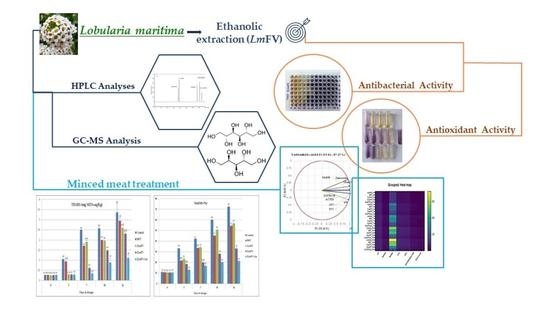
Biopreservative Effect of the Tunisian Halophyte Lobularia maritima Flavonoid Fraction, Used Alone and in Combination with Linalool in Stored Minced Beef Meat
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Flavonoid Extracts (LmFV)
2.3. HPLC Analyses of LmFV
2.4. GC-MS Analysis of the Extract after Derivatization
2.5. Antioxidant Activity
2.5.1. Assay of DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.5.2. Phosphomolybdenum Method
2.6. Antimicrobial Activity
Determination of MICs and MBCs
2.7. Meat Sample Preparation and Conditioning
2.7.1. Microbiological Analysis
2.7.2. Physicochemical Analysis (pH Analysis)
2.7.3. Physicochemical Analysis (Lipid Oxidation)
2.7.4. Physicochemical Analysis (Metmyoglobin (MetMb) Analysis)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Flavonoid Content of L. maritima Extract
3.2. Chemical Composition of L. maritima Extract after Derivatization
3.3. Antibacterial Activity
3.4. Antioxidant Activity
3.5. Microbiological Analysis
3.6. Physicochemical Analyses
3.6.1. pH Analysis
3.6.2. Evaluation of Lipid Oxidation
3.6.3. Evaluation of Protein Oxidation
3.7. Chemometric Analysis
3.7.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3.7.2. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA)
3.7.3. Heat Maps
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An Overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Yu, O. Metabolic Engineering of Flavonoids in Plants and Microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Khan, A.; Ahmad, I.; Alghamdi, S.; Rajab, B.S.; Babalghith, A.O.; Alshahrani, M.Y.; Islam, S.; Islam, M.R. Flavonoids a Bioactive Compound from Medicinal Plants and Its Therapeutic Applications. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, e5445291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addi, M.; Elbouzidi, A.; Abid, M.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Elamrani, A.; Hano, C. An Overview of Bioactive Flavonoids from Citrus Fruits. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuyckens, F.; Claeys, M. Mass Spectrometry in the Structural Analysis of Flavonoids. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, R.K.; Dubey, A.K.; Garg, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Fiorino, M.; Ameen, S.M.; Haddad, M.A.; Al-Hiary, M. Natural Polyphenols: Chemical Classification, Definition of Classes, Subcategories, and Structures. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1397–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, D.E.; Hurst, R.D. Polyphenolic Phytochemicals–Just Antioxidants or Much More? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 2900–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant Flavonoids: Classification, Distribution, Biosynthesis, and Antioxidant Activity. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cao, H.; Huang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Teng, H. Absorption, Metabolism and Bioavailability of Flavonoids: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7730–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczak, A.; Ożarowski, M.; Karpiński, T.M. Antibacterial Activity of Some Flavonoids and Organic Acids Widely Distributed in Plants. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antibacterial Activity of Flavonoids and Their Structure–Activity Relationship: An Update Review-Farhadi-2019-Phytotherapy Research-Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ptr.6208?casa_token=2JCbI__5rdQAAAAA%3Ax-9gdtvmcYpI1ZrpAac2DKb0CR0_FX_9LCag-VQhusZh2k-yvcaCQQEvQ6h-Cdmmqz-0G864vizxFjCT (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- Nguyen, W.; Grigori, L.; Just, E.; Santos, C.; Seleem, D. The in Vivo Anti-Candida Albicans Activity of Flavonoids. J. Oral Biosci. 2021, 63, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Aboody, M.S.; Mickymaray, S. Anti-Fungal Efficacy and Mechanisms of Flavonoids. