Progression to Obesity: Variations in Patterns of Metabolic Fluxes, Fat Accumulation, and Gastrointestinal Responses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Progression to Obesity
2.1. Calorie Intake
2.2. Energy Expenditure
2.3. Obesity as Body Weight Set Point
2.4. Utilization of Nutrients
2.5. Macronutrient Selection and Weight Control
3. Pathophysiology of Body Fat Distribution
3.1. Patterns of Fat Accumulation
3.2. Ectopic Fat
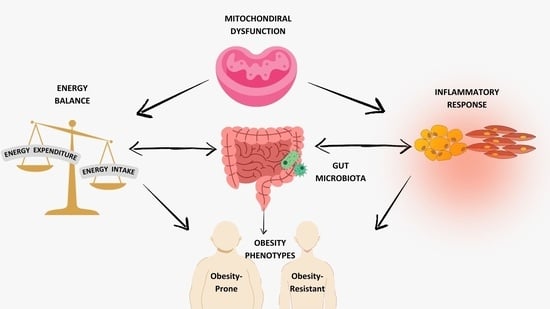
4. Contribution of Gastrointestinal Microbiota and Inflammation to Obesity
4.1. Microbiome in Obesity
4.2. Inflamamtion in Obesity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inoue, Y.; Qin, B.; Poti, J.; Sokol, R.; Gordon-Larsen, P. Epidemiology of Obesity in Adults: Latest Trends. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2018, 7, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD Collaborators. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abarca-Gómez, L.; Abdeen, Z.A.; Hamid, Z.A.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M.; Acosta-Cazares, B.; Acuin, C.; Adams, R.J.; Aekplakorn, W.; Afsana, K.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; et al. Worldwide Trends in Body-Mass Index, Underweight, Overweight, and Obesity from 1975 to 2016: A Pooled Analysis of 2416 Population-Based Measurement Studies in 128·9 Million Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, N.A.; Petito, L.C.; McCabe, M.; Allen, N.B.; O’Brien, M.J.; Carnethon, M.R.; Khan, S.S. Quantifying the Sex-Race/Ethnicity-Specific Burden of Obesity on Incident Diabetes Mellitus in the United States, 2001 to 2016: MESA and NHANES. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e018799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegal, K.M.; Kruszon-Moran, D.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Trends in Obesity Among Adults in the United States, 2005 to 2014. JAMA 2016, 315, 2284–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, C.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2017–2018. NCHS Data Brief 2020, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ajlouni, K.; Khader, Y.; Batieha, A.; Jaddou, H.; El-Khateeb, M. An Alarmingly High and Increasing Prevalence of Obesity in Jordan. Epidemiol. Health 2020, 42, e2020040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustami, M.; Matalka, K.Z.; Mallah, E.; Abu-Qatouseh, L.; Dayyih, W.A.; Hussein, N.; Safieh, N.A.; Elyyan, Y.; Hussein, N.; Arafat, T. The Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity Among Women in Jordan: A Risk Factor for Developing Chronic Diseases. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2021, 14, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, M.; Sorić, M.; Bovet, P.; Miranda, J.J.; Bhutta, Z.; Stevens, G.A.; Laxmaiah, A.; Kengne, A.-P.; Bentham, J. The Epidemiological Burden of Obesity in Childhood: A Worldwide Epidemic Requiring Urgent Action. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Muniesa, P.; Mártinez-González, M.-A.; Hu, F.B.; Després, J.-P.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Loos, R.J.F.; Moreno, L.A.; Bray, G.A.; Martinez, J.A. Obesity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preda, A.; Carbone, F.; Tirandi, A.; Montecucco, F.; Liberale, L. Obesity Phenotypes and Cardiovascular Risk: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Management. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 906–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, G.H. The Metabolic Phenotype in Obesity: Fat Mass, Body Fat Distribution, and Adipose Tissue Function. Obes. Facts 2017, 10, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neeland, I.J.; Poirier, P.; Després, J.-P. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Heterogeneity of Obesity: Clinical Challenges and Implications for Management. Circulation 2018, 137, 1391–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Berg, E.; Cheng, X.; Shen, W. How to Best Assess Abdominal Obesity. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2018, 21, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladabaum, U.; Mannalithara, A.; Myer, P.A.; Singh, G. Obesity, Abdominal Obesity, Physical Activity, and Caloric Intake in US Adults: 1988 to 2010. Am. J. Med. 2014, 127, 717–727.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiuge-Shimizu, A.; Kishida, K.; Funahashi, T.; Ishizaka, Y.; Oka, R.; Okada, M.; Suzuki, S.; Takaya, N.; Nakagawa, T.; Fukui, T.; et al. Absolute Value of Visceral Fat Area Measured on Computed Tomography Scans and Obesity-Related Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Large-Scale Japanese General Population (the VACATION-J Study). Ann. Med. 2012, 44, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Saltin, B. Exercise as Medicine—Evidence for Prescribing Exercise as Therapy in 26 Different Chronic Diseases. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.M. Metabolically Healthy Obesity: Definitions, Determinants and Clinical Implications. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2013, 14, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozanne, S.E. Epigenetic Signatures of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 973–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinsier, R.L.; Hunter, G.R.; Heini, A.F.; Goran, M.I.; Sell, S.M. The Etiology of Obesity: Relative Contribution of Metabolic Factors, Diet, and Physical Activity. Am. J. Med. 1998, 105, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, J.L.; Robb, S.W.; Benson, K.M.; White, A. Can the Social Vulnerability Index Be Used for More Than Emergency Preparedness? An Examination Using Youth Physical Fitness Data. J. Phys. Act. Health 2016, 13, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrzad, R. Chapter 4—Etiology of Obesity. In Obesity; Mehrzad, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 43–54. ISBN 978-0-12-818839-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, G.A. A Guide to Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome: Origins and Treatment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-429-13092-2. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, N.; Hunter, W.; Butera, K.; Willis, K.; Cleland, V.; Crawford, D.; Ball, K. Women’s Work. Maintaining a Healthy Body Weight. Appetite 2009, 53, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh-Taskar, P.; Nicklas, T.A.; Morales, M.; Yang, S.-J.; Zakeri, I.; Berenson, G.S. Tracking of Overweight Status from Childhood to Young Adulthood: The Bogalusa Heart Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 60, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.E.; Lewis, C.E.; Caveny, J.L.; Perkins, L.L.; Burke, G.L.; Bild, D.E. Longitudinal Changes in Adiposity Associated With Pregnancy: The CARDIA Study. JAMA 1994, 271, 1747–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowers, M.; Zheng, H.; Tomey, K.; Karvonen-Gutierrez, C.; Jannausch, M.; Li, X.; Yosef, M.; Symons, J. Changes in Body Composition in Women over Six Years at Midlife: Ovarian and Chronological Aging. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-B.; Shin, Y.-A. Males with Obesity and Overweight. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 29, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romieu, I.; Dossus, L.; Barquera, S.; Blottière, H.M.; Franks, P.W.; Gunter, M.; Hwalla, N.; Hursting, S.D.; Leitzmann, M.; Margetts, B.; et al. Energy Balance and Obesity: What Are the Main Drivers? Cancer Causes Control. 2017, 28, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.S.; Key, T.J.; Norat, T.; Scoccianti, C.; Cecchini, M.; Berrino, F.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Espina, C.; Leitzmann, M.; Powers, H.; et al. European Code against Cancer 4th Edition: Obesity, Body Fatness and Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015, 39, S34–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango-Angarita, A.; Rodríguez-Ramírez, S.; Serra-Majem, L.; Shamah-Levy, T. Dietary Energy Density and Its Association with Overweight or Obesity in Adolescents: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnowski, A. Energy Density, Palatability, and Satiety: Implications for Weight Control. Nutr. Rev. 1998, 56, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera-Crichton, D.; Tefft, N. Macronutrients and Obesity: Revisiting the Calories in, Calories out Framework. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2014, 14, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishnofsky, M. Caloric Equivalents of Gained or Lost Weight. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1958, 6, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jéquier, E. Pathways to Obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2002, 26, S12–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komarnytsky, S.; Retchin, S.; Vong, C.I.; Lila, M.A. Gains and Losses of Agricultural Food Production: Implications for the Twenty-First Century. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 13, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.D.; Sacks, G.; Chandramohan, D.; Chow, C.C.; Wang, Y.C.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Swinburn, B.A. Quantification of the Effect of Energy Imbalance on Bodyweight. Lancet 2011, 378, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, J.M. How Can Eating Behavior Be Regulated in the Complex Environments of Free-Living Humans? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1996, 20, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, D.; Young, H.A. Reducing Calorie Intake May Not Help You Lose Body Weight. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2017, 12, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, G.A.; Flatt, J.-P.; Volaufova, J.; Delany, J.P.; Champagne, C.M. Corrective Responses in Human Food Intake Identified from an Analysis of 7-d Food-Intake Records. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 1504–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosy-Westphal, A.; Hägele, F.A.; Müller, M.J. What Is the Impact of Energy Expenditure on Energy Intake? Nutrients 2021, 13, 3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, J.J.; Dowray, S.; Braxton, D.; Mihas, P.; Viera, A.J. Simplifying Healthful Choices: A Qualitative Study of a Physical Activity Based Nutrition Label Format. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Craig, C.L.; Gauvin, L. Adiposity, Physical Fitness and Incident Diabetes: The Physical Activity Longitudinal Study. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.; Schnohr, P.; Sørensen, T.I.A. Longitudinal Study of the Long-Term Relation between Physical Activity and Obesity in Adults. Int. J. Obes. 2004, 28, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleven, L.; Krell-Roesch, J.; Nigg, C.R.; Woll, A. The Association between Physical Activity with Incident Obesity, Coronary Heart Disease, Diabetes and Hypertension in Adults: A Systematic Review of Longitudinal Studies Published after 2012. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drenowatz, C. Reciprocal Compensation to Changes in Dietary Intake and Energy Expenditure within the Concept of Energy Balance. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, N.A.; Caudwell, P.; Hopkins, M.; Byrne, N.M.; Colley, R.; Hills, A.P.; Stubbs, J.R.; Blundell, J.E. Metabolic and Behavioral Compensatory Responses to Exercise Interventions: Barriers to Weight Loss. Obesity 2007, 15, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, J.E.; Herrmann, S.D.; Lambourne, K.; Szabo, A.N.; Honas, J.J.; Washburn, R.A. Does Increased Exercise or Physical Activity Alter Ad-Libitum Daily Energy Intake or Macronutrient Composition in Healthy Adults? A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, A.Y.; Wallman, K.E.; Fairchild, T.J.; Guelfi, K.J. High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise Attenuates Ad-Libitum Energy Intake. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alméras, N.; Lavallée, N.; Després, J.P.; Bouchard, C.; Tremblay, A. Exercise and Energy Intake: Effect of Substrate Oxidation. Physiol. Behav. 1995, 57, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, S.G.; Verhoef, S.P.; Westerterp, K.R. Weight Loss-Induced Reduction in Physical Activity Recovers during Weight Maintenance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, K.; Kayser, B.; Saris, W.H.M.; Pichard, C. Effects of Physical Activity on Food Intake. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keesey, R.E.; Hirvonen, M.D. Body Weight Set-Points: Determination and Adjustment1. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 1875S–1883S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, L.T.; Park, S.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, K.W.; Kwon, O. Hypothalamic Control of Energy Expenditure and Thermogenesis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolfe, D.F.; Brown, G.C. Cellular Energy Utilization and Molecular Origin of Standard Metabolic Rate in Mammals. Physiol. Rev. 1997, 77, 731–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiyala, K.J.; Morton, G.J.; Leroux, B.G.; Ogimoto, K.; Wisse, B.; Schwartz, M.W. Identification of Body Fat Mass as a Major Determinant of Metabolic Rate in Mice. Diabetes 2010, 59, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulloo, A.G.; Jacquet, J. Adaptive Reduction in Basal Metabolic Rate in Response to Food Deprivation in Humans: A Role for Feedback Signals from Fat Stores. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi-Mameghani, M.; Scott, J.A.; Der, G.; Lean, M.E.J.; Burns, C.M. Changes in Weight and Waist Circumference over 9 Years in a Scottish Population. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poppitt, S.D.; Prentice, A.M. Energy Density and Its Role in the Control of Food Intake: Evidence from Metabolic and Community Studies. Appetite 1996, 26, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckland, N.J.; James Stubbs, R.; Finlayson, G. Towards a Satiety Map of Common Foods: Associations between Perceived Satiety Value of 100 Foods and Their Objective and Subjective Attributes. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 152, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, R.E.; Laughlin, G.A.; LaCroix, A.Z.; Hartman, S.J.; Natarajan, L.; Senger, C.M.; Martínez, M.E.; Villaseñor, A.; Sears, D.D.; Marinac, C.R.; et al. Intermittent Fasting and Human Metabolic Health. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.; Martin, S.; Kuhn, I.; Cowan, A.; Brayne, C.; Lafortune, L. Barriers and Facilitators to the Uptake and Maintenance of Healthy Behaviours by People at Mid-Life: A Rapid Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, D. Cognitive and Autonomic Determinants of Energy Homeostasis in Obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, S.A.; Gill, C.; Welch, A.; Day, K.; Cassidy, A.; Khaw, K.T.; Sneyd, M.J.; Key, T.J.; Roe, L.; Day, N.E. Comparison of Dietary Assessment Methods in Nutritional Epidemiology: Weighed Records v. 24 h Recalls, Food-Frequency Questionnaires and Estimated-Diet Records. Br. J. Nutr. 1994, 72, 619–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jéquier, E. Nutrient Effects: Post-Absorptive Interactions. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1995, 54, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengeste, A.M.; Rustan, A.C.; Lund, J. Skeletal Muscle Energy Metabolism in Obesity. Obesity 2021, 29, 1582–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andriessen, C.; Fealy, C.E.; Veelen, A.; van Beek, S.M.M.; Roumans, K.H.M.; Connell, N.J.; Mevenkamp, J.; Moonen-Kornips, E.; Havekes, B.; Schrauwen-Hinderling, V.B.; et al. Three Weeks of Time-Restricted Eating Improves Glucose Homeostasis in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes but Does Not Improve Insulin Sensitivity: A Randomised Crossover Trial. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1710–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, C.C.; Li, K.W.; Alazraki, A.L.; Beysen, C.; Carrier, C.A.; Cleeton, R.L.; Dandan, M.; Figueroa, J.; Knight-Scott, J.; Knott, C.J.; et al. Dietary Sugar Restriction Reduces Hepatic de Novo Lipogenesis in Adolescent Boys with Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e150996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanillo-Campos, R.; Chaplin, A.; Romaguera, D.; Abete, I.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Martín, V.; Estruch, R.; Vidal, J.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Babio, N.; et al. Longitudinal Association of Dietary Carbohydrate Quality with Visceral Fat Deposition and Other Adiposity Indicators. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 2264–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hron, B.M.; Ebbeling, C.B.; Feldman, H.A.; Ludwig, D.S. Relationship of Insulin Dynamics to Body Composition and Resting Energy Expenditure Following Weight Loss. Obesity 2015, 23, 2216–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravussin, E.; Swinburn, B.A. Metabolic Predictors of Obesity: Cross-Sectional versus Longitudinal Data. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1993, 17 (Suppl. S3), S28–S31. [Google Scholar]
- Jitrapakdee, S.; Maurice, M.S.; Rayment, I.; Cleland, W.W.; Wallace, J.C.; Attwood, P.V. Structure, Mechanism and Regulation of Pyruvate Carboxylase. Biochem. J. 2008, 413, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshef, L.; Olswang, Y.; Cassuto, H.; Blum, B.; Croniger, C.M.; Kalhan, S.C.; Tilghman, S.M.; Hanson, R.W. Glyceroneogenesis and the Triglyceride/Fatty Acid Cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 30413–30416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merra, G.; Gratteri, S.; De Lorenzo, A.; Barrucco, S.; Perrone, M.A.; Avolio, E.; Bernardini, S.; Marchetti, M.; Di Renzo, L. Effects of Very-Low-Calorie Diet on Body Composition, Metabolic State, and Genes Expression: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malinowski, B.; Zalewska, K.; Węsierska, A.; Sokołowska, M.M.; Socha, M.; Liczner, G.; Pawlak-Osińska, K.; Wiciński, M. Intermittent Fasting in Cardiovascular Disorders—An Overview. Nutrients 2019, 11, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, G.F. Starvation in Man. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1976, 5, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Mosaoa, R.; Graham, G.T.; Kasprzyk-Pawelec, A.; Gadre, S.; Parasido, E.; Catalina-Rodriguez, O.; Foley, P.; Giaccone, G.; Cheema, A.; et al. Inhibition of the Mitochondrial Citrate Carrier, Slc25a1, Reverts Steatosis, Glucose Intolerance, and Inflammation in Preclinical Models of NAFLD/NASH. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 2143–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.C.; O’Neill, L.A.J. A Role for the Krebs Cycle Intermediate Citrate in Metabolic Reprogramming in Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, J. Use and Storage of Carbohydrate and Fat. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 61, 952S–959S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.R.; Cross, E.; Sanna, F.; Hodson, L. Dysregulation of Hepatic Metabolism with Obesity: Factors Influencing Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2022, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuk, J.L.; Saunders, T.J.; Davidson, L.E.; Ross, R. Age-Related Changes in Total and Regional Fat Distribution. Ageing Res. Rev. 2009, 8, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jura, M.; Kozak, L.P. Obesity and Related Consequences to Ageing. Age 2016, 38, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtue, S.; Vidal-Puig, A. Adipose Tissue Expandability, Lipotoxicity and the Metabolic Syndrome—An Allostatic Perspective. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malis, C.; Rasmussen, E.L.; Poulsen, P.; Petersen, I.; Christensen, K.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Astrup, A.; Vaag, A.A. Total and Regional Fat Distribution Is Strongly Influenced by Genetic Factors in Young and Elderly Twins. Obes. Res. 2005, 13, 2139–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilton, C.; Karpe, F.; Pinnick, K.E. Role of Developmental Transcription Factors in White, Brown and Beige Adipose Tissues. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Gesta, S.; Kahn, C.R. Beneficial Effects of Subcutaneous Fat Transplantation on Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeland, I.J.; Turer, A.T.; Ayers, C.R.; Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Vega, G.L.; Farzaneh-Far, R.; Grundy, S.M.; Khera, A.; McGuire, D.K.; de Lemos, J.A. Dysfunctional Adiposity and the Risk of Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes in Obese Adults. JAMA 2012, 308, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.D.; Kandula, N.R.; Lin, F.; Allison, M.A.; Carr, J.; Herrington, D.; Liu, K.; Kanaya, A.M. Less Favorable Body Composition and Adipokines in South Asians Compared with Other US Ethnic Groups: Results from the MASALA and MESA Studies. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karastergiou, K.; Smith, S.R.; Greenberg, A.S.; Fried, S.K. Sex Differences in Human Adipose Tissues—The Biology of Pear Shape. Biol. Sex Differ. 2012, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisner, B.H.; Zargooshi, J.; Berger, A.D.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Doyle, S.M.; Sheth, S.; Stoller, M.L. Gender Differences in Subcutaneous and Perirenal Fat Distribution. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2010, 32, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.P.; de Souza Santos, R.; Palmer, B.F.; Clegg, D.J. Determinants of Body Fat Distribution in Humans May Provide Insight about Obesity-Related Health Risks. J. Lipid. Res. 2019, 60, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, M.J.; Tchernof, A.; Sites, C.K.; Poehlman, E.T. Effect of Menopausal Status on Body Composition and Abdominal Fat Distribution. Int. J. Obes. 2000, 24, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouliot, M.C.; Després, J.P.; Moorjani, S.; Lupien, P.J.; Tremblay, A.; Nadeau, A.; Bouchard, C. Regional Variation in Adipose Tissue Lipoprotein Lipase Activity: Association with Plasma High Density Lipoprotein Levels. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 21, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verheggen, R.J.H.M.; Maessen, M.F.H.; Green, D.J.; Hermus, A.R.M.M.; Hopman, M.T.E.; Thijssen, D.H.T. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Effects of Exercise Training versus Hypocaloric Diet: Distinct Effects on Body Weight and Visceral Adipose Tissue. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 664–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadson, P.; Landini, L.; Helmiö, M.; Hannukainen, J.C.; Immonen, H.; Honka, M.-J.; Bucci, M.; Savisto, N.; Soinio, M.; Salminen, P.; et al. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Adipose Tissue Glucose Metabolism in Different Depots in Patients With or Without Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Cao, C.; Hur, J.; Cohen, J.; Chen, W.; Zong, X.; Colditz, G.; Yang, L.; Stamatakis, E.; Cao, Y. Association of Sedentary Patterns with Body Fat Distribution among US Children and Adolescents: A Population-Based Study. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, U.J.; Choi, M.-S. Obesity and Its Metabolic Complications: The Role of Adipokines and the Relationship between Obesity, Inflammation, Insulin Resistance, Dyslipidemia and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, G.; Castagneto Gissey, L.; Del Corpo, G.; Giordano, C.; Cerbelli, B.; Severino, A.; Manco, M.; Basso, N.