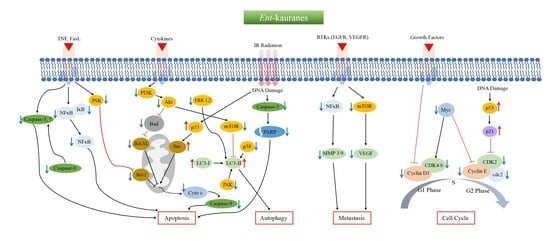
Mechanistic Pathways and Molecular Targets of Plant-Derived Anticancer ent-Kaurane Diterpenes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Methodology
2. Anticancer ent-Kauranes and Their Targets
2.1. Oridonin
2.2. Eriocalyxin B
2.3. Excisanin A
2.4. Ponicidin
2.5. Pharicins A and B
2.6. Jaridonin
2.7. Jungermannenones A and B
2.8. Effusanin E
2.9. Longikaurin A
2.10. Glaucocalyxins A and B
2.11. Lasiodin
2.12. Adenanthin
2.13. Kaurenic Acid
2.14. Weisiensin B
2.15. Inflexinol
2.16. Xerophilusin B
2.17. Henryin
2.18. 11α, 12α-epoxyleukamenin E
2.19. DEK
2.20. JDA-202
2.21. Pterisolic Acid G
2.22. Rabdoternin B and Maoecrystal I
2.23. CHKA
2.24. CrT1
2.25. Ent-16β-17α-dihydroxykaurane
2.26. Ent-11α-hydroxy-16-kauren-15-one
2.27. Hydroxy-15-oxo-zoapatlin
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 31 December 2019).
- Soerjomataram, I.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Parkin, D.M.; Ferlay, J.; Mathers, C.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Global burden of cancer in 2008: A systematic analysis of disability-adjusted life-years in 12 world regions. Lancet 2012, 380, 1840–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccioni, M.; Dal Ben, D.; Lambertucci, C.; Maggi, F.; Papa, F.; Thomas, A.; Santinelli, C.; Marucci, G. Antiproliferative evaluation of isofuranodiene on breast and prostate cancer cell lines. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 264829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVita, V.T.; Chu, E. A history of cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8643–8653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cragg, G.M.; Grothaus, P.G.; Newman, D.J. Impact of natural products on developing new anti-cancer agents. Chem Rev. 2009, 7, 3012–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. Summary of WHO guidelines for the assessment of herbal medicines. Herb. Gram. 1993, 28, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Nyirenda, K.K.; Saka, J.D.K.; Naidoo, D.; Maharaj, V.J.; Muller, C.J.F. Antidiabetic, anti-oxidant and antimicrobial activities of Fadogia ancylantha extracts from Malawi. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 143, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.B. History of Anticancer Drugs. In eLS; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sottomayor, M.; RosBarcelo, A. The vinca alkaloids: From biosynthesis and accumulation in plant cells, to uptake, activity and metabolism in animal cells. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2006, 33, 813–857. [Google Scholar]
- Barbuti, A.M.; Chen, Z.S. Paclitaxel through the ages of anticancer therapy: Exploring its role in chemoresistance and radiation therapy. Cancers 2015, 7, 2360–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, D.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. Recent progress in the development of natural ent-kaurane diterpenoids with anti-tumor activity. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, P.A.; de Oliveira, A.B.; Batista, R. Occurrence, biological activities and synthesis of kaurane diterpenes and their glycosides. Molecules 2007, 12, 455–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Chen, Q.Q.; Jin, Q.P.; Gao, J.; Zhao, P.J.; Lu, S.; Zeng, Y. IeCPS2 is potentially involved in the biosynthesis of pharmacologically active Isodon diterpenoids rather than gibberellin. Phytochemistry 2012, 76, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Feng, M.; Wang, E.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Hou, R.; Zhao, Y. An ent-Kaurane diterpenoid isolated from Rabdosia excisa suppresses Bcr-Abl protein expression in vitro and in vivo and induces apoptosis of CML cells. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1900443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wei, J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, L. Leukamenin E, an ent-kaurane diterpenoid, is a novel and potential keratin intermediate filament inhibitor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 846, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Ding, C.; Ye, N.; Liu, Z.; Wold, E.A.; Chen, H.; Wild, C.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, J. Discovery and development of natural product oridonin-inspired anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 122, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, Z.; Xie, F.; Li, M.; Liang, Z.; Xu, W.; Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H. Oridonin induces autophagy via inhibition of glucose metabolism in p53-mutated colorectal cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.F.; Yi, S.; Wen, L.; He, J.; Yang, L.J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, B.P.; Cui, G.H.; Chen, Y. Oridonin induces NPM mutant protein translocation and apoptosis in NPM1c+ acute myeloid leukemia cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.Y.; Xu, B.; Chen, S.F.; Chen, S.S.; Zhang, T.; Ren, J.; Xu, J. Effect of oridonin-mediated hallmark changes on inflammatory pathways in human pancreatic cancer (BxPC-3) cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14895–14903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.H.; Pi, J.; Jin, H.; Cai, J.Y. Oridonin-induced mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in esophageal cancer cells by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Ras/Raf pathways. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 3736–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasaturo, M.; Cotugno, R.; Fiengo, L.; Vinegoni, C.; Dal Piaz, F.; De Tommasi, N. The anti-tumor diterpene oridonin is a direct inhibitor of Nucleolin in cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yu, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, J.; Dong, X.; Ma, B.; Zhang, Q. Oridonin exerts anticancer effect on osteosarcoma by activating PPAR-γ and inhibiting Nrf2 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.C.; Ke, Y.; Zi, X.; Zhao, W.; Shi, X.J.; Liu, H.M. Jaridonin, a novel ent-kaurene diterpenoid from Isodon rubescens, inducing apoptosis via production of reactive oxygen species in esophageal cancer cells. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, L.; Xie, K.; Sheng, D.; Wan, X.; Zhu, G. Antiangiogenic effects of oridonin. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, Q.F.; Du, J.K.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.B.; Hu, Z.D.; Chen, S.P.; Du, Y.; Li, M.Z.; Xie, D.; Zou, J.; et al. Anti-tumour activity of longikaurin A (LK-A), a novel natural diterpenoid, in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, X.J.; Ding, L.; Zhou, W.; Ji, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, G.; Tang, K.; Ke, Y.; et al. Pro-apoptotic effects of JDA-202, a novel natural diterpenoid, on esophageal cancer through targeting peroxiredoxin I. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Tan, H.; Zhu, N.; Gao, H.; Lv, C.; Gang, J.; Ji, Y. Oridonin induces apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 2453–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadioglu, O.; Saeed, M.; Kuete, V.; Greten, H.J.; Efferth, T. Oridonin Targets Multiple Drug-Resistant Tumor Cells as Determined by in Silico and in Vitro Analyses. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, T.; Jin, F.; Wu, K.; Ye, Z.; Li, N. Oridonin enhances in vitro anticancer effects of lentinan in SMMC-7721 human hepatoma cells through apoptotic genes. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 5129–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Chen, X.; Qu, S.; Yao, B.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Jin, Y.; Ma, C. Oridonin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in hormone-independent prostate cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 2838–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Han, Q.; Duan, L.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, H. Oridonin increases anticancer effects of lentinan in HepG2 human hepatoblastoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 1999–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Guan, H. Oridonin inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis through blocking the Notch signaling. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.M.; Deng, X.; Zuo, Z.L.; Sun, H.D.; Zhao, Q.S.; Li, Y. Identification and validation of p50 as the cellular target of eriocalyxin B. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 11354–11364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Yue, G.G.L.; Chan, A.M.L.; Tsui, S.K.W.; Fung, K.P.; Sun, H.; Pu, J.; Lau, C.B.S. Eriocalyxin B, a novel autophagy inducer, exerts anti-tumor activity through the suppression of Akt/mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway in breast cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 142, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yue, G.G.; Lau, C.B.; Sun, H.; Fung, K.P.; Leung, P.C.; Han, Q.; Leung, P.S. Eriocalyxin B induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells through caspase- and p53-dependent pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 262, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Jiang, X.X.; Chen, Q.S.; Shi, W.Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, H.D.; Shen, Z.X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, S.J.; Zhao, W.L. Eriocalyxin B induces apoptosis in lymphoma cells through multiple cellular signaling pathways. Exp. Hematol. 2010, 38, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yue, G.G.L.; Liu, M.; Zuo, Z.; Lee, J.K.M.; Li, M.; Tsui, S.K.W.; Fung, K.P.; Sun, H.D.; Pu, J.; et al. Eriocalyxin B, a natural diterpenoid, inhibited VEGF-induced angiogenesis and diminished angiogenesis-dependent breast tumor growth by suppressing VEGFR-2 signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 82820–82835. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.M.; Chen, W.; Zhu, J.S.; Chen, W.X.; Chen, N.W. Eriocalyxin B blocks human SW1116 colon cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, cell cycle progression and angiogenesis via the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 2235–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; He, L.; Cao, P.; Yu, Q. Eriocalyxin B inhibits STAT3 signaling by covalently targeting STAT3 and blocking phosphorylation and activation of STAT3. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, J.; Tang, J.; Jiao, L.; Ji, J.; Chen, W.D.; Feng, G.K.; Gao, Y.H.; Zhu, X.F.; Deng, R. A diterpenoid compound, excisanin A, inhibits the invasive behavior of breast cancer cells by modulating the integrin β1/FAK/PI3K/AKT/β-catenin signaling. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Tang, J.; Xia, L.P.; Li, D.D.; Zhou, W.J.; Wang, L.L.; Feng, G.K.; Zeng, Y.X.; Gao, Y.H.; Zhu, X.F. ExcisaninA, a diterpenoid compound purified from Isodon MacrocalyxinD, induces tumor cells apoptosis and suppresses tumor growth through inhibition of PKB/AKT kinase activity and blockade of its signal pathway. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wu, X.Q.; Deng, R.; Sun, T.; Feng, G.K.; Zhu, X.F. Upregulation of sestrin 2 expression via JNK pathway activation contributes to autophagy induction in cancer cells. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Lu, Y.M.; Qu, G.Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.X.; Liao, X.H.; Kong, W.M. Ponicidin induces apoptosis via JAK2 and STAT3 signaling pathways in gastric carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1576–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hou, Y. Ponicidin induces apoptosis of human cervical cancer HeLa cell line through the PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 9, 23214–23221. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.J.; Huang, R.W.; Lin, D.J.; Peng, J.; Zhang, M.; Pan, X.; Hou, M.; Wu, X.Y.; Lin, Q.; Chen, F. Ponicidin, an ent-kaurane diterpenoid derived from a constituent of the herbal supplement PC-SPES, Rabdosia rubescens, induces apoptosis by activation of caspase-3 and mitochondrial events in lung cancer cells in vitro. Cancer Investig. 2006, 24, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Chen, C.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, W. Ponicidin suppresses HT29 cell growth via the induction of G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 5816–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.Z.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, W.L.; Lin, Q.S.; Sun, H.D.; Dai, W.; Chen, G.Q. Pharicin A, a novel natural ent-kaurene diterpenoid, induces mitotic arrest and mitotic catastrophe of cancer cells by interfering with BubR1 function. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 2897–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, Z.M.; Wu, Y.L.; Zhou, M.Y.; Liu, C.X.; Xu, H.Z.; Yan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Sun, H.D.; Chen, G.Q. Pharicin B stabilizes retinoic acid receptor-α and presents synergistic differentiation induction with ATRA in myeloid leukemic cells. Blood 2010, 116, 5289–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.C.; Su, N.; Shi, X.J.; Zhao, W.; Ke, Y.; Zi, X.; Zhao, N.M.; Qin, Y.H.; Zhao, H.W.; Liu, H.M. Jaridonin-induced G2/M phase arrest in human esophageal cancer cells is caused by reactive oxygen species-dependent Cdc2-tyr15 phosphorylation via ATM-Chk1/2-Cdc25C pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 282, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.X.; Lin, Z.M.; Wang, M.J.; Dong, Y.W.; Niu, H.M.; Young, C.Y.F.; Lou, H.X.; Yuan, H.Q. Jungermannenone A and B induce ROS-and cell cycle-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, M.; Zhao, M.; Qiu, H.; Shi, D.; Wang, J.; Tian, Y.; Lin, L.; Deng, W. Effusanin E suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell growth by inhibiting NF-κB and COX-2 signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.J.; Bai, H.Y.; Li, Z.H.; Zou, J.; Chen, J.W.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, J.X.; Mai, S.J.; Zeng, M.S.; Sun, H.D.; et al. Longikaurin A, a natural ent-kaurane, induces G2/M phase arrest via downregulation of Skp2 and apoptosis induction through ROS/JNK/c-Jun pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Du, Y.; Hu, X.Y.; Liu, M.Y.; Du, J.K.; Liu, X.M.; Yu, H.E.; Wang, T.Z.; Pu, J.X.; Zhong, Q.; et al. Longikaurin A, a natural ent-kaurane, suppresses stemness in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1672–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.H.; Zhang, Z.; Sima, Y.H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.W. Glaucocalyxin A and B-induced cell death is related to GSH perturbation in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Jin, X.; Hu, X.; Hu, X.; Liu, Z.; Yu, L. Glaucocalyxin A inhibits the growth of liver cancer Focus and SMMC-7721 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Sun, Y.