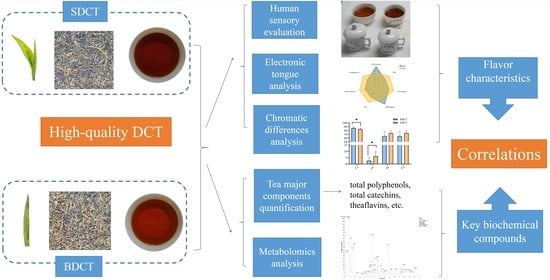
The Integration of Metabolomics, Electronic Tongue, and Chromatic Difference Reveals the Correlations between the Critical Compounds and Flavor Characteristics of Two Grades of High-Quality Dianhong Congou Black Tea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Tea Samples
2.3. Human Sensory Evaluation
2.4. Electronic Tongue Measurement
2.5. Chromatic Difference Assessment
2.6. Quantitative Determination of the Major Tea Chemical Components
2.7. Untargeted Metabolomics Based on LC-MS Analysis
2.8. Data Processing, Analysis, and Visualization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Human Sensory Evaluation
3.2. Electronic Tongue Profiles Measurement
3.3. Chromatic Difference Assessment
3.4. Quantitative Determination of the Major Chemical Constituents
3.5. Comprehensive Nontargeted Metabolomics Analysis
3.6. The Key Metabolic Characteristics
3.6.1. Flavan-3-ols and Their Derivatives
3.6.2. Phenolic Acids, Flavonols and Flavone/Flavonol Glycosides
3.6.3. Soluble Sugars, Amino Acids, and Organic Acids
3.7. Correlation Analysis between the Different Key Metabolites and the Sensory Indicators
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Wang, J.; Hua, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Dong, C.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, Y.; et al. Rutin, gamma-aminobutyric acid, gallic acid and caffeine negatively affect the sweet-mellow taste of Congou black tea infusions. Molecules 2019, 24, 4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, C.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Lyu, S.; Wang, Z.; Xie, F.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Z.; Sun, W. Relationship between the grade and the characteristic flavor of PCT (Panyong Congou black tea). Foods 2022, 11, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Yu, Q.; Shen, S.; Shan, X.; Hua, J.; Zhu, J.; Qiu, J.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Non-targeted metabolomics and electronic tongue analysis reveal the effect of rolling time on the sensory quality and nonvolatile metabolites of congou black tea. LWT 2022, 169, 113971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Li, T.; Wei, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhang, Z. Estimation of Congou black tea quality by an electronic tongue technology combined with multivariate analysis. Microchem. J. 2021, 163, 105899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Kong, Y.; Peng, X.; Li, C.; Liu, S.; Du, L.; Xiao, D.; Xu, Y. A comparative study of volatile components in Dianhong teas from fresh leaves of four tea cultivars by using chromatography-mass spectrometry, multivariate data analysis, and descriptive sensory analysis. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H.; Ouyang, W.; Li, J.; Hua, J.; Jiang, Y. Effects of Fermentation Temperature and Time on the Color Attributes and Tea Pigments of Yunnan Congou Black Tea. Foods 2022, 11, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Fu, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, T.; Xi, H.; Sun, S.; Cheng, Z. Profiling of volatile and non-volatile compounds in Dianhong by a combined approach of static headspace GC-MS and UPLC-MS. CyTA J. Food 2022, 20, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Gao, M.; Zhang, L.; Qiao, Y.; Li, J.; Du, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Characterization of the key aroma-active compounds in high-grade Dianhong tea using GC-MS and GC-O combined with sensory-directed flavor analysis. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Sun, Z.; Gao, J.; Peng, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, Z.; Dai, W. Metabolomics combined with proteomics provides a novel interpretation of the compound differences among Chinese tea cultivars (Camellia sinensis var. sinensis) with different manufacturing suitabilities. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 131976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Q. Prediction of black tea fermentation quality indices using NIRS and nonlinear tools. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Yasumatsu, M.; Hirotani, M.; Matsuo, Y.; Li, N.; Zhu, H.T.; Saito, Y.; Ishimaru, K.; Zhang, Y.J. New degradation mechanism of black tea pigment theaflavin involving condensation with epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Ning, J.; Zhang, Z. Multi-variable selection strategy based on near-infrared spectra for the rapid description of dianhong black tea quality. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 245, 118918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ren, G.; Sun, Y.; Jin, S.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhang, Z. Qualitative discrimination of Chinese dianhong black tea grades based on a handheld spectroscopy system coupled with chemometrics. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Long, P.; Meng, Q.; Ho, C.T.; Zhang, L. An emerging strategy for evaluating the grades of Keemun black tea by combinatory liquid chromatography-Orbitrap mass spectrometry-based untargeted metabolomics and inhibition effects on alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Han, Z.; Cui, Y.; Ho, C.T.; Wan, X.; Zhang, L. Identification of 4-O-p-coumaroylquinic acid as astringent compound of Keemun black tea by efficient integrated approaches of mass spectrometry, turbidity analysis and sensory evaluation. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, S.; Yu, Q.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Hua, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y. Chemical profile of a novel ripened Pu-erh tea and its metabolic conversion during pile fermentation. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shen, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Hua, J.; Yuan, H. Novel insight into the effect of fermentation time on quality of Yunnan Congou black tea. LWT 2022, 155, 112939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Yao, Y.; Hua, J.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H.; et al. Phytochemical comparison of different tea (Camellia sinensis) cultivars and its association with sensory quality of finished tea. LWT 2020, 117, 108595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasalvar, C.; Topal, B.; Serpen, A.; Bahar, B.; Pelvan, E.; Gokmen, V. Flavor characteristics of seven grades of black tea produced in Turkey. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6323–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Du, X.; Li, Y.Z.; Nie, C.N.; Wang, C.M.; Bian, J.L.; Luo, F. Are organic acids really related to the sour taste difference between Chinese black tea and green tea. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 2071–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X. Biochemistry of Tea, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 9, 31, 191–192. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Bruins, M.E.; de Bruijn, W.J.C.; Vincken, J.-P. A comparison of the phenolic composition of old and young tea leaves reveals a decrease in flavanols and phenolic acids and an increase in flavonols upon tea leaf maturation. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 86, 103385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liang, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, T.; Fan, Y.; Mao, X.; Wang, Y. Studies of quality development and major chemical composition of green tea processed from tea with different shoot maturity. LWT 2021, 142, 111055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, T.; Kotamreddy, J.N.R.; Ghosh, B.C.; Mitra, A. Changes in targeted metabolites, enzyme activities and transcripts at different developmental stages of tea leaves: A study for understanding the biochemical basis of tea shoot plucking. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 39, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sud, R.K.; Gulati, A.; Joshi, R.; Yadav, A.K.; Sharma, R.K. Germplasm appraisal of western Himalayan tea: A breeding strategy for yield and quality improvement. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2012, 60, 1501–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obanda, M.; Owuor, P.O.; Mang’oka, R. Changes in the chemical and sensory quality parameters of black tea due to variations of fermentation time and temperature. Food Chem. 2001, 75, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Dai, W.; Lu, M.; Lv, H.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, Q.; Lin, Z. Study of the dynamic changes in the non-volatile chemical constituents of black tea during fermentation processing by a non- targeted metabolomics approach. Food Res. Int. 2016, 79, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekant, W.; Fujii, K.; Shibata, E.; Morita, O.; Shimotoyodome, A. Safety assessment of green tea based beverages and dried green tea extracts as nutritional supplements. Toxicol Lett. 2017, 277, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Hu, Z.; Lu, M.; Li, P.; Tan, J.; Chen, M.; Lv, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; et al. Application of metabolomics profiling in the analysis of metabolites and taste quality in different subtypes of white tea. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Kouno, I. Chemistry of secondary polyphenols produced during processing of tea and selected foods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 11, 14–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scharbert, S.; Hofmann, T. Molecular definition of black tea taste by means of quantitative studies, taste reconstitution and omission experiments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5377–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Yu, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Analyzing the influence of withering degree on the dynamic changes in non-volatile metabolites and sensory quality of Longjing green tea by non-targeted metabolomics. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1104926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Wen, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wan, X.; Ho, C.T. LC-MS based metabolomics and sensory evaluation reveal the critical compounds of different grades of Huangshan Maofeng green tea. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharbert, S.; Holzmann, N.; Hofmann, T. Identification of the astringent taste compounds in black tea infusions by combining instrumental analysis and human bioresponse. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3498–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yang, Z. Understanding different regulatory mechanisms of proteinaceous and non-proteinaceous amino acid formation in tea (Camellia sinensis) provides new insights into the safe and effective alteration of tea flavor and function. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Group | Sample Number | Dry Tea Appearance (25%) | Liquor Color (10%) | Aroma (25%) | Tea Taste (30%) | Infused Leaf (10%) | Total Score (100%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDCT | 9 | 96.33 ± 0.5 a | 90 ± 2.96 | 86.22 ± 4.82 | 84.56 ± 2.92 | 88.22 ± 1.64 | 88.83 ± 1.78 |
| SDCT | 9 | 93.56 ± 0.88 b | 88.89 ± 2.93 | 85.67 ± 3.54 | 85 ± 2.60 | 87.89 ± 2.62 | 87.98 ± 1.71 |