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben Hsouna, A.; Dhibi, S.; Dhifi, W.; Ben Saad, R.; Brini, F.; Hfaidh, N.; Mnif, W. Essential Oil from Halophyte Lobularia Maritima: Protective Effects against CCl 4 -Induced Hepatic Oxidative Damage in Rats and Inhibition of the Production of Proinflammatory Gene Expression by Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 36758–36770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben Hsouna, A.; Ghneim-Herrera, T.; Ben Romdhane, W.; Dabbous, A.; Ben Saad, R.; Brini, F.; Abdelly, C.; Ben Hamed, K. Early Effects of Salt Stress on the Physiological and Oxidative Status of the Halophyte Lobularia Maritima. Funct. Plant Biol. 2020, 47, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouidhi, S.; Zidi, O.; Abdelwahed, S.; Souissi, Y.; Trabelsi, N.; Redissi, A.; Hamdi, M.; Trabelsi, E.; Amara, Y.; Bhiri, T.; et al. Investigation of the Chemical Composition and Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Lobularia Maritima: Potent Therapeutic Applications. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, e1981680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Geesink, G.H.; Ilian, M.A.; Morton, J.D.; Sedcole, R.; Bickerstaffe, R. Particulate Metmyoglobin Reducing Activity and Its Relationship with Meat Color. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6026–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, M.M.; Nute, G.R.; Hughes, S.I.; Enser, M.; Wood, J.D.; Richardson, R.I. Flavour Perception of Oxidation in Beef. Meat Sci. 2006, 72, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ahn, D.U. Lipid Oxidation and Its Implications to Meat Quality and Human Health. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linalool Affects the Antimicrobial Efficacy of Essential Oils|SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00284-015-0933-4 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Kamatou, G.P.; Viljoen, A.M. Linalool–A Review of a Biologically Active Compound of Commercial Importance. 2008. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1934578X0800300727 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Ben Hsouna, A.; Sadaka, C.; Generalić Mekinić, I.; Garzoli, S.; Švarc-Gajić, J.; Rodrigues, F.; Morais, S.; Moreira, M.M.; Ferreira, E.; Spigno, G.; et al. The Chemical Variability, Nutraceutical Value, and Food-Industry and Cosmetic Applications of Citrus Plants: A Critical Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immunomodulatory Effect of Linalool (Lin) against CCl4-induced Hepatotoxicity and Oxidative Damage in rats-Hsouna-Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry-Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://iubmb.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/bab.2371?casa_token=VNZ36HtX4AkAAAAA%3AQ45-SxhFo0Z9eOvYpKfBafnSr0v5BYCAnOnVEcUAah1nqe_9HXSKSM01gGtTummqMDFnNEXVDAyywFaZ (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Jabir, M.S.; Taha, A.; Sahib, U. Antioxidant Activity of Linalool. Eng. Technol. J. 2018, 36, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.H.; Huang, S.C.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B.H. Determination of Flavonoids and Saponins in GynostemmaPentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino by Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 626, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzoli, S.; Maggio, F.; Vinciguerra, V.; Rossi, C.; Donadu, M.G.; Serio, A. Chemical Characterization and Antimicrobial Properties of the Hydroalcoholic Solution of Echinacea purpurea (L.) Moench. and Propolis from Northern Italy. Molecules 2023, 28, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Hsouna, A.; Ben Halima, N.; Smaoui, S.; Hamdi, N. Citrus Lemon Essential Oil: Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities with Its Preservative Effect against Listeria Monocytogenes Inoculated in Minced Beef Meat. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prieto, P.; Pineda, M.; Aguilar, M. Spectrophotometric Quantitation of Antioxidant Capacity through the Formation of a Phosphomolybdenum Complex: Specific Application to the Determination of Vitamin E. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 269, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Akacha, B.; Švarc-Gajić, J.; Elhadef, K.; Ben Saad, R.; Brini, F.; Mnif, W.; Smaoui, S.; Ben Hsouna, A. The Essential Oil of Tunisian Halophyte Lobularia Maritima: A Natural Food Preservative Agent of Ground Beef Meat. Life 2022, 12, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsouna, A.B.; Boye, A.; Ackacha, B.B.; Dhifi, W.; Saad, R.B.; Brini, F.; Mnif, W.; Kačániová, M. Thiamine Demonstrates Bio-Preservative and Anti-Microbial Effects in Minced Beef Meat Storage and Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Animals 2022, 12, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eymard, S.; Carcouët, E.; Rochet, M.