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ma, B.; Yu, L.; Zhang, J.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Q. Glaucocalyxin A exerts anticancer effect on osteosarcoma by inhibiting GLI1 nuclear translocation via regulating PI3K/Akt pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, W.; Xie, J.; Xu, N.; Huang, L.; Xu, A.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Gao, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Liu, C.; et al. Glaucocalyxin A induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt pathway in human bladder cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Jiang, X.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Glaucocalyxin A activates FasL and induces apoptosis through activation of the JNK pathway in human breast cancer cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 5805–5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Cao, W.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Cheng, J.; Huang, H.; Huo, J.; Zhang, X. Glaucocalyxin A, a negative Akt regulator, specifically induces apoptosis in human brain glioblastoma U87MG cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2013, 45, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.H.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.W. Glaucocalyxin A induces apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells through mitochondria-mediated death pathway. Toxicol. Vitr. 2011, 25, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ur Rahman, M.S.; Zhang, L.; Wu, L.; Xie, Y.; Li, C.; Cao, J. Sensitization of gastric cancer cells to alkylating agents by glaucocalyxin B via cell cycle arrest and enhanced cell death. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2017, 11, 2431–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Bai, J.; Shen, F.; Sun, L.; He, Q.; Su, B. Glaucocalyxin B induces apoptosis and autophagy in human cervical cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 1751–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Deng, W.; Tian, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Fu, L.; Shi, D.; Zhao, M.; Luo, W. Lasiodin inhibits proliferation of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by simultaneous modulation of the Apaf-1/Caspase, AKT/MAPK and COX-2/NF-κB signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, J.K.; Huang, Y.; He, W.; Yan, Z.W.; Fan, L.; Liu, M.H.; Xiao, W.L.; Sun, H.D.; Chen, G.Q. Adenanthin targets peroxiredoxin I/II to kill hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.X.; Yin, Q.Q.; Zhou, H.C.; Wu, Y.L.; Pu, J.X.; Xia, L.; Liu, W.; Huang, X.; Jiang, T.; Wu, M.X.; et al. Adenanthin targets peroxiredoxin I and II to induce differentiation of leukemic cells. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Sequera, M.C.; Chiurillo, M.; Moscoso, J.; Dolinar, J.; Suarez, O.; Neira, N.; Mendoza, H.; Rivero-Paris, M. Kaurenic acid: Evaluation of the in vivo and in vitro antitumor activity on murine melanoma. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2011, 43, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peria, F.M.; Tiezzi, D.G.; Tirapelli, D.P.; Neto, F.S.; Tirapelli, C.R.; Ambrosio, S.; Oliveira, H.F.; Tirapelli, L. Kaurenoic acid antitumor activity in breast cancer cells. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, e13641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Cardoso, P.C.; da Rocha, C.A.; Leal, M.F.; de Oliveira Bahia, M.; Alcântara, D.D.; dos Santos, R.A.; dos Santos Gonçalves, N.; Ambrósio, S.R.; Cavalcanti, B.C.; Moreira-Nunes, C.A.; et al. Effect of diterpenoid kaurenoic acid on genotoxicity and cell cycle progression in gastric cancer cell lines. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, S.D.; Yang, D.J.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Yang, H. Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction of weisiensin B isolated from Rabdosia weisiensis C.Y. Wu in human hepatoma cells. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 10, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.A.; Chang, J.C.; Feng, X.L.; Ding, L. Apoptosis induced by weisiensin B isolated from Rabdosia weisiensis C.Y. Wu in K562. Pharmazie 2015, 70, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Ban, J.O.; Oh, J.H.; Hwang, B.Y.; Moon, D.C.; Jeong, H.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.; Kim, K.B.; Han, S.B.; et al. Inflexinol inhibits colon cancer cell growth through inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB activity via direct interaction with p50. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, R.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, C.; Luo, M.; Shi, X.