Cloning and Characterization of Drosophila melanogaster Juvenile Hormone Epoxide Hydrolases (JHEH) and Their Promoters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects, Cells, Chemicals and Incubation Conditions
Injections into Embryos
2.2. RNA Extraction and Purification
2.3. Cloning and Sequencing of JHEH 1, 2 and 3 cDNAs
2.3.1. Sequencing of JHEH 1
2.3.2. Sequencing of JHEH 2
2.3.3. Sequencing of JHEH 3
2.4. Identification of JHEH 1, 2 and 3 Promoter Regions and Introns
2.5. Northern Blot Analysis
2.5.1. JHEH 1, 2, 3
2.5.2. Sp1Transcription Factor (TF)
2.6. Molecular Modeling of JHEH 1, 2 and 3
2.7. Cloning and Characterization of JHEHs Promoters
2.7.1. JHEH 1 Promoter Assay
2.7.2. JHEH 2 Promoter Assay
2.7.3. JHEH 3 Promoter Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. cDNA Sequencing of JHEH 1, 2 and 3
3.2. Northern Blot Analyses
3.3. Molecular Modeling of JHEH 1, 2 and 3
3.4. Activities of JHEH 1, 2, 3 Promoters
3.4.1. JHEH 1 Promoter
3.4.2. JHEH 2 Promoter
3.4.3. JHEH 3 Promoter

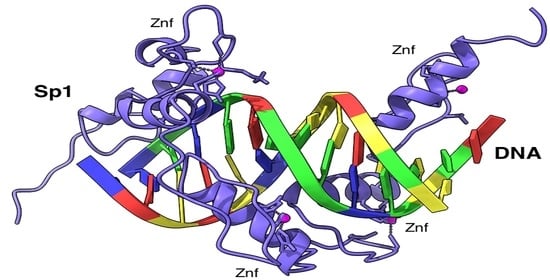
3.4.4. Northern Blot Analysis and dsRNA Knockdown of TF Sp1
3.5. The Effects of JH III, JH IIIA, 20HE and Farnesoic Acid on JHEH 3 Promoter
3.6. Effect of JHEH 3 pJHEH#3L3 Promoter on Transgenic D. Melanogaster
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riddiford, L.M. Cellular and molecular actions of juvenile hormone general considerations and premetamorphic actions. Adv. Insect Physiol. 1994, 24, 213–273. [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt, G.R.; Davey, K.G. Cellular and molecular actions of juvenile hormone. II. Roles of juvenile hormone in adult insects. Adv. Insect Physiol. 1996, 26, 1–156. [Google Scholar]
- Stay, B.; Tobe, S.S.; Bendena, W.G. Allatostatins: Identification, primary structure, function and distribution. Adv. Insect Physiol. 1994, 125, 267–337. [Google Scholar]
- Hammock, B.D.; Sparks, T.C. A rapid assay for insect juvenile hormone esterase activity. Anal. Biochem. 1977, 82, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Share, M.R.; Roe, R.M. A partition assay for the simultaneous determination of insect juvenile hormone esterase and epoxide hydrolase activity. Anal. Biochem. 1988, 169, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovsky, D.; Carlson, D.A.; Ujvary, I. In vivo and in vitro biosynthesis and metabolism of methyl farnesoate, juvenile hormone III, and juvenile hormone III acid in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. J. Med. Entomol. 1992, 29, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammock, B.D. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. In Comprehensive Insect Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology; Kerkut, G.A., Gilbert, L.I., Eds.; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; Volume 7, pp. 431–472. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, A.; Tanaka, H.; Tamura, T.; Shiotsuki, T. Precocious metamorphosis in transgenic silkworms overexpressing juvenile hormone esterase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11751–11756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Ekert, E.; Heylen, K.; Rougé, P.; Powell, C.A.; Shatters, R.G., Jr.; Smagghe, G.; Borovsky, D. Aedes aegypti juvenile hormone acid methyl transferase, the ultimate enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway of juvenile hormone III, exhibits substrate control. J. Insect Physiol. 2014, 64, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, R.M.; Venkatesh, K. Metabolism of juvenile hormones: Degradation and titer regulation. In Morphogenetic Hormones of Arthropods; Gupta, A.P., Ed.; Rutgers University Press: New Brunswick, NJ, Canada, 1990; pp. 126–179. [Google Scholar]
