Monitoring Genetic Erosion of Aromatic and Medicinal Plant Species in Alentejo (South Portugal)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
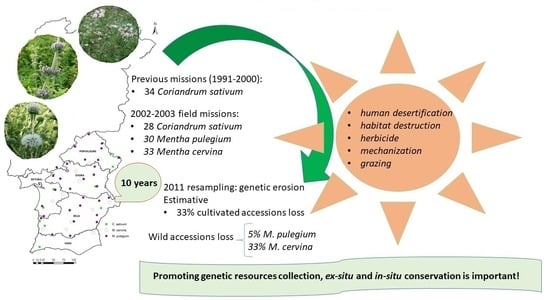
2. Results
2.1. Cultivated Accessions
2.2. Wild Accessions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Target Area of Study
4.2. Selection of Study Sites and Farmers
4.2.1. Sample Collection
4.2.2. Resampling (2011)
4.2.3. Data Collection and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Oosterhout, C.V.; Speak, S.A.; Birley, T.; Bortoluzzi, C.; Percival-Alwyn, L.; Urban, L.H.; Groombridge, J.J.; Segelbacher, G.; Morales, H.E. Genomic erosion in the assessment of species extinction risk and recovery potential. bioRxiv 2022. bioRxiv:13.507768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Monitoring the implementation of the Global Plan of Action for the Conservation and Sustainable Utilization of Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture. In Working paper CGRFA-9/02/07, Proceedings of the Ninth Regular Session of the Commission on Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture, Rome, Italy, 14–18 October 2002; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2002; Available online: http://www.fao.org/ag/cgrfa/docs9.htm (accessed on 22 June 2012).
- Brown, A.H.D. Indicators of Genetic Diversity, Genetic Erosion and Genetic Vulnerability for Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2008; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i1500e/i1500e20.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Diulgheroff, S. A Global Overview of assessing and monitoring genetic erosion of crop wild relatives and local varieties using WIEWS and other elements of the FAO Global System on PGR. Genetic Erosion and Pollution Assessment Methodologies 5, 5, pp. 5–14. 2006. Available online: https://cgspace.cgiar.org/bitstream/handle/10568/104626/1171.pdf?sequence=3#page=24 (accessed on 26 June 2012).
- Maxted, N.; Guarino, L. Genetic erosion and genetic pollution of crop wild relatives. Genetic erosion and pollution assessment methodologies. In Proceedings of the Forum Workshop, Terceira Island, Portugal, 8–11 September 2004; Biodiversity International: Rome, Italy, 2006; Volume 5, pp. 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Hoban, S.; Arntzen, J.A.; Bruford, M.W.; Godoy, J.A.; Hoelzel, A.R.; Segelbacher, G.; Vilà, C.; Bertorelle, G. Comparative evaluation of potential indicators and temporal sampling protocols for monitoring genetic erosion. Evol. Appl. 2014, 7, 984–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leroy, G. Inbreeding depression in livestock species: Review and meta-analysis. Anim. Genet. 2014, 45, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, A.W.; Engels, J.M.M. Plant Biodiversity and Genetic Resources Matter! Plants 2020, 9, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeswara Rao, B.R. Genetic Diversity, Genetic Erosion, Conservation of Genetic Resources, and Cultivation of Medicinal Plants. Genetic Diversity and Erosion in Plants. In Sustainable Development and Biodiversity; Ahuja, M., Jain, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, K.; Xhuveli, L.; Perrino, P.; Knüpffer, H. Estimating genetic erosion in landraces—Two case studies. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 1996, 43, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, K.; Laghetti, G. Genetic Erosion—Examples from Italy1,2. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2005, 52, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklu, Y.; Hammer, K. Farmers’ Perception and Genetic Erosion of Tetraploid Wheats Landraces in Ethiopia. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2005, 53, 1099–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsegaye, B.; Berg, T. Genetic erosion of Ethiopian tetraploid wheat landraces in Eastern Shewa, Central Ethiopia. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2007, 54, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean-Rodríguez, F.D.; Camacho-Villa, T.C.; Almekinders, C.J.M.; Pè, M.E.; Dell’acqua, M.; Costich, D.E. The abandonment of maize landraces over the last 50 years in Morelos, Mexico: A tracing study using a multi-level perspective. Agric. Hum. Values 2019, 36, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemma, A.Z.; Mekbib, F.; Abebe, K.A.; Bishaw, Z. Estimation of genetic erosion on Ethiopian tetraploid wheat landraces using different approaches. Genet. Resour. 2021, 2, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, C.K.; Brush, S.; Costich, D.E.; Curry, H.A.; Haan, S.; Engels, J.M.M.; Guarino, L.; Hoban, S.; Mercer, K.L.; Miller, A.J.; et al. Crop genetic erosion: Understanding and responding to loss of crop diversity. New Phytol. 2022, 233, 84–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghouti, I.; Cristobal, R.; Brenko, A.; Stara, K.; Markos, N.; Chapelet, B.; Hamrouni, L.; Buršić, D.; Bonet, J.-A. The Market Evolution of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants: A Global Supply Chain Analysis and an Application of the Delphi Method in the Mediterranean Area. Forests 2022, 13, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, A.M.; Rocha, F.; Lopes, V.; Bettencourt, E.; Figueiredo, A.C. Medicinal and aromatic plants—Portugal. In Medicinal and Aromatic Plants of The World, Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems (EOLSS); Developed under the Auspices of the UNESCO, Eolss Publishers: Oxford, UK, 2011; Available online: researchgate.net (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Barata, A.M.; Lopes, V.R. Estudo do setor das Plantas Aromáticas, Medicinais e Condimentares em Portugal. Edição do Banco Português de Germoplasma Vegetal (BPGV), Instituto Nacional de Investigação Agrária e Veterinária, Ministério da Agricultura 2021; p. 86. Available online: https://www.ccpam.pt/estudo-do-setor-das-plantas-aromaticas-medicinais-e-condimentares-em-portugal/ (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- El Hassani, F.Z. Characterization, activities, and ethnobotanical uses of Mentha species in Morocco. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Póvoa, O.; Espirito-Santo, M.D.; Vasconcelos, T.; Monteiro, A. Mentha cervina L. communities in Portugal. Lazaroa 2009, 30, 73–79. Available online: https://www.repository.utl.pt/handle/10400.5/17692 (accessed on 4 June 2023).
- Monteiro, A.; Póvoa, O.; Marinho, S.; Rodrigues, L.; Monteiro, P. Mentha pulegium e Mentha cervina. Os poejos na Boa Cozinha Portuguesa; Isapress: Lisboa, Portugal, 2007; Available online: https://www.repository.utl.pt/handle/10400.5/9424 (accessed on 6 May 2013).