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, F.; Pu, J.; Sun, H.; et al. Xerophilusin b induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells and does not cause toxicity in nude mice. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pu, J.; Jiang, S.; Su, J.; Kong, L.; Mao, B.; Sun, H.; Li, Y. Henryin, an ent-kaurane diterpenoid, inhibits Wnt signaling through interference with β-Catenin/TCF4 interaction in colorectal cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Yao, G.; Zhang, M.; Guo, G.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Cheng, L.; Shi, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A novel ent-kaurane diterpenoid executes antitumor function in colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Carcinogenesis 2014, 36, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Ouyang, W.; Gu, M.; Gao, Z.; Song, M.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, H. Novel ent-kaurane diterpenoid from Rubus corchorifolius L. f. inhibits human colon cancer cell growth via inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Wu, X.; Liao, H.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; He, X.; Zhang, X.; Ye, W.; Wu, H.; et al. Pteisolic acid G, a novel ent-kaurane diterpenoid, inhibits viability and induces apoptosis in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5540–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, R.; Li, X.N.; Du, X.; Wang, W.G.; Dong, K.; Su, J.; Li, Y.; Pu, J.X.; Sun, H.D. Bioactive ent-kaurane diterpenoids from Isodon rosthornii. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.M.; Weng, Z.Y.; Huang, S.X.; Pu, J.X.; Li, S.H.; Huang, H.; Yang, B.B.; Han, Y.; Xiao, W.L.; Li, M.N.; et al. Cytotoxic ent-kauranoids from the medicinal plant Isodon xerophilus. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kong, L.M.; Zhan, R.; Ye, Z.N.; Pu, J.X.; Sun, H.D.; Li, Y. Two natural ent-kauranoids as novel Wnt signaling inhibitors. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2014, 4, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Liang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Chung, H.Y. Anti-angiogenic activity and mechanism of kaurane diterpenoids from Wedelia chinensis. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sul, Y.H.; Lee, M.S.; Cha, E.Y.; Thuong, P.T.; Khoi, N.M.; Song, I.S. An ent-kaurane diterpenoid from Croton tonkinensis induces apoptosis by regulating AMP-activated protein kinase in SK-HEP1 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales, A.; Pérez, P.; Compagnone, R.M.R.; Suarez, A.I.; Arvelo, F.; Ramírez, J.L.; Galindo-Castro, I. Cytotoxic and proapoptotic activity of ent-16β-17α-dihydroxykaurane on human mammary carcinoma cell line MCF-7. Cancer Lett. 2005, 218, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.; Alvarez, A.; Francisco, F.; Suárez, A.I.; Compagnone, R.S.; Galindo-Castro, I. The natural diterpene ent-16β-17α-dihydroxykaurane downregulates Bcl-2 by disruption of the Ap-2α/Rb transcription activating complex and induces E2F1 upregulation in MCF-7 cells. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondoh, M.; Suzuki, I.; Sato, M.; Nagashima, F.; Simizu, S.; Harada, M.; Fujii, M.; Osada, H.; Asakawa, Y.; Watanabe, Y. Kaurene diterpene induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells partly through a caspase-8-dependent pathway. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 311, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dal Piaz, F.; Nigro, P.; Braca, A.; De Tommasi, N.; Belisario, M.A. 13-Hydroxy-15-oxo-zoapatlin, an ent-kaurane diterpene, induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells, affecting thiol-mediated redox regulation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 1409–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarwar, M.S.; Xia, Y.-X.; Liang, Z.-M.; Tsang, S.W.; Zhang, H.-J. Mechanistic Pathways and Molecular Targets of Plant-Derived Anticancer ent-Kaurane Diterpenes. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010144
Sarwar MS, Xia Y-X, Liang Z-M, Tsang SW, Zhang H-J. Mechanistic Pathways and Molecular Targets of Plant-Derived Anticancer ent-Kaurane Diterpenes. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(1):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010144
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarwar, Md. Shahid, Yi-Xuan Xia, Zheng-Ming Liang, Siu Wai Tsang, and Hong-Jie Zhang. 2020. "Mechanistic Pathways and Molecular Targets of Plant-Derived Anticancer ent-Kaurane Diterpenes" Biomolecules 10, no. 1: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010144
APA StyleSarwar, M. S., Xia, Y. -X., Liang, Z. -M., Tsang, S. W., & Zhang, H. -J. (2020). Mechanistic Pathways and Molecular Targets of Plant-Derived Anticancer ent-Kaurane Diterpenes. Biomolecules, 10(1), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010144