Cycloartane Saponins from Astragalus glycyphyllos and Their In Vitro Neuroprotective, Antioxidant, and hMAO-B-Inhibiting Effects
Abstract
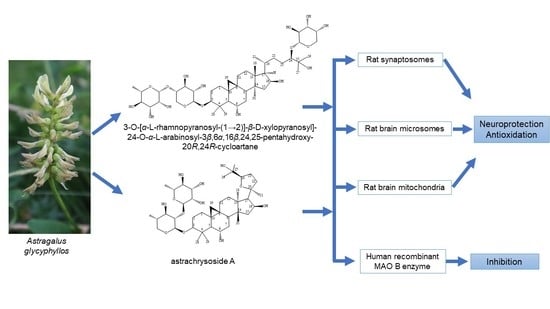
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
2.2. Extraction and Isolation of Compounds from Plant Material
2.3. In Vitro Pharmacological Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Identification of the Compounds
3.2. Pharmacological Investigation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asyov, B.; Petrova, A.; Dimitrov, D.; Vasilev, R. Conspectus of the Bulgarian Vascular Flora. Distribution Maps and Floristic Elements; Bulgarian Biodiversity Foundation: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Valev, S.A. Astragalus L. In Flora Republicae Popularis Bulgaricae; Yordanov, D., Ed.; Aedibus Academiae Scientiarum Bulgaricae: Sofia, Bulgaria, 1976; Volume 6, p. 167. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolov, S.D. (Ed.) Specialized Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants in Bulgaria; Labour Publishing House: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Krasteva, I.; Shkondrov, A.; Ionkova, I.; Zdraveva, P. Advances in Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Biotechnology of Bulgarian Astragalus Species. Phytochem. Rev. 2016, 15, 567–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elenga, P.A.; Nikolov, S.; Panova, D. Triterpene Glycosides from Astragalus glycyphyllos L. a New Natural Compound of the Overgrowing Parts of Astragalus glycyphyllos L. Pharmazie 1987, 42, 422–423. [Google Scholar]
- Elenga, P.A.; Nikolov, S.; Panova, D. Triterpene Glycosides and Sterols from Astragalus glycyphyllos L. Pharmazie 1986, 41, 41–42. [Google Scholar]
- Linnek, J.; Mitaine-Offer, A.C.; Miyamoto, T.; Lacaille-Dubois, M.A. Two Cycloartane-Type Glycosides from the Roots of Astragalus glycyphyllos. Planta Med. 2008, 74, PB141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkondrov, A.; Krasteva, I.; Bucar, F.; Kunert, O.; Kondeva-Burdina, M.; Ionkova, I. A New Tetracyclic Saponin from Astragalus glycyphyllos L. and Its Neuroprotective and HMAO-B Inhibiting Activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkondrov, A.; Simeonova, R.; Kondeva-Burdina, M.; Vitcheva, V.; Krasteva, I. Study to Evaluate the Antioxidant Activity of Astragalus glycyphyllos Extract in Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Oxidative Stress in Rats. Eur. J. Med. Plants 2015, 7, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, A.; Popov, G.; Shkondrov, A.; Toshkova, R.; Krasteva, I.; Kondeva-Burdina, M.; Manov, V. Antiproliferative and Antitumour Activity of Saponins from Astragalus glycyphyllos on Myeloid Graffi Tumour. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 267, 113519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassova, N.; Aluani, D.; Hristova-Avakumova, N.; Tzankova, V.; Kondeva-Burdina, M.; Rangelov, M.; Todorova, N.; Yancheva, D. Study on the Neuroprotective, Radical-Scavenging and MAO-B Inhibiting Properties of New Benzimidazole Arylhydrazones as Potential Multi-Target Drugs for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakefield, I.D.; Pollard, C.; Redfern, W.S.; Hammond, T.G.; Valentin, J.-P. The Application of in Vitro Methods to Safety Pharmacology. