Revised Harris–Benedict Equation: New Human Resting Metabolic Rate Equation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. REE, BMR, and RMR Predictive Equations
1.1.1. Harris–Benedict
1.1.2. Roza and Shizgal
1.1.3. Mifflin–St Jeor
1.1.4. FAO/WHO/UNU Equations
1.1.5. Owen
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Predictive Equations
2.3. Measures
2.3.1. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3.2. Indirect Calorimetry
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. International System of Units
3.2. Imperial System
3.3. Differences between Predictive Equations and Measurement RMR
3.4. Bland–Altman Plots of RMRP-RMRIC Differences
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Judge, A.; Dodd, M.S. Metabolism. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 607–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, M.; Yahagi, N. Basal metabolic rate. In Encyclopedia of Behavioral Medicine; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- McMurray, R.G.; Soares, J.; Caspersen, C.J.; McCurdy, T. Examining variations of resting metabolic rate of adults. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2014, 46, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rawson, E.S.; Branch, J.D.; Stephenson, T.J. Williams’ Nutrition for Health, Fitness and Sport; McGraw Hill LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.A.; Benedict, F.G. A biometric study of human basal metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1918, 4, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harris, J.A.; Benedict, F.G. A Biometric Study of Basal Metabolism in Man; Carnegie Institution of Washington: Washington, DC, USA, 1919; Publication No. 279. [Google Scholar]
- Roza, A.M.; Shizgal, H.M. The harris benedict equation reevaluated: Resting energy requirements and the body cell mass. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1984, 40, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mifflin, M.D.; St Jeor, S.T.; Hill, L.A.; Scott, B.J.; Daugherty, S.A.; Koh, Y.O. A new predictive equation for resting energy expenditure in healthy individuals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 51, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Livesey, G. Energy and protein requirements the 1985 report of the 1981 joint FAO/WHO/UNU expert consultation. Nutr. Bull. 1987, 12, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, O.E.; Kavle, E.; Owen, R.S.; Polansky, M.; Caprio, S.; Mozzoli, M.A.; Kendrick, Z.V.; Bushman, M.C.; Boden, G. A Reappraisal of caloric requirements in healthy women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1986, 44, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owen, O.E.; Holup, J.L.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Craig, E.S.; Polansky, M.; Smalley, K.J.; Kavle, E.C.; Bushman, M.C.; Owen, L.R.; Mozzoli, M.A. A reappraisal of the caloric requirements of men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1987, 46, 875–885. [Google Scholar]
- Schofield, W.N. Predicting basal metabolic rate, new standards and review of previous work. Hum. Nutr. Clin. Nutr. 1985, 39, 5–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marra, M.; Cioffi, I.; Morlino, D.; Vincenzo, O.D.; Pagano, M.C.; Imperatore, N.; Alfonsi, L.; Santarpia, L.; Castiglione, F.; Scalfi, L.; et al. New predictive equations for estimating resting energy expenditure in adults with Crohn’s disease. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frankenfield, D.C. Factors related to the assessment of resting metabolic rate in critically ill patients. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2018, 43, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, K.; McConville, M.; Kyba, M.; Keller-Ross, M. Resting metabolic rate in adults with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 46, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordenson, A.; Grönberg, A.M.; Hulthén, L.; Larsson, S.; Slinde, F. A validated disease specific prediction equation for resting metabolic rate in underweight patients with COPD. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2010, 7, 271–276. [Google Scholar]
