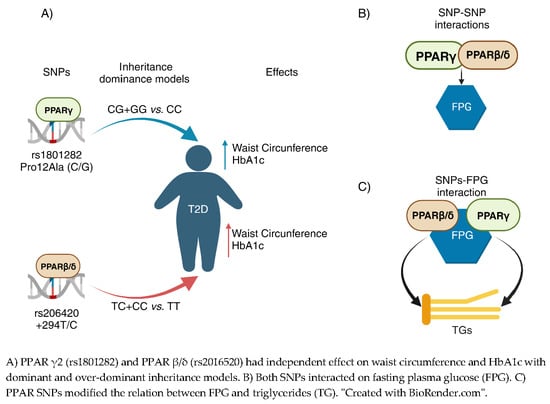
Metabolic Biomarkers in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: The Role of PPAR-γ2 and PPAR-β/δ Polymorphisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Phenotyping and Biochemical Data
2.3. Genotyping
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Characteristics
3.2. PPAR-γ2 rs18 01282 and PPAR-β/δ rs2016520
3.3. PPAR SNPs and Anthropometric Measures
3.4. PPAR SNPs and Glycemic Biomarkers
3.5. PPAR SNPs and Lipid Biomarkers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magliano, D.; Boyko, E.J. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; ISBN 978-2-930229-98-0. [Google Scholar]
- Basto-Abreu, A.; López-Olmedo, N.; Rojas-Martínez, R.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; Moreno-Banda, G.L.; Carnalla, M.; Rivera, J.A.; Romero-Martinez, M.; Barquera, S.; Barrientos-Gutiérrez, T. Prevalencia de prediabetes y diabetes en México: Ensanut 2022. Salud Pública México 2023, 65, s163–s168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellou, V.; Belbasis, L.; Tzoulaki, I.; Evangelou, E. Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Exposure-Wide Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Rani, J.; Bhat, M.A.; Vanita, V. Genetics of Diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 656–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Collister, J.A.; Clifton, L.; Hunter, D.J.; Littlejohns, T.J. Polygenic Risk of Prediabetes, Undiagnosed Diabetes, and Incident Type 2 Diabetes Stratified by Diabetes Risk Factors. J. Endocr. Soc. 2023, 7, bvad020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancks, M.P.; Carnethon, M.; Chen, H.; Cotch, M.F.; Klein, B.; Klein, R.; Szklo, M.; Bertoni, A. Diabetes Subgroups and Risk for Complications: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). J. Diabetes Complicat. 2021, 35, 107915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.D.; Harris-Hayes, M.; Schootman, M. Epidemiology of Diabetes and Diabetes-Related Complications. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighatpanah, M.; Nejad, A.S.M.; Haghighatpanah, M.; Thunga, G.; Mallayasamy, S. Factors That Correlate with Poor Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Complications. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2018, 9, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souliotis, K.; Koutsovasilis, A.; Vatheia, G.; Golna, C.; Nikolaidi, S.; Hatziagelaki, E.; Kotsa, K.; Koufakis, T.; Melidonis, A.; Papazafiropoulou, A.; et al. Profile and Factors Associated with Glycaemic Control of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Greece: Results from the Diabetes Registry. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofo Mato, E.P.; Guewo-Fokeng, M.; Essop, M.F.; Owira, P.M.O. Genetic Polymorphisms of Organic Cation Transporter 1 (OCT1) and Responses to Metformin Therapy in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Medicine 2018, 97, e11349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaqih, M.A.; Al-hawamdeh, A.; Amarin, Z.O.; Khader, Y.S.; Mhedat, K.; Allouh, M.Z. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in the ADIPOQ Gene Modifies Adiponectin Levels and Glycemic Control in Type Two Diabetes Mellitus Patients. BioMed Research International 2022, 2022, 6632442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Han, W.; Jiang, Y.; Peng, S.; Shan, Z.; Teng, W. The Type 2 Deiodinase Thr92Ala Polymorphism Is Associated with Worse Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 5928726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichane, S.; Dahal Lamichane, B.; Kwon, S.-M. Pivotal Roles of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) and Their Signal Cascade for Cellular and Whole-Body Energy Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.Z.; Althagafi, I.I.; Shamshad, H. Role of PPAR Receptor in Different Diseases and Their Ligands: Physiological Importance and Clinical Implications. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 166, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Pan, S.; Guo, Y.; Xu, P.; Zhai, Y. PPARs as Nuclear Receptors for Nutrient and Energy Metabolism. Molecules 2019, 24, 2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, T.B.; Levine, A.B. Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease; Saunders/Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-1-4160-2545-0. [Google Scholar]