| Compounds | BDCT (n = 9 × 3) | SDCT (n = 9 × 3) | p Value | Fold Changes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total polyphenols (%) | 15.66 ± 2.22 | 13.62 ± 0.71 | <0.05 | 1.14 |
| Total amino acids (%) | 3.37 ± 0.16 | 3.45 ± 0.18 | n. s. | 0.97 |
| Total soluble sugars (%) | 5.90 ± 0.46 | 6.09 ± 0.48 | n. s. | 0.99 |
| Caffeine (%) | 1.46 ± 0.42 | 1.72 ± 0.24 | n. s. | 0.88 |
| Total catechins (%) | 12.23 ± 1.95 | 9.20 ± 1.31 | <0.05 | 1.34 |
| EGCG (%) | 8.78 ± 1.43 | 6.82 ± 0.78 | <0.05 | 1.29 |
| ECG (%) | 1.52 ± 0.28 | 0.86 ± 0.18 | <0.05 | 1.77 |
| EGC (%) | 1.30 ± 0.24 | 0.98 ± 0.17 | <0.05 | 1.33 |
| EC (%) | 0.52 ± 0.22 | 0.30 ± 0.06 | <0.05 | 1.76 |
| C (%) | 0.10 ± 0.06 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | n. s. | 0.83 |
| TFs (%) | 0.22 ± 0.05 | 0.17 ± 0.04 | <0.001 | 1.36 |
| TRs (%) | 2.53 ± 0.32 | 2.64 ± 2.64 | n. s. | 0.96 |
| TBs (%) | 5.16 ± 0.70 | 5.30 ± 0.66 | n. s. | 1.03 |
| TFs/TRs | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | <0.001 | 1.41 |
| P/A value | 4.64 ± 0.58 | 3.98 ± 0.36 | <0.05 | 1.16 |
| No. | Metabolite Identification | m/z | RT/min | p Value | VIP | MS/MS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavan-3-ols and their derivatives | ||||||
| 1 | Epiafzelechin a | 273.0773 | 7.7 | <0.001 | 1.6 | 187, 189, 229, 255 |
| 2 | ECG a | 305.0665 | 5.1 | <0.001 | 1.1 | 125, 137, 165, 179, 219, 221, 261, 287 |
| 3 | EGCG a | 457.0767 | 6.6 | <0.001 | 1.5 | 169, 193, 287, 305, 331 |
| 4 | Procyanidin B1 a | 577.1351 | 5.2 | <0.001 | 1.1 | 125, 289, 407, 425, 451, 559 |
| 5 | Procyanidin C1 b | 865.1985 | 6.2 | <0.001 | 1.2 | 125, 289, 407, 577, 695, 713, 739, 847 |
| 6 | Theasinensin A b | 913.1469 | 5.8 | <0.001 | 1.5 | 285, 423, 573, 591, 743, 761 |
| 7 | Theasinensin B b | 761.1359 | 4.6 | <0.001 | 1.2 | 423, 483, 575, 593, 609, 635, 743 |
| 8 | Theasinensin F b | 897.1520 | 7.2 | <0.001 | 1.3 | 407, 727, 745 |
| 9 | TF-3,3′-G a | 867.1408 | 11.9 | <0.001 | 1.3 | 125, 169, 241 |
| Flavonols and flavone/flavonol glycosides | ||||||
| 10 | Apigenin 6-C-glucoside 8-C-arabinoside b | 563.1406 | 7.5 | <0.001 | 1.5 | 353, 383, 524, 443, 473, 503, 545 |
| 11 | Apigenin-6,8-C-diglucoside b | 593.1512 | 6.5 | <0.001 | 1.4 | 473, 353, 503, 383, 575 |
| 12 | Vitexin a | 431.0983 | 8.6 | <0.001 | 1.5 | 283, 311, 341 |
| 13 | Vitexin-2-O-rhamnoside a | 577.1563 | 8.6 | <0.001 | 1.1 | 413, 293, 457 |
| 14 | Vitexin-4″-O-glucoside b | 593.1506 | 8.1 | <0.001 | 1.5 | 293, 413 |
| 15 | Kaempferol a | 285.0414 | 12.2 | <0.001 | 1.4 | 227, 239, 211 |
| 16 | Kaempferol 3-O-galactosyl-rutinoside b | 755.204 | 8.7 | <0.001 | 1.4 | 285 |
| 17 | Kaempferol 3-O-glucosyl-rutinoside b | 755.204 | 9.1 | <0.001 | 1.6 | 285 |
| 18 | Kaempferol 3-O-β-rutinoside b | 593.1506 | 9.7 | <0.001 | 1.7 | 285, 327 |
| 19 | Kaempferol 7-(6″-galloylglucoside) b | 599.1075 | 9.8 | <0.001 | 1.6 | 125, 169, 313, 285, 447 |
| 20 | Kaempferol-3-O-galactoside b | 447.0933 | 9.7 | <0.001 | 1.7 | 255, 284, 285, 327, 357 |
| 21 | Dicoumaryl astragalin b | 739.1675 | 12.2 | <0.001 | 1.3 | 145, 285, 453, 593 |
| 22 | p-Coumaroylastragalin b | 593.1306 | 11.9 | <0.001 | 1.3 | 285, 307, 447 |
| 23 | Astragalin a | 447.0933 | 10.2 | <0.001 | 1.7 | 255, 284, 285, 327, 357 |
| 24 | Myricetin 3-O-glucoside b | 479.0825 | 7.7 | <0.001 | 1.3 | 316, 317, 271 |
| 25 | Quercetin a | 301.0348 | 12.0 | <0.001 | 1.6 | 107, 121, 151, 179 |
| 26 | Isoquercitrin a | 463.0882 | 9.0 | <0.001 | 1.7 | 301, 300 |
| 27 | Quercetin 3-arabinoside b | 433.0799 | 9.7 | <0.001 | 1.7 | 300, 271, 301, 255 |
| 28 | Quercetin 3-O-galactosyl-rutinoside b | 771.1989 | 8.0 | <0.001 | 1.6 | 301, 343, 609 |
| 29 | Quercetin 3-O-glucosyl-rutinoside b | 771.1989 | 8.2 | <0.001 | 1.5 | 301, 343, 609 |
