The Effect of Humic Acid and Polystyrene Fluorescence Nanoplastics on Solanum lycopersicum Environmental Behavior and Phytotoxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
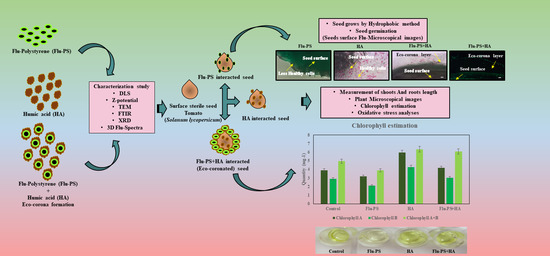
2. Results
2.1. Characterization Study
2.1.1. Particle Size
2.1.2. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
2.1.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR)
2.1.4. Three-Dimensional Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis
2.1.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.2. Effect of Flu−PS, HA, and Flu−PS+HA on Solanum lycopersicum (Seeds)
2.2.1. Seed Imaging by Fluorescence Optical Microscopy
2.2.2. Seed Germination
2.3. Effect of PS, HA, and PS+HA on Solanum lycopersicum (Plants)
2.3.1. Shoot and Root Length
2.3.2. Plant Imaging by Optical Microscopy
2.3.3. Photosynthetic Pigment Estimation
2.4. Oxidative Stress Analysis
2.4.1. ROS Production
2.4.2. Effects on Superoxide Dismutase Activity
2.4.3. Effects on Catalase Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Seed Collection
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Characterization Study
4.3.1. Particle Size Determination
4.3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.3.3. FTIR-Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
4.3.4. Three-Dimensional Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis
4.3.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
4.4. Seeds and Plant Growth
4.5. Plant Physiology
Photosynthetic Pigment Measurement
4.6. Oxidative Stress Analysis
4.6.1. Sample Preparation for Oxidative Stress Analysis
4.6.2. Overall Reactive Oxygen Species
4.6.3. Superoxide Dismutase
4.6.4. Catalase
4.6.5. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, R.C.; Olson, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at Sea: Where Is All the Plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabi, O.A.; Ologbonjaye, K.I.; Awosolu, O.; Alalade, O.E. Public and Environmental Health Effects of Plastic Wastes Disposal: A Review. J. Toxicol. Risk Assess. 2019, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Microplastic–an Emerging Contaminant of Potential Concern? Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2007, 3, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Yang, X.; Pelaez, A.M.; Huerta Lwanga, E.; Beriot, N.; Gertsen, H.; Garbeva, P.; Geissen, V. Macro- and Micro- Plastics in Soil-Plant System: Effects of Plastic Mulch Film Residues on Wheat (Triticum Aestivum) Growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, N. Mechanistic Implications of Plastic Degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 561–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Machado, A.A.; Lau, C.W.; Kloas, W.; Bergmann, J.; Bachelier, J.B.; Faltin, E.; Becker, R.; Görlich, A.S.; Rillig, M.C. Microplastics Can Change Soil Properties and Affect Plant Performance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6044–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the Marine Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Shim, W.J. Nanoplastics in the Aquatic Environment. Critical Review. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 325–340. ISBN 9783319165103. [Google Scholar]
- Botterell, Z.L.R.; Beaumont, N.; Dorrington, T.; Steinke, M.; Thompson, R.C.; Lindeque, P.K. Bioavailability and Effects of Microplastics on Marine Zooplankton: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, S.I.; Arfaioli, P.; Bardelli, T.; Ceccherini, M.T.; Nannipieri, P.; Pietramellara, G. Soil Pollution from Micro-and Nanoplastic Debris: A Hidden and Unknown Biohazard. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, Z.; Wollmann, C.; Schaefer, M.; Buchmann, C.; David, J.; Tröger, J.; Muñoz, K.; Frör, O.; Schaumann, G.E. Plastic Mulching in Agriculture. Trading Short-Term Agronomic Benefits for Long-Term Soil Degradation? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; Agrawal, A.; Dubey, S.; Kumar, J. Role of Decomposers in Agricultural Waste Management. In Biotechnological Applications of Biomass; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, L.A. Soil Organic Matter Forms and Functions. In Encylopedia of Forest Sciences; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yaseen, M.; Kirn, A.; Kashif, S.R.; Yaseen, M. Using Indigenous Humic Acid from Lignite to Increase Growth and Yield of Okra (Abelmoschus Esculentus L.). Soil Environ. 2010, 29, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Sara, T.; Francioso, O.; Quaggiotti, S.; Nardi, S. Humic Substances Biological Activity at the Plant-Soil Interface: From Environmental Aspects to Molecular Factors. Plant Signal Behav. 2010, 5, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Anthal, R. Humic Substances in Aquatic Ecosystems: A Review. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2007, 3297, 18462–18470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asli, S.; Neumann, P.M. Rhizosphere Humic Acid Interacts with Root Cell Walls to Reduce Hydraulic Conductivity and Plant Development. Plant Soil 2010, 336, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galambos, N.; Compant, S.; Moretto, M.; Sicher, C.; Puopolo, G.; Wäckers, F.; Sessitsch, A.; Pertot, I.; Perazzolli, M. Humic Acid Enhances the Growth of Tomato Promoted by Endophytic Bacterial Strains Through the Activation of Hormone-, Growth-, and Transcription-Related Processes. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 582267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Yao, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; He, B.; Hu, L.; Shi, J.; et al. Role of Protein Corona in the Biological Effect of Nanomaterials: Investigating Methods. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadare, O.O.; Wan, B.; Guo, L.H.; Xin, Y.; Qin, W.; Yang, Y. Humic Acid Alleviates the Toxicity of Polystyrene Nanoplastic Particles to: Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1466–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, F.; Lynch, I. Secreted Protein Eco-Corona Mediates Uptake and Impacts of Polystyrene Nanoparticles on Daphnia magna. J. Proteom. 2016, 137, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Jiang, R.; You, J.; Muir, D.C.G.; Zeng, E.Y. Microplastic Impacts on Microalgae Growth: Effects of Size and Humic Acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Wu, J.; Xiong, H.; Zeb, A.; Yang, T.; Su, X.; Su, L.; Liu, W. Impact of Polystyrene Nanoplastics (PSNPs) on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Mukherjee, A. Ageing with Algal EPS Reduces the Toxic Effects of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Freshwater Microalgae Scenedesmus Obliquus. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, J.; Kuriyama, Y.; Miyamoto, A.; Tokumoto, H.; Konishi, Y.; Nomura, T. Adhesion and Internalization of Functionalized Polystyrene Latex Nanoparticles toward the Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grassi, G.; Gabellieri, E.; Cioni, P.; Paccagnini, E.; Faleri, C.; Lupetti, P.; Corsi, I.; Morelli, E. Interplay between Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) from a Marine Diatom and Model Nanoplastic through Eco-Corona Formation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umamaheswari, S. FTIR Spectroscopic Study of Fungal Degradation of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) and Polystyrene Foam. Elixir Chem. Engg. 2013, 64, 19159–19164. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Qian, C.; Yu, H.Q. Induced Structural Changes of Humic Acid by Exposure of Polystyrene Microplastics: A Spectroscopic Insight. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könemann, T.; Savage, N.J.; Alex Huffman, J.; Pöhlker, C. Characterization of Steady-State Fluorescence Properties of Polystyrene Latex Spheres Using off- A Nd Online Spectroscopic Methods. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 3987–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niculăescu, C.; Olar, L.; Stefan, R.; Todica, M.; Pop, C.V. XRD and IR Investigations of Some Commercial Polystyrene Samples Thermally Degraded. Stud. Univ. Babes.-Bolyai. Chem. 2018, 63, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Bertoli, A.; Borges, A.C.; Gomes, R.; Garcia, J.; Trevisan, M. New Organomineral Complex from Humic Substances Extracted from Poultry Wastes: Synthesis, Characterization and Controlled Release Study. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2017, 29, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abobatta, W.F.; Mbarki, R. Effect of Humate Compounds and Magnetic Iron on Growth and Fruiting of Valencia Orange Trees (Citrus Sinensis L.). Ph.D. Thesis, Horticulture Research Institute, Giza, Egypt, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, S.; Mukherjee, A. Eco-Corona Reduces the Phytotoxic Effects of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Allium Cepa: Emphasizing the Role of ROS. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 198, 104850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrade da Silva, M.S.R.; de Melo Silveira dos Santos, B.; de Andrade Silva, C.S.R.; de Andrade da Silva, C.S.R.; de Sousa Antunes, L.F.; dos Santos, R.M.; Santos, C.H.B.; Rigobelo, E.C. Humic Substances in Combination With Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria as an Alternative for Sustainable Agriculture. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 719653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, R.O.; Domiciano, G.A.; Alves, W.S.; Melo, A.C.A.; Nogueira, F.C.S.; Canellas, L.P.; Olivares, F.L.; Zingali, R.B.; Soares, M.R. Evaluation of the Effects of Humic Acids on Maize Root Architecture by Label-Free Proteomics Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lian, J.; Liu, W.; Meng, L.; Wu, J.; Chao, L.; Zeb, A.; Sun, Y. Foliar-Applied Polystyrene Nanoplastics (PSNPs) Reduce the Growth and Nutritional Quality of Lettuce (Lactuca Sativa L.). Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meganid, A.S.; Al-Zahrani, H.S.; El-Metwally, M.S. Effect of Humic Acid Application on Growth and Chlorophyll Contents of Common Bean Plants (Phaseolus Vulgaris L.) Under Salinity Stress Conditions. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 4, 2651–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanachi, P.; Khoshnamvand, M.; Walker, T.R.; Hamidian, A.H. Nano-Sized Polystyrene Plastics Toxicity to Microalgae Chlorella Vulgaris: Toxicity Mitigation Using Humic Acid. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 245, 106123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Bai, X.; Ye, Z.; Gong, D.; Cao, J.; Hua, Z. Humic Acid Regulation of the Environmental Behavior and Phytotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles to: Lemna Minor. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 3712–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizhuveetil, U.; Omer, S.; Karunagaran, D.; Suraishkumar, G.K. Improved Redox Anti-Cancer Treatment Efficacy through Reactive Species Rhythm Manipulation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Dietz, T.; Carpenter, S.R.; Alberti, M.; Folke, C.; Moran, E.; Pell, A.N.; Deadman, P.; Kratz, T.; Lubchenco, J.; et al. Complexity of Coupled Human and Natural Systems. Science 2007, 317, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zorov, D.B.; Juhaszova, M.; Sollott, S.J. Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and ROS-Induced ROS Release. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 909–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, P.; Cai, M.; Wu, D.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Polystyrene Nanoplastic Exposure Induces Immobilization, Reproduction, and Stress Defense in the Freshwater Cladoceran Daphnia Pulex. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Yan, Y.; Pei, F.; Wu, M.; Gebreluel, T.; Zou, S.; Wang, C. Improvement on Lipid Production by Scenedesmus Obliquus Triggered by Low Dose Exposure to Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.; Xuan, Y.; Li, Q. Preparation of Polystyrene Spheres in Different Particle Sizes and Assembly of the PS Colloidal Crystals. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 3088–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, L.; Omer, S.; Jetly, N.; Jenifer, M.A.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Suraishkumar, G.K.; Mukherjee, A. Eco-Corona Formation Lessens the Toxic Effects of Polystyrene Nanoplastics towards Marine Microalgae Chlorella Sp. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Luo, Y.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Li, R.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Q. Confocal Measurement of Microplastics Uptake by Plants. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, M.; Basumatary, M. Estimation of the Chlorophyll Concentration in Seven Citrus Species of Kokrajhar District, BTAD, Assam, India. Tropical Plant Research 2018, 5, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Joseph, J.A. Original Contribution Quantifying cellular oxidative stress by dichlorofluorescein assay using microplate reader. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, Y. Generation of Superoxide Radical during Autoxidation of Hydroxylamine and an Assay for Superoxide Dismutase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1978, 186, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilancioglu, K.; Cokol, M.; Pastirmaci, I.; Erman, B.; Cetiner, S. Oxidative Stress Is a Mediator for Increased Lipid Accumulation in a Newly Isolated Dunaliella Salina Strain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e0091957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]














| Contents | Flu−PS | Flu−PS+HA |
|---|---|---|
| DLS size | 235.5 nm | 325.9 nm |
| Zeta potential (mV) | 89.7 mV | −96.6 mV |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lakshmikanthan, D.; Chandrasekaran, N. The Effect of Humic Acid and Polystyrene Fluorescence Nanoplastics on Solanum lycopersicum Environmental Behavior and Phytotoxicity. Plants 2022, 11, 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11213000
Lakshmikanthan D, Chandrasekaran N. The Effect of Humic Acid and Polystyrene Fluorescence Nanoplastics on Solanum lycopersicum Environmental Behavior and Phytotoxicity. Plants. 2022; 11(21):3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11213000
Chicago/Turabian StyleLakshmikanthan, Dhivya, and Natarajan Chandrasekaran. 2022. "The Effect of Humic Acid and Polystyrene Fluorescence Nanoplastics on Solanum lycopersicum Environmental Behavior and Phytotoxicity" Plants 11, no. 21: 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11213000
APA StyleLakshmikanthan, D., & Chandrasekaran, N. (2022). The Effect of Humic Acid and Polystyrene Fluorescence Nanoplastics on Solanum lycopersicum Environmental Behavior and Phytotoxicity. Plants, 11(21), 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11213000