- Frkic, R.L.; Richter, K.; Bruning, J.B. The Therapeutic Potential of Inhibiting PPARγ Phosphorylation to Treat Type 2 Diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Olson, P.; Hevener, A.; Mehl, I.; Chong, L.-W.; Olefsky, J.M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Ham, J.; Kang, H.; Peters, J.M.; et al. PPARδ Regulates Glucose Metabolism and Insulin Sensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3444–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hatano, B.; Zhao, M.; Yen, C.-C.; Kang, K.; Reilly, S.M.; Gangl, M.R.; Gorgun, C.; Balschi, J.A.; Ntambi, J.M.; et al. Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor δ/β in Hepatic Metabolic Regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, V.; Eeckhoute, J.; Lefebvre, P.; Staels, B. Distinct but Complementary Contributions of PPAR Isotypes to Energy Homeostasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1202–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, M.; Suh, J.M.; Hah, N.; Liddle, C.; Atkins, A.R.; Downes, M.; Evans, R.M. PPARγ Signaling and Metabolism: The Good, the Bad and the Future. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.-J.; Beamer, B.A.; Negri, C.; Silver, K.; Brown, K.A.; Yarnall, D.P.; Burns, D.K.; Roth, J.; Shuldiner, A.R. Molecular Scanning of the Human Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor g (hPPARg) Gene in Diabetic Caucasians: Identification of a Pro12Ala PPARg2 Missense Mutation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 241, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagou, V.; Scott, R.A.; Manios, Y.; Chen, T.J.; Wang, G.; Grammatikaki, E.; Kortsalioudaki, C.; Liarigkovinos, T.; Moschonis, G.; Roma-Giannikou, E.; et al. Impact of Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptors γ and δ on Adiposity in Toddlers and Preschoolers in the GENESIS Study. Obesity 2008, 16, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stryjecki, C.; Peralta-Romero, J.; Alyass, A.; Karam-Araujo, R.; Suarez, F.; Gomez-Zamudio, J.; Burguete-Garcia, A.; Cruz, M.; Meyre, D. Association between PPAR-Γ2 Pro12Ala Genotype and Insulin Resistance Is Modified by Circulating Lipids in Mexican Children. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.D.; Park, B.L.; Kim, L.H.; Jung, H.S.; Cho, Y.M.; Moon, M.K.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, H.K.; Park, K.S. Genetic Polymorphisms in Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor δ Associated with Obesity. Diabetes 2004, 53, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attianese, G.M.G.; Desvergne, B. Integrative and Systemic Approaches for Evaluating PPARβ/δ (PPARD) Function. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2015, 13, e001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Venzor, M.A.; Erives-Anchondo, N.R.; Moreno-González, J.G.; Moreno-Brito, V.; Licón-Trillo, A.; González-Rodríguez, E.; Hernández-Rodríguez, P.D.C.; Reza-López, S.A.; Loera-Castañeda, V.; Leal-Berumen, I. Pro12Ala PPAR-Γ2 and +294T/C PPAR-δ Polymorphisms and Association with Metabolic Traits in Teenagers from Northern Mexico. Genes 2020, 11, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Song, J.-F.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Li, C.-L.; Yin, X.-X.; Lu, Q. PPARD Rs2016520 (T/C) and NOS1AP Rs12742393 (A/C) Polymorphisms Affect Therapeutic Efficacy of Nateglinide in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secretaría de Salud. NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-015-SSA2-2010, Para La Prevención, Tratamiento y Control de La Diabetes Mellitus. Diario Oficial de La Federación 23 noviembre 2010. Estados Unidos Mexicanos. Available online: https://dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5168074&fecha=23/11/2010#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 20 November 2023).