- Alawad, A.O.; Merghani, T.H.; Ballal, M.A. Resting Metabolic Rate in Obese Diabetic and Obese Non-Diabetic Subjects and Its Relation to Glycaemic Control. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fairoosa, P.; Lanerolle, P.; De Lanerolle-Dias, M.; Wickramasinghe, V.P.; Waidyatilaka, I. Development of a new equation for the prediction of resting metabolic rate in Sri Lankan adults. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzer, S.; Agosti, F.; Silvestri, P.; Derumeaux-Burel, H.; Sartorio, A. Prediction of resting energy expenditure in severely obese Italian women. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2007, 30, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, R.; Pereira, G.; Alcantara, J.M.A.; Santos, R.; Hausen, M.; Itaborahy, A. New predictive resting metabolic rate equations for high-level athletes: A cross-validation study. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2022, 54, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, R.J.; Roberts, T.J.; Lee, K.A.; Bonsignore, J.L.; Anderson, M.L. Metabolic rate in adolescent athletes: The development and validation of new equations, and comparison to previous models. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2020, 30, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, B.A.; Nicoletti, C.F.; de Oliveira, C.C.; Pinhel, M.A.; Quinhoneiro, D.C.; Noronha, N.Y.; Marchini, J.S.; Nonino, C.B. A new resting metabolic rate equation for women with class III obesity. Nutrition 2018, 49, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- El Masri, D.; Itani, L.; Kreidieh, D.; Tannir, H.; El Ghoch, M. Predictive equations based on body composition for resting energy expenditure estimation in adults with obesity. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2020, 16, 381–386. [Google Scholar]
- Amano, Y. Estimated basal metabolic rate and maintenance fluid volume in children: A proposal for a new equation. Pediatr. Int. 2020, 62, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lührmann, P.M.; Herbert, B.M.; Krems, C.; Neuhäuser-Berthold, M. A new equation especially developed for predicting resting metabolic rate in the elderly for easy use in practice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2002, 41, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchizawa, A.; Hibi, M.; Sagayama, H.; Zhang, S.; Osumi, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Park, I.; Tokuyama, K.; Omi, N. Novel equations to estimate resting energy expenditure during sitting and sleeping. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 77, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, E.; Petridis, D.; Fasoulas, A.; Giaginis, C. Current clinical status on the estimation of energy requirement: Searching for a reliable equation to predict energy requirement in multiple populations. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 14, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Luque, R.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Márquez-Urrizola, C.; Ulloa, N.; Romero-Saldaña, M.; Molina-Recio, G. Accuracy of the resting energy expenditure estimation equations for healthy women. Nutrients 2021, 13, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obesity and Overweight (2021) World Health Organization. World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 24 November 2022).
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M. Obesity. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/obesity#there-is-a-10-fold-difference-in-death-rates-from-obesity-across-the-world (accessed on 24 December 2022).
- World Obesity Atlas 2022 World Obesity Federation. Available online: https://www.worldobesity.org/resources/resource-library/world-obesity-atlas-2022 (accessed on 24 December 2022).
- Europe’s Beating Cancer Plan. Available online: https://health.ec.europa.eu/publications/europes-beating-cancer-plan_en (accessed on 24 December 2022).
- Thom, G.; Gerasimidis, K.; Rizou, E.; Alfheeaid, H.; Barwell, N.; Manthou, E.; Fatima, S.; Gill, J.M.; Lean, M.E.; Malkova, D. Validity of Predictive Equations to Estimate RMR in Females with Varying BMI. J. Nutr. Sci. 2020, 9, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraki, M.I.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Jansen, L.T.; Anastasiou, C.; Papalazarou, A.; Yannakoulia, M.; Sidossis, L.S.; Kavouras, S.A. Validity of predictive equations for resting energy expenditure in Greek adults. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 72, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, P.; Kaifa, W.; Yong, Z.; Hong, Y.; Chao, W.; Lijuan, S.; Hongyu, W.; Dan, W.; Hua, J.; Shiliang, W. Establishment and Assessment of New Formulas for Energy Consumption Estimation in Adult Burn Patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warrier, V.; Krishan, K.; Shedge, R.; Kanchan, T. Height Assessment. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31855368/ (accessed on 13 December 2022).