-J.; Dumay, J.; Chopin, C.; Genot, C. Development of Lipid Oxidation during Manufacturing of Horse Mackerel Surimi. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Tu, J.; Zhou, H.; Lu, A.; Xu, B. A Comprehensive Insight into the Effects of Microbial Spoilage, Myoglobin Autoxidation, Lipid Oxidation, and Protein Oxidation on the Discoloration of Rabbit Meat during Retail Display. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spriha, S.E.; Abdur Rahman, S.M. A Review on Biological Activities of Sugars and Sugar Derivatives. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 20, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhibi, M.; Mechri, B.; Brahmi, F.; Skhiri, F.; Alsaifc, M.A.; Mohamed Hammami, M. Fatty acid profiles, antioxidant compounds and antiradical properties of Pinus halepensis Mill. cones and seeds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, B.; Rogers, K.; McLaughlin, F.; Daniels, D.; Yadav, A. Antimicrobial Activities of Leaf Extracts of Guava (Psidium guajava L.) on Two Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria. Int. J. Microbiol. 2013, 2, e746165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comprehensive Review of Antimicrobial Activities of Plant Flavonoids|SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11101-018-9591-z (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Jucá, M.M.; Cysne Filho, F.M.S.; de Almeida, J.C.; Mesquita, D.D.S.; Barriga, J.R.D.M.; Dias, K.C.F.; Barbosa, T.M.; Vasconcelos, L.C.; Leal, L.K.A.M.; Ribeiro, J.E.; et al. Flavonoids: Biological Activities and Therapeutic Potential. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Chen, Q.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Yun, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, W. Antimicrobial Activity and Proposed Action Mechanism of Linalool Against Pseudomonas Fluorescens. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 562094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Hsouna, A.; Michalak, M.; Ben Akacha, B.; Dhifi, W.; Ben Saad, R.; Brini, F.; Mnif, W. Assessment of the Phytochemical Composition, Antimicrobial Activity and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Lobularia Maritima Extracts on Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells and Their Capacity to Extend the Shelf Life of Raw Minced Beef. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 99, 105327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akacha, B.B.; Najar, B.; Venturi, F.; Quartacci, M.F.; Saad, R.B.; Brini, F.; Mnif, W.; Kačániová, M.; Ben Hsouna, A. A New Approach in Meat Bio-Preservation through the Incorporation of a Heteropolysaccharide Isolated from Lobularia maritima L. Foods 2022, 11, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 14:00–17:00. ISO 4833-2:2013. ISO. Available online: https://www.iso.org/cms/render/live/en/sites/isoorg/contents/data/standard/05/95/59509.html (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Antimicrobial Activity of Flavonoids from Sedum aizoon L. against Aeromonas in Culture Medium and in Frozen Pork-PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6804768/ (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Interactions between Components of the Essential Oil of Melaleuca alternifolia-Cox-2001-Journal of Applied Microbiology-Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://ami-journals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01406.x (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Sukhov, B.G.; Pogodaeva, N.N.; Kuznetsov, S.V.; Kupriyanovich, Y.N.; Yurinova, G.V.; Selivanova, D.S.; Pristavka, A.A.; Dzhioev, Y.P.; Popkova, S.M.; Rakova, E.B.; et al. Prebiotic effect of native noncovalent arabinogalactan—Flavonoid conjugates on bifidobacteria. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2014, 63, 2189–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juneja, V.K.; Bari, M.L.; Inatsu, Y.; Kawamoto, S.; Friedman, M. Control of Clostridium perfringens Spores by Green Tea Leaf Extracts during Cooling of Cooked Ground Beef, Chicken, and Pork. J. Food Prot. 2007, 70, 1429–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quelhas, I.; Petisca, C.; Viegas, O.; Melo, A.; Pinho, O.; Ferreira, I.M.P.L.V.O. Effect of Green Tea Marinades on the Formation of Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines and Sensory Quality of Pan-Fried Beef. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.; Cilla, I.; Antonio Beltrán, J.; Roncalés, P. Effect of Capsicum Annuum (Red Sweet and Cayenne) and Piper Nigrum (Black and White) Pepper Powders on the Shelf Life of Fresh Pork Sausages Packaged in Modified Atmosphere. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, S48–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergan, T. 1 Classification of Enterobacteriaceae. In Methods in Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; Volume 14, pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, H. Utilization of Natural Antioxidants: Green Tea Extract and Thymbra Spicata Oil in Turkish Dry-Fermented Sausage. Meat Sci. 2006, 73, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannan, R.G.; Mah, E. Grape Seed Extract Inhibits Lipid Oxidation in Muscle from Different Species during Refrigerated and Frozen Storage and Oxidation Catalyzed by Peroxynitrite and Iron/Ascorbate in a Pyrogallol Red Model System. Meat Sci. 2007, 77, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotta, L.; Castellani, F.; Palazzo, F.; NaceurHaouet, M.; Martino, G. Treatment Optimisation and Sample Preparation for the Evaluation of Lipid Oxidation in Various Meats Through TBARs Assays before Analysis. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1870–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, K.I.; Ishioroshi, M.; Samejima, K. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Effects of Garlic in Chicken Sausage. Lebensm. Wiss. Ie Technol. Food Sci. Technol. Sci. Technol. Aliment. 2004, 37, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carpenter, R.; O’Grady, M.N.; O’Callaghan, Y.C.; O’Brien, N.M.; Kerry, J.P. Evaluation of the Antioxidant Potential of Grape Seed and Bearberry Extracts in Raw and Cooked Pork. Meat Sci. 2007, 76, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, M.C.; Brewer, M.S. Effect of Natural Antioxidants on Oxidative Stability of Cooked, Refrigerated Beef and Pork. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, S282–S288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarıçoban, C.; Yilmaz, M.T. Effect of Thyme/Cumin Essential Oils and Butylated Hydroxyl Anisole/Butylated Hydroxyl Toluene on Physicochemical Properties and Oxidative/Microbial Stability of Chicken Patties. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; van Houwelingen-Koukaliaroglou, M. Implementation of Chemometrics for Quality Control and Authentication of Meat and Meat Products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 43, 173–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Pan, X.; Li, S.; Zhu, N.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Qiao, X.; Chen, W. Changes of Protein Oxidation, Lipid Oxidation and Lipolysis in Chinese Dry Sausage with Different Sodium Chloride Curing Salt Content. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2020, 9, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Acronym | Experimental Conditions | |
|---|---|---|
| Lot 1 | Control | Untreated control |
| Lot 2 | BHT | Processed with 0.01% BHT |
| Lot 3 | 1LmFV | Processed with LmFV at 2.3% (v/w) |
| Lot 4 | 2LmFV | Processed with LmFV at 4.6% (v/w) |
| Lot 5 | 2LmFV+Lin | Processed with LmFV at 4.6% and Lin at 0.46% (v/w) |
| N° | COMPONENTS | LmE. (%) 1 |
|---|---|---|
| SUGAR ALCOHOLS | ||
| 1 | Ribitol | 0.1 |
| 2 | Myo-inositol | 0.1 |
| 3 | Phytol | 0.1 |
| 4 | Glycerol | 0.2 |
| 5 | Arabitol | 36.1 |
| 6 | Mannitol | 49.6 |
| SUGARS | ||
| 7 | Turanose | 0.3 |
| 8 | Mannobiose | 0.7 |
| 9 | Trehalose | 10.4 |
| FATTY ACIDS | ||
| 10 | Lauric | 0.1 |
| 11 | Palmitic | 1.1 |
| 12 | Linoleic | 0.3 |
| 13 | Oleic | 0.1 |
| 14 | Stearic | 0.4 |
| TERPENES | ||
| 15 | Isoborneol | tr |
| 16 | Farnesol | 0.1 |
| 17 | Neophytadiene | 0.3 |
| 18 | Eugenol | tr |
