Site-Specific Proteasome Inhibitors
Abstract
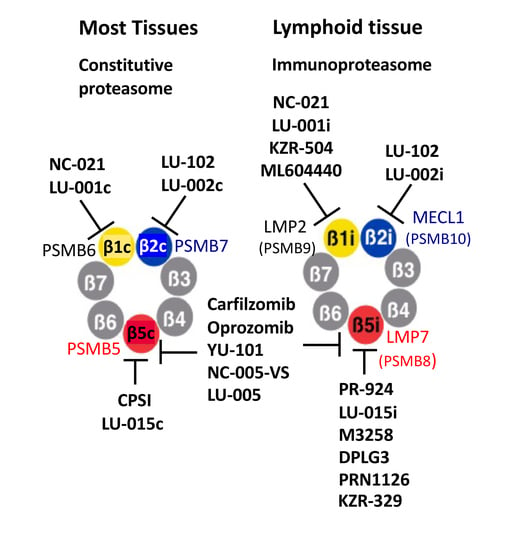
:1. Introduction

2. Chemical Structures of Proteasome Inhibitors
3. Site-Specific Inhibitors of the Chymotrypsin-like Sites
4. Site-Specific Inhibitors of the Caspase-like Sites
5. Specific Inhibitors of the Trypsin-like Sites
6. Converting Subunit-Specific Inhibitors into Activity-Based Probes
7. Using Site-Specific Inhibitors to Study the Role of Active Sites as Drug Targets in Cancer
8. Effect of Site-Specific Inhibitors on Protein Breakdown
9. Use of Site-Specific Immunoproteasome Inhibitors to Probe the Involvement of These Active Sites in Autoimmunity, Inflammation, and Antigen Presentation
10. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldberg, A.L. Protein degradation and protection against misfolded or damaged proteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 426, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershko, A.; Ciechanover, A. The ubiquitin system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 425–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coux, O.; Tanaka, K.; Goldberg, A.L. Structure and functions of the 20S and 26S proteasomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996, 65, 801–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Fonseca, P.; He, J.; Morris, E. Molecular Model of the Human 26S Proteasome. Mol. Cell 2012, 46, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakata, E.; Eisele, M.R.; Baumeister, W. Molecular and cellular dynamics of the 26S proteasome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Proteins Proteom. 2021, 1869, 140583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lander, G.C.; Estrin, E.; Matyskiela, M.E.; Bashore, C.; Nogales, E.; Martin, A. Complete subunit architecture of the proteasome regulatory particle. Nature 2012, 482, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Groll, M.; Ditzel, L.; Löwe, J.; Stock, D.; Bochtler, M.; Bartunik, H.D.; Huber, R. Structure of 20S proteasome from yeast at 2.4Å resolution. Nat. Cell Biol. 1997, 386, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, C.S.; Hochstrasser, M. Eukaryotic 20S proteasome catalytic subunit propeptides prevent active site inactivation by N-terminal acetylation and promote particle assembly. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 3575–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arendt, C.S.; Hochstrasser, M. Identification of the yeast 20S proteasome catalytic centers and subunit interactions required for active-site formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 7156–7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinemeyer, W.; Fischer, M.; Krimmer, T.; Stachon, U.; Wolf, D.H. The Active Sites of the Eukaryotic 20 S Proteasome and Their Involvement in Subunit Precursor Processing. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 25200–25209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kisselev, A.F.; van der Linden, W.A.; Overkleeft, H.S. Proteasome Inhibitors: An Expanding Army Attacking a Unique Target. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rock, K.L.; Gramm, C.; Rothstein, L.; Clark, K.; Stein, R.; Dick, L.; Hwang, D.; Goldberg, A.L. Inhibitors of the proteasome block the degradation of most cell proteins and the generation of peptides presented on MHC class I molecules. Cell 1994, 78, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombella, V.J.; Rando, O.J.; Goldberg, A.L.; Maniatis, T. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is required for processing the NF-kappa-B1 precursor protein and the activation of NF-kappa-B. Cell 1994, 78, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisselev, A.F.; Goldberg, A.L. Proteasome inhibitors: From research tools to drug candidates. Chem. Biol. 2001, 8, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borissenko, L.; Groll, M. 20S Proteasome and Its Inhibitors: Crystallographic Knowledge for Drug Development. Chem. Rev. 2007, 38, 687–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibaudeau, T.A.; Smith, D.M. A Practical Review of Proteasome Pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2019, 71, 170–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, J. The development of proteasome inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, A.L. Development of proteasome inhibitors as research tools and cancer drugs. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 199, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawasut, P.; Chauhan, D.; Laubach, J.; Hayes, C.; Fabre, C.; Maglio, M.; Mitsiades, C.; Hideshima, T.; Anderson, K.C.; Richardson, P.G. New Proteasome Inhibitors in Myeloma. Curr. Hematol. Malign. Rep. 2012, 7, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricker, L.D. Proteasome Inhibitor Drugs. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 60, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potts, B.C.; Albitar, M.C.; Anderson, K.C.; Baritaki, S.; Berkers, C.; Bonavida, B.; Chandra, J.; Chauchan, D.; Cusacck, J.C.; Fenical, W.; et al. Marizomib, a proteasome inhibitor for all seasons: Preclinical profile and a framewrok for clinical trials. Curr. Can. Drug Targets 2011, 11, 254–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchi, G.; Oliva, L.; Cascio, P.; Pengo, N.; Fontana, F.; Cerruti, F.; Orsi, A.; Pasqualetto, E.; Mezghrani, A.; Calbi, V.; et al. The proteasome load versus capacity balance determines apoptotic sensitivity of multiple myeloma cells to proteasome inhibition. Blood 2009, 113, 3040–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenci, S.; van Anken, E.; Sitia, R. Proteostenosis and plasma cell pathophysiology. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 23, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenci, S.; Oliva, L.; Cerruti, F.; Milan, E.; Bianchi, G.; Raule, M.; Mezghrani, A.; Pasqualetto, E.; Sitia, R.; Cascio, P. Pivotal Advance: Protein synthesis modulates responsiveness of differentiating and malignant plasma cells to proteasome inhibitors. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisselev, A.F.; Callard, A.; Goldberg, A.L. Importance of different active sites in protein breakdown by 26S proteasomes and the efficacy of proteasome inhibitors varies with the protein substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8583–8590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berkers, C.R.; Verdoes, M.; Lichtman, E.; Fiebiger, E.; Kessler, B.; Anderson, K.C.; Ploegh, H.L.; Ovaa, H.; Galardy, P.J. Activity probe for in vivo profiling of the specificity of proteasome inhibitor bortezomib. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altun, M.; Galardy, P.J.; Shringarpure, R.; Hideshima, T.; Leblanc, R.; Anderson, K.C.; Ploegh, H.L.; Kessler, B. Effects of PS-341 on the Activity and Composition of Proteasomes in Multiple Myeloma Cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7896–7901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Britton, M.; Lucas, M.M.; Downey, S.; Screen, M.; Pletnev, A.A.; Verdoes, M.; Tokhunts, R.A.; Amir, O.; Goddard, A.L.; Pelphrey, P.M.; et al. Selective Inhibitor of Proteasome’s Caspase-like Sites Sensitizes Cells to Specific Inhibition of Chymotrypsin-like Sites. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 1278–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, G. Microbial proteasomes as drug targets. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1010058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillaume, B.; Chapiro, J.; Stroobant, V.; Colau, D.; van Holle, B.; Parvizi, G.; Bousquet-Dubouch, M.-P.; Théate, I.; Parmentier, N.; van den Eynde, B.J. Two abundant proteasome subtypes that uniquely process some antigens presented by HLA class I molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18599–18604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murata, S.; Sasaki, K.; Kishimoto, T.; Niwa, S.-I.; Hayashi, H.; Takahama, Y.; Tanaka, K. Regulation of CD8+ T Cell Development by Thymus-Specific Proteasomes. Science 2007, 316, 1349–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kincaid, E.Z.; Che, J.W.; York, I.; Escobar, H.; Reyes-Vargas, E.; Delgado, J.C.; Welsh, R.M.; Karow, M.L.; Murphy, A.; Valenzuela, D.M.; et al. Mice completely lacking immunoproteasomes show major changes in antigen presentation. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 13, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rock, K.L.; Goldberg, A.L. Degradation of Cell Proteins and the Generation of MHC Class I-Presented Peptides. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 739–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muchamuel, T.; Basler, M.; Aujay, M.A.; Suzuki, E.; Kalim, K.W.; Lauer, C.; Sylvain, C.; Ring, E.R.; Shields, J.; Jiang, J. A selective inhibitor of the immunoproteasome subunit LMP7 blocks cytokine production and attenuates progression of experimental arthritis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basler, M.; Mundt, S.; Bitzer, A.; Schmidt, C.; Groettrup, M. The immunoproteasome: A novel drug target for autoimmune diseases. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Fehling, H.J.; Swat, W.; Laplace, C.; Kühn, R.; Rajewsky, K.; Müller, U.; von Boehmer, H. MHC Class I Expression in Mice Lacking the Proteasome Subunit LMP-7. Science 1994, 265, 1234–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kaert, L.; Ashton-Rickardt, P.G.; Eichelberger, M.; Gaczynska, M.; Nagashima, K.; Rock, K.L.; Goldberg, A.L.; Doherty, P.C.; Tonegawa, S. Altered peptidase and viral-specific T cell response in LMP2 mutant mice. Immunity 1994, 1, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basler, M.; Moebius, J.; Elenich, L.; Groettrup, M.; Monaco, J.J. An Altered T Cell Repertoire in MECL-1-Deficient Mice. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 6665–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, C.; Berger, T.; Groettrup, M.; Basler, M. Immunoproteasome Inhibition Impairs T and B Cell Activation by Restraining ERK Signaling and Proteostasis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cenci, S.; Mezghrani, A.; Cascio, P.; Bianchi, G.; Cerruti, F.; Fra, A.; Lelouard, H.; Masciarelli, S.; Mattioli, L.; Oliva, L.; et al. Progressively impaired proteasomal capacity during terminal plasma cell differentiation. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cascio, P.; Oliva, L.; Cerruti, F.; Mariani, E.; Pasqualetto, E.; Cenci, S.; Sitia, R. Dampening Ab responses using proteasome inhibitors following in vivo B cell activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basler, M.; Groettrup, M. Recent insights how combined inhibition of immuno/proteasome subunits enables therapeutic efficacy. Genes Immun. 