Carbohydrate Intake and Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery System during Two Subsequent Pregnancies in Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
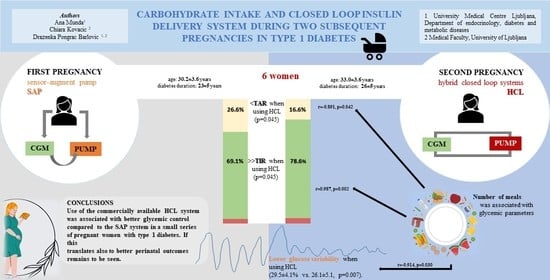
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Patterson, A.; Gich, I.; Amini, S.B.; Catalano, P.M.; de Leiva, A.; Corcoy, R. Insulin requirements throughout pregnancy in women with type 1 diabetes mellitus: Three changes of direction. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- American Diabetes Association. 14. Management of Diabetes in Pregnancy: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44 (Suppl. S1), S200–S210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battelino, T.; Danne, T.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Amiel, S.A.; Beck, R.; Biester, T.; Bosi, E.; Buckingham, B.A.; Cefalu, W.T.; Close, K.L.; et al. Clinical Targets for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation: Recommendations from the International Consensus on Time in Range. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva, J.D.; Lepore, G.; Batellino, T.; Arrieta, A.; Castaneda, J.; Grossman, B.; Shin, J.; Cohen, O. Real-World Performance of the MiniMed™ 780G System: First Report of Outcomes from 4120 Users. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2022, 24, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selby, N.M.; Taal, M.W. An updated overview of diabetic nephropathy: Diagnosis, prognosis, treatment goals and latest guidelines. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22 (Suppl. S1), 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergenstal, R.M.; Beck, R.W.; Close, K.L.; Grunberger, G.; Sacks, D.B.; Kowalski, A.; Brown, A.S.; Heinemann, L.; Aleppo, G.; Ryan, D.B.; et al. Glucose Management Indicator (GMI): A New Term for Estimating A1C from Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2275–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program, for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elo, S.; Kyngäs, H. The qualitative content analysis process. J. Adv. Nurs. 2008, 62, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, Z.A.; Wilinska, M.E.; Hartnell, S.; Temple, R.C.; Rayman, G.; Stanley, K.P.; Simmons, D.; Law, G.R.; Scott, E.M.; Hovorka, R.; et al. Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery during Pregnancy in Women with Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, Z.A.; Wilinska, M.E.; Hartnell, S.; Temple, R.C.; Rayman, G.; Stanley, K.P.; Simmons, D.; Law, G.R.; Scott, E.M.; Hovorka, R.; et al. Day-and-Night Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery in a Broad Population of Pregnant Women with Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Crossover Trial. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemieux, P.; Yamamoto, Y.M.; Donovan, L.E. Do-It-Yourself Artificial Pancreas System Use in Pregnant Women with Type 1 Diabetes in a Real-World Setting: 2 Case Reports. Can. J. Diabetes 2021, 45, 804–808.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütz-Fuhrmann, I.; Schültz, A.K.; Eichner, M.; Mader, J.K. Two Subsequent Pregnancies in a Woman with Type 1 Diabetes: Artificial Pancreas Was a Gamechanger. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2020, 14, 972–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polsky, S.; Akturk, H.K. Case series of a hybrid closed-loop system used in pregnancies in clinical practice. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, H.R. Continuous glucose monitoring targets in type 1 diabetes pregnancy: Every 5% time in range matters. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1123–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kristensen, K.; Ögge, L.E.; Sengpiel, V.; Kjölhede, K.; Dotevall, A.; Elfvin, A.; Knop, F.K.; Wiberg, N.; Katsarou, A.; Shaat, N.; et al. Continuous glucose monitoring in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes: An observational cohort study of 186 pregnancies. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feig, D.S.; Donovan, L.E.; Corcoy, R.; Murphy, K.E.; Amiel, S.A.; Hunt, K.F.; Asztalos, E.; Barrett, J.F.R.; Sanchez, J.J.; de Leiva, A.; et al. Continuous glucose monitoring in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes (CONCEPTT): A multicentre international randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 2347–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, E.M.; Murphy, H.R.; Kristensen, K.H.; Feig, D.S.; Kjölhede, K.; Englund-Ögge, L.; Berntorp, K.E.; Law, G.R. Continuous Glucose Monitoring Metrics and Birth Weight: Informing Management of Type 1 Diabetes Throughout Pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanenberg, R.J.; Welsh, J.B. Patient behaviors associated with optimum glycemic outcomes with sensor-augmented pump therapy: Insights from the STAR 3 study. Endocr. Pract. 2015, 21, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; James-Todd, T.M.; Isganaitis, E.; O’Connell, J.; Helman, S.; Wyckoff, J.A.; Serdy, S.; Halprin, E.; O’Brien, K.; Gupta, M.; et al. Associations of insulin pump and continuous glucose monitoring use with pregnancy-related outcomes in women with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 187, 109854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| First Pregnancy | Second Pregnancy | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 30.2 ± 3.6 | 33.0 ± 3.6 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 23 ± 5 | 26 ± 5 | <0.001 |
| Education (bachelor’s degree or higher), n (%) | 6 (100%) | 6 (100%) | NA |
| Smoking, n (%) | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Pre-conception BMI (kg/m2) | 23.1 ± 3.1 | 23.7 ± 4.1 | 0.347 |
| Pre-conception HbA1c, % | 6.7 ± 0.7 | 6.3 ± 0.6 | 0.100 |
| mmol/mol | 50.1 ± 7.7 | 45.2 ± 6.5 | |
| GWG (kg) | 12.0 ± 4.0 | 9.2 ± 4.9 | 0.433 |
| SBP, 1st trimester (mmHg) | 119.5 ± 11.5 | 125.0 ± 5.4 | 0.122 |
| DBP, 1st trimester (mmHg) | 71.0 ± 13.9 | 72.5 ± 13.6 | 0.707 |
| Nausea during pregnancy, n (%) | 4 (66.7) | 5 (83.3) | 0.317 |
| Vomiting during pregnancy, n (%) | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) | NA |
| Concomitant disease | Number of participants | ||
| Celiac disease | 1 | ||
| Juvenile arthritis | 1 | ||
| Hashimoto thyroiditis Retinopathy, non-proliferative | 1 4 | ||
| Retinopathy, pre-proliferative/proliferative | 0 | ||
| Diabetic kidney disease | 0 | ||
| Impaired hypoglycemia awareness | 5 |
| First Trimester | Second Trimester | Third Trimester | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Pregnancy | Second Pregnancy | p-Value | First Pregnancy | Second Pregnancy | p-Value | First Pregnancy | Second Pregnancy | p-Value | |
| Mean SG, mmol/L | 6.6 ± 0.5 (6.1, 7.3) | 6.4 ± 0.1 (6.3; 6.4) | 0.581 | 6.6 ± 0.3 (6.4, 7.0) | 6.1 ± 0.4 (5.7, 6.7) | 0.067 | 5.8 [5.7–6.0] (5.7, 6.7) | 6.4 [6.2–6.4] (5.6, 6.4) | 0.345 |
| TIR, % | 71.7 ± 6.2 (65.8, 80.0) | 73.7 ± 9.5 (65.8, 80.0) | 0.701 | 69.1 ± 6.7 (61.5, 76.0) | 78.6 ± 7.4 (69.0, 89.0) | 0.045 | 78.8 ± 7.2 (67.8, 85.3) | 83.6 ± 5.9 (75.0, 90.0) | 0.099 |