- Diederichsen, A. Coriander, Coriandrum sativum L. Promoting the Conservation and Use of Underutilized and Neglected Crops. Leibniz Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research; International Plant Genetic Resources Institute: Rome, Italy, 1996; 83p, ISBN 978-92-9043-284-5/92-9043-284-5. Available online: https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/104262 (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Almadanim, M.C.; Baleiras-Couto, M.M.; Pereira, H.S.; Carneiro, L.C.; Fevereiro, P.; Eiras-Dias, J.E.; Morais-Cecílio, L.; Viegas, W.; Veloso, M. Genetic diversity of the grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) cultivars most utilized for wine production in Portugal. Vitis 2007, 46, 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, J.; Ibáñez, J.; Teixeira-Santos, M.; Brazão, J.; Fevereiro, P.; Martínez-Zapater, J.M.; Eiras-Dias, J.E. Characterisation of the portuguese grapevine germplasm with 48 single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2016, 22, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, M.A.P.; Bebeli, P.J.; Bettencourt, E.; Costa, G.; Dias, S.; Santos, T.M.D.; Slaski, J.J. Cereal landraces genetic resources in worldwide GeneBanks. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 177–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocha, F.; Bettencourt, E.; Gaspar, C. Genetic Erosion Assessment through the Re-Collecting of Crop Germplasm. Counties of Arcos de Valdevez, Melgaço, Montalegre, Ponte da Barca and Terras de Bouro (Portugal). Plant Genet. Resour. Newsl. 2008, 154, 6–13. Available online: researchgate.net (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Barata, A.M.; Rocha, F.A.; Lopes, V.M.; Morgado, J.; Maia, J.; Bettencourt, E.; Dias, S.; Delgado, F.; Costa, M.; Farinha, N.; et al. Networking on conservation and use of medicinal, aromatic and culinary plants genetic resources in Portugal. Acta Hortic. 2011, 925, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso, M. The State of Regional and International Collaboration. State of Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture in Portugal. INRB. Oeiras. 2008. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i1500e/Portugal.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Cebolla-Cornejo, J.; Soler, S.; Nuez, F. Genetic erosion of traditional varieties of vegetable crops in Europe: Tomato cultivation in Valencia (Spain) as a case study. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2007, 1, 113–128. [Google Scholar]
- Bielsa, F.J.; Irisarri, P.; Errea, P.; Pina, A. Genetic diversity and structure of local pear cultivars from mountainous areas from Aragon (Northeastern Spain). Agronomy 2021, 11, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.H.D.; Hodgkin, T. Indicators of Genetic Diversity, Genetic Erosion, and Genetic Vulnerability for Plant Genetic Resources. In Genetic Diversity and Erosion in Plants. Sustainable Development and Biodiversity; Ahuja, M., Jain, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Póvoa, O.; Farinha, N.; Dias, S.S. Levantamento Etnobotânico Sobre Coentros e Poejos No Alentejo. 2012. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10400.26/4598 (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- Fadhel, N.B.; Boussa, M. Genetic diversity in wild Tunisian populations of Mentha pulegium L. (Lamiaceae). Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2004, 51, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D. Genetic erosion. No longer just an agricultural issue. Nativ. Plants J. 2004, 5, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basey, A.C.; Fant, J.B.; Kramer, A.T. Producing native plant materials for restoration: 10 rules to collect and maintain genetic diversity. Nativ. Plants J. 2015, 16, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotto, O.; Wessely, J.; Georges, D.; Klonner, G.; Schmid, M.; Dullinger, S.; Thuiller, W.; Guillaume, F. A dynamic eco-evolutionary model predicts slow response of alpine plants to climate warming. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kardos, M.; Armstrong, E.E.; Fitzpatrick, S.W.; Hauser, S.; Hedrick, P.W.; Miller, J.M.; Tallmon, D.A.; Funk, W.C. The crucial role of genome-wide genetic variation in conservation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2104642118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchetto, C.; Segatto, A.L.A.; Mäder, G.; Rodrigues, D.M.; Bonatto, S.L.; Freitas, L.B. High levels of genetic diversity and population structure in an endemic and rare species: Implications for conservation. AoB PLANTS 2016, 8, plw002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caballero, A.; Bravo, I.; Wang, J. Inbreeding load and purging: Implications for the short-term survival and the conservation management of small populations. Heredity 2017, 118, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riley, L.; McGlaughlin, M.; Helenurm, K. Limited Genetic Variability in Native Buckwheats (Eriogonum: Polygonaceae) on San Clemente Island. West. N. Am. Nat. 2018, 78, 722–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhalkatsi, M.; Ekhvaia, J.; Asanidze, Z. Diversity and Genetic Erosion of Ancient Crops and Wild Relatives of Agricultural Cultivars for Food: Implications for Nature Conservation in Georgia (Caucasus). Cap. 3. Perspectives on Nature Conservation—Patterns, Pressures and Prospects; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 51–91. Available online: http://www.intechopen.com/books/perspectives-on-nature-conservation-patterns-pressures-and-prospects (accessed on 22 June 2012).