- Campbell, B.; Zito, G.; Colquhoun, R.; Martinez, N.; St Louis, C.; Johnson, M.; Buchanan, L.; Lehn, M.; Smith, Y.; Cloer, B.; et al. Inter- and Intra-Day Test-Retest Reliability of the Cosmed Fitmate ProTm Indirect Calorimeter for Resting Metabolic Rate. J. Int. Soc. Sport. Nutr. 2014, 11, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lupinsky, L.; Singer, P.; Theilla, M.; Grinev, M.; Hirsh, R.; Lev, S.; Kagan, I.; Attal-Singer, J. Comparison between two metabolic monitors in the measurement of resting energy expenditure and oxygen consumption in diabetic and non-diabetic ambulatory and hospitalized patients. Nutrition 2015, 31, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compher, C.; Frankenfield, D.; Keim, N.; Roth-Yousey, L. Best practice methods to apply to measurement of resting metabolic rate in adults: A systematic review. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2006, 106, 881–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, K.; Dye, M. Basal metabolism of normal women. J. Biol. Chem. 1921, 47, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, L.; Schafer, A.I. Goldman-Cecil Medicine; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes—Global burden of disease and forecasted trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2019, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roger, V.L. Epidemiology of Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowes, H.M.; Burdon, C.A.; Taylor, N.A. The scaling of human basal and resting metabolic rates. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 121, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tur, J.A.; del Bibiloni, M. Anthropometry, body composition and resting energy expenditure in human. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavlidou, E.; Petridis, D.; Tolia, M.; Tsoukalas, N.; Poultsidi, A.; Fasoulas, A.; Kyrgias, G.; Giaginis, C. Estimating the Agreement between the Metabolic Rate Calculated from Prediction Equations and from a Portable Indirect Calorimetry Device: An Effort to Develop a New Equation for Predicting Resting Metabolic Rate. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankenfield, D.; Roth-Yousey, L.; Compher, C. Comparison of predictive equations for resting metabolic rate in healthy nonobese and obese adults: A systematic review. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2005, 105, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameters | Predictive Equations | Population Description | Age | R2 Male | R2 Female | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt, Gender, and Age Groups | FAO/WHO/UNU in kcal/d(1985) | n = 11,000 Many Ethnic groups and a broad BMI range | <3 | 0.97 | 0.97 | (60.9 × wt in kg) − 54 | (61. 3 × wt in kg) − 51 |
| 3–10 | 0.86 | 0.85 | (22.7 × wt in kg) + 495 | (22.43 × wt in kg) + 499 | |||
| 10–18 | 0.90 | 0.75 | (17.5 × wt in kg) + 651 | (12.2 × wt in kg) + 746 | |||
| 18–30 | 0.65 | 0.72 | (15.3 × wt in kg) + 679 | (14.7 × wt in kg) + 496 | |||
| 30–60 | 0.60 | 0.70 | (11.6 × wt in kg) + 879 | (8.7 × wt in kg) + 829 | |||
| >60 | 0.79 | 0.74 | (13.5 × wt in kg) + 487 | (10.5 × wt in kg) + 596 | |||
| Wt and Gender | Owen in kcal/d (1986 and 1987) | n = 60 M, multiple racial/ethnic volunteers 18–82 y, 60–17 1 kg n = 44 F (included 8 athletes), no specific racial/ethnic information provided, 18–65 y, 43–143 kg. | adults | 0.56 | 0.54 | 879 + (10.2 × wt in kg) | 795 + (7.18 × wt in kg) |
| Wt, Ht, Age, Gender | Harris–Benedict in kcal/d (1918, 1919) | n = 239, White normalweight, 16–63 y, 136 males (M) (weight mean 61.1 ± 10.3 Kg and mean ages 27 ± 9 y) 103 females (F) (mean weight 56.5 ± 11.5 Kg and mean ages 31 ± 4 y), Over a ten-year period | adults | 0.64 | 0.36 | (13.75 × wt in kg) + (5.003 × ht in cm) − (6.755 × age in y) + 66.47 | (9.563 × wt in kg) + (1.850 × htin cm) − (4.676 × age in y) + 655.1 |
| H–B rev. by Rosa and Shizgalin kcal/d (1984) | n = 337, 168 M, 169 F (with a wider age range from original H–B) | adults | 0.77 | 0.68 | (13.397 × wt in kg) + (4.799 × htin cm) − (5.677 × age in y) + 88.362 | (9.247 × wt in kg) + (3.098 × htin cm) − (4330 × age in y) + 447.593 | |
