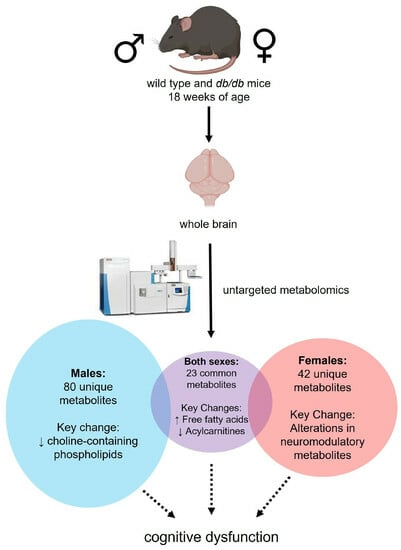
Sex Modifies the Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Murine Whole Brain Metabolome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Peripheral Metabolic Assessment
2.3. Metabolomics Tissue Preparation
2.4. LC-MS Analysis
2.5. Pathway Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Confirmation of Hyperglycemic, Hyperinsulinemic, and Hypercholesterolemic db/db Animal Model
3.2. Global Metabolic Profiles of the Brain Metabolome
3.3. Effect of T2DM on the Brain Metabolome
3.3.1. Metabolites Altered by T2DM
3.3.2. Metabolite Classes and Pathways Shifted by T2DM
3.4. Effect of Sex on the Brain Metabolome
3.4.1. Metabolites Altered by Sex
3.4.2. Comparison of Metabolites Altered by Sex in T2DM and Control Mice
3.4.3. Metabolite Classes and Pathways Altered by Sex
4. Discussion
4.1. Sex-Independent Consequences of T2DM on the Brain Metabolome
4.2. Sex-Dependent Consequences of T2DM on the Brain Metabolome
4.2.1. Sex-Dependent Effects of T2DM in Males
4.2.2. Sex-Dependent Effects of T2DM in Females
4.3. Potential Mechanisms of Sex Differences in the Brain Metabolome
4.4. Relevance to Human Disease
4.5. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peters, S.A.E.; Woodward, M. Sex Differences in the Burden and Complications of Diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2018, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ritter, R.; Sep, S.J.S.; van der Kallen, C.J.H.; van Greevenbroek, M.M.J.; Koster, A.; Eussen, S.J.P.M.; Dagnelie, P.C.; van Boxtel, M.; Schram, M.T.; Köhler, S.; et al. Sex Comparisons in the Association of Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes with Cognitive Function, Depression and Quality of Life: The Maastricht Study. Diabet. Med. J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2023, 40, e15115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Han, Q.; Gang, X.; Wang, G. Altered Brain Metabolites in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Related Complications—Evidence from 1H MRS Study. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessels, G.J.; Despa, F. Cognitive Decline and Dementia in Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautzky-Willer, A.; Harreiter, J.; Pacini, G. Sex and Gender Differences in Risk, Pathophysiology and Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr. Rev. 2016, 37, 278–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elling, D.; Surkan, P.J.; Enayati, S.; El-Khatib, Z. Sex Differences and Risk Factors for Diabetes Mellitus—An International Study from 193 Countries. Glob. Health 2018, 14, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choleris, E.; Galea, L.A.M.; Sohrabji, F.; Frick, K.M. Sex Differences in the Brain: Implications for Behavioral and Biomedical Research. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 85, 126–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaignard, P.; Fréchou, M.; Liere, P.; Thérond, P.; Schumacher, M.; Slama, A.; Guennoun, R. Sex Differences in Brain Mitochondrial Metabolism: Influence of Endogenous Steroids and Stroke. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2018, 30, e12497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Profant, M.; Wang, C. Metabolic Sex Dimorphism of the Brain at the Gene, Cell, and Tissue Level. J. Immunol. 2022, 208, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Gong, K.; Xu, H.; Tu, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; He, W.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Zhao, L.; et al. Optimized Integration of Metabolomics and Lipidomics Reveals Brain Region-Specific Changes of Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Type 1 Diabetic Mice with Cognitive Decline. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 43, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Yan, J.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Li, C.; Zhao, L.; Gao, H.; Zheng, H. Sex-Specific Metabolic Alterations in the Type 1 Diabetic Brain of Mice Revealed by an Integrated Method of Metabolomics and Mixed-Model. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2063–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zheng, H.; Fan, K.; Xia, N.; Li, J.; Yang, C.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y. NMR-Based Metabolomics Characterizes Metabolic Changes in Different Brain Regions of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice with Cognitive Decline. Metab. Brain Dis. 2020, 35, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, M.; Bai, G.; Hu, Y.; Hu, W.; Yan, Z.; Gao, H. Cognitive Decline in Type 2 Diabetic Db/Db Mice May Be Associated with Brain Region-Specific Metabolic Disorders. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Liang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Kobayashi, S.; Patel, J.; Li, C.; Cai, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, C.; et al. Comprehensive Lipidomic Profiling in Serum and Multiple Tissues from a Mouse Model of Diabetes. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, B.; Cai, M.; Lin, X.; Lou, S. Glucose Metabolic Alterations in Hippocampus of Diabetes Mellitus Rats and the Regulation of Aerobic Exercise. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 364, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chandrasekera, P.C.; Pippin, J.J. Leptin- and Leptin Receptor-Deficient Rodent Models: Relevance for Human Type 2 Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2014, 10, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-K.; Ahima, R.S. Physiology of Leptin: Energy Homeostasis, Neuroendocrine Function and Metabolism. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2015, 64, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.J. The Use of Animal Models in Diabetes Research. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 877–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Onaizi, M.; Al-Sarraf, A.; Braysh, K.; Kazem, F.; Al-Hussaini, H.; Rao, M.; Kilarkaje, N.; El Ali, A. Impaired Spatial Navigation and Age-Dependent Hippocampal Synaptic Dysfunction Are Associated with Chronic Inflammatory Response in Db/Db Mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2022, 56, 6003–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Sakamoto, K. Meta-Analysis of Cognitive and Behavioral Tests in Leptin- and Leptin Receptor-Deficient Mice. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 170, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0: Updated Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, P.G.; Nielsen, F.H.; Fahey, G.C. AIN-93 Purified Diets for Laboratory Rodents: Final Report of the American Institute of Nutrition Ad Hoc Writing Committee on the Reformulation of the AIN-76A Rodent Diet. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nezami Ranjbar, M.R.; Zhao, Y.; Tadesse, M.G.; Wang, Y.; Ressom, H.W. Evaluation of Normalization Methods for Analysis of LC-MS Data. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine Workshops, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 4–7 October 2012; pp. 610–617. [Google Scholar]
- Pathway Analysis with Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Data. Available online: http://impala.molgen.mpg.de/impala/impala/impala/impala/impala/# (accessed on 24 April 2023).
- Kamburov, A.; Cavill, R.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Herwig, R.; Keun, H.C. Integrated Pathway-Level Analysis of Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Data with IMPaLA. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2917–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavill, R.; Kamburov, A.; Ellis, J.K.; Athersuch, T.J.; Blagrove, M.S.C.; Herwig, R.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Keun, H.C. Consensus-Phenotype Integration of Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Data Implies a Role for Metabolism in the Chemosensitivity of Tumour Cells. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1001113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MetaboAnalyst. Available online: https://www.metaboanalyst.ca/MetaboAnalyst/ModuleView.xhtml (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; de Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.-É.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the Gap between Raw Spectra and Functional Insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W388–W396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsen, T.; de Vlieg, J.; Alkema, W. BioVenn—A Web Application for the Comparison and Visualization of Biological Lists Using Area-Proportional Venn Diagrams. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morpheus. Available online: https://software.broadinstitute.org/morpheus/ (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Johnson, J.L.; Johnson, L.A. Homeostasis of Lipid Metabolism in Disorders of the Brain. In Encyclopedia of Behavioral Neuroscience, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 372–382. ISBN 978-0-12-821636-1. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Fang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, X.; Yu, W.; Chen, S.; Ying, J.; Hua, F. Lipid Metabolism and Storage in Neuroglia: Role in Brain Development and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snowden, S.G.; Ebshiana, A.A.; Hye, A.; An, Y.; Pletnikova, O.; O’Brien, R.; Troncoso, J.; Legido-Quigley, C.; Thambisetty, M. Association between Fatty Acid Metabolism in the Brain and Alzheimer Disease Neuropathology and Cognitive Performance: A Nontargeted Metabolomic Study. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambrova, M.; Makrecka-Kuka, M.; Kuka, J.; Vilskersts, R.; Nordberg, D.; Attwood, M.M.; Smesny, S.; Sen, Z.D.; Guo, A.C.; Oler, E.; et al. Acylcarnitines: Nomenclature, Biomarkers, Therapeutic Potential, Drug Targets, and Clinical Trials. Pharmacol. Rev. 2022, 74, 506–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nałecz, K.A.; Miecz, D.; Berezowski, V.; Cecchelli, R. Carnitine: Transport and Physiological Functions in the Brain. Mol. Asp. Med. 2004, 25, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofano, A.; Sapere, N.; La Marca, G.; Angiolillo, A.; Vitale, M.; Corbi, G.; Scapagnini, G.; Intrieri, M.; Russo, C.; Corso, G.; et al. Serum Levels of Acyl-Carnitines along the Continuum from Normal to Alzheimer’s Dementia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, R.; Lord, J.; Xu, J.; Maddock, J.; Kim, M.; Dobson, R.; Legido-Quigley, C.; Wong, A.; Richards, M.; Proitsi, P. Metabolic Correlates of Late Midlife Cognitive Outcomes: Findings from the 1946 British Birth Cohort. Brain Commun. 2022, 4, fcab291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, M.; Gunn-Moore, F.J.; Platt, B.; Smith, T.K. Brain Region-Specific Lipid Alterations in the PLB4 hBACE1 Knock-in Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Mishra, A.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Desai, M.; Chen, S.; Mao, Z.; Do, L.; Bernstein, A.S.; Trouard, T.P.; et al. Evidence in Support of Chromosomal Sex Influencing Plasma Based Metabolome vs APOE Genotype Influencing Brain Metabolome Profile in Humanized APOE Male and Female Mice. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0225392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, V.R.; Oommen, A.M.; Varma, S.; Casanova, R.; An, Y.; Andrews, R.M.; O’Brien, R.; Pletnikova, O.; Troncoso, J.C.; Toledo, J.; et al. Brain and Blood Metabolite Signatures of Pathology and Progression in Alzheimer Disease: A Targeted Metabolomics Study. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, P.; Tomassoni, D.; Nittari, G.; Traini, E.; Amenta, F. Effects of Choline Containing Phospholipids on the Neurovascular Unit: A Review. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 988759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewett, B.E.; Sharma, S. Physiology, GABA. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Balado, J.; Eich, T.S. GABAergic Dysfunction, Neural Network Hyperactivity and Memory Impairments in Human Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 116, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlynárik, V.; Cacquevel, M.; Sun-Reimer, L.; Janssens, S.; Cudalbu, C.; Lei, H.; Schneider, B.L.; Aebischer, P.; Gruetter, R. Proton and Phosphorus Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 31, S87–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, L.H.; Melø, T.M.; Sæther, O.; Witter, M.P.; Sonnewald, U. Altered Neurochemical Profile in the McGill-R-Thy1-APP Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Longitudinal in Vivo 1H MRS Study. J. Neurochem. 2012, 123, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Edden, R.A.E.; Gao, F.; Wang, G.; Wu, L.; Zhao, B.; Wang, M.; Chan, Q.; Chen, W.; Barker, P.B. Decreased γ-Aminobutyric Acid Levels in the Parietal Region of Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 41, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siucinska, E. Γ-Aminobutyric Acid in Adult Brain: An Update. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 376, 112224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Williams, G.; Doherty, P. 2-Linoleoylglycerol Is a Partial Agonist of the Human Cannabinoid Type 1 Receptor That Can Suppress 2-Arachidonolyglycerol and Anandamide Activity. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2019, 4, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, S.; Halpern, M. Cannabinoids and Dementia: A Review of Clinical and Preclinical Data. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 2689–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aniello, A.; De Simone, A.; Spinelli, P.; D’Aniello, S.; Branno, M.; Aniello, F.; Rios, J.; Tsesarskaja, M.; Fisher, G. A Specific Enzymatic High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Method to Determine N-Methyl-d-Aspartic Acid in Biological Tissues. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 308, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, D.T.; Jane, D.E. Pharmacology of NMDA Receptors. In Biology of the NMDA Receptor; Van Dongen, A.M., Ed.; Frontiers in Neuroscience; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-1-4200-4414-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Reddy, P.H. Role of Glutamate and NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. JAD 2017, 57, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Huang, Y.-J.; Lin, C.-J.; Lane, H.-Y.; Tsai, G.E. NMDA Neurotransmission Dysfunction in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 5169–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa-de la Paz, L.; Zenteno, E.; Gulias-Cañizo, R.; Quiroz-Mercado, H. Taurine and GABA Neurotransmitter Receptors, a Relationship with Therapeutic Potential? Expert Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxham, M.N. Chapter 8—Neurotransmitter Receptors. In Fundamental Neuroscience, 4th ed.; Squire, L.R., Berg, D., Bloom, F.E., du Lac, S., Ghosh, A., Spitzer, N.C., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 163–187. ISBN 978-0-12-385870-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Xia, S.; He, J.; Lu, G.; Xie, Z.; Han, H. Roles of Taurine in Cognitive Function of Physiology, Pathologies and Toxication. Life Sci. 2019, 231, 116584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.Y.; Sun, H.S.; Shah, S.M.; Agovic, M.S.; Friedman, E.; Banerjee, S.P. Modes of Direct Modulation by Taurine of the Glutamate NMDA Receptor in Rat Cortex. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 728, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, D.J.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F. An Integrated View of Sex Differences in Metabolic Physiology and Disease. Mol. Metab. 2018, 15, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, J.L.; Belin de Chantemèle, E.J. Sex Hormones, Aging and Cardiometabolic Syndrome. Biol. Sex Differ. 2019, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevers Leuven, J.A. Sex Steroids and Lipoprotein Metabolism. Pharmacol. Ther. 1994, 64, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zore, T.; Palafox, M.; Reue, K. Sex Differences in Obesity, Lipid Metabolism, and Inflammation—A Role for the Sex Chromosomes? Mol. Metab. 2018, 15, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, A.P.; Chen, X. What Does the “Four Core Genotypes” Mouse Model Tell Us about Sex Differences in the Brain and Other Tissues? Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2009, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddan, J.M.; White, D.J.; Macpherson, H.; Scholey, A.; Pipingas, A. Glycerophospholipid Supplementation as a Potential Intervention for Supporting Cerebral Structure in Older Adults. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, T.; Yaguchi, T.; Nishizaki, T. DL- and PO-Phosphatidylcholines as a Promising Learning and Memory Enhancer. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaguchi, T.; Nagata, T.; Nishizaki, T. 1-Palmitoyl-2-Oleoyl-Sn-Glycero-3-Phosphocholine Improves Cognitive Decline by Enhancing Long-Term Depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 204, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Male | Female | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | db/db | WT | db/db | |
| Body weight (g) | 30.46 ± 2.988 | 46.78 ± 2.443 * | 20.65 ± 1.314 | 45.62 ± 5.197 * |
| Insulin (pg/mL) | 229.1 ± 131.7 | 2215 ± 1023 * | 182.2 ± 78.72 | 2197 ± 1350 * |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 146 ± 33.92 | 244 ± 72.13 * | 129.9 ± 13.72 | 290.5 ± 134 * |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 124.1 ± 35.88 | 278.1 ± 33.18 * | 77.03 ± 17.78 | 237.7 ± 43.64 * |
| GTT AUC (mg min/dL) | 27,369 ± 6475 | 56,142 ± 10,998 * | 23,465 ± 2475 | 58,602 ± 11,385 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Norman, J.E.; Nuthikattu, S.; Milenkovic, D.; Villablanca, A.C. Sex Modifies the Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Murine Whole Brain Metabolome. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13091012
Norman JE, Nuthikattu S, Milenkovic D, Villablanca AC. Sex Modifies the Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Murine Whole Brain Metabolome. Metabolites. 2023; 13(9):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13091012
Chicago/Turabian StyleNorman, Jennifer E., Saivageethi Nuthikattu, Dragan Milenkovic, and Amparo C. Villablanca. 2023. "Sex Modifies the Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Murine Whole Brain Metabolome" Metabolites 13, no. 9: 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13091012
APA StyleNorman, J. E., Nuthikattu, S., Milenkovic, D., & Villablanca, A. C. (2023). Sex Modifies the Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Murine Whole Brain Metabolome. Metabolites, 13(9), 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13091012