- Brush, S.B. In Situ Conservation of Landraces in Centers of Crop Diversity. Crop. Sci. 1995, 35, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Wouw, M.; Kik, C.; van Hintum, T.; van Treuren, R.; Visser, B. Genetic erosion in crops: Concept, research results and challenges. Plant Genet. Resour. Charact. Util. 2009, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- INE. Statistical Yearbook of Alentejo Region 2010; Instituto Nacional de Estatística; INE: Lisboa, Portugal, 2011; ISBN 978-989-25-0170-3. Available online: https://www.ine.pt/ngt_server/attachfileu.jsp?look_parentBoui=150343045&att_display=n&att_download=y (accessed on 6 June 2013).
- INE. Censos 2021. Resultados Definitivos—Portugal; INE: Lisboa, Portugal, 2021; ISBN 978-989-25-0619-7. Available online: https://censos.ine.pt/xportal/xmain?xpgid=censos21_produtos&xpid=CENSOS21&xlang=pt,https://www.pordata.pt/censos/resultados/populacao-alentejo-592 (accessed on 9 June 2013).
- Geleta, N.; Grausgruber, H. On-Farm Diversity and Genetic Erosion of Tetraploid Wheat Landraces in Ambo and Dandi Districts, West Shewa, Ethiopia. Sci. Technol. Arts Res. J. 2013, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelelcha, F.; Kumsa, F.; Kuma, T. On-farm genetic diversity of wheat (Triticum aestivum spp.) in Digalu Tijo District, Arsi zone, Ethiopia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Guarino, J. Assessing the threat of genetic erosion. In Collecting Plant Genetic Diversity: Technical Guidelines; Guarino, L., Ramanatha Rao, V., Reid, R., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1995; Chapter 4; pp. 67–74. Available online: http://cropgenebank.wikispaces.com/Collecting+Manual (accessed on 22 June 2012).
- Wei, X.; Jiang, M. Meta-analysis of genetic representativeness of plant populations under ex situ conservation in contrast to wild source populations. Conserv. Biol. 2021, 35, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Stojanović-Radić, Z.; Matejić, J.; Sharopov, F.; Antolak, H.; Kręgiel, D.; Sen, S.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Acharya, K.; Sharifi-Rad, R.; et al. Plants of Genus Mentha: From Farm to Food Factory. Plants 2018, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, M.P.; Mendonça, L.; Neves, B.G.; Varela, C.; Oliveira, P.; Cabral, C. Exploring Iberian Peninsula Lamiaceae as Potential Therapeutic Approaches in Wound Healing. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Region | Average Temperature (°C) | Annual Precipitation (mm) | Population Size 2011 (Inhabitants/km2) | Population Size 2021 (Inhabitants/km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alentejo | 23.7 | 22 | ||
| North Alentejo | 16 | 947 | 18.2 | 17 |
| Central Alentejo | 17 | 852 | 23.1 | 21 |
| South Alentejo | 17 | 817 | 14.5 | 13 |
| Littoral Alentejo | 17.8 | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Póvoa, O.; Lopes, V.; Barata, A.M.; Farinha, N. Monitoring Genetic Erosion of Aromatic and Medicinal Plant Species in Alentejo (South Portugal). Plants 2023, 12, 2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12142588
Póvoa O, Lopes V, Barata AM, Farinha N. Monitoring Genetic Erosion of Aromatic and Medicinal Plant Species in Alentejo (South Portugal). Plants. 2023; 12(14):2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12142588
Chicago/Turabian StylePóvoa, Orlanda, Violeta Lopes, Ana Maria Barata, and Noémia Farinha. 2023. "Monitoring Genetic Erosion of Aromatic and Medicinal Plant Species in Alentejo (South Portugal)" Plants 12, no. 14: 2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12142588
APA StylePóvoa, O., Lopes, V., Barata, A. M., & Farinha, N. (2023). Monitoring Genetic Erosion of Aromatic and Medicinal Plant Species in Alentejo (South Portugal). Plants, 12(14), 2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12142588