| 30 | Quercetin 7-(3-p-coumaroylglucoside) b | 609.1279 | 11.8 | <0.001 | 1.5 | 463, 300, 301 |
| 31 | Quercetin-3-O-galactoside b | 463.0882 | 8.8 | <0.001 | 1.7 | 301, 300, 293 |
| 32 | Quercetin-3-p-coumaroylrutinoside b | 755.1873 | 11.8 | <0.001 | 1.6 | 609, 591, 301, 271 |
| 33 | 3-Quercetin galloylglucoside b | 615.1027 | 8.4 | <0.001 | 1.4 | 463, 300, 301 |
| 34 | 7-Quercetin galloylglucoside b | 615.1027 | 8.4 | <0.001 | 1.4 | 463, 300, 301 |
| 35 | Rutin a | 609.1461 | 8.6 | <0.001 | 1.7 | 301, 343 |
| Amino acids | ||||||
| 36 | Aspartic acid a | 132.0296 | 0.7 | <0.001 | 1.3 | 88, 115 |
| 37 | Glutamine b | 146.0453 | 0.7 | <0.001 | 1.4 | 109, 127 |
| 38 | Histidine a | 154.0616 | 0.6 | <0.05 | 1.1 | 93, 137 |
| 39 | Phenylalanine a | 164.0711 | 2.4 | <0.001 | 1.3 | 97, 137, 147 |
| 40 | Theanine a | 173.0926 | 1.1 | <0.05 | 1.1 | 128, 155 |
| 41 | Tyrosine a | 180.066 | 1.2 | <0.001 | 1.4 | 72, 93, 119, 163 |
| Phenolic acids | ||||||
| 42 | Digalloylglucose b | 483.078 | 5.2 | <0.05 | 1.1 | 125, 169, 211,271, 313, 331 |
| 43 | Dihydroxy-benzoic acid b | 153.0182 | 6.2 | <0.05 | 1.6 | 109 |
| 44 | Quinic acid a | 191.0561 | 0.7 | <0.001 | 1.6 | 85, 93, 127, 173 |
| 45 | Shikimic acid a | 173.0455 | 0.8 | <0.001 | 1.1 | 73, 93, 111, 137 |
| 46 | Theogallin a | 343.0671 | 1.8 | <0.001 | 1.5 | 191 |
| 47 | p-Coumaric acid a | 163.04 | 5.2 | <0.001 | 1.4 | 119, 93 |
| 48 | 3-O-p-coumaroylquinic acid b | 337.0929 | 6.2 | <0.001 | 1.7 | 173 |
| Sugars | ||||||
| 49 | Glucose a | 179.0562 | 0.8 | <0.001 | 1.6 | 59, 71, 89, 101, 113 |
| 50 | Maltose a | 341.1089 | 0.8 | <0.001 | 1.3 | 113, 119, 143, 161, 179 |
| 51 | Raffinose a | 503.1612 | 0.7 | <0.001 | 1.4 | 89, 101, 179, 221 |
| 52 | ribonic acid b | 165.0398 | 0.7 | <0.001 | 1.1 | 75, 105, 129, 147 |
| Organic acids | ||||||
| 53 | Citric acid a | 191.0197 | 1.1 | <0.001 | 1.2 | 85, 111, 173 |
| 54 | Succinic acid a | 117.0187 | 1.3 | <0.001 | 1.1 | 73, 99 |
| Flavone | ||||||
| 55 | Hydroxy trimethoxyflavone b | 327.0893 | 8.0 | <0.05 | 1.6 | 237, 211, 265 |
| Nucleotide | ||||||
| 56 | UMP b | 323.0286 | 0.8 | <0.001 | 1.2 | 173, 211, 279, 305, 79, 193 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Shan, X.; Niu, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yuan, H.; Li, J.; Wu, T. The Integration of Metabolomics, Electronic Tongue, and Chromatic Difference Reveals the Correlations between the Critical Compounds and Flavor Characteristics of Two Grades of High-Quality Dianhong Congou Black Tea. Metabolites 2023, 13, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070864
Zhang S, Shan X, Niu L, Chen L, Wang J, Zhou Q, Yuan H, Li J, Wu T. The Integration of Metabolomics, Electronic Tongue, and Chromatic Difference Reveals the Correlations between the Critical Compounds and Flavor Characteristics of Two Grades of High-Quality Dianhong Congou Black Tea. Metabolites. 2023; 13(7):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070864
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shan, Xujiang Shan, Linchi Niu, Le Chen, Jinjin Wang, Qinghua Zhou, Haibo Yuan, Jia Li, and Tian Wu. 2023. "The Integration of Metabolomics, Electronic Tongue, and Chromatic Difference Reveals the Correlations between the Critical Compounds and Flavor Characteristics of Two Grades of High-Quality Dianhong Congou Black Tea" Metabolites 13, no. 7: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070864
APA StyleZhang, S., Shan, X., Niu, L., Chen, L., Wang, J., Zhou, Q., Yuan, H., Li, J., & Wu, T. (2023). The Integration of Metabolomics, Electronic Tongue, and Chromatic Difference Reveals the Correlations between the Critical Compounds and Flavor Characteristics of Two Grades of High-Quality Dianhong Congou Black Tea. Metabolites, 13(7), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070864