2020, 21, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, H.W.B.; Lowe, E.; Anderl, J.L.; Fan, A.; Muchamuel, T.; Bowers, S.; Moebius, D.C.; Kirk, C.; McMinn, D.L. Required Immunoproteasome Subunit Inhibition Profile for Anti-Inflammatory Efficacy and Clinical Candidate KZR-616 ((2S,3R)-N-((S)-3-(Cyclopent-1-en-1-yl)-1-((R)-2-methyloxiran-2-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-3-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-((S)-2-(2-morpholinoacetamido)propanamido)propenamide). J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 11127–11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löwe, J.; Stock, D.; Jap, B.; Zwickl, P.; Baumeister, W.; Huber, R. Crystal Structure of the 20 S Proteasome from the Archaeon T. acidophilum at 3.4 Å Resolution. Science 1995, 268, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groll, M.; Kim, K.B.; Kairies, N.; Huber, R.; Crews, C.M. Crystal structure of epoxomicin: 20S proteasome reveals a molecular basis for selectivity of alpha ‘, beta ‘-epoxyketone proteasome inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 1237–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, J.; Henneberg, F.; Mata, R.A.; Tittmann, K.; Schneider, T.R.; Stark, H.; Bourenkov, G.; Chari, A. The inhibition mechanism of human 20 S proteasomes enables next-generation inhibitor design. Science 2016, 353, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geurink, P.P.; van der Linden, W.A.; Mirabella, A.C.; Gallastegui, N.; de Bruin, G.; Blom, A.E.M.; Voges, M.J.; Mock, E.D.; Florea, B.I.; van der Marel, G.A.; et al. Incorporation of Non-natural Amino Acids Improves Cell Permeability and Potency of Specific Inhibitors of Proteasome Trypsin-like Sites. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1262–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Screen, M.; Britton, M.; Downey, S.L.; Verdoes, M.; Voges, M.J.; Blom, A.E.; Geurink, P.P.; Risseeuw, M.D.; Florea, B.I.; van der Linden, W.A.; et al. Nature of Pharmacophore Influences Active Site Specificity of Proteasome Inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 40125–40134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, J.; Behnke, M.; Chen, S.; Cruickshank, A.A.; Dick, L.R.; Grenier, L.; Klunder, J.M.; Ma, Y.-T.; Plamondon, L.; Stein, R.L. Potent and selective inhibitors of the proteasome: Dipeptidyl boronic acids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 8, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arastu-Kapur, S.; Anderl, J.L.; Kraus, M.; Parlati, F.; Shenk, K.D.; Lee, S.J.; Muchamuel, T.; Bennett, M.K.; Driessen, C.; Ball, A.J.; et al. Nonproteasomal Targets of the Proteasome Inhibitors Bortezomib and Carfilzomib: A Link to Clinical Adverse Events. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2734–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groll, M.; Korotkov, V.S.; Huber, E.M.; de Meijere, A.; Ludwig, A. A Minimal beta-Lactone Fragment for Selective beta5c or beta5i Proteasome Inhibitors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7810–7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elofsson, M.; Splittgerber, U.; Myung, J.; Mohan, R.; Crews, C.M. Towards subunit-specific proteasome inhibitors: Synthesis and evaluation of peptide alpha ‘, beta ‘-epoxyketones. Chem. Biol. 1999, 6, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demo, S.D.; Kirk, C.J.; Aujay, M.A.; Buchholz, T.J.; Dajee, M.; Ho, M.N.; Jiang, J.; Laidig, G.J.; Lewis, E.R.; Parlati, F.; et al. Antitumor Activity of PR-171, a Novel Irreversible Inhibitor of the Proteasome. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6383–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Besse, A.; Besse, L.; Kraus, M.; Mendez-Lopez, M.; Bader, J.; Xin, B.-T.; de Bruin, G.; Maurits, E.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Driessen, C. Proteasome Inhibition in Multiple Myeloma: Head-to-Head Comparison of Currently Available Proteasome Inhibitors. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 340–351.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Levitsky, K.; Parlati, F.; Bennett, M.K.; Arastu-Kapur, S.; Kellerman, L.; Woo, T.F.; Wong, A.F.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Niesvizky, R.; et al. Clinical activity of carfilzomib correlates with inhibition of multiple proteasome subunits: Application of a novel pharmacodynamic assay. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 173, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyburne, E.S.; Wilkins, O.M.; Sha, Z.; Williams, D.A.; Pletnev, A.A.; de Bruin, G.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Goldberg, A.L.; Cole, M.D.; Kisselev, A.F. Inhibition of the proteasome β2 site sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer cells to β5 inhibitors through a mechanism involving Nrf1 suppression. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirabella, A.C.; Pletnev, A.A.; Downey, S.; Florea, B.I.; Shabaneh, T.B.; Britton, M.; Verdoes, M.; Filippov, D.V.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Kisselev, A.F. Specific Cell-Permeable Inhibitor of Proteasome Trypsin-like Sites Selectively Sensitizes Myeloma Cells to Bortezomib and Carfilzomib. Chem. Biol. 2011, 18, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurink, P.; Liu, N.; Spaans, M.P.; Downey, S.; Nieuwendijk, A.M.C.H.V.D.; van der Marel, G.A.; Kisselev, A.F.; Florea, B.I.; Overkleeft, H.S. Incorporation of Fluorinated Phenylalanine Generates Highly Specific Inhibitor of Proteasome’s Chymotrypsin-like Sites. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2319–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blackburn, C.; Gigstad, K.M.; Hales, P.; Garcia, K.; Jones, M.; Bruzzese, F.J.; Barrett, C.; Liu, J.X.; Soucy, T.A.; Sappal, D.S. Characterization of a new series of non-covalent proteasome inhibitors with exquisite potency and selectivity for the 20S beta5-subunit. Biochem. J. 2010, 430, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, E.M.; Basler, M.; Schwab, R.; Heinemeyer, W.; Kirk, C.J.; Groettrup, M.; Groll, M. Immuno- and Constitutive Proteasome Crystal Structures Reveal Differences in Substrate and Inhibitor Specificity. Cell 2012, 148, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parlati, F.; Lee, S.J.; Aujay, M.; Suzuki, E.; Levitsky, K.; Lorens, J.B.; Micklem, D.R.; Ruurs, P.; Sylvain, C.; Lu, Y.; et al. Carfilzomib can induce tumor cell death through selective inhibition of the chymotrypsin-like activity of the proteasome. Blood 2009, 114, 3439–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huber, E.M.; Heinemeyer, W.; de Bruin, G.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Groll, M. A humanized yeast proteasome identifies unique binding modes of inhibitors for the immunosubunit beta5i. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 2602–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Bruin, G.; Huber, E.M.; Xin, B.T.; van Rooden, E.J.; Al-Ayed, K.; Kim, K.B.; Kisselev, A.F.; Driessen, C.; van der Stelt, M.; van der Marel, G.A. Structure-based design of beta1i or beta5i specific inhibitors of human immunoproteasomes. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6197–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basler, M.; Maurits, E.; de Bruin, G.; Koerner, J.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Groettrup, M. Amelioration of autoimmunity with an inhibitor selectively targeting all active centres of the immunoproteasome. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 175, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.; Busch, M.; Friese-Hamim, M.; Crosignani, S.; Fuchss, T.; Musil, D.; Rohdich, F.; Sanderson, M.P.; Seenisamy, J.; Walter-Bausch, G.; et al. Structure-Based Optimization and Discovery of M3258, a Specific Inhibitor of the Immunoproteasome Subunit LMP7 (β5i). J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 10230–10245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, M.P.; Friese-Hamim, M.; Walter-Bausch, G.; Busch, M.; Gaus, S.; Musil, D.; Rohdich, F.; Zanelli, U.; Downey-Kopyscinski, S.L.; Mitsiades, C.S. M3258 is a selective inhibitor of the immunoproteasome subunit LMP7 (beta5i) delivering efficacy in multiple myeloma models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladi, E.; Everett, C.; Stivala, C.E.; Daniels, B.E.; Durk, M.R.; Harris, S.F.; Huestis, M.; Purkey, H.; Staben, S.T.; Augustin, M.; et al. Design and Evaluation of Highly Selective Human Immunoproteasome Inhibitors Reveal a Compensatory Process That Preserves Immune Cell Viability. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 7032–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karreci, E.S.; Fan, H.; Uehara, M.; Mihali, A.B.; Singh, P.K.; Kurdi, A.T.; Solhjou, Z.; Riella, L.V.; Ghobrial, I.; Laragione, T.; et al. Brief treatment with a highly selective immunoproteasome inhibitor promotes long-term cardiac allograft acceptance in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E8425–E8432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.K.; Fan, H.; Jiang, X.; Shi, L.; Nathan, C.F.; Lin, G. Immunoproteasome beta5i-Selective Dipeptidomimetic Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 2127–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.D.L.A.; Bai, L.; Singh, P.K.; Murakami, N.; Fan, H.; Zhan, W.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, K.; Assker, J.P.; et al. Structure of human immunoproteasome with a reversible and noncompetitive inhibitor that selectively inhibits activated lymphocytes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubiella, C.; Baur, R.; Cui, H.; Huber, E.M.; Groll, M. Selective Inhibition of the Immunoproteasome by Structure-Based Targeting of a Non-catalytic Cysteine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 15888–15891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basler, M.; Lindstrom, M.M.; LaStant, J.J.; Bradshaw, J.M.; Owens, T.D.; Schmidt, C.; Maurits, E.; Tsu, C.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Kirk, C.J.; et al. Co-inhibition of immunoproteasome subunits LMP2 and LMP7 is required to block autoimmunity. EMBO Rep. 2018, 19, e46512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Angelo, N.G.; Warren, J.D.; Nathan, C.F.; Lin, G. Oxathiazolones Selectively Inhibit the Human Immunoproteasome over the Constitutive Proteasome. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosič, I.; Gobec, M.; Brus, B.; Knez, D.; Živec, M.; Konc, J.; Lešnik, S.; Ogrizek, M.; Obreza, A.; Žigon, D.; et al. Nonpeptidic Selective Inhibitors of the Chymotrypsin-Like (beta5i) Subunit of the Immunoproteasome. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 5745–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.; Hawley, R.C.; Lynch, S.M.; Narayanan, A. Substituted Thiazole Compounds. World Patent 2014/086701 A1, 6 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Verdoes, M.; Willems, L.I.; van der Linden, W.A.; Duivenvoorden, B.A.; van der Marel, G.A.; Florea, B.I.; Kisselev, A.F.; Overkleeft, H.S. A panel of subunit-selective activity-based proteasome probes. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 2719–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruin, G.; Xin, B.T.; Kraus, M.; van der Stelt, M.; van der Marel, G.A.; Kisselev, A.F.; Driessen, C.; Florea, B.I.; Overkleeft, H.S. A Set of Activity-Based Probes to Visualize Human (Immuno)proteasome Activities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 55, 4199–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, W.; Singh, P.K.; Ban, Y.; Qing, X.; ah Kioon, M.D.; Fan, H.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, R.; Sukenick, G.; Salmon, J. Structure-Activity Relationships of Noncovalent Immunoproteasome beta5i-Selective Dipeptides. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13103–13123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, T.; Brameld, K.A. LMP7 Inhibitors. U.S. Patent 10,654,843 B2, 19 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Li, D.; de Carvalho, L.P.S.; Deng, H.; Tao, H.; Vogt, G.; Wu, K.; Schneider, J.; Chidawanyika, T.; Warren, J.D.; et al. Inhibitors selective for mycobacterial versus human proteasomes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 461, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Baur, R.; le Chapelain, C.; Dubiella, C.; Heinemeyer, W.; Huber, E.M.; Groll, M. Structural Elucidation of a Nonpeptidic Inhibitor Specific for the Human Immunoproteasome. ChemBioChem 2017, 18, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Zhuang, R.; Kong, L.; He, R.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J. Immunoproteasome-selective inhibitors: An overview of recent developments as potential drugs for hematologic malignancies and autoimmune diseases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerfas, B.; Maresh, M.E.; Trader, D.J. The Immunoproteasome: An Emerging Target in Cancer and Autoimmune and Neurological Disorders. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 63, 1841–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, E.; Groll, M. A Nut for Every Bolt: Subunit-Selective Inhibitors of the Immunoproteasome and Their Therapeutic Potential. Cells 2021, 10, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, B.T.; de Bruin, G.; Huber, E.M.; Besse, A.; Florea, B.I.; Filippov, D.V.; van der Marel, G.A.; Kisselev, A.F.; van der Stelt, M.; Driessen, C.; et al. Structure-Based Design of beta5c Selective Inhibitors of Human Constitutive Proteasomes. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7177–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maréchal, X.; Genin, E.; Qin, L.; Sperandio, O.; Montes, M.; Basse, N.; Richy, N.; Miteva, M.; Reboud-Ravaux, M.; Vidal, J.; et al. 1,2,4-Oxadiazoles Identified by Virtual Screening and their Non-Covalent Inhibition of the Human 20S Proteasome. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2351–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisselev, A.F.; Akopian, T.N.; Castillo, V.; Goldberg, A.L. Proteasome Active Sites Allosterically Regulate Each Other, Suggesting a Cyclical Bite-Chew Mechanism for Protein Breakdown. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisselev, A.F.; Garcia-Calvo, M.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Peterson, E.; Pennington, M.; Ploegh, H.L.; Thornberry, N.A.; Goldberg, A.L. The Caspase-like Sites of Proteasomes, Their Substrate Specificity, New Inhibitors and Substrates, and Allosteric Interactions with the Trypsin-like Sites. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 35869–35877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myung, J.; Kim, K.B.; Lindsten, K.; Dantuma, N.P.; Crews, C.M. Lack of Proteasome Active Site Allostery as Revealed by Subunit-Specific Inhibitors. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, E.M.; de Bruin, G.; Heinemeyer, W.; Soriano, G.P.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Groll, M. Systematic Analyses of Substrate Preferences of 20S Proteasomes Using Peptidic Epoxyketone Inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7835–7842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Swieten, P.F.; Samuel, E.; Hernández, R.O.; Nieuwendijk, A.M.V.D.; Leeuwenburgh, M.A.; van der Marel, G.A.; Kessler, B.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Kisselev, A.F. A cell-permeable inhibitor and activity-based probe for the caspase-like activity of the proteasome. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 3402–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Linden, W.A.; Willems, L.I.; Shabaneh, T.B.; Li, N.; Ruben, M.; Florea, B.I.; van der Marel, G.A.; Kaiser, M.; Kisselev, A.F.; Overkleeft, H.S. Discovery of a potent and highly beta1 specific proteasome inhibitor from a focused library of urea-containing peptide vinyl sulfones and peptide epoxyketones. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groll, M.; Schellenberg, B.; Bachmann, A.S.; Archer, C.R.; Huber, R.; Powell, T.K.; Lindow, S.; Kaiser, M.; Dudler, R. A plant pathogen virulence factor inhibits the eukaryotic proteasome by a novel mechanism. Nature 2008, 452, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovhannisyan, A.; Pham, T.H.; Bouvier, D.; Piroyan, A.; Dufau, L.; Qin, L.; Cheng, Y.; Melikyan, G.; Reboud-Ravaux, M.; Bouvier-Durand, M. New C4- and C1-derivatives of furo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-ones and related compounds: Evidence for site-specific inhibition of the constitutive proteasome and its immunoisoform. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, D.; Lee, M.J.; Baek, A.; Yeo, I.J.; Miller, Z.; Baek, Y.M.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.-E.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, K.B. LMP2 Inhibitors as a Potential Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 3763–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Bhattarai, D.; Jang, H.; Baek, A.; Yeo, I.J.; Lee, S.; Miller, Z.; Lee, S.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, D.-E.; et al. Macrocyclic Immunoproteasome Inhibitors as a Potential Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 10934–10950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basler, M.; Lauer, C.; Moebius, J.; Weber, R.; Przybylski, M.; Kisselev, A.F.; Tsu, C.; Groettrup, M. Why the Structure but Not the Activity of the Immunoproteasome Subunit Low Molecular Mass Polypeptide 2 Rescues Antigen Presentation. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 1868–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, H.W.B.; Anderl, J.L.; Bradley, E.K.; Bui, J.; Jones, J.; Arastu-Kapur, S.; Kelly, L.M.; Lowe, E.; Moebius, D.C.; Muchamuel, T.; et al. Discovery of Highly Selective Inhibitors of the Immunoproteasome Low Molecular Mass Polypeptide 2 (LMP2) Subunit. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, Y.K.A.; Bargagna-Mohan, P.; Wehenkel, M.; Mohan, R.; Kim, K.B. LMP2-Specific Inhibitors: Chemical Genetic Tools for Proteasome Biology. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bogyo, M.; Shin, S.; McMaster, J.S.; Ploegh, H.L. Substrate binding and sequence preference of the proteasome revealed by active-site-directed affinity probes. Chem. Biol. 1998, 5, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loidl, G.; Groll, M.; Musiol, H.-J.; Ditzel, L.; Huber, R.; Moroder, L. Bifunctional inhibitors of the trypsin-like activity of eukaryotic proteasomes. Chem. Biol. 1999, 6, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marastoni, M.; Baldisserotto, A.; Cellini, S.; Gavioli, R.; Tomatis, R. Peptidyl Vinyl Ester Derivatives: New Class of Selective Inhibitors of Proteasome Trypsin-Like Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 5038–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artschwager, R.; Ward, D.J.; Gannon, S.; Brouwer, A.J.; van de Langemheen, H.; Kowalski, H.; Liskamp, R.M.J. Potent and Highly Selective Inhibitors of the Proteasome Trypsin-like Site by Incorporation of Basic Side Chain Containing Amino Acid Derived Sulfonyl Fluorides. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5395–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, B.T.; Huber, E.M.; de Bruin, G.; Heinemeyer, W.; Maurits, E.; Espinal, C.; Du, Y.; Janssens, M.; Weyburne, E.S.; Kisselev, A.F. Structure-Based Design of Inhibitors Selective for Human Proteasome beta2c or beta2i Subunits. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1626–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groll, M.; Götz, M.; Kaiser, M.; Weyher, E.; Moroder, L. TMC-95-Based Inhibitor Design Provides Evidence for the Catalytic Versatility of the Proteasome. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pawar, A.; Basler, M.; Goebel, H.; Salinas, G.O.A.; Groettrup, M.; Böttcher, T. Competitive Metabolite Profiling of Natural Products Reveals Subunit Specific Inhibitors of the 20S Proteasome. ACS Central Sci. 2020, 6, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, P.; Reboud-Ravaux, M.; Groll, M. Identification of a beta1/beta2-specific sulfonamide proteasome ligand by crystallographic screening. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 11275–11278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmony, K.C.; Lee, D.M.; Wu, Y.; Lee, N.R.; Wehenkel, M.; Lee, J.; Lei, B.; Zhan, C.G.; Kim, K.B. A bright approach to the immunoproteasome: Development of LMP2/beta1i-specific imaging probes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, L.K.; Lee, N.-R.; Jang, E.R.; Lei, B.; Zhan, C.-G.; Lee, W.; Kim, K.-B. Activity-based near-infrared fluorescent probe for LMP7: A chemical proteomics tool for the immunoproteasome in living cells. ChemBioChem 2012, 13, 1899–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.E.; Wu, Y.; Carmony, K.C.; Miller, Z.; Sharma, L.K.; Lee, D.-M.; Kim, D.-Y.; Lee, W.; Kim, K.-B. A FRET-based approach for identification of proteasome catalytic subunit composition. Mol. BioSyst. 2014, 10, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabaneh, T.B.; Downey, S.L.; Goddard, A.L.; Screen, M.; Lucas, M.M.; Eastman, A.; Kisselev, A.F. Molecular Basis of Differential Sensitivity of Myeloma Cells to Clinically Relevant Bolus Treatment with Bortezomib. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, M.; Bader, J.; Geurink, P.P.; Weyburne, E.S.; Mirabella, A.C.; Silzle, T.; Shabaneh, T.B.; van der Linden, W.A.; de Bruin, G.; Haile, S.R. The novel beta2-selective proteasome inhibitor LU-102 synergizes with bortezomib and carfilzomib to overcome proteasome inhibitor resistance of myeloma cells. Haematologica 2015, 100, 1350–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Downey-Kopyscinski, S.; Daily, E.W.; Gautier, M.; Bhatt, A.; Florea, B.I.; Mitsiades, C.S.; Richardson, P.G.; Driessen, C.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Kisselev, A.F. An inhibitor of proteasome beta2 sites sensitizes myeloma cells to immunoproteasome inhibitors. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2443–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, T.W.; Downey-Kopyscinski, S.L.; Fields, J.L.; Rahme, G.J.; Colley, W.C.; Israel, M.A.; Maksimenko, A.V.; Fiering, S.N.; Kisselev, A.F. Activity of immunoproteasome inhibitor ONX-0914 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia expressing MLL–AF4 fusion protein. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehenkel, M.; Ban, J.-O.; Ho, Y.-K.; Carmony, K.C.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, K.B. A selective inhibitor of the immunoproteasome subunit LMP2 induces apoptosis in PC-3 cells and suppresses tumour growth in nude mice. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.V.; Bandi, M.; Aujay, M.A.; Kirk, C.J.; Hark, D.E.; Raje, N.; Chauhan, D.; Anderson, K.C. PR-924, a selective inhibitor of the immunoproteasome subunit LMP-7, blocks multiple myeloma cell growth both in vitro and in vivo. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 152, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basler, M.; Kirk, C.J.; Groettrup, M. The immunoproteasome in antigen processing and other immunological functions. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirai, M.; Kadowaki, N.; Kitawaki, T.; Fujita, H.; Takaori-Kondo, A.; Fukui, R.; Miyake, K.; Maeda, T.; Kamihira, S.; Miyachi, Y.; et al. Bortezomib suppresses function and survival of plasmacytoid dendritic cells by targeting intracellular trafficking of Toll-like receptors and endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis. Blood 2011, 117, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodle, E.S.; Tremblay, S.; Rossi, A.; Rojas, C.C.; Alloway, R.; Roskin, K.; Allman, D.; Hildeman, D. Plasma cell targeting to prevent antibody-mediated rejection. Arab. Archaeol. Epigr. 2020, 20, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, J.; Brown, M.G.; Finley, D.; Monaco, J.J. MHC-linked LMP gene products specifically alter peptidase activities of the proteasome. Nat. Cell Biol. 1993, 365, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaczynska, M.; Rock, K.L.; Goldberg, A.L. Gamma-interferon and expression of MHC genes regulate peptide hydrolysis by proteasomes. Nature 1993, 365, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jr, A.B.; Kuzina, E.; Kudriaeva, A.; Kononikhin, A.; Kovalchuk, S.; Surina, Y.; Smirnov, I.; Lomakin, Y.; Bacheva, A.; Stepanov, A.; et al. Ubiquitin-independent proteosomal degradation of myelin basic protein contributes to development of neurodegenerative autoimmunity. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1901–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisselev, A.F.; Groettrup, M. Subunit specific inhibitors of proteasomes and their potential for immunomodulation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2014, 23, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Limanaqi, F.; Biagioni, F.; Gaglione, A.; Busceti, C.L.; Fornai, F. A Sentinel in the Crosstalk Between the Nervous and Immune System: The (Immuno)-Proteasome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeo, I.J.; Lee, M.J.; Baek, A.; Miller, Z.; Bhattarai, D.; Baek, Y.M.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, D.-E.; Hong, J.T.; et al. A dual inhibitor of the proteasome catalytic subunits LMP2 and Y attenuates disease progression in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Türker, F.; Cook, E.K.; Margolis, S.S. The proteasome and its role in the nervous system. Cell Chem. Biol. 2021, 28, 903–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltsev, A.; Funikov, S.; Burov, A.; Spasskaya, D.; Ignatyuk, V.; Astakhova, T.; Lyupina, Y.; Deikin, A.; Tutyaeva, V.; Bal, N.; et al. Immunoproteasome Inhibitor ONX-0914 Affects Long-Term Potentiation in Murine Hippocampus. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021, 16, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skorda, A.; Sklirou, A.D.; Sakellaropoulos, T.; Gianniou, D.D.; Kastritis, E.; Terpos, E.; Tsitsilonis, O.E.; Florea, B.I.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; et al. Non-lethal proteasome inhibition activates pro-tumorigenic pathways in multiple myeloma cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 8010–8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Activity: | Catalytic Subunit: | |
|---|---|---|
| Constitutive | Immunoproteasome | |
| Chymotrypsin-like (β5) | β5c (PSMB5) | β5i (LMP7, PSMB8) |
| Trypsin-like (β2) | β2c (PSMB7) | β2i (MECL1, PSMB10) |
| Caspase-like (β1) | β1c (PSMB6) | β1i (LMP2, PSMB9) |
| Site | Position Relative to Scissile (P1-P1′) Bond | |
|---|---|---|
| P3 | P1 | |
| β5c | Large hydrophobic | Small hydrophobic (Ala) |
| β5i | Small hydrophobic | Large hydrophobic (Trp, Phe) |
| β1c | Pro | Asp, Leu |
| β1i | Pro | Leu |