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 16, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, S.; Bagheri, M. In Vivo, in Vitro and Pharmacologic Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondeva-Burdina, M.; Krasteva, I.; Popov, G.; Manov, V. Neuroprotective and Antioxidant Activities of Saponins’ Mixture from Astragalus glycyphylloides in a Model of 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Oxidative Stress on Isolated Rat Brain Synaptosomes. Pharmacia 2019, 66, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasabova-Angelova, A.; Kondeva-Burdina, M.; Mitkov, J.; Georgieva, M.; Tzankova, V.; Zlatkov, A. Neuroprotective and MAOB Inhibitory Effects of a Series of Caffeine-8-Thioglycolic Acid Amides. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 56, e18255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznicek, G.; Susman, O.; Böhm, K. Bestimmung Der Reihenzugehörigkeit von Monosacchariden Aus Pflanzlichen Glykosiden Mittels GC—MS. Sci. Pharm 1993, 61, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Taupin, P.; Zini, S.; Cesselin, F.; Ben-Ari, Y.; Roisin, M.-P. Subcellular Fractionation on Percoll Gradient of Mossy Fiber Synaptosomes: Morphological and Biochemical Characterization in Control and Degranulated Rat Hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 1994, 62, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpay, M.; Dulger, G.; Sahin, I.E.; Dulger, B. Evaluating Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Capacity of Endemic Phlomis Russeliana from Turkey and Its Antiproliferative Effect on Human Caco-2 Cell Lines. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2019, 91, e20180404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mungarro-Menchaca, X.; Ferrera, P.; Morán, J.; Arias, C. β-Amyloid Peptide Induces Ultrastructural Changes in Synaptosomes and Potentiates Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Presence of Ryanodine. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 68, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robyt, J.F.; Ackerman, R.J.; Chittenden, C.G. Reaction of Protein Disulfide Groups with Ellman’s Reagent: A Case Study of the Number of Sulfhydryl and Disulfide Groups in Aspergillus Oryzae α-Amylase, Papain, and Lysozyme. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1971, 147, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, M.; Alizadeh, S.; Mahdavinia, M.; Dehghani, M.A. The Ameliorative Effect of Quercetin on Bisphenol A-Induced Toxicity in Mitochondria Isolated from Rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 7688–7696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindranath, V.; Anandatheerthavarada, H.K. Preparation of Brain Microsomes with Cytochrome P450 Activity Using Calcium Aggregation Method. Anal. Biochem. 1990, 187, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuy, D.; Sassi, A.; Dansette, P.M.; Plat, M. A New Potent Inhibitor of Lipid Peroxidation in Vitro and in Vivo, the Hepatoprotective Drug Anisyldithiolthione. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 135, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.P.; Lieberknecht, V.; Ramos-Hryb, A.B.; Olescowicz, G.; Ludka, F.K.; Tasca, C.I.; Gabilan, N.H.; Rodrigues, A.L.S. Creatine Affords Protection against Glutamate-Induced Nitrosative and Oxidative Stress. Neurochem. Int. 2016, 95, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista-Aguilera, O.M.; Esteban, G.; Bolea, I.; Nikolic, K.; Agbaba, D.; Moraleda, I.; Iriepa, I.; Samadi, A.; Soriano, E.; Unzeta, M.; et al. Design, Synthesis, Pharmacological Evaluation, QSAR Analysis, Molecular Modeling and ADMET of Novel Donepezil—Indolyl Hybrids as Multipotent Cholinesterase/Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors for the Potential Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 75, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polat, E.; Bedir, E.; Perrone, A.; Piacente, S.; Alankus-Caliskan, O. Triterpenoid Saponins from Astragalus wiedemannianus Fischer. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gariboldi, P.; Pelizzoni, F.; Tatò, M.; Verotta, L.; El-Sebakhy, N.; Asaad, A.M.; Abdallah, R.M.; Toaima, S.M. Cycloartane Triterpene Glycosides from Astragalus trigonus. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.K.; He, K.; Xu, H.X.; Zhang, Z.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Kikuchi, T.; Tezuka, Y. The structure of astrachrysosid A and the study of 2D-NMR on astrasieversianin XV and 7,2′-dihydroxy-3′,4′-dimethoxy-isoflavane-7-O-beta-D-glycoside. Yao Xue Xue Bao 1990, 25, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zarre, S.; Azani, N. Perspectives in Taxonomy and Phylogeny of the Genus Astragalus (Fabaceae): A Review. Prog. Biol. Sci. 2013, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, A.H.; Freeman, W.M.; Mitchell, S.G.; Burnette, T.A.; Hellmann, G.M.; Vrana, K.E. Induction of GADD45 and GADD153 in Neuroblastoma Cells by Dopamine-Induced Toxicity. Neurotoxicology 2002, 23, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, I.H.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, S.I.; Yang, H.D.; Moon, H.-I. Neuroprotective Activity of Triterpenoid Saponins from Platycodi Radix Against Glutamate-Induced Toxicity in Primary Cultured Rat Cortical Cells. Molecules 2007, 12, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.-Y.; Wang, S.; Li, C.-J.; Ma, J.; Chen, F.-Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, X.-L.; Zhang, D.-M. Dammarane-Type Saponins from the Leaves of Panax Notoginseng and Their Neuroprotective Effects on Damaged SH-SY5Y Cells. Phytochemistry 2018, 145, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yu, W.; Yang, T.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chai, L.; Gao, Y.; Dong, B.; Zhu, L. Panax Notoginseng Saponins Provide Neuroprotection by Regulating NgR1/RhoA/ROCK2 Pathway Expression, in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 190, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Jo, M.H.; Choe, K.; Khan, A.; Ahmad, S.; Saeed, K.; Kim, M.W.; Kim, M.O. Cycloastragenol, a Triterpenoid Saponin, Regulates Oxidative Stress, Neurotrophic Dysfunctions, Neuroinflammation and Apoptotic Cell Death in Neurodegenerative Conditions. Cells 2021, 10, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Qiu, J.; Yu, C. Astragaloside IV Attenuates the H2O2-Induced Apoptosis of Neuronal Cells by Inhibiting α-Synuclein Expression via the P38 MAPK Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 1772–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, W.-S.; Durairajan, S.S.K.; Lu, J.-H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, L.-X.; Kum, W.-F.; Koo, I.; Yung, K.K.L.; Li, M. Neuroprotective Effects of Astragaloside IV in 6-Hydroxydopamine-Treated Primary Nigral Cell Culture. Neurochem. Int. 2009, 55, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shkondrov, A.; Krasteva, I.; Bucar, F.; Kunert, O.; Kondeva-Burdina, M.; Ionkova, I. Flavonoids and Saponins from Two Bulgarian Astragalus Species and Their Neuroprotective Activity. Phytochem. Lett. 2018, 26, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öllinger, K.; Brunk, U.T. Cellular Injury Induced by Oxidative Stress Is Mediated through Lysosomal Damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 19, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, V.; Burkitt, M.J. Mitochondrial Metabolism of a Hydroperoxide to Free Radicals in Human Endothelial Cells: An Electron Spin Resonance Spin-Trapping Investigation. Biochem. J. 1994, 304, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Position | δC [ppm], Type | δH [ppm], (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 33.5, CH2 | 1.54, t (13.0) 1.21 |