- Millán, J.; Pintó, X.; Muñoz, A.; Zúñiga, M.; Rubiés-Prat, J.; Pallardo, L.F.; Masana, L.; Mangas, A.; Mijares, A.H.; Santos, P.G.; et al. Cocientes lipoproteicos: Significado fisiológico y utilidad clínica de los índices aterogénicos en prevención cardiovascular. Clínica E Investig. Arterioscler. 2010, 22, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, R.; Jamil, K.; Asimuddin, M.; Alqahtani, M.S.; Alshehri, M.; Mateen, A.; Wahab Ali Aduderman, A.; Shamsul Ola, M.; Malik, A. Molecular & Biochemical Analysis of Pro12Ala Variant of PPAR-Γ2 Gene in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2439–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams-October, Z.; Xhakaza, L.; Pearce, B.; Mandisa Masilela, C.; Benjeddou, M.; Vincent Adeniyi, O.; Johnson, R.; Jebio Ongole, J. Genetic Association of Solute Carrier Transporter Gene Variants with Metformin Response. Balk. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 24, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygiel-Górniak, B.; Mosor, M.; Marcinkowska, J.; Przysławski, J.; Nowak, J. Impact of the PPAR Gamma-2 Gene Polymorphisms on the Metabolic State of Postmenopausal Women. J. Biosci. 2016, 41, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntean, C.; Sasaran, M.O.; Crisan, A.; Banescu, C. Effects of PPARG and PPARGC1A Gene Polymorphisms on Obesity Markers. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 962852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Gómez, L.E.; Cruz, M.; Martínez-Nava, G.A.; Madrid-Marina, V.; Parra, E.; García-Mena, J.; Espinoza-Rojo, M.; Estrada-Velasco, B.I.; Piza-Roman, L.F.; Aguilera, P.; et al. A Replication Study of the IRS1, CAPN10, TCF7L2, and PPARG Gene Polymorphisms Associated with Type 2 Diabetes in Two Different Populations of Mexico: IRS1, CAPN10, TCF7L2, and PPARG Polymorphisms and T2D in Mexico Population. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2011, 75, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, A.G.; Chistiakov, D.A.; Minushkina, L.O.; Zateyshchikov, D.A.; Nosikov, V.V. Association of the CYBA, PPARGC1A, PPARG3, and PPARD Gene Variants with Coronary Artery Disease and Metabolic Risk Factors of Coronary Atherosclerosis in a Russian Population. Heart Vessels 2010, 25, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales-Reynoso, M.A.; Wence-Chavez, L.I.; Arredondo-Valdez, A.R.; Dumois-Petersen, S.; Barros-Núñez, P.; Gallegos-Arreola, M.P.; Flores-Martínez, S.E.; Sánchez-Corona, J. Protective Role of +294 T/C (Rs2016520) Polymorphism of PPARD in Mexican Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Genet. Mol. Res. 2017, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.-L.; Yin, R.-X.; Miao, L.; Wu, D.-F. The Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Delta +294T > C Polymorphism and Alcohol Consumption on Serum Lipid Levels. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Rakhis, S.A.; AlDuwayhis, N.M.; Aleid, N.; AlBarrak, A.N.; Aloraini, A.A. Glycemic Control for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e26180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basto-Abreu, A.C.; López-Olmedo, N.; Rojas-Martínez, R.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; De La Cruz-Góngora, V.V.; Rivera-Dommarco, J.; Shamah-Levy, T.; Romero-Martínez, M.; Barquera, S.; Villalpando, S.; et al. Prevalence of Diabetes and Glycemic Control in Mexico: National Results from 2018 and 2020. Salud Pública México 2021, 63, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Yan, L.; Lei, Y. The Relationship between High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C) and Glycosylated Hemoglobin in Diabetic Patients Aged 20 or above: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suprapti, B.; Izzah, Z.; Anjani, A.G.; Andarsari, M.R.; Nilamsari, W.P.; Nugroho, C.W. Prevalence of Medication Adherence and Glycemic Control among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Influencing Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study. Glob. Epidemiol. 2023, 5, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social. Diagnóstico y Tratamiento Farmacológico de la Diabetes Mellitus Tipo 2 en el Primer Nivel de Atención. Guía de Evidencias y Recomendaciones: Guía de Práctica Clínica; Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social: Cd. de Mexico, Mexico, 2018; pp. 1–55.
- World Health Organization Global Report on Diabetes; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-92-4-156525-7.
