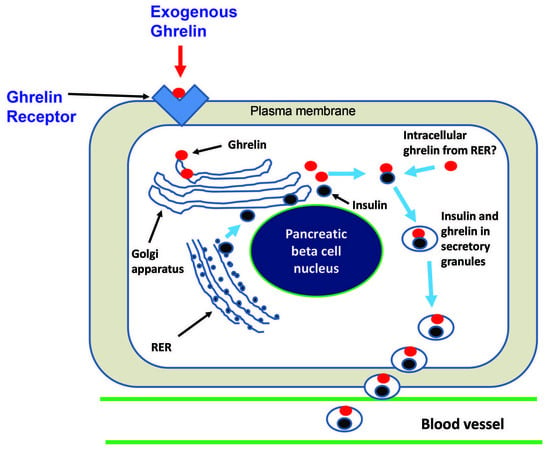
Exogenous Ghrelin Increases Plasma Insulin Level in Diabetic Rats †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Models
2.2. Induction of Experimental Diabetes Using Streptozotocin
2.3. Experimental Design
- Normal control (n = 6): Normal male rats were treated with 5 µg/kg body weight of saline.
- Normal treated (n = 6): Normal male rats were treated with 5 µg/kg body weight of ghrelin (amino acid chain 24–51).
- Diabetic control (n = 6): Diabetic male rats were treated with 5 µg/kg body weight of saline.
- Diabetic Treated (n = 6): Diabetic male rats were treated with 5 µg/kg body weight of ghrelin (amino acid chain 24–51).
- Pre-diabetic Treated (n = 6): Normal male rats were treated with 5 µg/kg body weight of ghrelin (amino acid chain 24–51) for 4 weeks before the induction of diabetes on the 5th week to determine whether ghrelin can prevent STZ-induced diabetes.
2.4. Fasting Blood Glucose and Body Weight Measurements
Glucose Tolerance Test
2.5. Blood and Tissue Collection
2.6. Tissue Processing
2.6.1. Tissue Processing for Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence Study
2.6.2. Avidin-Biotin Complex Staining
2.6.3. Double Labeling Immunofluorescence Staining
2.6.4. Tissue Processing for Electron Microscopy
2.6.5. Post-embedding Immuno-Gold Double Labeling for Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.7. Stimulation of CRL11065 Beta Cell Line with Ghrelin
2.8. Morphometric Analysis of Ghrelin and Insulin-Positive Cells
2.9. Morphometric Analysis of Secretory Granules in Pancreatic Beta Cells
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Ghrelin Treatment on Body Weight, Fasting Blood Glucose Level and Glucose Tolerance Test
Effect of Ghrelin Treatment on Glucose Tolerance Test
3.2. Effect of Ghrelin Treatment on the Pattern of Distribution of Insulin-Positive Cells
3.3. Effect of Ghrelin on Serum Insulin Level
3.4. Effect of Ghrelin on Insulin Release from CRL11065 Beta Cells
3.5. Co-Localization of Ghrelin with Insulin in Pancreatic Islet Cells
Ghrelin and Insulin
3.6. Immuno-Electron Microscopy of Ghrelin in Pancreatic Beta Cells
4. Discussion
Body Weight Gain, Blood Glucose and Glucose Tolerance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| STZ | Streptozotocin |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| NS | Normal saline |
| NGS | Normal goat serum |
| FBG | Fasting blood glucose |
| GTT | Glucose tolerance test |
| EDTA | Ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IF | Immunofluorescence |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered solution |
| ABC | Avidin-biotin complex |
| FITC | Fluorescein Isothiocyanate |
| RRX | Rhodamine Red-X |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| T1DM | Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus |
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
| β cells | Beta cells/Insulin secreting cells |
References
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stengel, A.; Taché, Y. Ghrelin—A pleiotropic hormone secreted from endocrine x/a-like cells of the stomach. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Shiimura, Y.; Ohgusu, H.; Kangawa, K.; Kojima, M. Structure, regulation and function of ghrelin. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 2012, 151, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, A.K.; Gong, Z.; Park, W.-M.; Zigman, J.M.; Sakata, I. Expression of Serum Retinol Binding Protein and Transthyretin within Mouse Gastric Ghrelin Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riley, L.G.; Hirano, T.; Grau, E.G. Rat ghrelin stimulates growth hormone and prolactin release in the tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Zoolog. Sci. 2002, 19, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.D.; McAllister, G.; Feighner, S.D.; Liu, Q.; Nargund, R.P.; Van der Ploeg, L.H.T. Orphan G-protein-coupled receptors and natural ligand discovery. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2001, 22, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahete, M.D.; Rincón-Fernández, D.; Villa-Osaba, A.; Hormaechea-Agulla, D.; Ibáñez-Costa, A.; Martínez-Fuentes, A.J. Ghrelin gene products, receptors, and GOAT enzyme: Biological and pathophysiological insight. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 220, R1–R24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersenn, S. Structure and regulation of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Minerva Endocrinol. 2002, 27, 243–256. [Google Scholar]
