Amantadine Combines Astroglial System Xc− Activation with Glutamate/NMDA Receptor Inhibition
Abstract
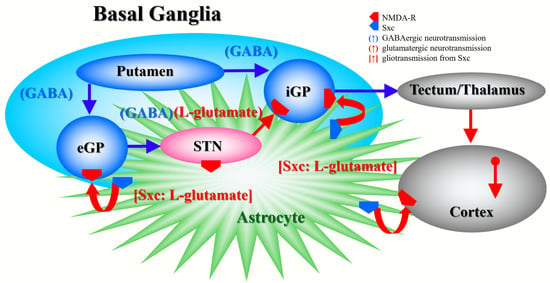
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Agents
2.2. Preparation of Microdialysis System
2.3. Preparation of Primary Astrocyte Culture
2.4. UHPLC and UHPLC/MS
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Microdialysis Study
3.1.1. Effects of Systemic Administration of MK801 and AMA on Extracellular L-glutamate Levels in the Globus Pallidus, Entorhinal Cortex and Entopeduncular Nucleus.
3.1.2. Effects of Local Administration of NAC and CPG into the Globus Pallidus, Entorhinal Cortex and Entopeduncular Nucleus on Extracellular L-glutamate Levels.
3.1.3. Interaction between Local Administration of AMA and CPG into the Globus Pallidus, Entorhinal Cortex and Entopeduncular Nucleus on L-glutamate Release.
3.1.4. Interaction between Local Administration of AMA and YM298198 into the Globus Pallidus, Entorhinal Cortex and Entopeduncular Nucleus on L-glutamate Release.
3.2. Primary Cultured Astrocyte Study
3.2.1. Acute Effects of AMA on Astroglial Sxc Activity.
3.2.2. Effects of AMA Administration for 7 Days on Intra-Astroglial Glutathione Level.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of AMA and MK801 on L-glutamate Release in the Globus Pallidus, Entorhinal Cortex and Entopeduncular Nucleus
4.2. Effects of AMA on Sxc Associated Transmission
4.3. Effects of AMA on CO-Induced Astroglial Damage
4.4. Clinical Implications of AMA Administration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciampor, F.; Bayley, P.M.; Nermut, M.V.; Hirst, E.M.; Sugrue, R.J.; Hay, A.J. Evidence that the amantadine-induced, m2-mediated conversion of influenza a virus hemagglutinin to the low ph conformation occurs in an acidic trans golgi compartment. Virology 1992, 188, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanpied, T.A.; Clarke, R.J.; Johnson, J.W. Amantadine inhibits nmda receptors by accelerating channel closure during channel block. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 3312–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerauer, C.; Rebernik, P.; Reither, H.; Nanoff, C.; Pifl, C. The noradrenaline transporter as site of action for the anti-parkinson drug amantadine. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 1708–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.F.; Kukkle, P.L.; Merello, M.; Lim, S.Y.; Poon, Y.Y.; Moro, E. Amantadine improves gait in pd patients with stn stimulation. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, J.; Katz, D.; Long, D.; DiPasquale, M.C.; Polansky, M.; Kalmar, K.; Giacino, J.; Childs, N.; Mercer, W.; Novak, P.; et al. Predictors of outcome in prolonged posttraumatic disorders of consciousness and assessment of medication effects: A multicenter study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacino, J.T.; Whyte, J.; Bagiella, E.; Kalmar, K.; Childs, N.; Khademi, A.; Eifert, B.; Long, D.; Katz, D.I.; Cho, S.; et al. Placebo-controlled trial of amantadine for severe traumatic brain injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Kawano, Y.; Shiroyama, T.; Ueda, Y. Memantine protects thalamocortical hyper-glutamatergic transmission induced by nmda receptor antagonism via activation of system xc−. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2019, 7, e00457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, T.; Iwata, N. Nmda receptor antagonists interventions in schizophrenia: Meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 47, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, F.; Mohammad-Karimi, M.; Seddighi, S.; Modabbernia, A.; Ashrafi, M.; Salehi, B.; Hammidi, S.; Motasami, H.; Hajiaghaee, R.; Tabrizi, M.; et al. Memantine add-on to risperidone for treatment of negative symptoms in patients with stable schizophrenia: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 33, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sani, G.; Serra, G.; Kotzalidis, G.D.; Romano, S.; Tamorri, S.M.; Manfredi, G.; Caloro, M.; Telesforo, C.L.; Caltagirone, S.S.; Panaccione, I.; et al. The role of memantine in the treatment of psychiatric disorders other than the dementias: A review of current preclinical and clinical evidence. CNS Drugs 2012, 26, 663–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javitt, D.C. Negative schizophrenic symptomatology and the PCP (phencyclidine) model of schizophrenia. Hillside J. Clin. Psychiatry 1987, 9, 12–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moghaddam, B.; Adams, B.W. Reversal of phencyclidine effects by a group ii metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist in rats. Science 1998, 281, 1349–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinney, G.G.; Burno, M.; Campbell, U.C.; Hernandez, L.M.; Rodriguez, D.; Bristow, L.J.; Conn, P.J. Metabotropic glutamate subtype 5 receptors modulate locomotor activity and sensorimotor gating in rodents. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 306, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapado-Castro, M.; Dodd, S.; Bush, A.I.; Malhi, G.S.; Skvarc, D.R.; On, Z.X.; Berk, M.; Dean, O.M. Cognitive effects of adjunctive n-acetyl cysteine in psychosis. Psychol. Med. 2017, 47, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.; Paskavitz, J.; Remington, R.; Rasmussen, S.; Shea, T.B. Efficacy of a vitamin/nutriceutical formulation for early-stage Alzheimer’s disease: A 1-year, open-label pilot study with an 16-month caregiver extension. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Dement. 2008, 23, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewerenz, J.; Hewett, S.J.; Huang, Y.; Lambros, M.; Gout, P.W.; Kalivas, P.W.; Massie, A.; Smolders, I.; Methner, A.; Pergande, M.; et al. The cystine/glutamate antiporter system x(c)(-) in health and disease: From molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 522–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S.P.; Peters, J.A.; Kelly, E.; Marrion, N.V.; Faccenda, E.; Harding, S.D.; Pawson, A.J.; Sharman, J.L.; Southan, C.; Davies, J.A.; et al. The concise guide to pharmacology 2017/18: Ligand-gated ion channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174 (Suppl. 1), S130–S159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S.P.; Kelly, E.; Marrion, N.V.; Peters, J.A.; Faccenda, E.; Harding, S.D.; Pawson, A.J.; Sharman, J.L.; Southan, C.; Davies, J.A.; et al. The concise guide to pharmacology 2017/18: Transporters. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174 (Suppl. 1), S360–S446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.A.; Warren, B.A.; Rhoderick, J.F.; Bridges, R.J. Differentiation of substrate and non-substrate inhibitors of transport system xc(-): An obligate exchanger of l-glutamate and l-cystine. Neuropharmacology 2004, 46, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, J.C.; Lilley, E. Implementing guidelines on reporting research using animals (arrive etc.): New requirements for publication in BJP. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3189–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, K.; Tanahashi, S.; Hoshikawa, M.; Shinagawa, R.; Okada, M. Zonisamide regulates basal ganglia transmission via astroglial kynurenine pathway. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76 Pt A, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, S.; Ohoyama, K.; Nagase, H.; Okada, M. Zonisamide enhances delta receptor-associated neurotransmitter release in striato-pallidal pathway. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Zhu, G.; Yoshida, S.; Hirose, S.; Kaneko, S. Protein kinase associated with gating and closing transmission mechanisms in temporoammonic pathway. Neuropharmacology 2004, 47, 485–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain: In Stereotoxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Academic Press: San Dieg, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuyama, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Okada, M. Cystine/glutamate antiporter and aripiprazole compensate nmda antagonist-induced dysfunction of thalamocortical l-glutamatergic transmission. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Okada, M.; Murakami, T.; Kawata, Y.; Kamata, A.; Kaneko, S. Interaction between carbamazepine, zonisamide and voltage-sensitive ca2+ channel on acetylcholine release in rat frontal cortex. Epilepsy Res. 2002, 49, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Okada, M.; Zhu, G.; Kaneko, S. Effects of zonisamide on neurotransmitter exocytosis associated with ryanodine receptors. Epilepsy Res. 2005, 67, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, K.; Okada, M. Effects of levetiracetam on astroglial release of kynurenine-pathway metabolites. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 4253–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, N.; Shimoda, T.; Manako, J.; Katsumata, S.; Shinagawa, R.; Ohno, H. Relevance of astrocytic activation to reductions of astrocytic gabaa receptors. Brain Res. 2006, 1089, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, S.; Hoshikawa, M.; Dai, K.; Saito, H.; Suzuki, N.; Niwa, O.; Okada, M. Ono-2506 inhibits spike-wave discharges in a genetic animal model without affecting traditional convulsive tests via gliotransmission regulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 1088–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juric, D.M.; Suput, D.; Brvar, M. Hyperbaric oxygen preserves neurotrophic activity of carbon monoxide-exposed astrocytes. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 253, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, B.; Ramadoss, S.; Chaudhuri, G.; Janzen, C.; Sen, S.; Mascharak, P.K. Carbon monoxide sensitizes cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines toward cisplatin via attenuation of levels of glutathione and nuclear metallothionein. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 191, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, S.; Ohoyama, K.; Hamaguchi, T.; Kashimoto, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Kanehara, S.; Suzuki, D.; Matsumoto, T.; Motomura, E.; Shiroyama, T.; et al. Effects of quetiapine on monoamine, gaba, and glutamate release in rat prefrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology 2009, 206, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Kawano, Y.; Shiroyama, T.; Suzuki, D.; Ueda, Y. Effects of acute and sub-chronic administrations of guanfacine on catecholaminergic transmissions in the orbitofrontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafting, T.; Fyhn, M.; Molden, S.; Moser, M.B.; Moser, E.I. Microstructure of a spatial map in the entorhinal cortex. Nature 2005, 436, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saga, Y.; Hoshi, E.; Tremblay, L. Roles of multiple globus pallidus territories of monkeys and humans in motivation, cognition and action: An anatomical, physiological and pathophysiological review. Front. Neuroanat. 2017, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapresle, J.; Fardeau, M. The central nervous system and carbon monoxide poisoning. Ii. Anatomical study of brain lesions following intoxication with carbon monixide (22 cases). Prog. Brain Res. 1967, 24, 31–74. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Eesa, M.; Scott, J.N. Toxic and acquired metabolic encephalopathies: MRI appearance. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 193, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejdak, K.; Nieoczym, D.; Czuczwar, M.; Kis, J.; Wlaz, P.; Turski, W.A. Orphenadrine-induced convulsive status epilepticus in rats responds to the nmda antagonist dizocilpine. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bido, S.; Marti, M.; Morari, M. Amantadine attenuates levodopa-induced dyskinesia in mice and rats preventing the accompanying rise in nigral gaba levels. J. Neurochem. 2011, 118, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.A.; Madayag, A.; Kristiansen, L.V.; Meador-Woodruff, J.H.; Haroutunian, V.; Raju, I. Contribution of cystine-glutamate antiporters to the psychotomimetic effects of phencyclidine. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 1760–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etoga, J.L.; Ahmed, S.K.; Patel, S.; Bridges, R.J.; Thompson, C.M. Conformationally-restricted amino acid analogues bearing a distal sulfonic acid show selective inhibition of system x(c)(-) over the vesicular glutamate transporter. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2680–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, R.A.; Pahwa, R.; Wargin, W.A.; Souza-Prien, C.J.; McClure, N.; Johnson, R.; Nguyen, J.T.; Patni, R.; Went, G.T. Pharmacokinetics of ads-5102 (amantadine) extended release capsules administered once daily at bedtime for the treatment of dyskinesia. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 58, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Okada, M.; Zhu, G.; Kaneko, S. Carbamazepine prevents breakdown of neurotransmitter release induced by hyperactivation of ryanodine receptor. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Yoshida, S.; Zhu, G.; Hirose, S.; Kaneko, S. Biphasic actions of topiramate on monoamine exocytosis associated with both soluble n-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors and ca(2+)-induced ca(2+)-releasing systems. Neuroscience 2005, 134, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohara, A.; Toya, T.; Tamura, S.; Watabiki, T.; Nagakura, Y.; Shitaka, Y.; Hayashibe, S.; Kawabata, S.; Okada, M. Radioligand binding properties and pharmacological characterization of 6-amino-n-cyclohexyl-n,3-dimethylthiazolo[3,2-a]benzimidazole-2-carboxamide (ym-298198), a high-affinity, selective, and noncompetitive antagonist of metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.D.; Kimmey, B.A.; Arreola, A.C.; Pierce, R.C. Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated activation of pkc gamma in the nucleus accumbens core promotes the reinstatement of cocaine seeking. Addict. Biol. 2015, 20, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, S.; Ohoyama, K.; Hamaguchi, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Suzuki, D.; Matsumoto, T.; Motomura, E.; Tanii, H.; Shiroyama, T.; Okada, M. Effects of zotepine on extracellular levels of monoamine, gaba and glutamate in rat prefrontal cortex. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, M.; Yokofujita, J.; Murakami, K. An ultrastructural study of the neural circuit between the prefrontal cortex and the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 54, 417–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisone, G.; Hakansson, K.; Borgkvist, A.; Santini, E. Signaling in the basal ganglia: Postsynaptic and presynaptic mechanisms. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 92, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanahashi, S.; Yamamura, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Motomura, E.; Okada, M. Clozapine, but not haloperidol, enhances glial d-serine and l-glutamate release in rat frontal cortex and primary cultured astrocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 1543–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaki, N.; Nakao, A.; Osako, T.; Nishimura, T.; Yamada, T.; Kohama, K.; Sakata, H.; Ishikawa-Aoyama, M.; Kotani, J. Can carbon monoxide-poisoned victims be organ donors? Med. Gas Res. 2014, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retamal, M.A.; Leon-Paravic, C.G.; Ezquer, M.; Ezquer, F.; Del Rio, R.; Pupo, A.; Martinez, A.D.; Gonzalez, C. Carbon monoxide: A new player in the redox regulation of connexin hemichannels. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, L.K. Clinical practice. Carbon monoxide poisoning. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shprecher, D.; Mehta, L. The syndrome of delayed post-hypoxic leukoencephalopathy. NeuroRehabilitation 2010, 26, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scragg, J.L.; Dallas, M.L.; Wilkinson, J.A.; Varadi, G.; Peers, C. Carbon monoxide inhibits l-type ca2+ channels via redox modulation of key cysteine residues by mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 24412–24419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boycott, H.E.; Dallas, M.L.; Elies, J.; Pettinger, L.; Boyle, J.P.; Scragg, J.L.; Gamper, N.; Peers, C. Carbon monoxide inhibition of cav3.2 t-type ca2+ channels reveals tonic modulation by thioredoxin. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 3395–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elies, J.; Dallas, M.L.; Boyle, J.P.; Scragg, J.L.; Duke, A.; Steele, D.S.; Peers, C. Inhibition of the cardiac na(+) channel nav1.5 by carbon monoxide. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 16421–16429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thom, S.R.; Fisher, D.; Zhang, J.; Bhopale, V.M.; Cameron, B.; Buerk, D.G. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and n-methyl-d-aspartate neurons in experimental carbon monoxide poisoning. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 194, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Paravic, C.G.; Figueroa, V.A.; Guzman, D.J.; Valderrama, C.F.; Vallejos, A.A.; Fiori, M.C.; Altenberg, G.A.; Reuss, L.; Retamal, M.A. Carbon monoxide (co) is a novel inhibitor of connexin hemichannels. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 36150–36157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juric, D.M.; Finderle, Z.; Suput, D.; Brvar, M. The effectiveness of oxygen therapy in carbon monoxide poisoning is pressure- and time-dependent: A study on cultured astrocytes. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 233, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Beppu, T.; Fujisawa, Y.; Onodera, M.; Ogasawara, K.; Sasaki, M.; Ehara, S.; Sakai, A.; Endo, S. Effect of free radical scavenger, edaravone, for patients with carbon monoxide poisoning. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2015, 139, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penton-Rol, G.; Lagumersindez-Denis, N.; Muzio, L.; Bergami, A.; Furlan, R.; Fernandez-Masso, J.R.; Nazabal-Galvez, M.; Llopiz-Arzuaga, A.; Herrera-Rolo, T.; Veliz-Rodriguez, T.; et al. Comparative neuroregenerative effects of c-phycocyanin and ifn-beta in a model of multiple sclerosis in mice. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, R.J.; Natale, N.R.; Patel, S.A. System xc(-) cystine/glutamate antiporter: An update on molecular pharmacology and roles within the cns. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evonuk, K.S.; Baker, B.J.; Doyle, R.E.; Moseley, C.E.; Sestero, C.M.; Johnston, B.P.; De Sarno, P.; Tang, A.; Gembitsky, I.; Hewett, S.J.; et al. Inhibition of system xc(-) transporter attenuates autoimmune inflammatory demyelination. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janaky, R.; Ogita, K.; Pasqualotto, B.A.; Bains, J.S.; Oja, S.S.; Yoneda, Y.; Shaw, C.A. Glutathione and signal transduction in the mammalian cns. J. Neurochem. 1999, 73, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, V.; Jenei, Z.; Janaky, R.; Saransaari, P.; Oja, S.S. Glutathione is an endogenous ligand of rat brain n-methyl-d-aspartate (nmda) and 2-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate (ampa) receptors. Neurochem. Res. 1997, 22, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakano, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Suzuki, D.; Motomura, E.; Okada, M. Amantadine Combines Astroglial System Xc− Activation with Glutamate/NMDA Receptor Inhibition. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9050191
Nakano T, Hasegawa T, Suzuki D, Motomura E, Okada M. Amantadine Combines Astroglial System Xc− Activation with Glutamate/NMDA Receptor Inhibition. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(5):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9050191
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakano, Tomosuke, Toshiki Hasegawa, Dai Suzuki, Eishi Motomura, and Motohiro Okada. 2019. "Amantadine Combines Astroglial System Xc− Activation with Glutamate/NMDA Receptor Inhibition" Biomolecules 9, no. 5: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9050191
APA StyleNakano, T., Hasegawa, T., Suzuki, D., Motomura, E., & Okada, M. (2019). Amantadine Combines Astroglial System Xc− Activation with Glutamate/NMDA Receptor Inhibition. Biomolecules, 9(5), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9050191