- Wojtasek, H.; Prestwich, G.D. Key disulfide bonds in an insect hormone binding protein: cDNA cloning of a juvenile hormone binding protein of Heliothis virescens and ligand binding by native and mutant forms. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 5234–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anspaugh, D.D.; Roe, R.M. Regulation of JH epoxide hydrolase versus JH esterase activity in the cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni, by juvenile hormone and xenobiotics. J. Insect Physiol. 2005, 51, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.M.; Healy, M.J.; Oakshott, J.G. Characterization of juvenile hormone esterase in Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1992, 22, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halarnkar, P.P.; Jackson, G.P.; Straub, K.M.; Schooley, D.A. Juvenile hormone catabolism in Manduca sexta: Homologue selectivity of catabolism and identification of a diol-phosphate conjugate as a major end product. Experientia 1993, 49, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassiter, M.T.; Apperson, C.S.; Roe, R.M. Juvenile hormone metabolism during the fourth stadium and pupal stage of the Southern House Mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus. J. Insect Physiol. 1995, 41, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Jia, N.; Hu, C.; Jiang, Y.-L.; Yang, J.-P.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Li, W.-F.; Zhou, C.-Z. Crystal structure of juvenile hormone epoxide hydrolase from the silkworm Bombyx mori. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2014, 82, 3224–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtasek, H.; Prestwich, G.D. An insect juvenile hormone-specific epoxide hydrolase is related to vertebrate microsomal epoxide hydrolases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 220, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, M.; Kamimura, M.; Kikuchi, K.; Yasukochi, Y.; Kiuchi, M.; Shinoda, T.; Shiotsuki, T. cDNA cloning and characterization of Bombyx mori juvenile hormone esterase: An inducible gene by the imidazole insect growth regulator KK-42. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackert, A.; Hartfelder, K.; Bitondi, M.M.; Simões, Z.L. The juvenile hormone (JH) epoxide hydrolase gene in the honeybee (Apis mellifera) genome encodes a protein which has negligible participation in JH degradation. J. Insect Physiol. 2010, 56, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniai, K.; Inceoglu, A.B.; Yukuhiro, K.; Hammock, B.D. Characterization and cDNA cloning of a clofibrate-inducible microsomal epoxide hydrolase in Drosophila melanogaster. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 4696–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harshman, L.G.; James, A.A. Differential gene expression in insects: Transcriptional control. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1998, 43, 671–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papantonis, A.; Swevers, L.; Iatrou, K. Chorion genes: A landscape of their evolution, structure, and regulation. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, A.S.; Li, C.H.; Zamudio, A.V.; Sigova, A.A.; Hannett, N.M.; Day, D.S.; Abraham, B.J.; Cohen, M.A.; Nabet, B.; Buckley, D.L.; et al. YY1 is a structural regulator of enhancer-promoter loops. Cell 2017, 171, 1573–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyata, Y.; Tokumoto, S.; Sogame, Y.; Deviatiiarov, R.; Okada, J.; Cornette, R.; Gusev, O.; Shagimardanova, E.; Sakurai, M.; Kikawada, T. Identifcation of a novel strong promoter from the anhydrobiotic midge, Polypedilum vanderplanki, with conserved function in various insect cell lines. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tan, A.; Palli, S.R. Identification and functional analysis of promoters of heat-shock genes from the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bleckmann, M.; Fritz, M.H.-Y.; Bhuju, S.; Jarek, M.; Schürig, M.; Geffers, R.; Benes, V.; Besir, H.; van den Heuvel, J. Genomic Analysis and Isolation of RNA Polymerase II Dependent Promoters from Spodoptera frugiperda. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgel, P.; Meister, M.; Kappler, C.; Lemaitre, B.; Reichhart, J.-M.; Hoffmann, J.A. Insect immunity: The diptericin promoter contains multiple functional regulatory sequences homologous to mammalian acute-phase response elements. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 197, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgel, P.; Kappler, C.; Langley, E.; Gross, I.; Nicholas, E.; Reichhart, J.