- Unniappan, S.; Peter, R.E. Structure, distribution and physiological functions of ghrelin in fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2005, 140, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeghate, E.; Hameed, R.S. Immunohistochemical localization of orexin-B, orexin-1 receptor, ghrelin, GHS-R in the lacrimal gland of normal and diabetic rats. Peptides 2005, 26, 2585–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muta, H.; Sugita, Y.; Furuta, T.; Shiimura, Y.; Ohshima, K.; Nakashima, K.; Sato, K.; Morioka, M.; Abe, H.; Nozawa, T.; et al. Expression of the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor axis and its functional role in promoting tumor growth in primary central nervous system lymphomas. Neuropathology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeghate, E.; Parvez, H. Mechanism of ghrelin-evoked glucagon secretion from the pancreas of diabetic rats. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2002, 23, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gnanapavan, S.; Kola, B.; Bustin, S.A.; Morris, D.G.; McGee, P.; Fairclough, P. The Tissue Distribution of the mRNA of Ghrelin and Subtypes of Its Receptor, GHS-R., in Humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin: Structure and Function. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 495–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-M.; Wang, G.; Englander, E.W.; Kojima, M.; Greeley, G.H. Ghrelin, a new gastrointestinal endocrine peptide that stimulates insulin secretion: Enteric distribution, ontogeny, influence of endocrine, and dietary manipulations. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Yoshimoto, A.; Takaya, K.; Hosoda, K.; Ariyasu, H.; Yahata, K. Kidney produces a novel acylated peptide, ghrelin. FEBS Lett. 2000, 486, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosoda, H.; Kojima, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin: Two major forms of rat ghrelin peptide in gastrointestinal tissue. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 279, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualillo, O.; Caminos, J.; Blanco, M.; Garcìa-Caballero, T.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin, a novel placental-derived hormone. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, N.; Saito, T.; Yagyu, T.; Jiang, B.-H.; Kitagawa, K.; Inagaki, C. GH, GH Receptor, GH Secretagogue Receptor, and Ghrelin Expression in Human T Cells, B Cells, and Neutrophils. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4284–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papotti, M.; Ghè, C.; Cassoni, P.; Catapano, F.; Deghenghi, R.; Ghigo, E. Growth hormone secretagogue binding sites in peripheral human tissues. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 3803–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volante, M.; AllÌa, E.; Gugliotta, P.; Funaro, A.; Broglio, F.; Deghenghi, R. Expression of Ghrelin and of the, G.H.; Secretagogue Receptor by Pancreatic Islet Cells and Related Endocrine Tumors. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Hashiguchi, S.; Dezaki, K.; Mondal, M.S.; Hosoda, H. Ghrelin Is Present in Pancreatic α-Cells of Humans and Rats and Stimulates Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 2002, 51, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andralojc, K.M.; Mercalli, A.; Nowak, K.W.; Albarello, L.; Calcagno, R.; Luzi, L. Ghrelin-producing epsilon cells in the developing and adult human pancreas. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masuda, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Inomata, N.; Ohnuma, N.; Tanaka, S.; Itoh, Z.; Hosoda, H.