Calcium Oxalate Crystals in Leaves of the Extremophile Plant Colobanthus quitensis (Kunth) Bartl. (Caryophyllaceae)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
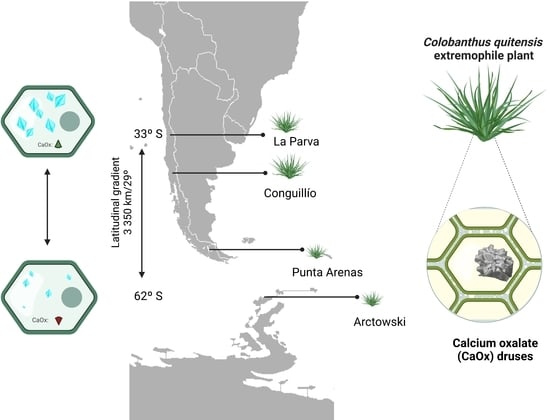
2.1. Differences in Colobanthus quitensis Provenances
2.2. CaOx Crystal Presence in C. quitensis Leaves
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
3.2. Chlorophyll Fluorescence
3.3. CaOx Crystals Measurements in the Leaves
3.4. Electron Microscopy
3.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pueschel, C.M. Calcium oxalate mineralisation in the algae. Phycologia 2019, 58, 331–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooulakou, G.; Giannopoulos, A.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Bresta, P.; Dotsika, E.; Orkoula, M.G.; Kontoyiannis, C.G.; Fasseas, C.; Liakopoulos, G.; Klapa, M.I.; et al. “Alarm photosynthesis”: Calcium oxalate crystals as an internal CO2 source in plants. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2577–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franceschi, V.R.; Nakata, P.A. Calcium oxalate in plants: Formation and Function. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2005, 56, 41–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, É.A.S. Do calcium oxalate crystals protect against herbivory? Sci. Nat. 2021, 108, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, V.; Horner, H.T.; Khan, I.A. New and unusual forms of calcium oxalate raphide crystals in the plant kingdom. J. Plant Res. 2014, 127, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webb, M.A. Cell-mediated crystallization of calcium oxalate in plants. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, R.; Shivay, Y.S. Oxalic acid/oxalates in plants: From self-defence to phytoremediation. Curr. Sci. 2017, 112, 1665–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, W.P.; Klapper, H.; Barbier, B.; Ensikat, H.J.; Dronskowski, R.; Müller, P.; Ostendorp, G.; Tye, A.; Bauer, R.; Barthlott, W. Diversity of calcium oxalate crystals in Cactaceae. Can. J. Bot. 2007, 85, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, E.A.S. Are calcium oxalate crystals a dynamic calcium store in plants? New Phytol. 2019, 223, 1707–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karabourniotis, G.; Horner, H.T.; Bresta, P.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Liakopoulos, G. New insights into the functions of carbon–calcium inclusions in plants. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Espinoza, O.; González-Ramírez, D.; Bresta, P.; Karabourniotis, G.; Bravo, L.A. Decomposition of calcium oxalate crystals in Colobanthus quitensis under CO2 limiting conditions. Plants 2020, 9, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuba-Díaz, M.; Cerda, G.; Rivera, C.; Gómez, A. Genome size comparison in Colobanthus quitensis populations show differences in species ploidy. Polar Biol. 2017, 40, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulc’h, P.-N.; Caullireau, E.; Faucher, E.; Gouerou, M.; Guérin, A.; Miray, R.; Couée, I. Abiotic stress signalling in extremophile land plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 5771–5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarrete-Gallegos, A.; Bravo, L.A.; Molina-Montenegro, M.A.; Corcuera, L.J. Respuestas antioxidantes en dos ecotipos de Colobanthus quitensis (Caryophyllaceae) expuestos a alta radiación UV-B y baja temperatura. Rev. Chil. Hist. Nat. 2012, 85, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gianoli, E.; Inostroza, P.; Zúñiga-Feest, A.; Reyes-Díaz, M.; Cavieres, L.A.; Bravo, L.A.; Corcuera, L.J. Ecotypic differentiation in morphology and cold resistance in populations of Colobanthus quitensis (Caryophyllaceae) from the Andes of central Chile and the maritime Antarctic. Arct. Antarct Alp. Res. 2004, 36, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuba-Díaz, M.; Acuña, D.; Fuentes-Lillo, E. Antarctic pearlwort (Colobanthus quitensis) populations respond differently to pre-germination treatments. Polar Biol. 2019, 42, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuba-Díaz, M.; Rivera-Mora, C.; Navarrete, E.; Klagges, M. Advances of native and non-native Antarctic species to in vitro conservation: Improvement of disinfection protocols. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, J.; Androsiuk, P.; Chwedorzewska, K.J.; Cuba-Díaz, M.; Górecki, R.; Giełwanowska, I. Range-wide pattern of genetic variation in Colobanthus Quitensis. Polar Biol. 2018, 41, 2467–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, G.; Marticorena, A.; Rodriguez, R.; Larrain, A. Estudio anatómico del tallo y hoja de Colobanthus quitensis (Kunth) Bartl. en isla Rey Jorge, Antártica. Ser. Cient. Ina. 1994, 44, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sáez, P.L.; Bravo, L.A.; Cavieres, L.A.; Vallejos, V.; Sanhueza, C.; Font-Carrascosa, M.; Gil-Pelegrín, E.; Javier Peguero-Pina, J.; Galmés, J. Photosynthetic limitations in two Antarctic vascular plants: Importance of leaf anatomical traits and Rubisco kinetic parameters. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2871–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavieres, L.A.; Sáez, P.; Sanhueza, C.; Sierra-Almeida, A.; Rabert, C.; Corcuera, L.J.; Alberdi, M.; Bravo, L.A. Ecophysiological traits of Antarctic vascular plants: Their importance in the responses to climate change. Plant Ecol. 2016, 217, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuba-Díaz, M.; Klagges, M.; Fuentes-Lillo, E.; Cordero, C.; Acuña, D.; Opazo, G.; Troncoso-Castro, J.M. Phenotypic variability and genetic differentiation in continental and island populations of Colobanthus quitensis (Caryophyllaceae: Antarctic pearlwort). Polar Biol. 2017, 41, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mantovani, A.; Vieira, R.C. Leaf micromorphology of Antarctic pearlwort Colobanthus quitensis (Kunth) Bartl. Polar Biol. 2000, 23, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Almeida, Á.; Casanova-Katny, M.A.; Bravo, L.A.; Corcuera, L.J.; Cavieres, L.A. Photosynthetic responses to temperature and light of Antarctic and Andean populations of Colobanthus quitensis (Caryophyllaceae). Rev. Chil. Hist. Nat. 2007, 80, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, L.A.; Saavedra-Mella, F.A.; Vera, F.; Guerra, A.; Cavieres, L.A.; Ivanov, A.G.; Huner, N.P.A.; Corcuera, L.J. Effect of cold acclimation on the photosynthetic performance of two ecotypes of Colobanthus quitensis (Kunth) Bartl. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 3581–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Moreno, M.J.; Omranian, N.; Sáez, P.; Figueroa, C.M.; Del-Saz, N.; Elso, M.; Poblete, L.; Orf, I.; Cuadros-Inostroza, A.; Cavieres, L.; et al. Cytochrome respiration pathway and sulphur metabolism sustain stress tolerance to low temperature in the Antarctic species Colobanthus quitensis. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova-Katny, M.A.; Bravo, L.A.; Molina-Montenegro, M.; Corcuera, L.J.; Cavieres, L.A. Photosynthetic performance of Colobanthus quitensis (Kunth) Bartl. (Caryophyllaceae) in a high-elevation site of the Andes of central Chile. Rev. Chil. Hist. Nat. 2006, 79, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascuñán-Godoy, L.; García-Plazaola, J.I.; Bravo, L.A.; Corcuera, L.J. Leaf functional and micro-morphological photoprotective attributes in two ecotypes of Colobanthus quitensis from the Andes and Maritime Antarctic. Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Ge, C.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q. Expression analysis of oxalate metabolic pathway genes reveals oxalate regulation patterns in spinach. Molecules 2018, 23, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakata, P.A.; McConn, M. Isolated Medicago truncatula mutants with increased calcium oxalate crystal accumulation have decreased ascorbic acid levels. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 45, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, P.A.; McConn, M. Genetic evidence for differences in the pathways of druse and prismatic calcium oxalate crystal formation in Medicago truncatula. Funct. Plant Biol. 2007, 34, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Villemereuil, P.; Gaggiotti, O.E.; Goudet, J. Common garden experiments to study local adaptation need to account for population structure. J. Ecol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prychid, C.J.; Rudall, P.J. Calcium oxalate crystals in monocotyledons: A review of their structure and systematics. Ann. Bot. 1999, 84, 725–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çinbilgel, İ.; Karadeniz, A.; Gökceoglu, M. Morphological and Anatomical Study on Endemic Saponaria pamphylica Boiss. & Heldr. (Caryophyllaceae). J. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2007, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Tütüncü, S.; Öztürk, N.; Dane, F. Occurrence, types and distribution of calcium oxalate crystals in leaves and stems of some species of poisonous plants. Bot. Stud. 2014, 55, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jianu, L.D.; Bercu, R.; Popoviciu, D.R. Silene thymifolia Sibth. et Sm. (Caryophyllaceae)—A vulnerable species in Romania: Anatomical aspects of vegetative organs. Not. Sci. Biol. 2021, 13, 10875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.L.; Warwick, N.W.M.; Prychid, C.J. Does aridity influence the morphology, distribution and accumulation of calcium oxalate crystals in Acacia (Leguminosae: Mimosoideae)? Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 73, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquation. A Guide to Analysing Rapid Light Curves. Available online: https://aquation.com.au/white-papers/a-guide-to-analyzing-rapid-light-curves/ (accessed on 9 July 2021).
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karnovsky, M.J. A Formaldehyde-Glutaraldehyde Fixative of High Osmolality for Use in Electron Microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 1965, 27, 137-8A. [Google Scholar]
- Love, J.; Selker, R.; Marsman, M.; Jamil, T.; Dropmann, D.; Verhagen, J.; Ly, A.; Gronau, Q.F.; Šmíra, M.; Epskamp, S.; et al. JASP: Graphical Statistical Software for Common Statistical Designs. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 88, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez-Espinoza, O.; González-Ramírez, D.; Méndez-Gómez, J.; Guillén-Watson, R.; Medaglia-Mata, A.; Bravo, L.A. Calcium Oxalate Crystals in Leaves of the Extremophile Plant Colobanthus quitensis (Kunth) Bartl. (Caryophyllaceae). Plants 2021, 10, 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091787
Gómez-Espinoza O, González-Ramírez D, Méndez-Gómez J, Guillén-Watson R, Medaglia-Mata A, Bravo LA. Calcium Oxalate Crystals in Leaves of the Extremophile Plant Colobanthus quitensis (Kunth) Bartl. (Caryophyllaceae). Plants. 2021; 10(9):1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091787
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez-Espinoza, Olman, Daniel González-Ramírez, Jairo Méndez-Gómez, Rossy Guillén-Watson, Alejandro Medaglia-Mata, and León A. Bravo. 2021. "Calcium Oxalate Crystals in Leaves of the Extremophile Plant Colobanthus quitensis (Kunth) Bartl. (Caryophyllaceae)" Plants 10, no. 9: 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091787
APA StyleGómez-Espinoza, O., González-Ramírez, D., Méndez-Gómez, J., Guillén-Watson, R., Medaglia-Mata, A., & Bravo, L. A. (2021). Calcium Oxalate Crystals in Leaves of the Extremophile Plant Colobanthus quitensis (Kunth) Bartl. (Caryophyllaceae). Plants, 10(9), 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091787