Automatic Assignment of Molecular Ion Species to Elemental Formulas in Gas Chromatography/Methane Chemical Ionization Accurate Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
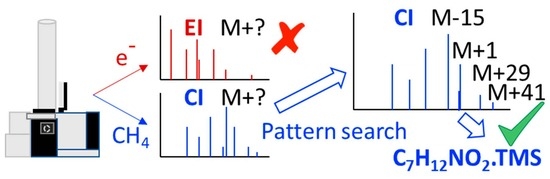
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Data Analysis and Molecular Assignment Algorithms
3. Results
3.1. CI Pattern of Molecular Ion Species
3.2. Overall Detection Rate of Molecular Ion Species in GC-CI-QTOF MS
3.3. Automatic Calculation of Elemental Formulas
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry: Combined Targeted and Untargeted Profiling. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2016, 114, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allwood, J.W.; Erban, A.; de Koning, S.; Dunn, W.B.; Luedemann, A.; Lommen, A.; Kay, L.; Löscher, R.; Kopka, J.; Goodacre, R. Inter-laboratory reproducibility of fast gas chromatography-electron impact-time of flight mass spectrometry (GC-EI-TOF/MS) based plant metabolomics. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, J. A Brief History of Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 5678–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Kind, T.; Bremer, P.L.; Tantillo, D.J.; Fiehn, O. Beyond the Ground State: Predicting Electron Ionization Mass Spectra Using Excited-State Molecular Dynamics. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 4403–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leogrande, P.; Jardines, D.; Martinez-Brito, D.; de la Torre, X.; Parr, M.K.; Botrè, F. Low-energy electron ionization optimization for steroidomics analysis using high-resolution mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 35, e9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIST EI Library. Available online: https://chemdata.nist.gov/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=chemdata:start#libraries (accessed on 11 August 2023).
- MoNA—MassBank of North America. Available online: https://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/ (accessed on 11 August 2023).
- Wishart, D.S.; Jewison, T.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.; Knox, C.; Liu, Y.; Djoumbou, Y.; Mandal, R.; Aziat, F.; Dong, E.; et al. HMDB 3.0—The Human Metabolome Database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Kind, T.; Tantillo, D.J.; Fiehn, O. Predicting in silico electron ionization mass spectra using quantum chemistry. J. Cheminform. 2020, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Kind, T.; Bremer, P.L.; Tantillo, D.J.; Fiehn, O. Quantum Chemical Prediction of Electron Ionization Mass Spectra of Trimethylsilylated Metabolites. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dührkop, K.; Fleischauer, M.; Ludwig, M.; Aksenov, A.A.; Melnik, A.V.; Meusel, M.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Rousu, J.; Böcker, S. SIRIUS 4: A rapid tool for turning tandem mass spectra into metabolite structure information. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.; Fiehn, O. Mass spectral fragmentation of trimethylsilylated small molecules. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2018, 37, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.; Tsugawa, H.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Mehta, S.; Mueller, M.; Zheng, Y.; Ogiwara, A.; Meissen, J.; Showalter, M.; Takeuchi, K.; et al. Identifying metabolites by integrating metabolome databases with mass spectrometry cheminformatics. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, W.J.; Schwarz, H. Chemical Ionization—A Mass-Spectrometric Analytical Procedure of Rapidly Increasing Importance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1978, 17, 424–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munson, M.S.B.; Field, F.H. Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry. I. General Introduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88, 2621–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Ikeda, K.; Takahashi, M.; Satoh, A.; Mori, Y.; Uchino, H.; Okahashi, N.; Yamada, Y.; Tada, I.; Bonini, P.; et al. A lipidome atlas in MS-DIAL 4. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djoumbou Feunang, Y.; Eisner, R.; Knox, C.; Chepelev, L.; Hastings, J.; Owen, G.; Fahy, E.; Steinbeck, C.; Subramanian, S.; Bolton, E.; et al. ClassyFire: Automated chemical classification with a comprehensive, computable taxonomy. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bräkling, S.; Kroll, K.; Stoermer, C.; Rohner, U.; Gonin, M.; Benter, T.; Kersten, H.; Klee, S. Parallel Operation of Electron Ionization and Chemical Ionization for GC–MS Using a Single TOF Mass Analyzer. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 6057–6064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gas Chromatograph | Agilent 7890A GC System |
