A Nucleotide Metabolism-Related Gene Signature for Risk Stratification and Prognosis Prediction in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on an Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Approach
Abstract
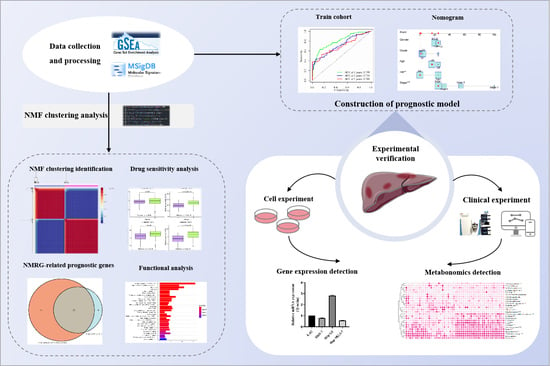
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Processing
2.2. Pan-Cancer Analysis
2.3. Differentially Expressed Prognostic NMRG Identification
2.4. Non-Negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) Clustering Determination of NMRG Modification Subtypes
2.5. Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA) and NMRGs Different Expression Analysis
2.6. Differences in the Prognosis, Immune Checkpoint Genes, and Drug Sensitivity between Distinct NMRG-Based Clusters
2.7. DEG Identification and Functional Analysis
2.8. Construction and Verification of a Prognostic Signature Based on NMRGs
2.9. Creating a Predictive Nomogram That Incorporates Clinical Characteristics and Risk Scores
2.10. Reagents
2.11. Cell Culture
2.12. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.13. Participants and Criteria
2.14. Serum Sample Pretreatment and Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Pan-Cancer Introduction with Respect to Differences in NMRGs
3.2. Identification of Differentially Expressed Prognostic NMRGs
3.3. NMF Clustering Identification of Molecular Typing Based on the NMRG
3.4. Functional Analysis for the NMRG Clusters
3.5. Determination and Verification of an NMRG-Based Prognostic Signature
3.6. Predictive Efficiency of the Risk Signature Validation in the GEO Cohort
3.7. Nomogram Development and Verification
3.8. The Expression of Hub Gene in Different HCC Cell Lines
3.9. Metabolic Profiles of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Differential Analysis of Nucleotide Metabolites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Llovet, J.M.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Pikarsky, E.; Sangro, B.; Schwartz, M.; Sherman, M.; Gores, G. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, F.; Wong, N.K.; He, J.; Zhang, R.; Sun, R.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Koike, K.; et al. Global liver disease burdens and research trends: Analysis from a Chinese perspective. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarin, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Al Mahtab, M.; Akbar, S.; Jia, J.; Tian, Q.; Aggarwal, R.; Muljono, D.H.; et al. Liver diseases in the Asia-Pacific region: A Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology Commission. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 167–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Dong, X.; Li, H.; Cao, M.; Sun, D.; He, S.; Yang, F.; Yan, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, N.; et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: Profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathbone, M.P.; Middlemiss, P.J.; Kim, J.K.; Gysbers, J.W.; DeForge, S.P.; Smith, R.W.; Hughes, D.W. Adenosine and its nucleotides stimulate proliferation of chick astrocytes and human astrocytoma cells. Neurosci. Res. 1992, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Understanding the Intersections between Metabolism and Cancer Biology. Cell 2017, 168, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.N.; Thompson, C.B. The Emerging Hallmarks of Cancer Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhong, M.; Xiong, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hong, X. Emerging roles of nucleotide metabolism in cancer development: Progress and prospect. Aging 2021, 13, 13349–13358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Adler, L.; Karathia, H.; Carmel, N.; Rabinovich, S.; Auslander, N.; Keshet, R.; Stettner, N.; Silberman, A.; Agemy, L.; et al. Urea Cycle Dysregulation Generates Clinically Relevant Genomic and Biochemical Signatures. Cell 2018, 174, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshet, R.; Lee, J.S.; Adler, L.; Iraqi, M.; Ariav, Y.; Lim, L.; Lerner, S.; Rabinovich, S.; Oren, R.; Katzir, R.; et al. Targeting purine synthesis in ASS1-expressing tumors enhances the response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepp, O.; Loos, F.; Liu, P.; Kroemer, G. Extracellular nucleosides and nucleotides as immunomodulators. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 280, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V. Adenosine as an endogenous immunoregulator in cancer pathogenesis: Where to go. Purinergic Signal 2013, 9, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geeleher, P.; Cox, N.; Huang, R.S. pRRophetic: An R package for prediction of clinical chemotherapeutic response from tumor gene expression levels. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Laird, P.W. Interplay between the cancer genome and epigenome. Cell 2013, 153, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J.; Emeny, R.T.; Hölzel, D. Positive lymph nodes do not metastasize. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012, 31, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kandimalla, R.; Huang, H.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Gao, F.; Goel, A.; Wang, X. Molecular subtyping of colorectal cancer: Recent progress, new challenges and emerging opportunities. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 55, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panther, E.; Corinti, S.; Idzko, M.; Herouy, Y.; Napp, M.; la Sala, A.; Girolomoni, G.; Norgauer, J. Adenosine affects expression of membrane molecules, cytokine and chemokine release, and the T-cell stimulatory capacity of human dendritic cells. Blood 2003, 101, 3985–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Qing, G. Targeting oncogenic Myc as a strategy for cancer treatment. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2018, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, C.V.; Le, A.; Gao, P. MYC-induced cancer cell energy metabolism and therapeutic opportunities. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6479–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pópulo, H.; Lopes, J.M.; Soares, P. The mTOR signalling pathway in human cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 1886–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, L.N.; Rakijas, J.B.; Pandit, S.K.; Westendorp, B.; Chen, H.Z.; Huntington, J.T.; Tang, X.; Bae, S.; Srivastava, A.; Senapati, S.; et al. E2f8 mediates tumor suppression in postnatal liver development. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2955–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, L.N.; Bae, S.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tang, X.; Srivastava, A.; Koivisto, C.; Martin, C.K.; Ridolfi, E.; Miller, G.C.; Zorko, S.M.; et al. Dosage-dependent copy number gains in E2f1 and E2f3 drive hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, W.; Bian, B.; Xia, Y.; Dou, S.; Gayet, O.; Bigonnet, M.; Santofimia-Castaño, P.; Cong, M.; Peng, L.; Dusetti, N.; et al. E2F signature is predictive for the pancreatic adenocarcinoma clinical outcome and sensitivity to E2F inhibitors, but not for the response to cytotoxic-based treatments. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motegi, A.; Masutani, M.; Yoshioka, K.I.; Bessho, T. Aberrations in DNA repair pathways in cancer and therapeutic significances. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 58, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochez, L.; Chevolet, I.; Kruse, V. The rationale of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibition for cancer therapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 76, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaysher, J. Lipid metabolism and cancer. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2013, 24, 530–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, S.; Tan, J.; Li, B. Prognostic values of GMPS, PR, CD40, and p21 in ovarian cancer. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; He, N.; Chen, C.; Zhang, N.; Lin, Y.; Xia, Q. Identification of novel blood-based HCC-specific diagnostic biomarkers for human hepatocellular carcinoma. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 1908–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Burkhardt, D.B.; Hartman, A.A.; Hu, X.; Eastman, A.E.; Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Zhong, M.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Guo, S. MLL-AF9 initiates transformation from fast-proliferating myeloid progenitors. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Guan, Y.F.; Hancock, S.E.; Wahi, K.; van Geldermalsen, M.; Zhang, B.K.; Pang, A.; Nagarajah, R.; Mak, B.; Freidman, N.; et al. Inhibition of guanosine monophosphate synthetase (GMPS) blocks glutamine metabolism and prostate cancer growth. J. Pathol. 2021, 254, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, P.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Z. Uridine-cytidine kinase 2 promotes metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the Stat3 pathway. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 6339–6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jamal, M.; Xie, T.; Sun, J.; Song, T.; Yin, Q.; Li, J.; Pan, S.; Zeng, X.; Xie, S.; et al. Uridine-cytidine kinase 2 (UCK2): A potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2734–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; He, P.; Mao, Y.; Li, P.; Luh, F.; Ding, G.; Liu, X.; Yen, Y. Overexpression of Uridine-Cytidine Kinase 2 Correlates with Breast Cancer Progression and Poor Prognosis. J. Breast Cancer 2017, 20, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lua, I.; Li, Y.; Zagory, J.A.; Wang, K.S.; French, S.W.; Sévigny, J.; Asahina, K. Characterization of hepatic stellate cells, portal fibroblasts, and mesothelial cells in normal and fibrotic livers. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, A.; de Campos, R.P.; Tsao, M.; Braganhol, E.; Furlanetto, T.W.; Wink, M.R. Extracellular ATP is Differentially Metabolized on Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Cells Surface in Comparison to Normal Cells. Cancer Microenviron. 2018, 11, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.A., Jr.; Cappellari, A.R.; de Marchi, F.O.; Gehring, M.P.; Zaparte, A.; Brandão, C.A.; Lopes, T.G.; da Silva, V.D.; Pinto, L.; Savio, L.; et al. Potential role of P2X7R in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma proliferation. Purinergic Signal. 2017, 13, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braganhol, E.; Zanin, R.F.; Bernardi, A.; Bergamin, L.S.; Cappellari, A.R.; Campesato, L.F.; Morrone, F.B.; Campos, M.M.; Calixto, J.B.; Edelweiss, M.I.; et al. Overexpression of NTPDase2 in gliomas promotes systemic inflammation and pulmonary injury. Purinergic Signal. 2012, 8, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, D.K.; Tse, A.P.; Xu, I.M.; Di Cui, J.; Lai, R.K.; Li, L.L.; Koh, H.Y.; Tsang, F.H.; Wei, L.L.; Wong, C.M.; et al. Hypoxia inducible factor HIF-1 promotes myeloid-derived suppressor cells accumulation through ENTPD2/CD39L1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwahana, H.; Oka, J.; Mizusawa, N.; Kudo, E.; Ii, S.; Yoshimoto, K.; Holmes, E.W.; Itakura, M. Molecular cloning of human amidophosphoribosyltransferase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 190, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, T.; Kondo, M.; Honda, S.; Iwahana, H.; Moritani, M.; Ii, S.; Yoshimoto, K.; Itakura, M. Amidophosphoribosyltransferase limits the rate of cell growth-linked de novo purine biosynthesis in the presence of constant capacity of salvage purine biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 17719–17725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibi, N.; Parveen, Z.; Nawaz, M.S.; Kamal, M.A. In Silico Structure Modeling and Molecular Docking Analysis of Phosphoribosyl Pyrophosphate Amidotransferase (PPAT) with Antifolate Inhibitors. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2019, 19, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Bao, M.; Huang, J.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S. Identification and Validation of Novel Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 541479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Zhu, X.; Ke, Y.; Xiao, D.; Liang, C.; Chen, J.; Chang, Y. LncRNA FTX inhibition restrains osteosarcoma proliferation and migration via modulating miR-320a/TXNRD1. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2020, 21, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.; Quan, Y.; Zhan, M.; Liao, H.; Li, Y.; Lu, L. miR-125b-5p inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting TXNRD1. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; McGrath, K.L.; Di Trapani, G.; Charoentong, P.; Shah, F.; King, M.M.; Clarke, F.M.; Tonissen, K.F. The thioredoxin system in breast cancer cell invasion and migration. Redox Biol. 2016, 8, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.; Roca, M.S.; Ciardiello, C.; Costantini, S.; Budillon, A. Oxidative Stress Gene Expression Profile Correlates with Cancer Patient Poor Prognosis: Identification of Crucial Pathways Might Select Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 2597581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Xu, I.M.; Chiu, D.K.; Leibold, J.; Tse, A.P.; Bao, M.H.; Yuen, V.W.; Chan, C.Y.; Lai, R.K.; Chin, D.W.; et al. Induction of Oxidative Stress through Inhibition of Thioredoxin Reductase 1 Is an Effective Therapeutic Approach for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1768–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhan, T.; Ke, T.; Huang, X.; Ke, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, H. Increased expression of RRM2 by human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein promotes angiogenesis in cervical cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Ge, C.; Li, H.; Zhao, F.; Hou, H.; Chen, T.; Jiang, G.; Xie, H.; Cui, Y.; Yao, M.; et al. Ribonucleotide reductase M2B inhibits cell migration and spreading by early growth response protein 1-mediated phosphatase and tensin homolog/Akt1 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Jin, C.; Xu, M.; Zhou, L.; Li, D.; Yin, Y. Bifunctional enzyme ATIC promotes propagation of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating AMPK-mTOR-S6 K1 signaling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2017, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Song, Q.; Li, J.; Du, K.; Chen, Y.; Zou, C.; Mo, Z. Carcinogenic effect of adenylosuccinate lyase (ADSL) in prostate cancer development and progression through the cell cycle pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha-Mehlitz, S.; Bianco, G.; Coto-Llerena, M.; Kancherla, V.; Bantug, G.R.; Gallon, J.; Ercan, C.; Panebianco, F.; Eppenberger-Castori, S.; von Strauss, M.; et al. Adenylosuccinate lyase is oncogenic in colorectal cancer by causing mitochondrial dysfunction and independent activation of NRF2 and mTOR-MYC-axis. Theranostics 2021, 11, 4011–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Gupta, R.S. Adenosine kinase and ribokinase--the RK family of proteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2875–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhulai, G.; Oleinik, E.; Shibaev, M.; Ignatev, K. Adenosine-Metabolizing Enzymes, Adenosine Kinase and Adenosine Deaminase, in Cancer. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipley, L.A.; Brown, T.J.; Cornpropst, J.D.; Hamilton, M.; Daniels, W.D.; Culp, H.W. Metabolism and disposition of gemcitabine, and oncolytic deoxycytidine analog, in mice, rats, and dogs. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1992, 20, 849–855. [Google Scholar]
- Weizman, N.; Krelin, Y.; Shabtay-Orbach, A.; Amit, M.; Binenbaum, Y.; Wong, R.J.; Gil, Z. Macrophages mediate gemcitabine resistance of pancreatic adenocarcinoma by upregulating cytidine deaminase. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3812–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maréchal, R.; Bachet, J.B.; Mackey, J.R.; Dalban, C.; Demetter, P.; Graham, K.; Couvelard, A.; Svrcek, M.; Bardier-Dupas, A.; Hammel, P.; et al. Levels of gemcitabine transport and metabolism proteins predict survival times of patients treated with gemcitabine for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basbous, J.; Aze, A.; Chaloin, L.; Lebdy, R.; Hodroj, D.; Ribeyre, C.; Larroque, M.; Shepard, C.; Kim, B.; Pruvost, A.; et al. Dihydropyrimidinase protects from DNA replication stress caused by cytotoxic metabolites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 1886–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, M.; Nomoto, S.; Oya, H.; Shimizu, D.; Takami, H.; Hibino, S.; Hashimoto, R.; Kobayashi, D.; Tanaka, C.; Yamada, S.; et al. Dihydropyrimidinase-like 3 facilitates malignant behavior of gastric cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, T.; Liu, J.; Ma, S.; Wang, M.; Yuan, Q.; Huang, A.; Wu, Z.; Shang, D.; Yin, P. A Nucleotide Metabolism-Related Gene Signature for Risk Stratification and Prognosis Prediction in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on an Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Approach. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13111116
Wei T, Liu J, Ma S, Wang M, Yuan Q, Huang A, Wu Z, Shang D, Yin P. A Nucleotide Metabolism-Related Gene Signature for Risk Stratification and Prognosis Prediction in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on an Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Approach. Metabolites. 2023; 13(11):1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13111116
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Tianfu, Jifeng Liu, Shurong Ma, Mimi Wang, Qihang Yuan, Anliang Huang, Zeming Wu, Dong Shang, and Peiyuan Yin. 2023. "A Nucleotide Metabolism-Related Gene Signature for Risk Stratification and Prognosis Prediction in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on an Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Approach" Metabolites 13, no. 11: 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13111116
APA StyleWei, T., Liu, J., Ma, S., Wang, M., Yuan, Q., Huang, A., Wu, Z., Shang, D., & Yin, P. (2023). A Nucleotide Metabolism-Related Gene Signature for Risk Stratification and Prognosis Prediction in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on an Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Approach. Metabolites, 13(11), 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13111116