| Bacterial Strains | LmFV (mg/mL) | Lin (mg/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MBC/MIC | Antibacterial Activity | |
| Gram-positive | ||||||
| Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579 | 4.8 ± 1.05 | >30 | 0.7 ± 0.55 | >5 | - | - |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 2.7 ± 0.95 | >30 | 0.23 ± 0.08 | 5 | 21 | Bacteriostatic |
| Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212 | 3.7 ± 0.00 | >30 | 0.23 ± 0.08 | 2.5 | 10 | Bacteriostatic |
| Micrococcus luteus ATCC 1880 | 2.7 ± 0.95 | >30 | 0.23 ± 0.08 | >5 | - | - |
| Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 1911 | 2.3 ± 0.41 | >30 | 0.46 ± 0.15 | >5 | - | - |
| Gram-negative | ||||||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 | 5.8 ± 0.12 | >30 | 0.46 ± 0.15 | 1.2 | 2 | Bactericidal |
| Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 3.7 ± 0.00 | >30 | 0.38 ± 0.23 | 2.5 | 6 | Bacteriostatic |
| Salmonella enterica ATCC 43972 | 2.75 ± 0.34 | >30 | 0.46 ± 0.15 | >5 | - | - |
| Antioxidant Activity (IC50 (µg/mL)) | BHT | LmFV | Lin |
|---|---|---|---|
| DPPH radical scavenging activity | 22.38 ± 0.34 | 50.78 ± 0.14 | 5.64 ± 0.25 |
| Phosphomolybdenum assay | 51.87 ± 0.46 | 87.02 ± 0.81 | 24.73 ± 0.27 |
| Samples | Days of Refrigerated Storage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 7 | 10 | 14 | |
| Enterobacteriaceae counts | |||||
| Control | <1 aA | 1.47 ± 0.07 bAB | 1.80 ± 0.35 bB | 2.83 ± 0.14 dBC | 3.46 ± 0.47 aC |
| BHT | <1 aA | 1.13 ± 0.13 bAB | 1.49 ± 0.45 abB | 2.62 ± 0.22 cBC | 3.26 ± 0.34 aC |
| 1LmFV | <1 aA | 1.22 ± 0.07 bAB | 1.69 ± 0.28 bBC | 2.66 ± 0.55 cdCD | 3.16 ± 0.44 aD |
| 2LmFV | <1 aA | <1 aA | 1.08 ± 0.08 abAB | 2.03 ± 0.25 bBC | 2.53 ± 0.47 aC |
| 2LmFV+Lin | <1 aA | <1 aA | <1 aA | 1.22 ± 0.02 aB | 1.72 ± 0.52 aB |
| Salmonella | |||||
| Control | <1 aA | <1 aA | 1.69 ± 0.01 cAB | 1.99 ± 0.06 bB | 2.93 ± 0.94 dB |
| BHT | <1 aA | <1 aA | 1.08 ± 0.12 bAB | 1.55 ± 0.62 bB | 2.11 ± 0.27 bB |
| 1LmFV | <1 aA | <1 aA | <1 aA | 1.20 ± 0.13 bB | 1.91 ± 0.63 aB |
| 2LmFV | <1 aA | <1 aA | <1 aA | 1.02 ± 0.02 bAB | 1.65 ± 0.77 bB |
| 2LmFV+Lin | <1 aA | <1 aA | <1 aA | <1 aA | 1.02 ± 0.29 aA |
| Samples | Days of Refrigerated Storage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 7 | 10 | 14 | |
| Control | 5.21 ± 0.00 aA | 6.68 ± 0.02 bB | 6.94 ± 0.04 cC | 7.25 ± 0.05 dD | 7.46 ± 0.02 eE |
| BHT | 5.18 ± 0.00 aA | 6.34 ± 0.0 bB | 6.68 ± 0.08 bcBC | 6.94 ± 0.05 cC | 7.03 ± 0.02 cC |
| 1LmFV | 5.19 ± 0.02 aA | 6.37 ± 0.01 bB | 6.71 ± 0.03 cBC | 6.92 ± 0.01 dC | 7.25 ± 0.04 eD |
| 2LmFV | 5.23 ± 0.00 aA | 6.31 ± 0.1 abB | 6.59 ± 0.01 bB | 6.58 ± 0.02 bB | 6.69 ± 0.01 bB |
| 2LmFV+Lin | 5.19 ± 0.01 aA | 5.52 ± 0.02 abA | 5.82 ± 0.08 cA | 6.02 ± 0.02 cdA | 6.17 ± 0.02 dA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben Akacha, B.; Garzoli, S.; Ben Saad, R.; Brini, F.; Mnif, W.; Kačániová, M.; Ben Hsouna, A. Biopreservative Effect of the Tunisian Halophyte Lobularia maritima Flavonoid Fraction, Used Alone and in Combination with Linalool in Stored Minced Beef Meat. Metabolites 2023, 13, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030371
Ben Akacha B, Garzoli S, Ben Saad R, Brini F, Mnif W, Kačániová M, Ben Hsouna A. Biopreservative Effect of the Tunisian Halophyte Lobularia maritima Flavonoid Fraction, Used Alone and in Combination with Linalool in Stored Minced Beef Meat. Metabolites. 2023; 13(3):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030371
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen Akacha, Boutheina, Stefania Garzoli, Rania Ben Saad, Faical Brini, Wissem Mnif, Miroslava Kačániová, and Anis Ben Hsouna. 2023. "Biopreservative Effect of the Tunisian Halophyte Lobularia maritima Flavonoid Fraction, Used Alone and in Combination with Linalool in Stored Minced Beef Meat" Metabolites 13, no. 3: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030371
APA StyleBen Akacha, B., Garzoli, S., Ben Saad, R., Brini, F., Mnif, W., Kačániová, M., & Ben Hsouna, A. (2023). Biopreservative Effect of the Tunisian Halophyte Lobularia maritima Flavonoid Fraction, Used Alone and in Combination with Linalool in Stored Minced Beef Meat. Metabolites, 13(3), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030371