- Saleh, R.; Zahid, Z.I.; Rahman, M.A.; Jain, P.; Alam, A.; Kawaichi, M.; Reza, H.M. Prevalence of PPAR-Γ2 (Rs1801282), RETN (Rs3745367) and ADIPOQ (Rs2241766) SNP Markers in the Bangladeshi Type 2 Diabetic Population. Meta Gene 2016, 10, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, J.; Song, M.; Zheng, Y.; Mo, Z.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Z. PPAR-Γ2 and PTPRD Gene Polymorphisms Influence Type 2 Diabetes Patients’ Response to Pioglitazone in China. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarbrick, M.M.; Chapman, C.M.; McQuillan, B.M.; Hung, J.; Thompson, P.L.; Beilby, J.P. A Pro12Ala Polymorphism in the Human Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-Gamma 2 Is Associated with Combined Hyperlipidaemia in Obesity. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2001, 144, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Potapov, V.A.; Khodirev, D.S.; Shamkhalova, M.S.; Shestakova, M.V.; Nosikov, V.V. The PPARγ Pro12Ala Variant Is Associated with Insulin Sensitivity in Russian Normoglycaemic and Type 2 Diabetic Subjects. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 2010, 7, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saremi, L. Association between PRO12ALa Polymorphism of PARγ2 Gene and Coronary Artery Disease in Iranian Population with Type Two Diabetes Mellitus. Acta Endocrinol. Buchar. 2022, 18, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Li, N.; Hu, R.; Yu, Y.; Xu, K.; Ling, H.; Lu, Q.; Yang, T.; Wang, T.; Yin, X. Effects of PPARD Gene Variants on the Therapeutic Responses to Exenatide in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 949990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, C.; Nie, H.; Pang, Q.; Wang, R.; Zeng, Z.; Song, Y. G Allele of the Rs1801282 Polymorphism in PPARγ Gene Confers an Increased Risk of Obesity and Hypercholesterolemia, While T Allele of the Rs3856806 Polymorphism Displays a Protective Role Against Dyslipidemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 919087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeb, S.S.; Fajas, L.; Nemoto, M.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Mykkänen, L.; Kuusisto, J.; Laakso, M.; Fujimoto, W.; Auwerx, J. A Pro12Ala Substitution in PPARgamma2 Associated with Decreased Receptor Activity, Lower Body Mass Index and Improved Insulin Sensitivity. Nat. Genet. 1998, 20, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaki, M.; Matsuda, M.; Maeda, N.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Makishima, M.; Shimomura, I. Induction of Adiponectin, a Fat-Derived Antidiabetic and Antiatherogenic Factor, by Nuclear Receptors. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, S.; Argmann, C.; Feige, J.N.; Koutnikova, H.; Champy, M.-F.; Dali-Youcef, N.; Schadt, E.E.; Laakso, M.; Auwerx, J. The Pro12Ala PPARγ2 Variant Determines Metabolism at the Gene-Environment Interface. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavinasab, F.; Tähtinen, T.; Jokelainen, J.; Koskela, P.; Vanhala, M.; Oikarinen, J.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Laakso, M. Effect of the Pro12Ala Polymorphism of the PPARγ2 Gene on Serum Adiponectin Changes. Endocrine 2005, 27, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska-Skrendo, A.; Massidda, M.; Tocco, F.; Leźnicka, K. The Influence of the Differentiation of Genes Encoding Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors and Their Coactivators on Nutrient and Energy Metabolism. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skogsberg, J.; Kannisto, K.; Cassel, T.N.; Hamsten, A.; Eriksson, P.; Ehrenborg, E. Evidence That Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptor Delta Influences Cholesterol Metabolism in Men. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolehmainen, M.; Uusitupa, M.I.J.; Alhava, E.; Laakso, M.; Vidal, H. Effect of the Pro12Ala Polymorphism in the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR) Γ2 Gene on the Expression of PPARγ Target Genes in Adipose Tissue of Massively Obese Subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leońska-Duniec, A.; Cieszczyk, P.; Jastrzębski, Z.; Jażdżewska, A.; Lulińska-Kuklik, E.; Moska, W.; Ficek, K.; Niewczas, M.; Maciejewska-Skrendo, A. The Polymorphisms of the PPARD Gene Modify Post-Training Body Mass and Biochemical Parameter Changes in Women. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsgaard, C.T.; Vuholm, S.; Teisen, M.N.; Stark, K.D.; Lauritzen, L. Does Polymorphisms in PPAR and APOE Genes Modify Associations between Fatty Acid Desaturase (FADS), n-3 Long-Chain PUFA and Cardiometabolic Markers in 8–11-Year-Old Danish Children? Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loera Morales, J., III; Martínez Bautista, H.; Torres Yañez, E.E.; Almazán Orta, L.; Vázquez Martínez, V.H. Prevalencia y factores asociados a adherencia terapéutica de pacientes con diabetes mellitus 2: Post pandemia por COVID 19. Arch. En Med. Fam. 2023, 25, 235–245. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía, (INEGI) Censo de Población y Vivienda 2020. Derechohabiencia. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/temas/derechohabiencia/ (accessed on 20 November 2023).