| Mifflin in kcal/d (1990) | n = 498, 19–78 y (mean ages 44 ± 14 y), 251 M (mean weight 87.5 ±14.4 Kg) 247 F (mean weight 70.2 ± 14.1 Kg) | adults | 0.71 | 0.71 | (9.99 × wt in kg) + (6.25 × ht in cm) − (4.92 × age in y) + 5 | (9.99 × wt in kg) + (6.25 ×ht in cm) − (4.92 × age in y) − 161 | |
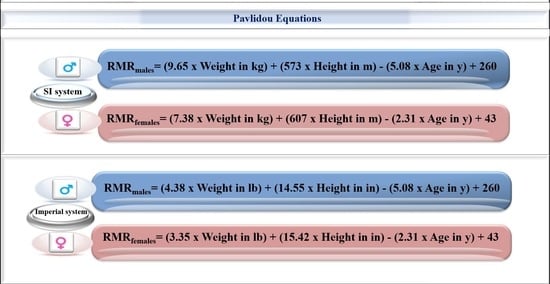
| Pavlidou (Proposed New Equations), in kcal/d (2022) | n = 722, Caucasians 173 M, 18–78 y, 55–177 kg, BMI: 20–48 Kg/m2 n = 549 F, 19–76 y, 43–139 kg, BMI:17–47 Kg/m2 | adults | 0.95 | 0.86 | (9.65 × wt in kg) + (573 × ht in m) − (5.08 × age in y) + 260 | (7.38 × wt in kg) + (607 × ht in m) − (2.31 × age in y) + 43 | |
| (4.38 × wt in pounds) + (14.55 × ht in inches) − (5.08 × age in y) + 260 | 3.35 × wt in pounds) + (15.42 × ht in inches) − (2.31 × age in y) + 43 |
| Characteristics | Males | Females | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 173 | 549 | 722 |
| Age range (years) | 18 to 78 | 19 to 76 | 18 to 78 |
| Age mean ± SD (years) | 39 ± 13 | 38 ± 12 | 38 ± 13 |
| Weight range (kg) | 55 to 157 | 43 to 139 | 43 to 157 |
| Weight mean ± SD (kg) | 99 ± 19 | 78 ± 16 | 83 ± 19 |
| Height range (m) | 1.5 to 2.03 | 1.48 to 1.86 | 1.48 to 2.03 |
| Height mean ± SD (m) | 1.78 ± 0.08 | 1.64 ± 0.06 | 1.68 ± 0.09 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 20 to 48 | 17 to 47 | 17 to 48 |
| BMI mean ± SD (kg/m2) | 31 ± 6 | 29 ± 6 | 29 ± 6 |
| RMRIC range (kcal/24 h) | 1039 to 2595 | 908 to 2492 | 908 to 2595 |
| RMRIC mean ± SD (kcal/24 h) | 2006 ± 346 | 1533 ± 308 | 1646 ± 376 |
| Males | Difference RMRP-RMRICMin (Kcal/d) | Difference RMRP-RMRICMax (Kcal/d) | Bias % * | Max Negative Error | Max Positive Error | RMSE (Kcal/d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pavlidou (New Equation) | 20.38 | 545.49 | 8.32% | −21.26% | 16.39% | 204.61 |
| Harris–Benedict | 8.51 | 513.7 | 9.06% | −28.83% | 23.18% | 222.71 |
| Mifflin–StJeor | 5 | 671 | 9.24% | −26.61% | 11.12% | 254.60 |
| Owen | 1.84 | 641.2 | 10.17% | −25.34% | 14.35% | 275.27 |
| WHO/FAO/UNU | 11.05 | 973.6 | 11% | −58.90% | 21.31% | 281.32 |
| Females | Difference RMRP-RMRICMin (Kcal/d) | Difference RMRP-RMRICMax (Kcal/d) | Bias % * | Max Negative Error | Max Positive Error | RMSE (Kcal/d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pavlidou (New Equation) | 2.31 | 366.8 | 8.93% | −18.82% | 27.2% | 175.55 |
| Harris–Benedict | 1.76 | 378.65 | 9.49% | −20.62% | 30.15% | 186.21 |
| Mifflin–StJeor | 0.5 | 476 | 11.23% | −25.94% | 26.9% | 204.92 |
| Owen | 11.6 | 612.03 | 13.38% | −30.52% | 26.01% | 252.78 |
| WHO/FAO/UNU | 5.22 | 466.77 | 10.31% | −20.86% | 38.88% | 193.41 |
| Males | Pavlidou (New Equation) | Harris–Benedict | Mifflin–StJeor | Owen | WHO/FAO/UNU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | −29.3 | −12.17 | −154.4 | −178.28 | −5.68 |
| Average ABS | 171.32 | 185.22 | 198.34 | 219.31 | 216.91 |
| SD | 205.08 | 225.21 | 205.02 | 212.42 | 284.85 |
| Females | Pavlidou (New Equation) | Harris–Benedict | Mifflin–StJeor | Owen | WHO/FAO/UNU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | 2.42 | −6.09 | −72.77 | −181.06 | −3.66 |
| Average ABS | 131.78 | 140.47 | 170.4 | 213.54 | 153.8 |
| SD | 176.23 | 186.85 | 192.32 | 177.12 | 194.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavlidou, E.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; Seroglou, K.; Giaginis, C. Revised Harris–Benedict Equation: New Human Resting Metabolic Rate Equation. Metabolites 2023, 13, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020189
Pavlidou E, Papadopoulou SK, Seroglou K, Giaginis C. Revised Harris–Benedict Equation: New Human Resting Metabolic Rate Equation. Metabolites. 2023; 13(2):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020189
Chicago/Turabian StylePavlidou, Eleni, Sousana K. Papadopoulou, Kyriakos Seroglou, and Constantinos Giaginis. 2023. "Revised Harris–Benedict Equation: New Human Resting Metabolic Rate Equation" Metabolites 13, no. 2: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020189
APA StylePavlidou, E., Papadopoulou, S. K., Seroglou, K., & Giaginis, C. (2023). Revised Harris–Benedict Equation: New Human Resting Metabolic Rate Equation. Metabolites, 13(2), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020189