| TBR, % | 4.6 ± 3.7 (1.0, 9.5) | 6.3 ± 5.7 (2.0, 14.0) | 0.218 | 4.3 ± 2.4 (1.6, 6.7) | 4.8 ± 3.1 (2.0, 10.0) | 0.193 | 5.9 ± 4.7 (1.7, 13.3) | 2.6 ± 1.8 (1.0, 5.0) | 0.081 |
| TAR, % | 23.8 ± 5.4 (19.0, 31.5) | 20.0 ± 3.9 (16.0, 25.0) | 0.415 | 26.6 ± 5.9 (18.8, 31.8) | 16.6 ± 5.9 (8.0, 22.0) | 0.045 | 15.3 ± 4.4 (6.0, 20.0) | 13.8 ± 5.4 (6.0, 20.0) | 0.534 |
| GMI, mmol/mol | 43.5 ± 2.4 (41.4, 47.1) | 42.7 ± 0.2 (42.4, 42.8) | 0.581 | 44.0 ± 1.4 (42.8, 45.7) | 41.4 ± 1.9 (39.5, 44.2) | 0.067 | 40.0 [39.5–40.9] | 42.8 [41.9–42.8] | 0.345 |
| CV, % | 33.8 ± 5.4 (26.6, 39.7) | 32.1 ± 7.3 (26.6, 42.2) | 0.725 | 29.7 [28.1–31.9] | 28.4 [27.4–29.3] | 0.080 | 29.5 ± 4.1 (25.0, 36.2) | 26.1 ± 5.1 (21.0, 34.4) | 0.007 |
| HbA1c, % | 5.6 ± 0.4 (5.0, 6.0) | 5.8 ± 0.3 (5.3, 6.1) | 0.310 | 5.5 ± 0.4 (5.0, 6.0) | 5.7 ± 0.3 (5.1, 6.0) | 0.205 | 6.0 ± 0.3 (5.5, 6.3) | 6.0 ± 0.3 (5.6, 6.3) | 0.749 |
| mmol/mol | 35.2 ± 4.8 (31.2, 42.1) | 39.3 ± 3.1 (34.4, 43.2) | 36.4 ± 4.2 (31.2, 42.1) | 38.3 ± 3.5 (32.2, 42.1) | 41.6 ± 3.5 (36.6, 45.4) | 42.1 ± 3.0 (37.7, 45.4) | |||
| Total insulin (IU) | 40.3 ± 14.4 (29.4, 61.1) | 42.0 ± 9.6 (33.6, 55.8) | 0.614 | 47.9 ± 21.0 (34.3, 90.2) | 43.7 ± 9.7 (33.6, 59.5) | 0.494 | 69.8 ± 40.6 (41.2, 141.3) | 66.8 ± 16.8 (52.3, 90.4) | 0.822 |
| Total insulin per body weight (IU/kg) | 0.55 ± 0.17 (0.38, 0.76) | 0.56 ± 0.10 (0.47, 0.65) | 0.868 | 0.66 ± 0.21 (0.49, 1.1) | 0.60 ± 0.11 (0.44, 0.72) | 0.518 | 0.89 ± 0.36 (0.63, 1.52) | 0.89 ± 0.18 (0.67, 1.14) | 0.987 |
| Total bolus insulin (IU) | 22.0 ± 8.0 (15.5, 33.6) | 23.4 ± 4.5 (17.1, 27.9) | 0.792 | 27.7 ± 14.9 (13.7, 57.0) | 31.3 ± 5.3 (24.5, 36.8) | 0.516 | 29.4 [22.3–31.4] | 44.2 [41.9–59.4] | 0.500 |
| Total bolus insulin per body weight (IU/kg) | 0.30 ± 0.09 (0.20, 0.42) | 0.31 ± 0.07 (0.24, 0.39) | 0.837 | 0.37 ± 0.15 (0.24, 0.67) | 0.44 ± 0.09 (0.32, 0.55) | 0.430 | 0.49 [0.33–0.46] | 0.65 [0.65–0.73] | 0.138 |
| Daily bolus insulin (%) | 54.8 ± 5.4 (49.0, 62.0) | 57.0 ± 12.7 (43.0, 72.0) | 0.798 | 59.0 [56.0–61.0] | 74.0 [73.0–75.0] | 0.046 | 41.0 ± 10.3 (41.0, 68.0) | 76.2 ± 3.8 (72.0, 80.0) | 0.015 |
| Total basal insulin (IU) | 18.3 ± 7.0 (12.0, 27.3) | 18.6 ± 9.1 (10.9, 31.8) | 0.908 | 18.6 [16.6–20.6] | 11.2 [9.1–11.9] | 0.028 | 27.6 [27.1–28.8] | 17.2 [48.0–55.0] | 0.043 |
| Total basal insulin per body weight (IU/kg) | 0.25 ± 0.09 (0.17, 0.34) | 0.24 ± 0.10 (0.13, 0.37) | 0.856 | 0.28 ± 0.08 (0.20, 0.39) | 0.17 ± 0.04 (0.12, 0.25) | 0.005 | 0.42 [0.39–0.42] | 0.19 [0.16–0.27] | 0.043 |
| Daily basal insulin (%) | 45.3 ± 5.4 (38.0, 51.0) | 43.0 ± 12.7 (28.0, 57.0) | 0.798 | 41.0 [39.0–44.0] | 26.0 [25.0–27.0] | 0.046 | 48.4 ± 10.3 (32.0, 59.0) | 23.8 ± 3.8 (20.0, 28.0) | 0.015 |
| Daily carbs (g) | 177.0 ± 45.2 (120.0, 227.0) | 166.8 ± 92.7 (98.0, 298.0) | 0.815 | 204.5 ± 69.7 (144.0, 313.0) | 221.0 ± 58.6 (124.0, 282.0) | 0.726 | 211.8 ± 60.4 (143.0, 288.0) | 235.0 ± 53.6 (152.0, 287.0) | 0.648 |
| Number of meals | 8.7 ± 3.5 (5.1, 12.8) | 5.5 ± 3.8) (2.5, 11.1) | 0.058 | 9.1 ± 1.8 (6.5, 11.1) | 9.4 ± 3.7 (3.9, 14.6) | 0.849 | 9.9 ± 0.7 (9.1, 10.7) | 9.6 ± 3.6 (3.9, 12.8) | 0.839 |
| Sensor time, % | 79.8 ± 19.2 (55.6, 95.5) | 70.8 ± 18.6 (48.0, 90.0) | 0.531 | 81.0 ± 12.2 (62.2, 94.0) | 83.0 ± 25.8 (37.0, 97.0) | 0.879 | 90.2 ± 5.7 (82.9, 96.1) | 94.2 ± 3.4 (90.0, 97.0) | 0.112 |
| Number of Meals | Daily Carbs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Trimester | Second Trimester | Third Trimester | First Trimester | Second Trimester | Third Trimester | |
| r p | r p | r p | r p | r p | r p | |
| Daily carbohydrates, g | 0.936 0.006 | 0.855 0.030 | 0.752 0.143 | / | / | / |