| SNP | Sequence | Major Alelle Genotype | Heterozygous Genotype | Minor Alelle Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1801282 | P1: 5′-GTGTATCAGTGAAGGAATCGCTTTCTTG-3 P2: 5′-TTGTGATATGTTTGCAGACAAGGTATCAG TGAAGGAATCGCTTTGTGC-3′ P3: 5′-TTTCTGTGTTTATTCCCATCTCTCCC-3′ | 230 bp | 230 and 250 bp | 250 bp |
| rs2016520 | F: 5′-CATGGTATAGCACTGCAGGAA-3′ R: 5′-CTTCCTCCTGTGGCTGCTC-3′ | 269 bp | 269, 167, and 102 bp | 167 and 102 bp |
| PPAR-γ2 rs1801282 | PPAR-β/δ rs2016520 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Genotype n (%) | CC 238 (76.77) | CG 67 (21.61) | GG 5 (1.61) | H-WE p | TT 231 (73.57) | TC 79 (25.16) | CC 4 (1.27) | H-WE p |
| 0.99 | 0.63 | |||||||
| Allele | C | G | T | C | ||||
| n | 543 | 77 | 541 | 87 | ||||
| (%) | (87.58) | (12.42) | (86.15) | (13.85) | ||||
| Variable | PPAR-γ2 rs1801282 | PPAR-β/δ rs2016520 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC (n = 238) Md (IQR) | CG + GG (n = 73) Md (IQR) | p | TT (n = 231) Md (IQR) | TC + CC (n = 83) Md (IQR) | p | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 31 (27–35) | 31 (28–33) | 0.768 | 31 (27–35) | 32 (28–35) | 0.238 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 101 (95–110) | 106 (99–115) | 0.029 | 100 (95–110) | 103 (100–115) | 0.052 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 144 (114–179) | 157 (127–207) | 0.026 | 145 (117–177) | 158 (125–195) | 0.089 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7 (6–9) | 8 (6–10) | 0.057 | 7 (6–9) | 8 (6–10) | 0.080 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 177 (126–235) | 181 (138–254) | 0.250 | 174 (124–227) | 190 (155–282) | 0.026 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 194 (164–220) | 192 (168–218) | 0.838 | 193 (165–217) | 189 (163–226) | 0.526 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 44 (36–54) | 47 (38–56) | 0.260 | 44 (37–54) | 46 (37–56) | 0.457 |
| LDL-C (mg/d L) | 110 (80–134) | 99 (73–132) | 0.224 | 109 (79–132) | 103 (65–140) | 0.671 |
| VLDL (mg/dL) | 35 (25–47) | 36 (28–51) | 0.250 | 35 (25–45) | 38 (31–56) | 0.026 |
| TC/HDL-C index | 4 (3–5) | 4 (3–5) | 0.303 | 4 (3–5) | 4 (3–5) | 0.964 |
| Variable | Dominant Model n = 213 | Over-Dominant Model n = 213 |
|---|---|---|
| β (95%CI) p | β (95%CI) p | |
| PPAR-γ2 rs1801282 | 0.09 (0.02, 0.16) a 0.011 | 0.08 (0.01, 0.16) c 0.020 |
| PPAR-β/δ rs2016520 | 0.10 (0.03, 0.16) b 0.005 | 0.10 (0.04, 0.17) d 0.003 |
| Body mass index e | ||
| Overweight | −0.11 (−0.21, −0.006) 0.038 | −0.11 (−0.21, −0.005) 0.041 |
| Obesity grade I | −0.15 (−0.25, −0.05) 0.004 | −0.15 (−0.25, −0.04) 0.005 |
| Obesity grade II | −0.11 (−0.22, 0.01) 0.064 | −0.11 (−0.22, 0.01) 0.066 |
| Obesity grade III | −0.18 (−0.31, −0.05) 0.005 | −0.18 (−0.31, −0.05) 0.006 |
| Age at the time ofT2D diagnosis (years) | −0.01 (−0.01, −0.004) <0.001 | −0.01 (−0.01, −0.004) <0.001 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | −0.003 (−0.005, −0.0004) 0.020 | −0.003 (−0.005, −0.0003) 0.024 |
