Assessment of Exposure to Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) Metabolites and Bisphenol A (BPA) and Its Importance for the Prevention of Cardiometabolic Diseases
Abstract
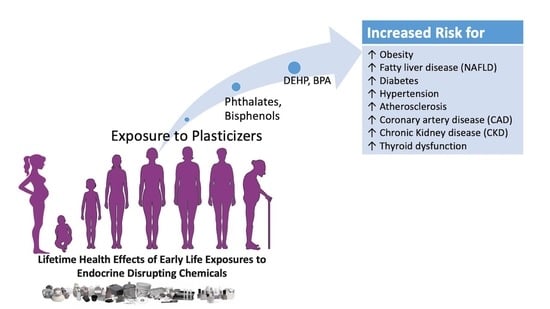
:1. Introduction
1.1. Fate of Phthalates and Bisphenols in Humans
1.2. Disrupting Action of DEHP and BPA
1.3. Biomonitoring Studies
1.4. Research Gaps and Aim
2. Experimental Design
2.1. The LIFE-PERSUADED Project
2.2. Chemicals for Preparation of Standard Solutions
2.3. Preparation of Quality Control Samples
2.4. Collection of Urine Samples
2.5. Equipment
3. Procedure
3.1. Preparation of Standard Curves
3.2. Preparation of Samples for Mass Spectrometry Analysis
3.3. Instrumental Conditions
3.3.1. Analyses of DEHP metabolites by LC/QTOF
| Time | Solvent A (%) | Solvent B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 67 | 33 |
| 4 | 67 | 33 |
| 6 | 40 | 60 |
| 7 | 5 | 95 |
| 10 | 67 | 33 |
| 12 | 67 | 33 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Ionization mode | Negative ionization |
| Capillary voltage | −2250 |
| Nozzle voltage | −300 |
| Nebulizer pressure | 35 |
| Dry gas temperature | 300 °C |
| Dry gas flow rate | 8 L/min |
| Sheath gas temperature | 350 °C |
| Sheath gas flow rate | 11 L/min |
3.3.2. Analyses of BPA by LC/QTOF
3.3.3. Analyses of BPA by GC/MS
3.4. Assessment of Limit of Detection (LOD) and Quantification (LOQ) of the Method
3.5. Assessment of Reagent Blank and Spike Recovery
3.6. Calculations of EDCs Concentrations and Assessment of Exposure
4. Results
4.1. Quantification of DEHP Metabolites by UHPLC/QTOF
4.1.1. Recovery and Matrix Effect of DEHP Metabolites
4.1.2. Limit of Detection (LOD) and Quantification (LOQ) of DEHP Metabolites
4.1.3. Working Range and Linearity of DEHP Method
4.1.4. Stability, Reproducibility of the Analysis, and Precision of DEHP Method
4.2. Quantification of Bisphenol A (BPA) by UHPLC/QTOF and GC/MS
4.2.1. Working Range and Linearity of BPA Methods
4.2.2. Stability, Reproducibility of the Analysis, and Precision of BPA Methods
4.2.3. Limit of Detection (LOD) and Quantification (LOQ) of BPA by GC/MS
4.3. Validation of the Methods during the HBM4EU Project
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



| Compound | Molecular Formula | MW | m/z [M-H]− |
|---|---|---|---|
| MEHP | C16H22O4 | 278 | 277.1445 |
| 13C4MEHP | C12[13C]4H22O4 | 282 | 281.1580 |
| MEOHP | C16H20O5 | 292 | 291.1238 |
| 13C4 MEOHP | C12[13C]4H20O5 | 296 | 295.1372 |
| MEHHP | C16H22O5 | 294 | 293.1394 |
| 13C4 MEHHP | C12[13C]4H22O5 | 298 | 297.1529 |
References
- Crisp, T.M.; Clegg, E.D.; Cooper, R.L.; Wood, W.P.; Anderson, D.G.; Baetcke, K.P.; Hoffmann, J.L.; Morrow, M.S.; Rodier, D.J.; Schaeffer, J.E.; et al. Environmental endocrine disruption: An effects assessment and analysis. Environ. Health Perspect 1998, 106 (Suppl. 1), 11–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Newbold, R.R.; Padilla-Banks, E.; Jefferson, W.N.; Heindel, J.J. Effects of endocrine disruptors on obesity. Int. J. Androl. 2008, 31, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobstein, T.; Brownell, K.D. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals and obesity risk: A review of recommendations for obesity prevention policies. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallio, M.; Diano, N.; Masarone, M.; Gravina, A.G.; Patane, V.; Romeo, M.; Di Sarno, R.; Errico, S.; Nicolucci, C.; Abenavoli, L.; et al. Chemical Effect of Bisphenol A on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Yoo, E.R.; Li, A.A.; Cholankeril, G.; Tighe, S.P.; Kim, W.; Harrison, S.A.; Ahmed, A. Elevated urinary bisphenol A levels are associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among adults in the United States. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Deretzi, G.; Zavos, C.; Mantzoros, C.S. The emerging role of endocrine disruptors in pathogenesis of insulin resistance: A concept implicating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr. Mol. Med. 2012, 12, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Fan, J.; Ye, J.; Rao, X.; Li, Y. Phthalates exposure is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among US adults. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 224, 112665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wei, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Z.; Song, L.; Wei, Z.; Lv, Z.; Chen, X.; Xia, W.; et al. Developmental exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate impairs endocrine pancreas and leads to long-term adverse effects on glucose homeostasis in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 301, E527–E538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Ning, B.; Waqar, A.B.; Niimi, M.; Li, S.; Satoh, K.; Shiomi, M.; Ye, T.; Dong, S.; Fan, J. Bisphenol A exposure induces metabolic disorders and enhances atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemic rabbits. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, P.; Balasubramanian, K. Gestational exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) impairs pancreatic beta-cell function in F1 rat offspring. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 232, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xu, X.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, X. Phthalate exposure as a risk factor for hypertension. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 20550–20561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R.; Tackitt, S.; Gievers, L.; Iragorri, S.; Sage, K.; Cornwall, T.; O’Riordan, D.; Merchant, J.; Rozansky, D. Phthalate-associated hypertension in premature infants: A prospective mechanistic cohort study. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wehbe, Z.; Nasser, S.A.; El-Yazbi, A.; Nasreddine, S.; Eid, A.H. Estrogen and Bisphenol A in Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2020, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Hong, Y.C. Bisphenol A, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Diseases: Epidemiological, Laboratory, and Clinical Trial Evidence. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2016, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, P.M.; Lind, L. Circulating levels of bisphenol A and phthalates are related to carotid atherosclerosis in the elderly. Atherosclerosis 2011, 218, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.C.; Hwang, J.S.; Torng, P.L.; Wu, C.; Lin, C.Y.; Sung, F.C. Phthalate exposure increases subclinical atherosclerosis in young population. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.C.; Hwang, J.J.; Sun, C.W.; Wang, S.L. Urinary phthalate metabolites, coronary heart disease, and atherothrombotic markers. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariana, M.; Cairrao, E. Phthalates Implications in the Cardiovascular System. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2020, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranciere, F.; Lyons, J.G.; Loh, V.H.; Botton, J.; Galloway, T.; Wang, T.; Shaw, J.E.; Magliano, D.J. Bisphenol A and the risk of cardiometabolic disorders: A systematic review with meta-analysis of the epidemiological evidence. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melzer, D.; Osborne, N.J.; Henley, W.E.; Cipelli, R.; Young, A.; Money, C.; McCormack, P.; Luben, R.; Khaw, K.T.; Wareham, N.J.; et al. Urinary bisphenol A concentration and risk of future coronary artery disease in apparently healthy men and women. Circulation 2012, 125, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, M.H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, M.; Attina, T.M.; Naidu, M.; Karthikraj, R.; Kannan, K.; Warady, B.A.; Furth, S.; Vento, S.; et al. Serially assessed bisphenol A and phthalate exposure and association with kidney function in children with chronic kidney disease in the US and Canada: A longitudinal cohort study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malits, J.; Attina, T.M.; Karthikraj, R.; Kannan, K.; Naidu, M.; Furth, S.; Warady, B.A.; Vento, S.; Trachtman, H.; Trasande, L. Renal Function and exposure to Bisphenol A and phthalates in children with Chronic Kidney Disease. Environ. Res. 2018, 167, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.J.; Wu, P.Y.; Huang, J.C.; Chen, S.C. Environmental Pollution and Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latini, G.; Gallo, F.; Dipaola, L.; De Angelis, S.; Olivieri, A. Pre- plus postnatal exposures to di-(2-ethylhexyl)-phthalate and thyroid dysfunction in prematurely born children. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2014, 37, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, C.; Li, L.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, G.; Lu, X. Combined effects of di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and bisphenol A on thyroid hormone homeostasis in adolescent female rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 40882–40892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorini, F.; Bustaffa, E.; Coi, A.; Iervasi, G.; Bianchi, F. Bisphenols as Environmental Triggers of Thyroid Dysfunction: Clues and Evidence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Papandonatos, G.D.; Calafat, A.M.; Yolton, K.; Lanphear, B.P.; Chen, A.; Braun, J.M. Gestational and childhood exposure to phthalates and child behavior. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, L.; Lind, L.; Lind, P.M. Associations between circulating levels of bisphenol A and phthalate metabolites and coronary risk in the elderly. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 80, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.; Arbuckle, T.E.; MacPherson, S.; Braun, J.M.; Feeley, M.; Gaudreau, E. Phthalate and BPA Exposure in Women and Newborns through Personal Care Product Use and Food Packaging. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10813–10826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, R.; Meeker, J.D.; Park, S.; Silva, M.J.; Calafat, A.M. Temporal variability of urinary phthalate metabolite levels in men of reproductive age. Environ. Health Perspect 2004, 112, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, R.; Calafat, A.M. Phthalates and human health. Occup. Environ. Med. 2005, 62, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halden, R.U. Plastics and health risks. Annu Rev. Public Health 2010, 31, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frederiksen, H.; Skakkebaek, N.E.; Andersson, A.M. Metabolism of phthalates in humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calafat, A.M.; Silva, M.J.; Reidy, J.A.; Earl Gray, L.; Samandar, E.; Preau, J.L.; Herbert, A.R.; Needham, L.L. Mono-(3-carboxypropyl) phthalate, a metabolite of di-n-octyl phthalate. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2006, 69, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.J.; Barr, D.B.; Reidy, J.A.; Kato, K.; Malek, N.A.; Hodge, C.C.; Hurtz, D., 3rd; Calafat, A.M.; Needham, L.L.; Brock, J.W. Glucuronidation patterns of common urinary and serum monoester phthalate metabolites. Arch. Toxicol. 2003, 77, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latini, G. Monitoring phthalate exposure in humans. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 361, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erythropel, H.C.; Maric, M.; Nicell, J.A.; Leask, R.L.; Yargeau, V. Leaching of the plasticizer di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) from plastic containers and the question of human exposure. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9967–9981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Li, S.S. Epigenetic effects of environmental chemicals bisphenol a and phthalates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 10143–10153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.; Newbold, S.K. The 1st World Nursing Informatics Leadership Conference. Comput. Inform. Nurs. 2008, 26, 61–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, E.; Chiarelli, F. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Insulin Resistance in Children. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoshtari-Yeganeh, B.; Zarean, M.; Mansourian, M.; Riahi, R.; Poursafa, P.; Teiri, H.; Rafiei, N.; Dehdashti, B.; Kelishadi, R. Systematic review and meta-analysis on the association between phthalates exposure and insulin resistance. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 9435–9442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Chou, E.L.; Baecker, A.; You, N.C.; Song, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liu, S. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals, risk of type 2 diabetes, and diabetes-related metabolic traits: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Diabetes 2016, 8, 516–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengozzi, A.; Carli, F.; Biancalana, E.; Della Latta, V.; Seghieri, M.; Gastaldelli, A.; Solini, A. Phthalates Exposure as Determinant of Albuminuria in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavasoglu, N.U.; Koksal, C.; Dagdeviren, M.; Aktug, H.; Yavasoglu, A. Induction of oxidative stress and histological changes in liver by subacute doses of butyl cyclohexyl phthalate. Environ. Toxicol. 2014, 29, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkekoglu, P.; Zeybek, N.D.; Giray, B.K.; Rachidi, W.; Kizilgun, M.; Hininger-Favier, I.; Favier, A.; Asan, E.; Hincal, F. The effects of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate on rat liver in relation to selenium status. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 95, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, R.M.; Moore, M.R.; Cifone, M.A.; Finney, D.C.; Guest, D. Chronic peroxisome proliferation and hepatomegaly associated with the hepatocellular tumorigenesis of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate and the effects of recovery. Toxicol. Sci. 1999, 50, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.H.; Chen, T.J.; Chen, S.S.; Hsiao, P.C.; Yang, R.C. Activation of Trim17 by PPARgamma is involved in di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP)-induced apoptosis on Neuro-2a cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 206, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) 117-81-7. 2016. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2016-09/documents/bis-2-ethylhexyl-phthalate.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Yilmaz, B.; Terekeci, H.; Sandal, S.; Kelestimur, F. Endocrine disrupting chemicals: Exposure, effects on human health, mechanism of action, models for testing and strategies for prevention. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, I.; Oriente, F.; D’Esposito, V.; Liguoro, D.; Liguoro, P.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Cabaro, S.; D’Andrea, F.; Beguinot, F.; Formisano, P.; et al. Low-dose Bisphenol-A regulates inflammatory cytokines through GPR30 in mammary adipose cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2019, 63, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.Z.; Althagafi, I.I.; Shamshad, H. Role of PPAR receptor in different diseases and their ligands: Physiological importance and clinical implications. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 166, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desvergne, B.; Feige, J.N.; Casals-Casas, C. PPAR-mediated activity of phthalates: A link to the obesity epidemic? Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2009, 304, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, C.H.; Waxman, D.J. Activation of PPARalpha and PPARgamma by environmental phthalate monoesters. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 74, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grun, F.; Blumberg, B. Endocrine disrupters as obesogens. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2009, 304, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feige, J.N.; Gelman, L.; Rossi, D.; Zoete, V.; Metivier, R.; Tudor, C.; Anghel, S.I.; Grosdidier, A.; Lathion, C.; Engelborghs, Y.; et al. The endocrine disruptor monoethyl-hexyl-phthalate is a selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma modulator that promotes adipogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 19152–19166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajagopal, G.; Bhaskaran, R.S.; Karundevi, B. Maternal di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate exposure alters hepatic insulin signal transduction and glucoregulatory events in rat F1 male offspring. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019, 39, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, G.; Bhaskaran, R.S.; Karundevi, B. Developmental exposure to DEHP alters hepatic glucose uptake and transcriptional regulation of GLUT2 in rat male offspring. Toxicology 2019, 413, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Arevalo, M.; Alonso-Magdalena, P.; Rebelo Dos Santos, J.; Quesada, I.; Carneiro, E.M.; Nadal, A. Exposure to bisphenol-A during pregnancy partially mimics the effects of a high-fat diet altering glucose homeostasis and gene expression in adult male mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Chang, H.; Xia, W.; Mao, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, S. F0 maternal BPA exposure induced glucose intolerance of F2 generation through DNA methylation change in Gck. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 228, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xia, W.; Wang, D.Q.; Wan, Y.J.; Xu, B.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.Y.; Xu, S.Q. Hepatic DNA methylation modifications in early development of rats resulting from perinatal BPA exposure contribute to insulin resistance in adulthood. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ding, D.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Lu, H.; Lu, Y.; Chi, Y.; Sun, X.; Ye, G.; Zhu, H.; et al. Downregulation of miR-192 causes hepatic steatosis and lipid accumulation by inducing SREBF1: Novel mechanism for bisphenol A-triggered non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acconcia, F.; Pallottini, V.; Marino, M. Molecular Mechanisms of Action of BPA. Dose Response 2015, 13, 1559325815610582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perez, P.A.; Toledo, J.; Sosa, L.D.V.; Peinetti, N.; Torres, A.I.; De Paul, A.L.; Gutierrez, S. The phthalate DEHP modulates the estrogen receptors alpha and beta increasing lactotroph cell population in female pituitary glands. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, D.B.; Wang, R.Y.; Needham, L.L. Biologic monitoring of exposure to environmental chemicals throughout the life stages: Requirements and issues for consideration for the National Children’s Study. Environ. Health Perspect 2005, 113, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.M.; Bennett, D.H.; Barkoski, J.; Ye, X.; Calafat, A.M.; Tancredi, D.; Hertz-Picciotto, I. Variability of urinary concentrations of phthalate metabolites during pregnancy in first morning voids and pooled samples. Environ. Int. 2019, 122, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.J.; Samandar, E.; Preau, J.L., Jr.; Reidy, J.A.; Needham, L.L.; Calafat, A.M. Quantification of 22 phthalate metabolites in human urine. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 860, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, E.Y.; Kim, P.G.; Kho, Y.L. Determination of Phthalate Metabolites in Human Serum and Urine as Biomarkers for Phthalate Exposure Using Column-Switching LC-MS/MS. Saf. Health Work 2011, 2, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monfort, N.; Ventura, R.; Balcells, G.; Segura, J. Determination of five di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate metabolites in urine by UPLC-MS/MS, markers of blood transfusion misuse in sports. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 908, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.X.; Wang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Q.W. Rapid and sensitive analysis of phthalate metabolites, bisphenol A, and endogenous steroid hormones in human urine by mixed-mode solid-phase extraction, dansylation, and ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 4313–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewalque, L.; Pirard, C.; Dubois, N.; Charlier, C. Simultaneous determination of some phthalate metabolites, parabens and benzophenone-3 in urine by ultra high pressure liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 949, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myridakis, A.; Balaska, E.; Gkaitatzi, C.; Kouvarakis, A.; Stephanou, E.G. Determination and separation of bisphenol A, phthalate metabolites and structural isomers of parabens in human urine with conventional high-pressure liquid chromatography combined with electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2509–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhan, M.; Zou, X.; Qu, W.; Zhou, Y. Rapid and sensitive determination of nine bisphenol analogues, three amphenicol antibiotics, and six phthalate metabolites in human urine samples using UHPLC-MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3871–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.Y.; Shih, C.L.; Liao, P.C. Exposure Marker Discovery of Phthalates Using Mass Spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 6, S0062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esteban Lopez, M.; Goen, T.; Mol, H.; Nubler, S.; Haji-Abbas-Zarrabi, K.; Koch, H.M.; Kasper-Sonnenberg, M.; Dvorakova, D.; Hajslova, J.; Antignac, J.P.; et al. The European human biomonitoring platform—Design and implementation of a laboratory quality assurance/quality control (QA/QC) programme for selected priority chemicals. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 234, 113740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rocca, C.; Maranghi, F.; Tait, S.; Tassinari, R.; Baldi, F.; Bottaro, G.; Buzzigoli, E.; Carli, F.; Cianfarani, S.; Conte, R.; et al. The LIFE PERSUADED project approach on phthalates and bisphenol A biomonitoring in Italian mother-child pairs linking exposure and juvenile diseases. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 25618–25625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tait, S.; Carli, F.; Busani, L.; Buzzigoli, E.; Della Latta, V.; Deodati, A.; Fabbrizi, E.; Gaggini, M.; Maranghi, F.; Tassinari, R.; et al. Biomonitoring of Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) in Italian children and adolescents: Data from LIFE PERSUADED project. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, S.; Carli, F.; Busani, L.; Ciociaro, D.; Della Latta, V.; Deodati, A.; Fabbrizi, E.; Pala, A.P.; Maranghi, F.; Tassinari, R.; et al. Italian Children Exposure to Bisphenol A: Biomonitoring Data from the LIFE PERSUADED Project. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chan, C.O.; Lau, C.C.; Yu, Z.; Mok, D.K.; Chen, S. Simultaneous determination of eight anthraquinones in Semen Cassiae by HPLC-DAD. Phytochem. Anal. 2012, 23, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.L.; Winefordner, J.D. Limit of Detection a Closer Look at the IUPAC Definition. Anal. Chem. 1983, 55, 712A–724A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, B.K.; Esteban, M.; Koch, H.M.; Castano, A.; Koslitz, S.; Canas, A.; Casteleyn, L.; Kolossa-Gehring, M.; Schwedler, G.; Schoeters, G.; et al. The European COPHES/DEMOCOPHES project: Towards transnational comparability and reliability of human biomonitoring results. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU). No 10/2011 of 14 January 2011 on Plastic Materials and Articles Intended to Come into Contact with Food (Text with EEA Relevance). 2011. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2011:012:0001:0089:en:PDF (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Efsa Panel on Food Contact Materials, E.; Processing, A.; Silano, V.; Barat Baviera, J.M.; Bolognesi, C.; Chesson, A.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Crebelli, R.; Gott, D.M.; Grob, K.; et al. Update of the risk assessment of di-butylphthalate (DBP), butyl-benzyl-phthalate (BBP), bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP), di-isononylphthalate (DINP) and di-isodecylphthalate (DIDP) for use in food contact materials. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Authority, E.F.S. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC) related to Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) for use in food contact materials. EFSA J. 2005, 3, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Authority, E.F.S. Toxicokinetics of Bisphenol A—Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Food additives, Flavourings, Processing aids and Materials in Contact with Food (AFC). EFSA J. 2008, 6, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Proposed Designation of Di-Ethylhexyl Phthalate (DEHP) (1,2-Benzene- dicarboxylic acid, 1,2-bis (2-ethylhexyl) ester) (CASRN 117-81-7) as a High-Priority Substance for Risk Evaluation. 