 | 451.6 ± 47.9 |
| No. | a RI | Conpound | c Odor Quality | b FD Factor (Log4) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese Black Cattle | Holstein | |||||
| Type A | Type B | |||||
| 1 | 983 | 2,3-Butanedione | Buttery | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| 2 | 1105 | Hexanal | Fresh leaves | 5 | 5 | 3 |
| 3 | 1123 | 3-Methyl-2-butene-1-thiol | Burnt | - | - | <1 |
| 4 | 1291 | Octanal | Green fresh | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 1299 | 2-Methyl-3-furanthiol | Nuts | 7 | 7 | 5 |
| 6 | 1331 | 2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline | Grain | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| 7 | 1371 | 1,5-Octadien-3-one | Green, Metallic | 5 | 4 | 5 |
| 8 | 1423 | Nonanal | Oil oxidation | 7 | 7 | 5 |
| 9 | 1438 | (E)-2-octenal | Grassy-smelling | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 10 | 1441 | Methional | Stewed potatoes | 7 | 6 | 7 |
| 11 | 1501 | Decanal | Green fresh | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| 12 | 1530 | (E)-2-Nonenal | Oil oxidation | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| 13 | 1577 | (2E,6Z)-Nona-2,6-dienal | Cucumber | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 14 | 1623 | Butyric acid | Cheese odor | 1 | 4 | 2 |
| 15 | 1669 | Isovaleric acid | Cheese odor | 2 | - | 2 |
| 16 | 1684 | γ-Hexalactone | Sweet milk | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| 17 | 1690 | (2E,4E)-2,4-Nonadienal | Oil oxidation | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| 18 | 1731 | 2-Acetyl-1-thiazoline | Grain | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 19 | 1757 | 2-Undecenal | Oil oxidation | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| 20 | 1787 | γ-Heptalactone | Sweet milk | 1 | 4 | - |
| 21 | 1800 | (E,E)-2,4-Decadienal | Oil oxidation | 7 | 7 | 5 |
| 22 | 1842 | Hexanoic acid | Dust cloth | 6 | 5 | 7 |
| 23 | 1890 | γ-Octalactone | Lactone, Sweet Scent | 4 | 7 | 3 |
| 24 | 1928 | β-Ionone | Violet | <1 | 2 | 2 |
| 25 | 1941 | Maltol | Sweet yogurt | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| 26 | 1989 | 4,5-Epoxy-2(E)-decenal | Metal | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| 27 | 2004 | γ-Nonalactone | Lactone, Sweet Scent | 4 | 5 | 2 |
| 28 | 2021 | Franeol | Sweet yogurt | 5 | 3 | 5 |
| 29 | 2099 | γ-Decalactone | Lactone, Sweet Scent | 7 | 7 | 6 |
| 30 | 2171 | 4-Vinyl guaiacol | Smoky | 6 | 7 | 7 |
| 31 | 2185 | δ-Decalactone | Lactone, Sweet Scent | 5 | 7 | 5 |
| 32 | 2188 | 2-Aminoacetopheone | Grape | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| 33 | 2256 | 4-Vinyl phenol | Smoky | <1 | - | 3 |
| 34 | 2288 | Decanoic acid | Dust cloth | 4 | 4 | 6 |
| 35 | 2361 | 9-Decenoic acid | Dust cloth | <1 | - | <1 |
| 36 | 2368 | Indole | Indole | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| 37 | 2445 | 3-Methoxyphenol | Vanilla | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 38 | 2459 | 3-Methylindole | Indole | <1 | 1 | <1 |
| 39 | 2537 | Vanillin | Chocolate, vanilla | 5 | 6 | 6 |
