Glucagon as a Therapeutic Approach to Severe Hypoglycemia: After 100 Years, Is It Still the Antidote of Insulin?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The “Numbers” of Hypoglycemia
3. Pathophysiology of Hypoglycemia and Its Consequences
4. How to Minimize Hypoglycemia in Diabetes Treatment
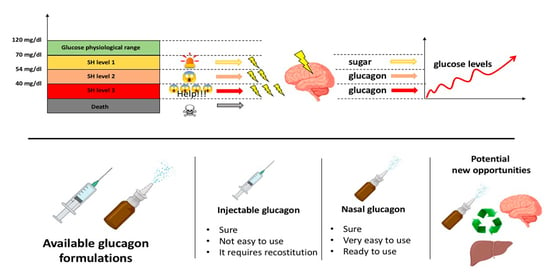
5. Treatment of Severe Hypoglycemia (SH)
6. Current Strategies (Treatment) for SH
7. New Strategies (Treatment) for SH
7.1. Nasal Glucagon
7.2. Liquid Glucagon
7.3. Other, Ongoing or Discontinued, New Glucagon Formulations
8. Why Do We Have to Use Novel Routes of Administration if We Can Use Injective Glucagon?
9. Glucagon: Insulin Antidote or Main Driver of Diabetes Homeostasis?
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sherwin, R.S. Bringing light to the dark side of insulin: A journey across the blood-brain barrier. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cryer, P.E. Banting Lecture. Hypoglycemia: The limiting factor in the management of IDDM. Diabetes 1994, 43, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes, A. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S15–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.R.; Bolli, G.B. Beyond the era of NPH insulin–long-acting insulin analogs: Chemistry, comparative pharmacology, and clinical application. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2008, 10, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, V.C. A Review of the Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Degludec and Glargine 300 U/mL in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, S12–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcellati, F.; Lucidi, P.; Candeloro, P.; Cioli, P.; Marinelli Andreoli, A.; Curti, G.; Bolli, G.B.; Fanelli, C.G. Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Modulation of Hepatic Glucose Production With Insulin Glargine U300 and Glargine U100 at Steady State With Individualized Clinical Doses in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucidi, P.; Candeloro, P.; Cioli, P.; Marinelli Andreoli, A.; Pascucci, C.; Gambelunghe, A.; Bolli, G.B.; Fanelli, C.G.; Porcellati, F. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Head-to-Head Comparison of Clinical, Equivalent Doses of Insulin Glargine 300 units. mL(−1) and Insulin Degludec 100 units. mL(−1) in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.R.; Bolli, G.B. The continuing quest for better subcutaneously administered prandial insulins: A review of recent developments and potential clinical implications. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cryer, P.E. The barrier of hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 3169–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Workgroup on Hypoglycemia; American Diabetes Association. Defining and reporting hypoglycemia in diabetes: A report from the American Diabetes Association Workgroup on Hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seaquist, E.R.; Anderson, J.; Childs, B.; Cryer, P.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; Fish, L.; Heller, S.R.; Rodriguez, H.; Rosenzweig, J.; Vigersky, R. Hypoglycemia and diabetes: A report of a workgroup of the American Diabetes Association and the Endocrine Society. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1384–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clayton, D.C.; Woo, V.; Yale, J.F. Canadian Diabetes Association Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert. Hypoglycemia. Can. J. Diabetes 2013, 37 (Suppl. 1), S69–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UK Hypoglycaemia Study Group. Risk of hypoglycaemia in types 1 and 2 diabetes: Effects of treatment modalities and their duration. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedersen-Bjergaard, U.; Pramming, S.; Heller, S.R.; Wallace, T.M.; Rasmussen, A.K.; Jorgensen, H.V.; Matthews, D.R.; Hougaard, P.; Thorsteinsson, B. Severe hypoglycaemia in 1076 adult patients with type 1 diabetes: Influence of risk markers and selection. Diabetes Metab Res. Rev. 2004, 20, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, L.; Fidler, C.; Ditchfield, A.; Stissing, T. Hypoglycemia Event Rates: A Comparison Between Real-World Data and Randomized Controlled Trial Populations in Insulin-Treated Diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2016, 7, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- The DCCT Research Group. Epidemiology of severe hypoglycemia in the diabetes control and complications trial. Am. J. Med. 1991, 90, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorda, C.B.; Ozzello, A.; Gentile, S.; Aglialoro, A.; Chiambretti, A.; Baccetti, F.; Gentile, F.M.; Lucisano, G.; Nicolucci, A.; Rossi, M.C.; et al. Incidence and risk factors for severe and symptomatic hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Results of the HYPOS-1 study. Acta Diabetol. 