2019. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/assessing-and-managing-chemicals-under-tsca/risk-evaluation-di-ethylhexyl-phthalate-12-benzene (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Edwards, L.; McCray, N.L.; VanNoy, B.N.; Yau, A.; Geller, R.J.; Adamkiewicz, G.; Zota, A.R. Phthalate and novel plasticizer concentrations in food items from U.S. fast food chains: A preliminary analysis. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colborn, T.; vom Saal, F.S.; Soto, A.M. Developmental effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in wildlife and humans. Environ. Health Perspect 1993, 101, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffernan, A.L.; Thompson, K.; Eaglesham, G.; Vijayasarathy, S.; Mueller, J.F.; Sly, P.D.; Gomez, M.J. Rapid, automated online SPE-LC-QTRAP-MS/MS method for the simultaneous analysis of 14 phthalate metabolites and 5 bisphenol analogues in human urine. Talanta 2016, 151, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Song, N.R.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, J.; Pyo, H. Simultaneous analysis of urinary phthalate metabolites of residents in Korea using isotope dilution gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tankiewicz, M.; Olkowska, E.; Berg, A.; Wolska, L. Advancement in Determination of Phthalate Metabolites by Gas Chromatography Eliminating Derivatization Step. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kondo, F.; Ikai, Y.; Hayashi, R.; Okumura, M.; Takatori, S.; Nakazawa, H.; Izumi, S.; Makino, T. Determination of five phthalate monoesters in human urine using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, G.; Campo, L.; Mercadante, R.; Santos, P.M.; Missineo, P.; Polledri, E.; Fustinoni, S. Development and validation of a liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method to quantify metabolites of phthalates, including di-2-ethylhexyl terephthalate (DEHTP) and bisphenol A, in human urine. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 34, e8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deceuninck, Y.; Bichon, E.; Durand, S.; Bemrah, N.; Zendong, Z.; Morvan, M.L.; Marchand, P.; Dervilly-Pinel, G.; Antignac, J.P.; Leblanc, J.C.; et al. Development and validation of a specific and sensitive gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of bisphenol A residues in a large set of food items. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1362, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| MEHP | MEOHP | MEHHP | BPA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spike (ng/mL) | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 10.4 |
| Blank (ng/mL) | 0.28 ± 0.01 | ND | ND | 0.69 ± 0.006 |
| Urine + spike (ng/mL) | 4.16 ± 0.15 | 3.75 ± 0.20 | 4.60 ± 0.13 | 9.6 ± 0.17 |
| Recovery % | 94% | 79% | 102% | 91.99% |
| Matrix Effect % | 90% | 102% | 105% | NA |
| DHEP Metabolites | LOD (ng/mL) | LOQ (ng/mL) | MDL (ng/mL) | SNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEHP | 0.28 | 0.58 | 0.238 | 11.30 |
| MEOHP | 0.18 | 0.48 | 0.096 | 14.50 |
| MEHHP | 0.11 | 0.24 | 0.131 | 10.60 |
| Concentration | Ref Value ng/mL | Replicates | Average | Precision (RSD%) | Trueness (Bias%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ng/mL | ||||||
| MEHP | Low | 0.567 | 9 | <LOQ | - | - |
| High | 5.89 | 9 | 6.65 | 14.43 | 12.96 | |
| MEOHP | Low | 1.74 | 9 | 1.63 | 23.91 | 6.22 |
| High | 14.6 | 9 | 13.32 | 7.55 | 8.74 | |
| MEHHP | Low | 4.12 | 9 | 3.71 | 14.96 | 9.87 |
| High | 32.3 | 9 | 30.64 | 13.01 | 5.14 | |
| BPA | Low | 0.763 | 8 | 0.751 | 19.17 | 1.55 |
| High | 8.4 | 8 | 6.456 | 13.29 | 23.14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carli, F.; Ciociaro, D.; Gastaldelli, A. Assessment of Exposure to Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) Metabolites and Bisphenol A (BPA) and Its Importance for the Prevention of Cardiometabolic Diseases. Metabolites 2022, 12, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020167
Carli F, Ciociaro D, Gastaldelli A. Assessment of Exposure to Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) Metabolites and Bisphenol A (BPA) and Its Importance for the Prevention of Cardiometabolic Diseases. Metabolites. 2022; 12(2):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020167
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarli, Fabrizia, Demetrio Ciociaro, and Amalia Gastaldelli. 2022. "Assessment of Exposure to Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) Metabolites and Bisphenol A (BPA) and Its Importance for the Prevention of Cardiometabolic Diseases" Metabolites 12, no. 2: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020167
APA StyleCarli, F., Ciociaro, D., & Gastaldelli, A. (2022). Assessment of Exposure to Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) Metabolites and Bisphenol A (BPA) and Its Importance for the Prevention of Cardiometabolic Diseases. Metabolites, 12(2), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020167