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin Stimulates Gastric Acid Secretion and Motility in Rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, K.; Yang, P. Mechanisms of Ghrelin anti-heart failure: Inhibition of Ang II-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by down-regulating, AT 1R expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaya, N.; Moriya, J.; Yasumura, Y. Effects of ghrelin administration on left ventricular function, exercise capacity, and muscle wasting in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 2004, 110, 3674–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, A.N.; Wang, J.; Wahed, A.S. The Association between Kidney Disease and Diabetes Remission in Bariatric Surgery Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 74, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchett, N.R.; Maziarz, M.; Shu, X.O. Serum ghrelin and esophageal and gastric cancer in two cohorts in China. Int. J. Cancer 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoto, I.; Matsumoto, M.; Uchikado, Y.; Kita, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Sasaki, K.; Setoyama, T.; Okumura, H.; Owaki, T.; Ishigami, S. Immunohistochemical Evidence of Association between Ghrelin Expression and Tumor Growth in Esophageal Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 2727–2733. [Google Scholar]
- Gahete, M.D.; Córdoba-Chacón, J.; Hergueta-Redondo, M. A novel human ghrelin variant (In1-ghrelin) and ghrelin-O-acyltransferase are overexpressed in breast cancer: Potential pathophysiological relevance. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanfranco, F.; Baldi, M.; Cassoni, P.; Bosco, M.; Ghé, C.; Muccioli, G. Ghrelin and prostate cancer. Vitam Horm. 2008, 77, 301–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Xiao, K.; Yu, M. Ghrelin but not nesfatin-1 affects certain forms of learning and memory in both rats and mice. Brain Res. 2013, 1541, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goshadrou, F.; Kermani, M.; Ronaghi, A.; Sajjadi, S. The effect of ghrelin on, M.K.;-801 induced memory impairment in rats. Peptides 2013, 44, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-García, F.; Juárez-Aguilar, E.; Santiago-García, J.; Cardinali, D.P. Ghrelin and Its Interactions with Growth Hormone, Leptin and Orexins: Implications for the Sleep-Wake Cycle and Metabolism. Sleep Med. Rev. 2014, 18, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agawa, S.; Futagami, S.; Yamawaki, H.; Ikeda, G.; Noda, H.; Kirita, K.; Higuchi, K.; Murakami, M.; Kodaka, Y.; Ueki, N. Acylated ghrelin levels were associated with depressive status, physical quality of life, endoscopic findings based on Kyoto classification in Japan. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2019, 65, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koopmann, A.; Bach, P.; Schuster, R. Ghrelin modulates mesolimbic reactivity to alcohol cues in alcohol-addicted subjects: A functional imaging study. Addict. Biol. 2019, 24, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broglio, F.; Arvat, E.; Benso, A. Ghrelin, a natural, G.H.; secretagogue produced by the stomach, induces hyperglycemia and reduces insulin secretion in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5083–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yada, T.; Damdindorj, B.; Rita, R.S. Ghrelin signalling in β-cells regulates insulin secretion and blood glucose. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Davis, H.W.; Summer, S. Acute administration of unacylated ghrelin has no effect on Basal or stimulated insulin secretion in healthy humans. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2309–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granata, R.; Volante, M.; Settanni, F. Unacylated ghrelin and obestatin increase islet cell mass and prevent diabetes in streptozotocin-treated newborn rats. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 45, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delhanty, P.J.; Neggers, S.J.; van der Lely, A.J. Mechanisms in endocrinology: Ghrelin: The differences between acyl- and des-acyl ghrelin. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 167, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adeghate, E.; Ponery, A.S. Ghrelin stimulates insulin secretion from the pancreas of normal and diabetic rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2002, 14, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeghate, E. Effect of subcutaneous pancreatic tissue transplants on streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. II. Endocrine and metabolic functions. Tissue Cell 1999, 31, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeghate, E.; Donáth, T. Morphological findings in long-term pancreatic tissue transplants in the anterior eye chamber of rats. Pancreas 1990, 5, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeghate, E.; Ponery, A.S. Diabetes mellitus influences the degree of co-localization of calcitonin-gene-related peptide with insulin and glucagon in the rat pancreas. Pancreas 2004, 29, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, S.; Nurulain, S.M.; Rashed, H.; Lotfy, M.; Emerald, S.B.; Koturan, S.; Tekes, K.; Adeghate, E. Diabetes-induced changes in the morphology and nociceptinergic innervation of the rat uterus. J. Mol. Histol. 2016, 47, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfy, M.; Singh, J.; Rashed, H.; Tariq, S.; Zilahi, E.; Adeghate, E. Mechanism of the beneficial and protective effects of exenatide in diabetic rats. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 220, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adeghate, E.; Saeed, Z.; D’Souza, C.; Tariq, S.; Kalász, H.; Tekes, K. Effect of nociceptin on insulin release in normal and diabetic rat pancreas. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 374, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, J.E.; Bateman, J.L.; Ostrom, C.E.; Florant, G.L. Peripheral ghrelin stimulates feeding behavior and positive energy balance in a sciurid hibernator. Horm. Behav. 2011, 59, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyland, L.; Park, S.B.; Abdelaziz, Y.; Abizaid, A. Ghrelin infused into the dorsomedial hypothalamus of male mice increases food intake and adiposity. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 220, 112882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, B.K.; Zigman, J.M. Ghrelin as a Survival Hormone. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.P.; Ronveaux, C.C.; de Lartigue, G.; Geary, N.; Asarian, L.; Raybould, H.E. Deletion of leptin receptors in vagal afferent neurons disrupts estrogen signaling, body weight, food intake and hormonal controls of feeding in female mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 316, E568–E577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppner, K.M.; Müller, T.D.; Tong, J.; Tschöp, M.H. Ghrelin in the control of energy, lipid, and glucose metabolism. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 514, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chabot, F.; Caron, A.; Laplante, M.; St-Pierre, D.H. Interrelationships between ghrelin, insulin and glucose homeostasis: Physiological relevance. World J. Diabetes 2014, 5, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golchoobian, R.; Nabavizadeh, F.; Roghani, M.; Foroumadi, A.; Mohammadian, M. Ghrelin Alleviates MD MA-Induced Disturbance of Serum Glucose and Lipids Levels in the Rat. Acta Med. Iran. 2017, 55, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Xiaolei, Z.; Al-Sanaban, H.; Chengrui, X.; Shengyi, Y. Ghrelin inhibits insulin release by regulating the expression of inwardly rectifying potassium channel 6.2 in islets. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 343, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierup, N.; Yang, S.; McEvilly, R.J.; Mulder, H.; Sundler, F. Ghrelin is expressed in a novel endocrine cell type in developing rat islets and inhibits insulin secretion from, INS-1 (832/13) cells. J. Histochem Cytochem. 2004, 52, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dezaki, K.; Sone, H.; Koizumi, M.; Nakata, M.; Kakei, M.; Nagai, H. Blockade of pancreatic islet-derived ghrelin enhances insulin secretion to prevent high-fat diet-induced glucose intolerance. Diabetes 2006, 55, 3486–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakata, N.; Yoshimatsu, G.; Kodama, S. Development and characteristics of pancreatic epsilon cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vignjević, S.; Todorović, V.; Damjanović, S.; Budeč, M.; Mitrović, O.; Djikić, D.; Drndarević, N.; Mićić, M.; Mišković-Krivokapić, J.; Djuričić, S.; et al. Similar developmental patterns of ghrelin- and glucagon-expressing cells in the human pancreas. Cells Tissues Organs 2012, 196, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, N.; Dağistanli, F.K.; Sacan, O.; Yanardag, R.; Bolkent, S. Obestatin and insulin in pancreas of newborn diabetic rats treated with exogenous ghrelin. Acta Histochem. 