| 2 | 30.7, CH2 | 1.91, m 1.66 |
| 3 | 89.3, CH | 3.18, d (~13) |
| 4 | 43.2, C | - |
| 5 | 54.8, CH | 1.35, d (9.9) |
| 6 | 69.6, CH | 3.44, m |
| 7 | 38.8, CH2 | 1.33 1.45 |
| 8 | 48.8, CH | 1.79, dd (12.0, 4.2) |
| 9 | 22.1, C | - |
| 10 | 30.4, C | - |
| 11 | 27.0, CH2 | 1.191.97 |
| 12 | 33.9, CH2 | 1.66 1.60, td (12.0, 3.2) |
| 13 | 46.4, C | - |
| 14 | 47.4, C | - |
| 15 | 48.8, CH2 | 1.99 1.38 |
| 16 | 73.1, CH | 4.40, m |
| 17 | 58.1, CH | 1.66 |
| 18 | 19.2, CH3 | 1.13 s |
| 19 | 31.9, CH2 | 0.37, d (4.0) 0.52, d (4.0) |
| 20 | 32.5, CH | 1.75 |
| 21 | 18.7, CH3 | 0.93, d (6.5) |
| 22 | 34.6, CH2 | 2.08, brt (12.5) 0.96 |
| 23 | 30.4, CH2 | 1.701.25 |
| 24 | 92.5, CH | 3.30 |
| 25 | 74.9, C | - |
| 26 | 26.4, CH3 | 1.15, s |
| 27 | 24.0, CH3 | 1.18, s |
| 28 | 16.8, CH3 | 1.02, s |
| 29 | 28.6, CH3 | 1.28, s |
| 30 | 20.4, CH3 | 1.54, t (13.0) 1.21 |
| Xyl-I | ||
| 1 | 106.2, CH | 4.37, d (~6.9) |
| 2 | 78.9, CH | 3.42 |
| 3 | 78.8, CH | 3.42 |
| 4 | 71.6, CH | 3.47 |
| 5 | 66.5, CH2 | 3.17, t (10.6) 3.84, dd (11.0, 5.3) |
| Rha-II | ||
| 1 | 102.1, CH | 5.33, brs |
| 2 | 72.2, CH | 3.94, brs |
| 3 | 72.2, CH | 3.74, dd (9.3, 2.8) |
| 4 | 74.0, CH | 3.38, t (9.6) |
| 5 | 70.1, CH | 3.98, dq (9.4, 6.1) |
| 6 | 18.1, CH3 | 1.23, d (6.3) |
| Ara-III | ||
| 1 | 107.4, CH | 4.38, d (7.5) |
| 2 | 73.7, CH | 3.58 |
| 3 | 75.0, CH | 3.49 |
| 4 | 70.2, CH | 3.78, brs |
| 5 | 68.0, CH2 | 3.56 3.87, dd (12.5, 1.8) |
| Atom | S1 | 24 S A. brachypterus [25] | 24 R A. stereocalyx [26] |
|---|---|---|---|
| δC [ppm] | δC [ppm] | δC [ppm] | |
| C-21 | 18.7 | 17.5 | 18.2 |
| C-20 | 32.5 | 30.9 | 32.4 |
| C-22 | 34.6 | 33.0 | 34.2 |
| C-23 | 30.4 | 29.4 | 30.1 |
| C-24 | 92.5 | 89.7 | 91.8 |
| C-25 | 74.9 | 73.5 | 75.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stambolov, I.; Shkondrov, A.; Kunert, O.; Bucar, F.; Kondeva-Burdina, M.; Krasteva, I. Cycloartane Saponins from Astragalus glycyphyllos and Their In Vitro Neuroprotective, Antioxidant, and hMAO-B-Inhibiting Effects. Metabolites 2023, 13, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070857
Stambolov I, Shkondrov A, Kunert O, Bucar F, Kondeva-Burdina M, Krasteva I. Cycloartane Saponins from Astragalus glycyphyllos and Their In Vitro Neuroprotective, Antioxidant, and hMAO-B-Inhibiting Effects. Metabolites. 2023; 13(7):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070857
Chicago/Turabian StyleStambolov, Ivan, Aleksandar Shkondrov, Olaf Kunert, Franz Bucar, Magdalena Kondeva-Burdina, and Ilina Krasteva. 2023. "Cycloartane Saponins from Astragalus glycyphyllos and Their In Vitro Neuroprotective, Antioxidant, and hMAO-B-Inhibiting Effects" Metabolites 13, no. 7: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070857
APA StyleStambolov, I., Shkondrov, A., Kunert, O., Bucar, F., Kondeva-Burdina, M., & Krasteva, I. (2023). Cycloartane Saponins from Astragalus glycyphyllos and Their In Vitro Neuroprotective, Antioxidant, and hMAO-B-Inhibiting Effects. Metabolites, 13(7), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070857