| γ-Hexalactone | γ-Heptalactone | γ-Octalactone | γ-Nonalactone | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese Black | ||||
| Type A | 141.3 ±16.9 (0.12) | 14.2 ± 6.8 (0.48) | 191.5 ± 131.3 (0.69) | 115.8±44.2 (0.38) |
| Type B | 185.9 ± 63.3 (0.34) | 23.2 ± 30.3 (1.30) | 414.9 ± 215.7 (0.52) | 210.0 ± 106.9 (0.51) |
| Holstein | 34.3 ± 13.0 (0.38) | 3.7 ± 0.8 (0.22) | 43.8 ± 20.3 (0.46) | 24.9±10.9(0.44) |
| Japanese Black | ||||
| Type A | 94.3 ± 73.2 (0.78) | 376.6 ± 267.9 (0.71) | 353.5 ± 278.4 (0.79) | 696.6 ± 436.3 (0.63) |
| Type B | 154.8 ± 47.2 (0.30) | 367.1 ± 197.5 (0.54) | 621.7 ± 281.7 (0.45) | 1224.7 ± 686.0 (0.56) |
| Holstein | 21.3 ± 8.8 (0.41) | 64.8 ± 36.7 (0.57) | 78.2 ± 38.7 (0.49) | 324.1 ± 201.1 (0.62) |
| Grilled Beef Flavor | γ-Hexalactone | γ-Heptalactone | γ-Octalactone | γ-Nonalactone | γ-Decalactone | δ-Decalactone | γ-Undecalactone | Vanillin | Total Lactone |
| Oily | 0.818 | 0.467 | 0.637 | 0.653 | 0.730 | 0.537 | 0.712 | 0.467 | 0.798 |
| Sweet | 0.657 | 0.422 | 0.624 | 0.657 | 0.674 | 0.347 | 0.610 | 0.520 | 0.684 |
| Beef flavor | −0.882 | −0.489 | −0.606 | −0.695 | −0.732 | −0.624 | −0.764 | −0.550 | −0.846 |
| Wagyu beef aroma | 0.801 | 0.508 | 0.618 | 0.662 | 0.765 | 0.636 | 0.765 | 0.429 | 0.844 |
| Overall flavor | 0.807 | 0.464 | 0.648 | 0.695 | 0.763 | 0.560 | 0.727 | 0.492 | 0.820 |
| Boiled Beef Flavor | γ-Hexalactone | γ-Heptalactone | γ-Octalactone | γ-Nonalactone | γ-Decalactone | δ-Decalactone | γ-Undecalactone | Vanillin | Total Lactone |
| Oily | 0.786 | 0.470 | 0.604 | 0.642 | 0.729 | 0.541 | 0.697 | 0.437 | 0.782 |
| Sweet | 0.765 | 0.474 | 0.653 | 0.709 | 0.746 | 0.446 | 0.701 | 0.506 | 0.776 |
| Beef flavor | −0.837 | −0.400 | −0.637 | −0.699 | −0.662 | −0.487 | −0.692 | −0.497 | −0.777 |
| Wagyu beef aroma | 0.773 | 0.408 | 0.661 | 0.648 | 0.719 | 0.601 | 0.659 | 0.462 | 0.795 |
| Overall flavor | 0.771 | 0.446 | 0.607 | 0.627 | 0.739 | 0.604 | 0.688 | 0.445 | 0.794 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ueda, S.; Yamanoue, M.; Sirai, Y.; Iwamoto, E. Exploring the Characteristic Aroma of Beef from Japanese Black Cattle (Japanese Wagyu) via Sensory Evaluation and Gas Chromatography-Olfactometry. Metabolites 2021, 11, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11010056
Ueda S, Yamanoue M, Sirai Y, Iwamoto E. Exploring the Characteristic Aroma of Beef from Japanese Black Cattle (Japanese Wagyu) via Sensory Evaluation and Gas Chromatography-Olfactometry. Metabolites. 2021; 11(1):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11010056
Chicago/Turabian StyleUeda, Shuji, Minoru Yamanoue, Yasuhito Sirai, and Eiji Iwamoto. 2021. "Exploring the Characteristic Aroma of Beef from Japanese Black Cattle (Japanese Wagyu) via Sensory Evaluation and Gas Chromatography-Olfactometry" Metabolites 11, no. 1: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11010056
APA StyleUeda, S., Yamanoue, M., Sirai, Y., & Iwamoto, E. (2021). Exploring the Characteristic Aroma of Beef from Japanese Black Cattle (Japanese Wagyu) via Sensory Evaluation and Gas Chromatography-Olfactometry. Metabolites, 11(1), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11010056