2012, 114, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bando, M.; Iwakura, H.; Ariyasu, H.; Koyama, H.; Hosoda, K.; Adachi, S.; Nakao, K.; Kangawa, K.; Akamizu, T. Overexpression of intraislet ghrelin enhances β-cell proliferation after streptozotocin-induced β-cell injury in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 305, E140–E148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfy, M.; Adeghate, J.; Kalasz, H.; Singh, J.; Adeghate, E. Chronic Complications of Diabetes Mellitus: A Mini Review. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2017, 13, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeghate, E.; Schattner, P.; Dunn, E. An update on the etiology and epidemiology of diabetes mellitus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1084, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeghate, E. Visfatin: Structure, function and relation to diabetes mellitus and other dysfunctions. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1851–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, C.; Patanè, M.; Vicario, N.; Di Bella, V.; Cosentini, I.; Barresi, V.; Gulino, R.; Pellitteri, R.; Russo, A.; Stanzani, S. Olfactory Ensheathing Cells express both Ghrelin and Ghrelin Receptor in vitro: A new hypothesis in favor of a neurotrophic effect. Neuropeptides 2020, 79, 101997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ayed, M.S.; Al-Shaibari, K.S.; Alshehri, D.; Alzahrani, M.J.; Nasser, I.; Alaamri, H.S.; Alaseeri, W.A.; Mahfouz, A.A.; Alsareii, S.A.; Asaad, A.M.; et al. Serum Ghrelin Levels in Saudi Obese Asthmatic School-Children-Correlation with Interleukin-4, Interleukin-5, and Interleukin-21. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soleyman-Jahi, S.; Sadeghi, F.; Pastaki Khoshbin, A.; Khani, L.; Roosta, V.; Zendehdel, K. Attribution of Ghrelin to Cancer; Attempts to Unravel an Apparent Controversy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, S.L.; Vestergaard, E.T.; Larraufie, P.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F.; Jørgensen, J.O.L.; Holst, J.J.; Kuhre, R.E. Ghrelin Does Not Directly Stimulate Secretion of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeghate, E.; Hameed, R.S.; Ponery, A.S.; Tariq, S.; Sheen, R.S.; Shaffiullah, M.; Donáth, T. Streptozotocin causes pancreatic beta cell failure via early and sustained biochemical and cellular alterations. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2010, 118, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Primary | Dilution | Secondary | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ghrelin (Phoenix Pharmaceuticals, Burlingame, CA, USA) | 1:100 | RRX FITC (Jackson Laboratories, Bar Harbor, ME, USA) | 1:100 |
| Insulin (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) | 1:1000 | FITC (Jackson Laboratories, Bar Harbor, ME, USA) | 1:100 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elabadlah, H.; Hameed, R.; D’Souza, C.; Mohsin, S.; Adeghate, E.A. Exogenous Ghrelin Increases Plasma Insulin Level in Diabetic Rats. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040633
Elabadlah H, Hameed R, D’Souza C, Mohsin S, Adeghate EA. Exogenous Ghrelin Increases Plasma Insulin Level in Diabetic Rats. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(4):633. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040633
Chicago/Turabian StyleElabadlah, Haba, Rasheed Hameed, Crystal D’Souza, Sahar Mohsin, and Ernest A. Adeghate. 2020. "Exogenous Ghrelin Increases Plasma Insulin Level in Diabetic Rats" Biomolecules 10, no. 4: 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040633
APA StyleElabadlah, H., Hameed, R., D’Souza, C., Mohsin, S., & Adeghate, E. A. (2020). Exogenous Ghrelin Increases Plasma Insulin Level in Diabetic Rats. Biomolecules, 10(4), 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040633