2015, 52, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, N.C.; Beck, R.W.; Miller, K.M.; Clements, M.A.; Rickels, M.R.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Maahs, D.M.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Bergenstal, R.; Smith, E.; et al. State of Type 1 Diabetes Management and Outcomes from the T1D Exchange in 2016–2018. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2019, 21, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettus, J.H.; Zhou, F.L.; Shepherd, L.; Preblick, R.; Hunt, P.R.; Paranjape, S.; Miller, K.M.; Edelman, S.V. Incidences of Severe Hypoglycemia and Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Prevalence of Microvascular Complications Stratified by Age and Glycemic Control in U.S. Adult Patients With Type 1 Diabetes: A Real-World Study. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 2220–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lane, W.; Bailey, T.S.; Gerety, G.; Gumprecht, J.; Philis-Tsimikas, A.; Hansen, C.T.; Nielsen, T.S.S.; Warren, M.; Group Information; The SWITCH 1. Effect of Insulin Degludec vs Insulin Glargine U100 on Hypoglycemia in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes: The SWITCH 1 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segel, S.A.; Paramore, D.S.; Cryer, P.E. Hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in advanced type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2002, 51, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cryer, P.E.; Davis, S.N.; Shamoon, H. Hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hepburn, D.A.; MacLeod, K.M.; Pell, A.C.; Scougal, I.J.; Frier, B.M. Frequency and symptoms of hypoglycaemia experienced by patients with type 2 diabetes treated with insulin. Diabet. Med. 1993, 10, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahola, A.J.; Saraheimo, M.; Freese, R.; Makimattila, S.; Forsblom, C.; Groop, P.H.; FinnDiane Study, G. Fear of hypoglycaemia and self-management in type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerich, J.E.; Langlois, M.; Noacco, C.; Karam, J.H.; Forsham, P.H. Lack of glucagon response to hypoglycemia in diabetes: Evidence for an intrinsic pancreatic alpha cell defect. Science 1973, 182, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolli, G.B.; Tsalikian, E.; Haymond, M.W.; Cryer, P.E.; Gerich, J.E. Defective glucose counterregulation after subcutaneous insulin in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Paradoxical suppression of glucose utilization and lack of compensatory increase in glucose production, roles of insulin resistance, abnormal neuroendocrine responses, and islet paracrine interactions. J. Clin. Invest. 1984, 73, 1532–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolli, G.; de Feo, P.; Compagnucci, P.; Cartechini, M.G.; Angeletti, G.; Santeusanio, F.; Brunetti, P.; Gerich, J.E. Abnormal glucose counterregulation in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Interaction of anti-insulin antibodies and impaired glucagon and epinephrine secretion. Diabetes 1983, 32, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbelaez, A.M.; Xing, D.; Cryer, P.E.; Kollman, C.; Beck, R.W.; Sherr, J.; Ruedy, K.J.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Mauras, N.; Tsalikian, E.; et al. Blunted glucagon but not epinephrine responses to hypoglycemia occurs in youth with less than 1 yr duration of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatric Diabetes 2014, 15, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, P.; Porcellati, F.; Busciantella Ricci, N.; Candeloro, P.; Cioli, P.; Nair, K.S.; Santeusanio, F.; Bolli, G.B.; Fanelli, C.G. Effect of oral amino acids on counterregulatory responses and cognitive function during insulin-induced hypoglycemia in nondiabetic and type 1 diabetic people. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanelli, C.G.; Epifano, L.; Rambotti, A.M.; Pampanelli, S.; Di Vincenzo, A.; Modarelli, F.; Lepore, M.; Annibale, B.; Ciofetta, M.; Bottini, P.; et al. Meticulous prevention of hypoglycemia normalizes the glycemic thresholds and magnitude of most of neuroendocrine responses to, symptoms of, and cognitive function during hypoglycemia in intensively treated patients with short-term IDDM. Diabetes 1993, 42, 1683–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanelli, C.; Pampanelli, S.; Lalli, C.; Del Sindaco, P.; Ciofetta, M.; Lepore, M.; Porcellati, F.; Bottini, P.; Di Vincenzo, A.; Brunetti, P.; et al. Long-term intensive therapy of IDDM patients with clinically overt autonomic neuropathy: Effects on hypoglycemia awareness and counterregulation. Diabetes 1997, 46, 1172–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, N.H.; Skor, D.A.; Cryer, P.E.; Levandoski, L.A.; Bier, D.M.; Santiago, J.V. Identification of type I diabetic patients at increased risk for hypoglycemia during intensive therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 308, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.S.; Conner, C.; Aagren, M.; Smith, D.M.; Bouchard, J.; Brett, J. Evidence linking hypoglycemic events to an increased risk of acute cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desouza, C.V.; Bolli, G.B.; Fonseca, V. Hypoglycemia, diabetes, and cardiovascular events. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitmer, R.A.; Karter, A.J.; Yaffe, K.; Quesenberry, C.P., Jr.; Selby, J.V. Hypoglycemic episodes and risk of dementia in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 2009, 301, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnston, S.S.; Conner, C.; Aagren, M.; Ruiz, K.; Bouchard, J. Association between hypoglycaemic events and fall-related fractures in Medicare-covered patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, R.G.; Van Houten, H.K.; Ziegenfuss, J.Y.; Shah, N.D.; Wermers, R.A.; Smith, S.A. Increased mortality of patients with diabetes reporting severe hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1897–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, A.J.; Fox, K.M.; Grandy, S.; Group, S.S. Self-reported hypoglycemia and impact on quality of life and depression among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 96, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laiteerapong, N.; Karter, A.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Moffet, H.H.; Sudore, R.; Schillinger, D.; John, P.M.; Huang, E.S. Correlates of quality of life in older adults with diabetes: The diabetes & aging study. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1749–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leiter, L.A.; Yale, J.F.; Chiasson, J.L.; Harris, S.; Kleinstiver, P.; Sauriol, L. Assessment of the impact of fear of hypoglycemic episodes on glycemic and hypogly-cemia management. Can. J. Diabetes 2005, 29, 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- Fisman, E.Z.; Motro, M.; Tenenbaum, A.; Leor, J.; Boyko, V.; Mandelzweig, L.; Sherer, Y.; Adler, Y.; Behar, S. Is hypoglycaemia a marker for increased long-term mortality risk in patients with coronary artery disease? An 8-year follow-up. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2004, 11, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, T.; Lyyra-Laitinen, T.; Huopio, H.; Vauhkonen, I.; Halonen, T.; Hartikainen, J.; Niskanen, L.; Laakso, M. Electrocardiographic alterations during hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in healthy subjects. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2008, 13, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, G.V.; Woodward, A.; Casson, I.F.; Weston, P.J. Cardiac arrhythmia and nocturnal hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes--the ‘dead in bed’ syndrome revisited. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, R.T.; Harris, N.D.; Ireland, R.H.; Lee, S.; Newman, C.; Heller, S.R. Mechanisms of abnormal cardiac repolarization during insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galloway, P.J.; Thomson, G.A.; Fisher, B.M.; Semple, C.G. Insulin-induced hypoglycemia induces a rise in C-reactive protein. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 861–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razavi Nematollahi, L.; Kitabchi, A.E.; Stentz, F.B.; Wan, J.Y.; Larijani, B.A.; Tehrani, M.M.; Gozashti, M.H.; Omidfar, K.; Taheri, E. Proinflammatory cytokines in response to insulin-induced hypoglycemic stress in healthy subjects. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2009, 58, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommerfield, A.J.; Wilkinson, I.B.; Webb, D.J.; Frier, B.M. Vessel wall stiffness in type 1 diabetes and the central hemodynamic effects of acute hypoglycemia. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E1274–E1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, B.M.; Hepburn, D.A.; Smith, J.G.; Frier, B.M. Responses of peripheral blood cells to acute insulin-induced hypoglycaemia in humans: Effect of alpha-adrenergic blockade. Horm. Metab. Res. Suppl. Ser. 1992, 26, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, W.; Abraira, C.; Moritz, T.; Reda, D.; Emanuele, N.; Reaven, P.D.; Zieve, F.J.; Marks, J.; Davis, S.N.; Hayward, R.; et al. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Group, A.C.; Patel, A.; MacMahon, S.; Chalmers, J.; Neal, B.; Billot, L.; Woodward, M.; Marre, M.; Cooper, M.; Glasziou, P.; et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2560–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group; Gerstein, H.C.; Miller, M.E.; Byington, R.P.; Goff, D.C., Jr.; Bigger, J.T.; Buse, J.B.; Cushman, W.C.; Genuth, S.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; et al. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2545–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skyler, J.S.; Bergenstal, R.; Bonow, R.O.; Buse, J.; Deedwania, P.; Gale, E.A.; Howard, B.V.; Kirkman, M.S.; Kosiborod, M.; Reaven, P.; et al. Intensive glycemic control and the prevention of cardiovascular events: Implications of the ACCORD, ADVANCE, and VA Diabetes Trials: A position statement of the American Diabetes Association and a Scientific Statement of the American College of Cardiology Foundation and the American Heart Association. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zoungas, S.; Patel, A.; Chalmers, J.; de Galan, B.E.; Li, Q.; Billot, L.; Woodward, M.; Ninomiya, T.; Neal, B.; MacMahon, S.; et al. Severe hypoglycemia and risks of vascular events and death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonds, D.E.; Miller, M.E.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Buse, J.B.; Byington, R.P.; Cutler, J.A.; Dudl, R.J.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Kimel, A.R.; Hoogwerf, B.; et al. The association between symptomatic, severe hypoglycaemia and mortality in type 2 diabetes: Retrospective epidemiological analysis of the ACCORD study. BMJ 2010, 340, b4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerich, J.E.; Mokan, M.; Veneman, T.; Korytkowski, M.; Mitrakou, A. Hypoglycemia unawareness. Endocr. Rev. 1991, 12, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, J.; Schopman, J.E.; Zammitt, N.N.; Frier, B.M. Prevalence of impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in adults with Type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2008, 25, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.E.; Asvold, B.O.; Frier, B.M.; Aune, S.E.; Hansen, L.I.; Bjorgaas, M.R. Hypoglycaemia symptoms and impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in adults with Type 1 diabetes: The association with diabetes duration. Diabet. Med. 2014, 31, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, J.N.; Allen, K.V.; Deary, I.J.; Frier, B.M. Hypoglycaemia in insulin-treated Type 2 diabetes: Frequency, symptoms and impaired awareness. Diabet. Med. 2003, 20, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaquist, E.R.; Miller, M.E.; Bonds, D.E.; Feinglos, M.; Goff, D.C., Jr.; Peterson, K.; Senior, P.; Investigators, A. The impact of frequent and unrecognized hypoglycemia on mortality in the ACCORD study. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, R.D. Insulin hypoglycæmia changes in nervous manifestations. Lancet 1941, 238, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryer, P. Hypoglycemia in Diabetes: Pathophysiology, Prevalence, and Prevention, 3rd ed.; American Diabetes Association: Alexandria, Egypt, 2016; pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dagogo-Jack, S. Philip, E. Cryer, MD: Seminal Contributions to the Understanding of Hypoglycemia and Glucose Counterregulation and the Discovery of HAAF (Cryer Syndrome). Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 2193–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dagogo-Jack, S.E.; Craft, S.; Cryer, P.E. Hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Recent antecedent hypoglycemia reduces autonomic responses to, symptoms of, and defense against subsequent hypoglycemia. J. Clin. Invest. 1993, 91, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.K.; Hung, M.; Sharma, A.; Chan, O.; Varner, M.W.; Staskus, G.; Fisher, S.J. Impaired Awareness of Hypoglycemia Continues to Be a Risk Factor for Severe Hypoglycemia Despite the Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring System in Type 1 Diabetes. Endocrine Practice 2019, 25, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ang, L.C.; Tan, W.B.; Xin, X.; Bee, Y.M.; Goh, S.Y.; Teh, M.M. A study to evaluate the prevalence of impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in adults with type 2 diabetes in outpatient clinic in a tertiary care centre in Singapore. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 8, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lipska, K.J.; Warton, E.M.; Huang, E.S.; Moffet, H.H.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Krumholz, H.M.; Karter, A.J. HbA1c and risk of severe hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes: The Diabetes and Aging Study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3535–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, I.; Zelnick, L.R.; Batacchi, Z.; Robinson, N.; Dighe, A.; Manski-Nankervis, J.E.; Furler, J.; O’Neal, D.N.; Little, R.; Trence, D.; et al. Hypoglycemia in People with Type 2 Diabetes and CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2019, 14, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Zoysa, N.; Rogers, H.; Stadler, M.; Gianfrancesco, C.; Beveridge, S.; Britneff, E.; Choudhary, P.; Elliott, J.; Heller, S.; Amiel, S.A. A psychoeducational program to restore hypoglycemia awareness: The DAFNE-HART pilot study. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Little, S.A.; Leelarathna, L.; Walkinshaw, E.; Tan, H.K.; Chapple, O.; Lubina-Solomon, A.; Chadwick, T.J.; Barendse, S.; Stocken, D.D.; Brennand, C.; et al. Recovery of hypoglycemia awareness in long-standing type 1 diabetes: A multicenter 2 × 2 factorial randomized controlled trial comparing insulin pump with multiple daily injections and continuous with conventional glucose self-monitoring (HypoCOMPaSS). Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cox, D.; Gonder-Frederick, L.; Polonsky, W.; Schlundt, D.; Julian, D.; Clarke, W. A multicenter evaluation of blood glucose awareness training-II. Diabetes Care 1995, 18, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, D.; Lawrence, I.; Mansell, P.; Thompson, G.; Amiel, S.; Campbell, M.; Heller, S. Improved biomedical and psychological outcomes 1 year after structured education in flexible insulin therapy for people with type 1 diabetes: The U.K. DAFNE experience. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1638–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolinder, J.; Antuna, R.; Geelhoed-Duijvestijn, P.; Kroger, J.; Weitgasser, R. Novel glucose-sensing technology and hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes: A multicentre, non-masked, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, P.; Ramasamy, S.; Green, L.; Gallen, G.; Pender, S.; Brackenridge, A.; Amiel, S.A.; Pickup, J.C. Real-time continuous glucose monitoring significantly reduces severe hypoglycemia in hypoglycemia-unaware patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 4160–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haak, T.; Hanaire, H.; Ajjan, R.; Hermanns, N.; Riveline, J.P.; Rayman, G. Flash Glucose-Sensing Technology as a Replacement for Blood Glucose Monitoring for the Management of Insulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes: A Multicenter, Open-Label Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liebl, A.; Davidson, J.; Mersebach, H.; Dykiel, P.; Tack, C.J.; Heise, T. A novel insulin combination of insulin degludec and insulin aspart achieves a more stable overnight glucose profile than insulin glargine: Results from continuous glucose monitoring in a proof-of-concept trial. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Beers, C.A.; De Vries, J.H.; Kleijer, S.J.; Smits, M.M.; Geelhoed-Duijvestijn, P.H.; Kramer, M.H.; Diamant, M.; Snoek, F.J.; Serne, E.H. Continuous glucose monitoring for patients with type 1 diabetes and impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia (IN CONTROL): A randomised, open-label, crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickels, M.R.; Peleckis, A.J.; Dalton-Bakes, C.; Naji, J.R.; Ran, N.A.; Nguyen, H.L.; O’Brien, S.; Chen, S.; Lee, I.; Schutta, M.H. Continuous Glucose Monitoring for Hypoglycemia Avoidance and Glucose Counterregulation in Long-Standing Type 1 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinemann, L.; Freckmann, G.; Ehrmann, D.; Faber-Heinemann, G.; Guerra, S.; Waldenmaier, D.; Hermanns, N. Real-time continuous glucose monitoring in adults with type 1 diabetes and impaired hypoglycaemia awareness or severe hypoglycaemia treated with multiple daily insulin injections (HypoDE): A multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.; Jugnee, N.; El Laboudi, A.; Spanudakis, E.; Anantharaja, S.; Oliver, N. A randomized controlled pilot study of continuous glucose monitoring and flash glucose monitoring in people with Type 1 diabetes and impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia. Diabet Med. 2018, 35, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.; Jugnee, N.; Anantharaja, S.; Oliver, N. Switching from Flash Glucose Monitoring to Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Hypoglycemia in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes at High Hypoglycemia Risk: The Extension Phase of the I HART CGM Study. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2018, 20, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preau, Y.; Armand, M.; Galie, S.; Schaepelynck, P.; Raccah, D. Impact of Switching from Intermittently Scanned to Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems in a Type 1 Diabetes Patient French Cohort: An Observational Study of Clinical Practices. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2021, 23, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.M.; Charleer, S.; Fieuws, S.; De Block, C.; Hilbrands, R.; Van Huffel, L.; Maes, T.; Vanhaverbeke, G.; Dirinck, E.; Myngheer, N.; et al. Comparing real-time and intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring in adults with type 1 diabetes (ALERTT1): A 6-month, prospective, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 2275–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, M.; Lara, M.; Conget, I. Sustained efficacy of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in type 1 diabetes subjects with recurrent non-severe and severe hypoglycemia and hypoglycemia unawareness: A pilot study. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2010, 12, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, P.; Shin, J.; Wang, Y.; Evans, M.L.; Hammond, P.J.; Kerr, D.; Shaw, J.A.; Pickup, J.C.; Amiel, S.A. Insulin pump therapy with automated insulin suspension in response to hypoglycemia: Reduction in nocturnal hypoglycemia in those at greatest risk. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2023–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, J.L.; Sherr, J.L.; Cengiz, E.; Carria, L.; Roy, A.; Voskanyan, G.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Weinzimer, S.A. Effect of insulin feedback on closed-loop glucose control: A crossover study. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2012, 6, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steil, G.M. Algorithms for a closed-loop artificial pancreas: The case for proportional-integral-derivative control. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinzimer, S.A.; Steil, G.M.; Swan, K.L.; Dziura, J.; Kurtz, N.; Tamborlane, W.V. Fully automated closed-loop insulin delivery versus semiautomated hybrid control in pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes using an artificial pancreas. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, S.A.; Kovatchev, B.P.; Raghinaru, D.; Lum, J.W.; Buckingham, B.A.; Kudva, Y.C.; Laffel, L.M.; Levy, C.J.; Pinsker, J.E.; Wadwa, R.P.; et al. Six-Month Randomized, Multicenter Trial of Closed-Loop Control in Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1707–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauschmann, M.; Allen, J.M.; Wilinska, M.E.; Thabit, H.; Stewart, Z.; Cheng, P.; Kollman, C.; Acerini, C.L.; Dunger, D.B.; Hovorka, R. Day-and-Night Hybrid Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery in Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes: A Free-Living, Randomized Clinical Trial. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burckhardt, M.A.; Abraham, M.B.; Dart, J.; Smith, G.J.; Paramalingam, N.; O’Dea, J.; de Bock, M.; Davis, E.A.; Jones, T.W. Impact of Hybrid Closed Loop Therapy on Hypoglycemia Awareness in Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes and Impaired Hypoglycemia Awareness. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2021, 23, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, S.A.; Speight, J.; Leelarathna, L.; Walkinshaw, E.; Tan, H.K.; Bowes, A.; Lubina-Solomon, A.; Chadwick, T.J.; Stocken, D.D.; Brennand, C.; et al. Sustained Reduction in Severe Hypoglycemia in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes Complicated by Impaired Awareness of Hypoglycemia: Two-Year Follow-up in the HypoCOMPaSS Randomized Clinical Trial. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frier, B.M. Hypoglycaemia in diabetes mellitus: Epidemiology and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, B.B. Glucagon and regulation of glucose metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 284, E671–E678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piro, S.; Maniscalchi, E.T.; Monello, A.; Pandini, G.; Mascali, L.G.; Rabuazzo, A.M.; Purrello, F. Palmitate affects insulin receptor phosphorylation and intracellular insulin signal in a pancreatic alpha-cell line. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4197–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gromada, J.; Franklin, I.; Wollheim, C.B. Alpha-cells of the endocrine pancreas: 35 years of research but the enigma remains. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 84–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes, A. 6. Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, S61–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibb, F.W.; McKnight, J.A.; Clarke, C.; Strachan, M.W.J. Preserved C-peptide secretion is associated with fewer low-glucose events and lower glucose variability on flash glucose monitoring in adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, T.A.; Sievenpiper, J.L. Controversies about sugars: Results from systematic reviews and meta-analyses on obesity, cardiometabolic disease and diabetes. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slama, G.; Traynard, P.Y.; Desplanque, N.; Pudar, H.; Dhunputh, I.; Letanoux, M.; Bornet, F.R.; Tchobroutsky, G. The search for an optimized treatment of hypoglycemia. Carbohydrates in tablets, solutin, or gel for the correction of insulin reactions. Arch. Intern. Med. 1990, 150, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.B.; Jones, T.W.; Naranjo, D.; Karges, B.; Oduwole, A.; Tauschmann, M.; Maahs, D.M. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: Assessment and management of hypoglycemia in children and adolescents with diabetes. Pediatric. Diabetes 2018, 19 (Suppl. 