|---|---|
| Mass Spectrometer | 7200 accurate mass QTOF mass spectrometer |
| GC column | DB5 MS column 30 m + 10 m integrated guard, 0.25 mm id, 0.25 μm film |
| GC parameters, injection | 1 μL in 25 s splitless mode at 250 °C |
| GC parameters, separation | Initial temperature of 60 °C with a hold time of 0.5 min, a temperature ramp of 10 °C/min to 325 °C, and a final hold time of 10 min at 325 °C. |
| EI ion source | temperature, 230 °C; energy, 70 eV |
| Chemical ionization | Ion source 300 °C; CI electron energy 135 eV; CI methane gas flow rate 20% |
| MS parameters, tuning | Autotune using FC43 (Perfluoro tributylamine) |
| MS parameters, data acquisition | m/z 50–1200 at 5 Hz scan rate and 750 V detector voltage in both electron ionization (EI) mode and chemical ionization (CI) mode |
| MS data processing | Peak detection, deconvolution by MS-DIAL 4 [13,16] |
| Class | # | Detected by CI (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Carboxylic acids and deriv. | 77 | 83.1 |
| Organooxygen compounds | 47 | 55.3 |
| Benzene and substituted deriv. | 35 | 77.1 |
| Fatty acyls | 29 | 89.7 |
| Phenols | 26 | 73.1 |
| Indoles and deriv. | 15 | 86.7 |
| Organonitrogen compounds | 11 | 63.6 |
| Hydroxy acids and deriv. | 9 | 88.9 |
| Phenylpropanoic acids | 8 | 87.5 |
| Prenol lipids | 8 | 25.0 |
| Cinnamic acids and deriv. | 7 | 71.4 |
| Pyridines and derivatives | 7 | 100.0 |
| Steroids and steroid deriv. | 7 | 14.3 |
| Purine nucleosides | 6 | 100.0 |
| [M]+ | 15 | 4% |
| [M − H]+ | 24 | 7% |
| [M + H]+ | 255 | 74% |
| Not recognized by algorithm | 51 | 15% |
| Total | 345 | Derivatized standards |
| Observed m/z | Theoretical | Mass Error [mDa] | Ion Species | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3,4-dihydroxy-phenylacetic acid | 384.1612 | 384.1608 | −0.4 | [M]+ 3TMS |
| 369.1377 | 369.1374 | −0.3 | [M − CH3]+ 3TMS | |
| 413.2004 | 413.2000 | −0.4 | [M + C2H5]+ 3TMS | |
| 425.1996 | 425.2000 | 0.4 | [M + C3H5]+ 3TMS | |
| 457.2088 | 457.2082 | −0.6 | [M + TMS]+ 3TMS | |
| phosphoric acid | 315.1031 | 315.1033 | 0.2 | [M + H]+ 3TMS |
| 299.0719 | 299.0720 | 0.1 | [M − CH3]+ 3TMS | |
| 343.1345 | 343.1346 | 0.1 | [M + C2H5]+ 3TMS | |
| 355.1342 | 355.1346 | 0.4 | [M + C3H5]+ 3TMS | |
| 387.1428 | 387.1428 | 0.0 | [M + TMS]+ 3TMS | |
| 2,5-dihydroxy-phenylacetic acid | 384.1608 | 384.1608 | 0.0 | [M]+ 3TMS |
| 369.1374 | 369.1374 | 0.0 | [M − CH3]+ 3TMS | |
| 413.1995 | 413.2000 | 0.5 | [M + C2H5]+ 3TMS | |
| 425.1985 | 425.2000 | 1.5 | [M + C3H5]+ 3TMS | |
| 457.2082 | 457.2082 | 0.0 | [M + TMS]+ 3TMS |
| Correct Formula | Molecular Ion Species | [M − CH3]+ | W/Isotope Pattern |
|---|---|---|---|
| No hit | 7.9% | 6.9% | 12.8% |
| Top-10 | 91.7% | 93.1% | 87.2% |
| Top-5 | 87.6% | 91.0% | 83.4% |
| Top-3 | 83.1% | 86.9% | 78.6% |
| Top hit | 60.7% | 71.4% | 59.0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Valdiviez, L.; Ye, H.; Fiehn, O. Automatic Assignment of Molecular Ion Species to Elemental Formulas in Gas Chromatography/Methane Chemical Ionization Accurate Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites 2023, 13, 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080962
Wang S, Valdiviez L, Ye H, Fiehn O. Automatic Assignment of Molecular Ion Species to Elemental Formulas in Gas Chromatography/Methane Chemical Ionization Accurate Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites. 2023; 13(8):962. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080962
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shunyang, Luis Valdiviez, Honglian Ye, and Oliver Fiehn. 2023. "Automatic Assignment of Molecular Ion Species to Elemental Formulas in Gas Chromatography/Methane Chemical Ionization Accurate Mass Spectrometry" Metabolites 13, no. 8: 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080962
APA StyleWang, S., Valdiviez, L., Ye, H., & Fiehn, O. (2023). Automatic Assignment of Molecular Ion Species to Elemental Formulas in Gas Chromatography/Methane Chemical Ionization Accurate Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites, 13(8), 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080962