| Mean SG, mmol/L | −0.427 0.399 | −0.225 0.668 | −0.632 0.253 | −0.223 0.672 | 0.185 0.726 | −0.507 0.384 |
| TIR, % | 0.550 0.259 | 0.628 0.182 | 0.987 0.002 | 0.631 0.179 | 0.508 0.303 | 0.727 0.164 |
| TBR, % | −0.443 0.379 | −0.559 0.249 | −0.532 0.357 | −0.587 0.221 | −0.805 0.053 | −0.411 0.492 |
| TAR, % | −0.623 0.187 | −0.509 0.303 | −0.891 0.042 | −0.618 0.191 | −0.251 0.631 | −0.650 0.235 |
| GMI, mmol/mol | −0.427 0.399 | −0.225 0.668 | −0.632 0.253 | −0.223 0.672 | 0.185 0.726 | −0.507 0.384 |
| CV, % | −0.542 0.267 | −0.776 0.070 | −0.914 0.030 | −0.635 0.176 | −0.766 0.076 | −0.668 0.218 |
| HbA1c, % | 0.482 0.333 | 0.122 0.818 | 0.043 0.945 | 0.618 0.191 | 0.373 0.466 | 0.645 0.251 |
| Total insulin (IU) | −0.702 0.120 | −0.813 0.049 | −0.970 0.006 | −0.501 0.312 | −0.671 0.145 | −0.678 0.209 |
| Total bolus insulin per body weight (IU/kg) | −0.614 0.195 | −0.115 0.828 | −0.527 0.361 | −0.484 0.331 | −0.245 0.639 | −0.391 0.515 |
| Total bolus insulin (IU) | 0.061 0.909 | −0.680 0.137 | −0.932 0.021 | 0.382 0.455 | −0.451 0.369 | −0.681 0.205 |
| Total bolus insulin per body weight (IU/kg) | 0.620 0.190 | 0.189 0.720 | −0.349 0.565 | 0.664 0.150 | 0.088 0.868 | −0.301 0.622 |
| Daily bolus insulin, % | 0.939 0.005 | 0.714 0.111 | 0.734 0.158 | 0.907 0.013 | 0.790 0.061 | 0.394 0.632 |
| Total basal insulin (IU) | −0.834 0.039 | −0.818 0.047 | −0.979 0.004 | −0.736 0.095 | −0.785 0.064 | −0.625 0.260 |
| Total basal per body weight (IU/kg) | −0.914 0.011 | −0.618 0.191 | −0.872 0.054 | −0.837 0.038 | −0.785 0.095 | −0.535 0.353 |
| Daily basal insulin, % | −0.939 0.005 | −0.714 0.111 | −0.734 0.158 | −0.907 0.013 | −0.790 0.061 | −0.294 0.632 |
| Autocorrection bolus, % | 0.658 0.543 | −0.304 0.558 | −0.957 0.011 | 0.996 0.054 | 0.039 0.942 | −0.802 0.103 |
| Sensor time, % | 0.549 0.259 | 0.760 0.079 | 0.847 0.070 | 0.736 0.096 | 0.825 0.043 | 0.591 0.294 |
| When Using the HCLs during Pregnancy |
|---|
| -women spent more time in TIR (3.5–7.8 mmol/L or 63–140 mg/dL) than when using SAPs. |
| -women spent less time in TAR (above 7.8 mmol/L or 140 mg/dL) than when using SAPs. |
| -had lower glucose variability than when using SAPs. |
| -higher meal frequency was associated with higher TIR. |
| -higher meal frequency was associated with lower TAR. |
| -higher meal frequency was associated with lower glycemic variability. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munda, A.; Kovacic, C.; Pongrac Barlovic, D. Carbohydrate Intake and Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery System during Two Subsequent Pregnancies in Type 1 Diabetes. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111137
Munda A, Kovacic C, Pongrac Barlovic D. Carbohydrate Intake and Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery System during Two Subsequent Pregnancies in Type 1 Diabetes. Metabolites. 2022; 12(11):1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111137
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunda, Ana, Chiara Kovacic, and Drazenka Pongrac Barlovic. 2022. "Carbohydrate Intake and Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery System during Two Subsequent Pregnancies in Type 1 Diabetes" Metabolites 12, no. 11: 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111137
APA StyleMunda, A., Kovacic, C., & Pongrac Barlovic, D. (2022). Carbohydrate Intake and Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery System during Two Subsequent Pregnancies in Type 1 Diabetes. Metabolites, 12(11), 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111137