27), 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedia, N. Treatment of severe diabetic hypoglycemia with glucagon: An underutilized therapeutic approach. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2011, 4, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thieu, V.T.; Mitchell, B.D.; Varnado, O.J.; Frier, B.M. Treatment and prevention of severe hypoglycaemia in people with diabetes: Current and new formulations of glucagon. Diabetes Obes Metab 2020, 22, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yale, J.F.; Dulude, H.; Egeth, M.; Piche, C.A.; Lafontaine, M.; Carballo, D.; Margolies, R.; Dissinger, E.; Shames, A.R.; Kaplowitz, N.; et al. Faster Use and Fewer Failures with Needle-Free Nasal Glucagon Versus Injectable Glucagon in Severe Hypoglycemia Rescue: A Simulation Study. Diabetes Technol. Ther 2017, 19, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherr, J.L.; Ruedy, K.J.; Foster, N.C.; Piche, C.A.; Dulude, H.; Rickels, M.R.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Bethin, K.E.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Fox, L.A.; et al. Glucagon Nasal Powder: A Promising Alternative to Intramuscular Glucagon in Youth With Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pontiroli, A.E.; Alberetto, M.; Secchi, A.; Dossi, G.; Bosi, I.; Pozza, G. Insulin given intranasally induces hypoglycaemia in normal and diabetic subjects. Br. Med. J. 1982, 284, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pontiroli, A.E.; Alberetto, M.; Pozza, G. Metabolic effects of intranasally administered glucagon: Comparison with intramuscular and intravenous injection. Acta Diabetol. Lat. 1985, 22, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freychet, L.; Rizkalla, S.W.; Desplanque, N.; Basdevant, A.; Zirinis, P.; Tchobroutsky, G.; Slama, G. Effect of intranasal glucagon on blood glucose levels in healthy subjects and hypoglycaemic patients with insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet 1988, 1, 1364–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, C.B.; Dulude, H.; Piche, C.; Rufiange, M.; Sadoune, A.A.; Rampakakis, E.; Carballo, D.; Triest, M.; Zhang, M.X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Effects of common cold and concomitant administration of nasal decongestant on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of nasal glucagon in otherwise healthy participants: A randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reno, F.E.; Normand, P.; McInally, K.; Silo, S.; Stotland, P.; Triest, M.; Carballo, D.; Piche, C. A novel nasal powder formulation of glucagon: Toxicology studies in animal models. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rickels, M.R.; Ruedy, K.J.; Foster, N.C.; Piche, C.A.; Dulude, H.; Sherr, J.L.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Bethin, K.E.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Wadwa, R.P.; et al. Intranasal Glucagon for Treatment of Insulin-Induced Hypoglycemia in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Crossover Noninferiority Study. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seaquist, E.R.; Dulude, H.; Zhang, X.M.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R.; Tsoukas, G.M.; Conway, J.R.; Weisnagel, S.J.; Gerety, G.; Woo, V.C.; Zhang, S.; et al. Prospective study evaluating the use of nasal glucagon for the treatment of moderate to severe hypoglycaemia in adults with type 1 diabetes in a real-world setting. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1316–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuhisa, M.; Takita, Y.; Nasu, R.; Nagai, Y.; Ohwaki, K.; Nagashima, H. Nasal glucagon as a viable alternative for treating insulin-induced hypoglycaemia in Japanese patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes: A phase 3 randomized crossover study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontiroli, A.E.; Tagliabue, E. Intranasal versus injectable glucagon for hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Diabetol. 2020, 57, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohlmann, J.; Mitchell, B.D.; Bajpai, S.; Osumili, B.; Valentine, W.J. Nasal Glucagon Versus Injectable Glucagon for Severe Hypoglycemia: A Cost-Offset and Budget Impact Analysis. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2019, 13, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, V.; Newswanger, B.; Prestrelski, S.; Andre, A.D.; Garibaldi, M. Human Factors Usability and Validation Studies of a Glucagon Autoinjector in a Simulated Severe Hypoglycemia Rescue Situation. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2019, 21, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, L.M.; Castle, J.R. Stable Liquid Glucagon: Beyond Emergency Hypoglycemia Rescue. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2018, 12, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hawkes, C.P.; De Leon, D.D.; Rickels, M.R. Novel Preparations of Glucagon for the Prevention and Treatment of Hypoglycemia. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeb, L.C.; Dulude, H.; Guzman, C.B.; Zhang, S.; Reiner, B.J.; Piche, C.A.; Pradhan, S.; Zhang, X.M. A phase 3 multicenter, open-label, prospective study designed to evaluate the effectiveness and ease of use of nasal glucagon in the treatment of moderate and severe hypoglycemia in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes in the home or school setting. Pediatric. Diabetes 2018, 19, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suico, J.G.; Hovelmann, U.; Zhang, S.; Shen, T.; Bergman, B.; Sherr, J.; Zijlstra, E.; Frier, B.M.; Plum-Morschel, L. Glucagon Administration by Nasal and Intramuscular Routes in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes During Insulin-Induced Hypoglycaemia: A Randomised, Open-Label, Crossover Study. Diabetes Ther. 2020, 11, 1591–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Dean, E.D.; Quittner-Strom, E.; Zhu, Y.; Chowdhury, K.H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Li, N.; Ye, R.; Lee, Y.; et al. Glucagon blockade restores functional beta-cell mass in type 1 diabetic mice and enhances function of human islets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022142118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J.; Holland, W.; Gromada, J.; Lee, Y.; Unger, R.H.; Yan, H.; Sloop, K.W.; Kieffer, T.J.; Damond, N.; Herrera, P.L. Insulin and Glucagon: Partners for Life. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filippello, A.; Urbano, F.; Di Mauro, S.; Scamporrino, A.; Di Pino, A.; Scicali, R.; Rabuazzo, A.M.; Purrello, F.; Piro, S. Chronic Exposure to Palmitate Impairs Insulin Signaling in an Intestinal L-cell Line: A Possible Shift from GLP-1 to Glucagon Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filippello, A.; Di Mauro, S.; Scamporrino, A.; Malaguarnera, R.; Torrisi, S.A.; Leggio, G.M.; Di Pino, A.; Scicali, R.; Purrello, F.; Piro, S. High Glucose Exposure Impairs L-Cell Differentiation in Intestinal Organoids: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippello, A.; Scamporrino, A.; Di Mauro, S.; Malaguarnera, R.; Di Pino, A.; Scicali, R.; Purrello, F.; Piro, S. Direct Effects of D-Chiro-Inositol on Insulin Signaling and Glucagon Secretion of Pancreatic Alpha Cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, S.; Xiao, C.; Stahel, P.; Koulajian, K.; Giacca, A.; Lewis, G.F. Evaluation of the specific effects of intranasal glucagon on glucose production and lipid concentration in healthy men during a pancreatic clamp. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Risk Factors | Precipitating Factors |
|---|---|
| A history of severe hypoglycemia | Insulin overdose in relation to CHO intake |
| Hypoglycemia unawareness | Delayed or missed meal |
| Stringent glycemic control | Prolonged exercise without control of glucose levels w/o insulin or food adjustments |
| Disease duration | Prolonged fasting Prolonged fasting in the presence of long-acting insulin analogs therapies |
| Increasing duration of insulin therapy (T2DM) | Alcohol ingestion |
| Extremes of age (very young and very old) | Factors influencing s.c. insulin absorption |
| Diabetic neuropathy | Intercurrent acute illnesses |
| Renal or hepatic impairment | |
| Neoplasms | |
| Number of drugs other than antidiabetic agents | |
| Social isolation | |
| Lack of proper patients education |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porcellati, F.; Di Mauro, S.; Mazzieri, A.; Scamporrino, A.; Filippello, A.; De Fano, M.; Fanelli, C.G.; Purrello, F.; Malaguarnera, R.; Piro, S. Glucagon as a Therapeutic Approach to Severe Hypoglycemia: After 100 Years, Is It Still the Antidote of Insulin? Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11091281
Porcellati F, Di Mauro S, Mazzieri A, Scamporrino A, Filippello A, De Fano M, Fanelli CG, Purrello F, Malaguarnera R, Piro S. Glucagon as a Therapeutic Approach to Severe Hypoglycemia: After 100 Years, Is It Still the Antidote of Insulin? Biomolecules. 2021; 11(9):1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11091281
Chicago/Turabian StylePorcellati, Francesca, Stefania Di Mauro, Alessio Mazzieri, Alessandra Scamporrino, Agnese Filippello, Michelantonio De Fano, Carmine Giuseppe Fanelli, Francesco Purrello, Roberta Malaguarnera, and Salvatore Piro. 2021. "Glucagon as a Therapeutic Approach to Severe Hypoglycemia: After 100 Years, Is It Still the Antidote of Insulin?" Biomolecules 11, no. 9: 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11091281
APA StylePorcellati, F., Di Mauro, S., Mazzieri, A., Scamporrino, A., Filippello, A., De Fano, M., Fanelli, C. G., Purrello, F., Malaguarnera, R., & Piro, S. (2021). Glucagon as a Therapeutic Approach to Severe Hypoglycemia: After 100 Years, Is It Still the Antidote of Insulin? Biomolecules, 11(9), 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11091281