-M.; Hoffmann, J.A. Drosophila immunity. A sequence homologous to mammalian interferon consensus response element enhances the activity of the diptericin promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, Z.; Jung, C.; Bandilla, P.; Ludwig, C.; Heron, M.; Kiesel, A.S.; Museridz, M.; Philippou-Massier, J.; Nikolov, M.; Schnepf, A.R.M.; et al. Large-scale analysis of Drosophila core promoter function using synthetic promoters. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2022, 18, e9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thummel, C.S.; Boulet, A.M.; Lipshitz, H.D. Vectors for Drosophila P-element-mediated transformation and tissue culture transformation. Gene 1988, 74, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovsky, D.; Carlson, D.A. In vitro assay for biosynthesis and metabolism of juvenile hormone by exposed corpora allata of Aedes aegypti (diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1992, 20, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, R.M.; Kallapu, V.; Linderman, R.J.; Viviani, F.; Harris, S.V.; Walker, E.A.; Thompson, D.M. Mechanism of Action and Cloning of Epoxide Hydrolase From the Cabbage Looper, Trichoplusia ni. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1996, 32, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debernard, S.; Morisseau, C.; Severson, T.F.; Feng, L.; Wojtasek, H.; Prestwich, G.D.; Hammock, B.D. Expression and characterization of the recombinant juvenile hormone epoxide hydrolase (JHEH) from Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 28, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohman, M.A. Rapid amplification of complementary DNA ends for generation of full length complementary DNAs: Thermal RACE. Methods Enzymol. 1993, 8, 340–356. [Google Scholar]
- Borovsky, D.; Janssen, I.; Broeck, J.; Huybrechts, R.; Verhaert, P.; Bondt, H.L.; Bylemans, D.; de Loof, A. Molecular sequencing and modeling of Neobellieria bullata trypsin: Evidence for translational control with Neb TMOF. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 237, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.-H.; De Bondt, H.L.; Powell, C.C.; Bullock, R.C.; Borovsky, D. Sequencing and characterization of the citrus weevil Diaprepes abbreviatus, trypsin cDNA; effect of Aedes trypsin modulating oostatic factor on trypsin biosynthesis. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 262, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krieger, E.; Koraimann, G.; Vriend, G. Increasing the precision of comparative models with YASARA NOVA-a self-parameterizing force field. Proteins 2002, 57, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reetz, M.T.; Bocola, M.; Wang, L.-W.; Sanchis, J.; Cronin, A.; Arand, M.; Zou, J.; Archelas, A.; Bottalla, A.-L.; Naworyta, A.; et al. Directed evolution of an enantioselective epoxide hydrolase: Uncovering the source of enantioselectivity at each evolutionary stage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7334–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, J.; Hallberg, B.M.; Bergfors, T.; Oesch, F.; Arand, M.; Mowbray, S.L.; Jones, T.A. Structure of Aspergillus niger epoxide hydrolase at 1.8 A resolution: Implications for the structure and function of the mammalian microsomal class of epoxide hydrolases. Structure 2000, 8, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. Procheck: A program to check the stereochemistry of protein structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, F.; Feytmans, E. Assessing protein structures with a non-local atomic interaction energy. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 277, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkert, P.; Biasini, M.; Schwede, T. Toward the estimation of the absolute quality of individual protein structure models. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, K.; Bordoli, L.; Kopp, J.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: A web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grosdidier, A.; Zoete, V.; Michielin, O. Fast docking using the CHARMM force field with EADock DSS. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 2149–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera-a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reese, M.G. Application of a time-delay neural network to promoter annotation in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Comput. Chem. 2001, 26, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Wang, B.; Wang, B.; Ma, L. Characterization and Expression Profiles of Juvenile Hormone Epoxide Hydrolase From Lymantria dispar (Lepidoptera: Lymantridae) and RNA Interference by Ingestion. J. Insect Sci. 2018, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusun, A.; Li, M.; Liang, X.; Yang, T.; Yang, B.; Wang, G. Juvenile Hormone Epoxide Hydrolase: A Promising Target for Hemipteran Pest Management. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrillas-Mury, C.; Graf, R.; Hagedorn, H.H.; Wells, M.A. cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of a blood meal-induced trypsin from the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. 1991, 21, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Ge, W.; Feng, Q.; Palli, S.R.; Li, S. Antagonistic actions of juvenile hormone and 20-hydroxyecdysone within the ring gland determine developmental transitions in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 115, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, W.; Han, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, P.; Xu, H. Post-translational modification control of RNA-binding protein hnRNPK function. Open Biol. 2019, 9, 180239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bownes, M.; Rembold, H. The titre of juvenile hormone during the pupal and adult stages of the life cycle of Drosophila melanogaster. Eur. J. Biochem. 1987, 164, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddiford, L.M.; Cherbas, P.; Truman, J.W. Ecdysone receptors and their biological actions. Vitam. Horm. 2000, 60, 1–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kethidi, D.R.; Xi, Z.; Palli, S.R. Developmental and hormonal regulation of juvenile hormone esterase gene in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Insect Physiol. 2005, 51, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Calculated Parameters | JHEH 1 | JHEH 2 | JHEH 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ramachandran outliers | L94 (A) | M240 (A) | T58 (A) |
| A72 (B) | G273 (A) | D66 (B) | |
| QMEAN value | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.70 |
| ANOLEA calculated of amino | 28 over 450 (A) | 26 over 439 (A) | 16 over 437 (A) |
| acids residues exhibiting energetic | 29 over 450 (B) | 23 over 439 (B) | 10 over 437 (B) |
| values over the threshold |
| Hours after Adult | Groups | JH IIIA | JH IIIAD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eclosion | N | Cpm ± SEM | Cpm ± SEM |
| 3 | 3 | 50,000 ± 6000 | 22,000 ± 2500 |
| 24 | 3 | 40,000 ± 5000 | 32,000 ± 1800 |
| 48 | 3 | 30,000 ± 6000 | 38,000 ± 4200 |
| 72 | 3 | 34,000 ± 4450 | 40,000 ± 6000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borovsky, D.; Breyssens, H.; Buytaert, E.; Peeters, T.; Laroye, C.; Stoffels, K.; Rougé, P. Cloning and Characterization of Drosophila melanogaster Juvenile Hormone Epoxide Hydrolases (JHEH) and Their Promoters. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070991
Borovsky D, Breyssens H, Buytaert E, Peeters T, Laroye C, Stoffels K, Rougé P. Cloning and Characterization of Drosophila melanogaster Juvenile Hormone Epoxide Hydrolases (JHEH) and Their Promoters. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(7):991. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070991
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorovsky, Dov, Hilde Breyssens, Esther Buytaert, Tom Peeters, Carole Laroye, Karolien Stoffels, and Pierre Rougé. 2022. "Cloning and Characterization of Drosophila melanogaster Juvenile Hormone Epoxide Hydrolases (JHEH) and Their Promoters" Biomolecules 12, no. 7: 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070991
APA StyleBorovsky, D., Breyssens, H., Buytaert, E., Peeters, T., Laroye, C., Stoffels, K., & Rougé, P. (2022). Cloning and Characterization of Drosophila melanogaster Juvenile Hormone Epoxide Hydrolases (JHEH) and Their Promoters. Biomolecules, 12(7), 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070991