| Variable | PPAR-γ2 rs1801282-CC & PPAR-β/δ rs2016520-TT n = 168 | PPAR-γ2 rs1801282-CG + GG & PPAR-β/δ rs2016520-TT n = 61 | PPAR-γ2 rs1801282-CC & PPAR-β/δ rs2016520-TC + CC n = 50 | PPAR-γ2 rs1801282-CG + GG & PPAR-β/δ rs2016520-TC + CC n = 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β (95%CI) p | β (95%CI) p | β (95%CI) p | β (95%CI) p | |
| Body mass index | ||||
| Overweight | 0.23 (0.013, 0.454) 0.038 | 0.31 (−0.457, 1.072) 0.422 | 0.44 (−0.008, 0.890) 0.054 | 0.49 (−0.257, 1.242) 0.174 |
| Obesity class I | 0.26 (0.038, 0.474) 0.022 | 0.27 (−0.500, 1.048) 0.479 | 0.24 (−0.205, 0.690) 0.282 | 0.93 (0.263, 1.598) 0.011 |
| Obesity class II | 0.28 (0.030, 0.521) 0.028 | 0.17 (−0.658, 1.004) 0.677 | 0.18 (−0.307, 0.672) 0.458 | 0.99 (0.247, 1.726) 0.014 |
| Obesity class III | 0.19 (−0.093, 0.470) 0.187 | −0.03 (−0.970, 0.914) 0.952 | 0.52 (−0.108, 1.144) 0.103 | 0.18 (−0.577, 0.946) 0.600 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 0.002 (0.00, 0.003) 0.005 | 0.00 (−0.002, 0.002) 0.983 | 0.004 (0.002, 0.005) <0.001 | 0.002 (0.00, 0.004) 0.033 |
| Adj R2 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.61 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reza-López, S.A.; González-Gurrola, S.; Morales-Morales, O.O.; Moreno-González, J.G.; Rivas-Gómez, A.M.; González-Rodríguez, E.; Moreno-Brito, V.; Licón-Trillo, A.; Leal-Berumen, I. Metabolic Biomarkers in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: The Role of PPAR-γ2 and PPAR-β/δ Polymorphisms. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13121791
Reza-López SA, González-Gurrola S, Morales-Morales OO, Moreno-González JG, Rivas-Gómez AM, González-Rodríguez E, Moreno-Brito V, Licón-Trillo A, Leal-Berumen I. Metabolic Biomarkers in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: The Role of PPAR-γ2 and PPAR-β/δ Polymorphisms. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(12):1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13121791
Chicago/Turabian StyleReza-López, Sandra A., Susana González-Gurrola, Oscar O. Morales-Morales, Janette G. Moreno-González, Ana M. Rivas-Gómez, Everardo González-Rodríguez, Verónica Moreno-Brito, Angel Licón-Trillo, and Irene Leal-Berumen. 2023. "Metabolic Biomarkers in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: The Role of PPAR-γ2 and PPAR-β/δ Polymorphisms" Biomolecules 13, no. 12: 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13121791
APA StyleReza-López, S. A., González-Gurrola, S., Morales-Morales, O. O., Moreno-González, J. G., Rivas-Gómez, A. M., González-Rodríguez, E., Moreno-Brito, V., Licón-Trillo, A., & Leal-Berumen, I. (2023). Metabolic Biomarkers in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: The Role of PPAR-γ2 and PPAR-β/δ Polymorphisms. Biomolecules, 13(12), 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13121791