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Bornstein, S.R.; et al. New Insight into the Mechanisms of Ectopic Fat Deposition Improvement after Bariatric Surgery. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, D.L.; Tchoukalova, Y.; Tam, C.S.; Covington, J.D.; Xie, W.; Schwarz, J.-M.; Bajpeyi, S.; Ravussin, E. Effect of 8 Weeks of Overfeeding on Ectopic Fat Deposition and Insulin Sensitivity: Testing the “Adipose Tissue Expandability” Hypothesis. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2789–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.H. Are Fatty Acids Gluconeogenic Precursors? J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2235–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, Y.; Mahankali, A.; Matsuda, M.; Glass, L.; Mahankali, S.; Ferrannini, E.; Cusi, K.; Mandarino, L.J.; DeFronzo, R.A. Improved Glycemic Control and Enhanced Insulin Sensitivity in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects Treated with Pioglitazone. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, D.E. Skeletal Muscle Fat Oxidation: Timing and Flexibility Are Everything. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1699–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, G.H.; Moors, C.C.M.; Jocken, J.W.E.; van der Zijl, N.J.; Jans, A.; Konings, E.; Diamant, M.; Blaak, E.E. Altered Skeletal Muscle Fatty Acid Handling in Subjects with Impaired Glucose Tolerance as Compared to Impaired Fasting Glucose. Nutrients 2016, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, S.; Ghergurovich, J.M.; Morscher, R.J.; Jang, C.; Teng, X.; Lu, W.; Esparza, L.A.; Reya, T.; Zhan, L.; Guo, J.Y.; et al. Glucose Feeds the TCA Cycle via Circulating Lactate. Nature 2017, 551, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komarnytsky, S.; Wagner, C.; Gutierrez, J.; Shaw, O.M. Berries in Microbiome-Mediated Gastrointestinal, Metabolic, and Immune Health. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2023, 12, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vong, C.I.; Rathinasabapathy, T.; Moncada, M.; Komarnytsky, S. All Polyphenols Are Not Created Equal: Exploring the Diversity of Phenolic Metabolites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2077–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, M.; Gutierrez, J.; Komarnytsky, S. Essential Minerals and Metabolic Adaptation of Immune Cells. Nutrients 2023, 15, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, G.K.; Mullin, G.E. The Gut Microbiome and Obesity. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaoutari, A.E.; Armougom, F.; Gordon, J.I.; Raoult, D.; Henrissat, B. The Abundance and Variety of Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes in the Human Gut Microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Mitchell, A.L.; Boland, M.; Forster, S.C.; Gloor, G.B.; Tarkowska, A.; Lawley, T.D.; Finn, R.D. A New Genomic Blueprint of the Human Gut Microbiota. Nature 2019, 568, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraj, S.; Hemarajata, P.; Versalovic, J. The Human Gut Microbiome and Body Metabolism: Implications for Obesity and Diabetes. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Price, J.; Abu-Ali, G.; Huttenhower, C. The Healthy Human Microbiome. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.L.; Wolin, M.J. Fermentations by Saccharolytic Intestinal Bacteria. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1979, 32, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudek-Wicher, R.K.; Junka, A.; Bartoszewicz, M. The Influence of Antibiotics and Dietary Components on Gut Microbiota. Gastroenterol. Rev. 2018, 13, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albenberg, L.; Esipova, T.V.; Judge, C.P.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, J.; Laughlin, A.; Grunberg, S.; Baldassano, R.N.; Lewis, J.D.; Li, H.; et al. Correlation between Intraluminal Oxygen Gradient and Radial Partitioning of Intestinal Microbiota. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1055–1063.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overall, J.; Bonney, S.A.; Wilson, M.; Beermann, A.; Grace, M.H.; Esposito, D.; Lila, M.A.; Komarnytsky, S. Metabolic Effects of Berries with Structurally Diverse Anthocyanins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An Obesity-Associated Gut Microbiome with Increased Capacity for Energy Harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäckhed, F.; Manchester, J.K.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. Mechanisms Underlying the Resistance to Diet-Induced Obesity in Germ-Free Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, T.; Sharma, R. Fermentation Potential of the Gut Microbiome: Implications for Energy Homeostasis and Weight Management. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquant, G.; Grill, J.-P.; Seksik, P. Impact of N-Acyl-Homoserine Lactones, Quorum Sensing Molecules, on Gut Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatini, K.M.; Durand, P.-J.; Rathinasabapathy, T.; Esposito, D.; Komarnytsky, S. Bitter Receptors and Glucose Transporters Interact to Control Carbohydrate and Immune Responses in the Gut. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 682.6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Huh, J.Y.; Sohn, J.H.; Choe, S.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Lim, C.Y.; Jo, A.; Park, S.B.; Han, W.; Kim, J.B. Lipid-Overloaded Enlarged Adipocytes Provoke Insulin Resistance Independent of Inflammation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 1686–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-Y.; van de Wall, E.; Laplante, M.; Azzara, A.; Trujillo, M.E.; Hofmann, S.M.; Schraw, T.; Durand, J.L.; Li, H.; Li, G.; et al. Obesity-Associated Improvements in Metabolic Profile through Expansion of Adipose Tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2621–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, N.; Kubota, T.; Kajiwara, E.; Iwamura, T.; Kumagai, H.; Watanabe, T.; Inoue, M.; Takamoto, I.; Sasako, T.; Kumagai, K.; et al. Differential Hepatic Distribution of Insulin Receptor Substrates Causes Selective Insulin Resistance in Diabetes and Obesity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Goeddel, D.V. TNF-R1 Signaling: A Beautiful Pathway. Science 2002, 296, 1634–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, L.N.; Oberbach, A.; Costford, S.R.; Chan, K.L.; Sams, A.; Blüher, M.; Klip, A. Expression of Anti-Inflammatory Macrophage Genes within Skeletal Muscle Correlates with Insulin Sensitivity in Human Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1623–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Moon, K.M.; Kim, C.Y. Tight Junction in the Intestinal Epithelium: Its Association with Diseases and Regulation by Phytochemicals. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 2645465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Oyang, L.; Lin, J.; Tan, S.; Han, Y.; Wu, N.; Yi, P.; Tang, L.; Pan, Q.; Rao, S.; et al. The Cancer Metabolic Reprogramming and Immune Response. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schéle, E.; Grahnemo, L.; Anesten, F.; Hallén, A.; Bäckhed, F.; Jansson, J.-O. Regulation of Body Fat Mass by the Gut Microbiota: Possible Mediation by the Brain. Peptides 2016, 77, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, A.; Camilleri, M.; Abu Dayyeh, B.; Calderon, G.; Gonzalez, D.; McRae, A.; Rossini, W.; Singh, S.; Burton, D.; Clark, M.M. Selection of Antiobesity Medications Based on Phenotypes Enhances Weight Loss: A Pragmatic Trial in an Obesity Clinic. Obesity 2021, 29, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Tissues | Carbohydrates (Glucose, Glycogen) | Proteins (Mobilizable) | Fats (Triacylglycerols) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | 400 | 400 | 450 |
| Muscle | 1200 | 24,000 | 450 |
| Adipose | 80 | 40 | 135,000 |
| Blood | 60 | 0 | 45 |
| Brain | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Metabolite | Flux Rate (nmol g−1 min−1) |
|---|---|
| Lactate | 374.4 ± 112.4 |
| Glucose | 150.9 ± 46.7 |
| Acetate | 72.7 ± 17.5 |
| Alanine | 70.2 ± 5.4 |
| Pyruvate | 57.3 ± 14.2 |
| Glycerol | 53.3 ± 2.1 |
| Glutamine | 45.6 ± 4.7 |
| 3-Hydroxybutyrate | 43.3 ± 17.1 |
| Palmitic acid | 24.6 ± 4.2 |
| Citrate | 16.2 ± 6.6 |
| Succinate | 3.1 ± 1.1 |
| Malate | 2.0 ± 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milhem, F.; Komarnytsky, S. Progression to Obesity: Variations in Patterns of Metabolic Fluxes, Fat Accumulation, and Gastrointestinal Responses. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13091016
Milhem F, Komarnytsky S. Progression to Obesity: Variations in Patterns of Metabolic Fluxes, Fat Accumulation, and Gastrointestinal Responses. Metabolites. 2023; 13(9):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13091016
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilhem, Fadia, and Slavko Komarnytsky. 2023. "Progression to Obesity: Variations in Patterns of Metabolic Fluxes, Fat Accumulation, and Gastrointestinal Responses" Metabolites 13, no. 9: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13091016
APA StyleMilhem, F., & Komarnytsky, S. (2023). Progression to Obesity: Variations in Patterns of Metabolic Fluxes, Fat Accumulation, and Gastrointestinal Responses. Metabolites, 13(9), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13091016