| β2c, β2i | Basic, branched hydrophobic | Basic |
| Compound | IC50 * | Fold-Selectivity (IC50(βx)/IC50(β5i)) | Sp | Source | Assay | Ref | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nM | β1i | β5c | β2i | β2c | β1c | |||||
| ONX-0914 | 5.7 | 9 | 81 | 103 | 192 | >1750 | h | Raji | ABP | [63] |
| 39 | 7.4 | 11 | 23 | 24 | >325 | h | MOLT4 | PrC | [43] | |
| 98 | 3.3 | 4 | 7 | 9 | >250 | m | A20 | PrC | [43] | |
| KZR-616 | 39 | 3.4 | 18 | 16 | 15.5 | >270 | h | MOLT4 | ABP | [43] |
| 57 | 3.1 | 8.4 | 9 | 15 | >430 | m | A20 | PrC | [43] | |
| PR-924 | 25 | 92 | 740 | >4000 | >4000 | >4000 | h | Raji | ABP | [63] |
| 39 | 57 | 15 | >640 | >640 | >640 | h | MOLT4 | PrC | [43] | |
| 573 | 8.3 | 2.4 | m | A20 | PrC | [43] | ||||
| KZR-329 | 34 | 54 | 79 | >735 | >735 | >735 | h | MOLT4 | PrC | [43] |
| 374 | 10.5 | 7.1 | m | A20 | PrC | [43] | ||||
| LU-005i | 6.6 | 45 | 44 | 62 | 378 | >1500 | h | Raji | ABP | [63] |
| 160 | 0.6 | 19 | 3 | 19 | h | 20S | FS | [64] | ||
| 380 | 0.05 | 10 | 0.5 | n.i. | m | 20S | FS | [64] | ||
| LU-015i | 8.3 | 554 | 855 | >1200 | >1200 | >1200 | h | Raji | ABP | [63] |
| M3258 | 3.6 | >104 | 694 | >104 | >104 | >104 | h | 20S | FS | [65] |
| Comp 22 | 4.1 | 2100 | 2200 | >4800 | h | 20S | FS | [67] | ||
| Comp 8 | 1.4 | 0.81 | 543 | 3000 | h | 20S | FS | [67] | ||
| DPLG3 | 4.5 | >7300 | 7200 | >7300 | >7300 | >7300 | h | 20S | FS | [68] |
| 9 | 1500 | m | 20S | FS | [68] | |||||
| PKS2252 | 5.5 | 13600 | h | 20S | FS | [69] | ||||
| PKS21221 | 4 | >104 | 27.5 | >104 | >104 | >104 | h | 20S | FS | [70] |
| CA-4 | 0.36 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | h | 20S | FS | [71] |
| PRN1126 | ~8 | >1000 | ~30 | >1000 | >1000 | >1000 | h | 20S | FS | [72] |
| ~300 | >>300 | ~7 | ~100 | >>300 | >>300 | m | 20S | FS | [72] | |
| HT2106 | 240 | >>40 | >40 | >>40 | h | 20S | FS | [73] | ||
| Comp 42 | 13 | >1000 | 83 | >1000 | >1000 | >1000 | h | 20S | FS | [74] |
| Comp 30 | 9 | 630 | 24 | 842 | 995 | 681 | h | 20S | FS | [74] |
| Ro19 | 25 | 800 | 70 | 800 | 800 | 800 | h | Ramos | FS | [75] |
| IC50 nM | Fold-Selectivity (IC50(βx)/ IC50(β5c)) | Species | Source | Assay | Ref | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β5i | β1c | β2c | β1i | β2i | ||||||
| CPSI (PR-893) | 17 | 21 | 164 | 523 | 13 | 182 | h | Extract * | PrC | [61] |
| PR-825 | 20 | 15 | 200 | 500 | 15 | 500 | h | MOLT4 | PrC | [34] |
| 25 | 7 | 70 | 160 | 5 | 70 | m | A20 | PrC | [34] | |
| LU-005c | 75 | 222 | >1300 | >1300 | >1300 | >1300 | h | Raji | ABP | [85] |
| LU-015c | 150 | 52 | >666 | >666 | >666 | >666 | h | Raji | ABP | [85] |
| LU-005c-trans | 5 | 2600 | >2 × 104 | >2 × 104 | >2 × 104 | >2 × 104 | h | Raji | ABP | [85] |
| LU-015c-trans | 30 | 814 | >3570 | >3570 | >3570 | >3570 | h | Raji | ABP | [85] |
| Compound 4h | 37 | n.t. | >270 | >270 | h | 20S | FS | [86] | ||
| Compound | IC50 | Fold-Selectivity (IC50(βx)/ IC50(β1i)) | Proteas. Source | Assay | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nM | β1c | β5i | β5c | β2i | β2c | ||||
| UK-101 | 104 | 144 | 30 | 10 | 163 | 240 | Raji | ABP | [63] |
| LU-001i | 95 | 250 | 210 | 210 | >100 | >100 | Raji | ABP | [63] |
| DB-310 | 70 | 8.4 | >140 | >140 | h-i20S * | FS | [95] | ||
| DB-60 | 184 | 46 | 2.2 | 25 | h20S | FS | [96] | ||
| KZR-504 | 50 | ~900 | 94 | 135 | >4900 | >4900 | MOLT4 | PrC | [98] |
| ML604440 | 10 | >100 | >100 | m20S | FS | [97] | |||
| Comp | IC50, μM | Sp | Source | Ass | Ref | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β2c | β2i | β5c | β5i | β1c | β1i | h | Raji | ABP | [104] | |
| LU-102 | 0.013 | 0.020 | 1.3 | 1.2 | >100 | >100 | h | Raji | ABP | [104] |
| LU-002c | 0.005 | 0.14 | 1.3 | 2.8 | >100 | >100 | h | Raji | ABP | [104] |
| LU-012c | 0.007 | 0.11 | 0.75 | 2.1 | >100 | >100 | h | Raji | ABP | [104] |
| LU-002i | 12.1 | 0.22 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | h | Raji | ABP | [104] |
| Comp 87 | 19 | 0.19 | >100 | 28 | 53 | >100 | h | Raji | ABP | [104] |
| Comp 10 | 0.41 | 0.071 | 0.49 | 0.35 | >25 | >25 | h | MOLT4 | PrC | [43] |
| 0.57 | 0.31 | 0.38 | 1.92 | >25 | >25 | m | A20 | PrC | [43] | |
| Comp 39 | 2.5 | 0.057 | 5.0 | 0.046 | >100 | >100 | h | Raji | ABP | [104] |
| Cell Lines Derived From | β5 Inhibitor * | β1 and β2 Inhibitors | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple myeloma | NC-005 | NC-001 | [28] |
| HeLa | NC-005-vs | NC-001 | [48] |
| Multiple myeloma | LU-005, Cfz | NC-001, NC-022 | [57] |
| Multiple myeloma | carfilzomib | LU-102 | [47] |
| Primary ALL | LU-015i | LU-001i | [77] |
| Bortezomib and carfilzomib-resistant myeloma | NC-005 carfilzomib | NC-001, LU-102 LU-102 | [54] [112] |
| Triple-negative breast, lung, liver, ovarian cancer | carfilzomib | NC-021 & LU-102 | [56] |
| Myeloma | ONX-0914 | LU-102 | [113] |
| ALL | ONX-0914 | LU-102 | [114] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kisselev, A.F. Site-Specific Proteasome Inhibitors. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12010054
Kisselev AF. Site-Specific Proteasome Inhibitors. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleKisselev, Alexei F. 2022. "Site-Specific Proteasome Inhibitors" Biomolecules 12, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12010054
APA StyleKisselev, A. F. (2022). Site-Specific Proteasome Inhibitors. Biomolecules, 12(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12010054