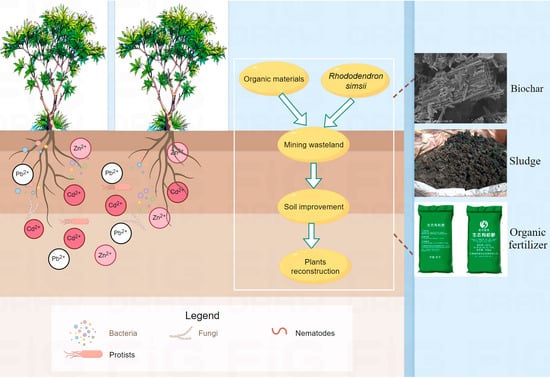
Organic Materials Promote Rhododendron simsii Growth and Rhizosphere Soil Properties in a Lead–Zinc Mining Wasteland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Organic Materials on Soil pH
2.2. Available Nutrient Contents in Rhizosphere Soil of R. simsii
2.3. Cd/Pb Content and Speciation in the Rhizosphere Soil of R. simsii
2.4. Effects of Three Organic Materials on the Growth of R. simssi
2.5. The Accumulation of N, P, K, Cd, and Pb in R. simsii
2.6. Correlations between Plant Growth and Soil Available Nutrients and Different Fractions of Heavy Metals
3. Discussion
3.1. Effects of Three Organic Materials on the Promotion of Soil Available Nutrients
3.2. Effects of Organic Materials on the Bioavailability of Cd and Pb in Soil
3.3. Effects of Three Organic Materials on Plant Growth Characteristics
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Area
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Sampling and Measurements of Soil Properties
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, X.N.; Lü, Z.F.; Wu, Q.J.; Li, Z.M.; Ding, G.F. Research on development and utilization status of lead-zinc mine energy resource base in China. China Energy Environ. Prot. 2020, 42, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, G.; Li, X.J.; Chen, J.B.; Wu, Y. Thoughts on the layout of China’s metal mineral resources supply system. Nat. Resour. Econ. China 2023, 36, 4–9+59. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Liu, M.; Chen, Z. Removal of metalloids and heavy metals from acid mine drainage using biosynthesized Fe/Cu NPs. Biochem. Eng. J. 2024, 201, 109158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasemodel, M.C.; Sakamoto, I.K.; Varesche, M.B.A.; Rodrigues, V.G.S. Potentially toxic metal contamination and microbial community analysis in an abandoned Pb and Zn mining waste deposit. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.C.; Zheng, Y.J.; He, X.F.; Li, X.X.; Zhang, X.F. Analysis of the Report on the national general survey of soil contamination. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2017, 36, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Ankita, B.; Suparna, P.; Subhabrata, P. Silicon as a powerful element for mitigation of cadmium stress in rice: A review for global food safety. Plant Stress 2023, 10, 100237. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.Z.; Liu, W.S.; Deng, L.; Zhu, M.Y.; Qi, D.H.; Guo, P.J. Accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in dominant species growing on Lanping lead/zinc mining wasteland with different pollution gradients. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2014, 8, 5027–5034. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, G.C.; Penido, E.S.; Alvarenga, I.F.S.; Teodoro, J. Amending potential of organic and industrial by-products applied to heavy metal-rich mining soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 162, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; DeLuca, T.H.; Cleveland, C.C. Biochar additions alter phosphorus and nitrogen availability in agricultural ecosystems: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintala, R.; Schumacher, T.E.; McDonald, L.M.; Clay, D.E.; Malo, D.D.; Papiernik, S.E.; Clay, S.A.; Julson, J.L. Phosphorus Sorption and Availability from Biochars and Soil/Biochar Mixtures. CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, T.; Liu, K.S.; Wang, L.X.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Y. Effects of different amendments for the reclamation of coastal saline soil on soil nutrient dynamics and electrical conductivity responses. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 159, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanomi, G.; Zotti, M.; Abd-ElGawad, A.M.; Iacomino, G.; Nappi, A.; Grauso, L.; Idbella, M. Plant-growth promotion by biochar-organic amendments mixtures explained by selective chemicals adsorption of inhibitory compounds. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.M.; Peng, W.X.; Bao, L.; Yu, X.L.; Dong, X.Q.; Lai, M.L.; Liang, Z.Q.; Xie, S.Y.; Douglass, F.; Zeng, S.C. Biochar alleviating heavy metals phytotoxicity in sludge-amended soil varies with plant adaptability. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Cheng, K.K.; Huo, X.J.; Meng, P.P.; Cai, Z.H.; Wang, Z.K.; Zhou, J. Bioorganic fertilizer promotes pakchoi growth and shapes the soil microbial structure. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1040437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.J.; Li, F.P.; Lu, S.; Xie, W.Q.; Gu, H.H. Effect of sewage sludge compost addition on activity of heavy metal and growth of alflfa in lead/zinc tailings. Min. Res. Dev. 2022, 42, 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.K.; Chen, C.M.; Li, H.S.; Hei, L.; Zeng, L.P.; Wei, Z.B.; Chen, Y.M.; Wu, Q.T. Comprehensive recycling of fresh municipal sewage sludge to fertilize garden plants and achieve low carbon emission: A pilot study. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1023356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; He, S.L.; Zhang, J.Q.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Wang, S.Q.; Shu, T.; Bai, J. Chemical remediation for Cu and Cd polluted soils in adjacent area of mine. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2012, 40, 3339–3340+3373. [Google Scholar]
- van der Heyde, M.; Bunce, M.; Dixon, K.; Wardell-Johnson, G.; White, N.E.; Nevill, P. Changes in soil microbial communities in post mine ecological restoration: Implications for monitoring using high throughput DNA sequencing. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 142262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, L.K.; McAssey, E.V.; Wilde, H.D. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Rhododendron canescens, a Native Azalea for Urban Landscaping. HortScience 2019, 54, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzykowski, M.; Antonkiewicz, J.; Gruba, P.; Pająk, M. Content of Zn, Cd and Pb in purple moor-grass in soils heavily contaminated with heavy metals around a zinc and lead ore tailing landfill. Open Chem. 2018, 16, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.X.; Liu, F.S.; Zhan, F.D.; Li, B.; Chen, J.J.; Zu, Y.Q.; Li, Y.; He, Y.M. Growth adaptability of 13 Rhododendron varieties in complex polluted cropland in a plateau lead- zinc mining area. Chin. J. Ecol. 2023, 42, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.T.; Feng, L.; Zhang, L.Q. Effects of application of composted municipal sludge on physicochemical prop erties of desert land soil and growth of tall fescue. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 11, 2462–2468. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Wu, C.; Qiu, G.H. Study on the law of Soil Heavy Metals Pollution Around Lead-zinc Mining Areas in China. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 46, 739–744. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.L.; Cen, Z.Y.; Xie, H.X.; Pan, Y.H.; Liao, C.; Shao, Z.F.; Chen, H.L. Effectsof bio-organic fertilizer on the growth of Cassava and the physical and chemical biological character of soil. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2008, 17, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Duan, W.Y.; Chen, F.Y.; Li, S.; Tao, W.M.; Tang, R.Y. The mechanism of biochar facilitate ryegrass growth in arid soils. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 352–359. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Wei, L.L.; Sun, J.N.; Shao, H.B.; Chang, S.X. What is more important for enhancing nutrient bioavailability with biochar application into a sandy soil: Direct or indirect mechanism? Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast-Miller, M.T.; Duvall, M.; Sohi, S.P. Biochar-root interactions are mediated by biochar nutrient content and impacts on soil nutrient availability. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Rong, X.M.; Zhang, Y.P.; Tian, C. Application of biochar in dryland soil decreasing loss of nitrogen and improving nitrogen using rate. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Gondek, K.; Mierzwa-Hersztek, M. Effect of low-temperature biochar derived from pig manure and poultry litter on mobile and organic matter-bound forms of Cu, Cd, Pb and Zn in sandy soil. Soil Use Manag. 2016, 3, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ying, D.X.; Zhang, F.; Tan, C.Y.; Peng, B. Analysis of effect mechanism and risk of biochar on soil fertility and environmental quality. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 248–257. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, C.C.; Wang, J.W.; Cai, K.Z. The effects of organic fertilizers on soil fertility and soil environmental quality: A review. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 25, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Leva, M.; Regina, R.; Kristina, A.V.; Danute, K.; Alvyra, S.; Viia, L. Effect of long-term application of organic fertilizers on improving organic matter quality in acid soil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2022, 68, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.J.; Yao, D.H.; Fan, Z.; Wu, J.F.; Wei, Z.Q. Long-term substitution of mineral fertilizer with green manure and straw increases hydrolysable organic nitrogen and N supply capacity in reddish paddy soils. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2022, 28, 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Kołodziej, B.; Stachyra, M.; Antonkiewicz, J.; Bielińska, E.; Wiśniewski, J. The effect of harvest frequency on yielding and quality of energy raw material of reed canary grass grown on municipal sewage sludge. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 85, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonia, B.; Haroun, C. On the sustainability of land applications of sewage sludge: How to apply the sewage biosolid in order to improve soil fertility and increase crop yield? Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131122. [Google Scholar]
- Song, U.; Lee, E.J. Environmental and economical assessment of sewage sludge compost application on soil and plants in a landfill. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.H.; Ji, X.H.; Wu, J.M.; Huang, J.; Guan, D.; Zhu, J. Effects of different organic fertilizers on bioavailability of Cd and Zn in soil. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 826–832. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, S.; Saeed, D.A.; Rizwan, M.; Khan, M.N.; Aziz, O.; Bashir, S.; Imrahim, M.; Ditta, A.; Akmal, M.; Mumtaz, M.A.; et al. Impact of different amendments on biochemical responses of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) plants grown in lead-cadmium contaminated soil. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 132, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.M.; Yu, G.W.; Cai, X.; Long, X.X. Immobilization of Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn in a Multi-Metal Contaminated Acidic Soil using Inorganic Amendment Mixtures. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2017, 11, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporale, A.G.; Pigna, M.; Sommella, A.; Conte, P. Effect of pruning-derived biochar on heavy metals removal and water dynamics. Biol. Fertil. Soils Coop. J. Int. Soc. Soil Sci. 2014, 50, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Shi, L.Z.; Xue, S.G.; Li, W.C.; Jiang, X.X.; Rajendran, M.; Qian, Z.Y. Effect of sulfur-iron modified biochar on the available cadmium and bacterial community structure in contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.D.; Lin, T.; Wu, K.Y.; Mo, Y.F.; Tang, Q.; Li, G.J.; Zhu, Y. Combined contribution of biochar and introduced AM fungi on lead stability and microbial community in polluted agricultural soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1284321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netherway, P.; Reichman, S.M.; Laidlaw, M.; Scheckel, K.; Pingitore, N.; Gascó, G.; Méndez, A.; Surapaneni, A.; Paz-Ferreiro, J. Phosphorus-Rich biochars can transform lead in an urban contaminated soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.J.; Zhou, D.L.; Ye, W.L.; Fan, T.; Ma, Y.H. Research progress of bio-organic fertilizer in soil improvement and heavy metal pollution remediation. Environ. Pollut. Control 2019, 41, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.X.; Gu, H.Q.; Zhou, J.L.; Ye, Z.W.; Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, S.Y. Calcium oxide-modified activated sludge as a low-cost biomass adsorbent for Cd(II) removal in aqueous solution: Biosorption behavior and mechanism. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 13, 8915–8925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.X.; Wei, J.G.; Yu, H.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Zeng, Q.L.; Liu, H.J.; Jiang, J.F. Effects of different fertilization treatments on growth and physiological indexes of seedling of Vaccinium corymbosum and physicochemical properties of soil. J. Plant Resour. Environ. 2021, 30, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.T.; Xiao, L.; Feng, W.X.; Li, R.B.; Bai, K.L.; Li, Q.B.; Zeng, S.C. Effects of Application of Biochar and Compound Fertilizer on Growth and Nutrient Absorption of Phoebe zhennan. Guangxi Sci. 2023, 30, 869–875. [Google Scholar]
- Rita, R.A.; Angela, L. Effect of biochar and inorganic or organic fertilizer co-application on soil properties, plant growth and nutrient content in Swiss Chard. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.M.; Li, X.Y.; Li, C.; He, L.S.; Liu, X.Q.; Xiao, Z.; Sun, X.B.; Shi, G.L.; Su, J.L.; Chen, J.H. Biochar pyrolyzed at low temperature enhanced acidophilous plant growth by promoting rhizospheric microbes in a slightly alkaline urban soil. Biochar 2021, 3, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 14–114. [Google Scholar]
- NY/T 2017-2011; Deternination of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium in Plants. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- GB/T 23739-2009; Soil Quality-Analysis of Available Lead and Cadmium Contents in Soils-Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 7, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Treatments | Huolieniao | Yingshanhong |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 7.80 ± 0.04 b | 7.71 ± 0.03 a |
| B | 8.13 ± 0.04 a | 7.79 ± 0.03 a |
| OF | 7.67 ± 0.02 c | 7.57 ± 0.04 b |
| S | 7.57 ± 0.04 d | 7.42 ± 0.05 c |
| Plant | Treatments | Plant Height/cm | Chcanopy/cm | Branch Number | Uppermost Branch Number | Uppermost Leaves Number | Root Length/cm | Root Volume/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huolieniao | CK | 76.5 ± 1.1 b | 38.9 ± 4.0 b | 6.3 ± 1.0 a | 5.2 ± 0.9 a | 41.5 ± 15. 1 a | 8.0 ± 0.26 b | 42.79 ± 5.5 a |
| B | 85.3 ± 2.3 a | 50.7 ± 7.7 a | 6.7 ± 0.4 a | 6.1 ± 0.7 a | 30 ± 1.7 ab | 9.44 ± 0.62 a | 46.17 ± 6.3 a | |
| OF | 84.9 ± 2.4 a | 52.8 ± 3.6 a | 7.1 ± 0.4 a | 5.8 ± 1.2 a | 24.3 ± 2.6 b | 8.9 ± 0.35 ab | 51.38 ± 8.8 a | |
| S | 84.1 ± 3.0 a | 47.8 ± 1.5 a | 7.3 ± 0.9 a | 5.6 ± 0.4 a | 35.6 ± 4.8 ab | 9.1 ± 1.0 ab | 47.68 ± 7.6 a | |
| Yingshanhong | CK | 55.7 ± 1. 6 c | 32.9 ± 1.9 b | 7.3 ± 1.5 a | 4.2 ± 0.8 a | 5.5 ± 0.2 a | 7.3 ± 0.5 b | 34. 1 ± 4.9 a |
| B | 63.3 ± 2.3 a | 37.3 ± 2.3 b | 7.7 ± 2.0 a | 3.3 ± 1.1 a | 5.9 ± 0.6 a | 8.9 ± 0.7 a | 37.8 ± 5.7 a | |
| OF | 61.5 ± 2.1 ab | 49.6 ± 7.6 a | 7.3 ± 1.5 a | 4.4 ± 2.2 a | 9.1 ± 4.5 a | 8.8 ± 0.9 a | 38.2 ± 1.0 a | |
| S | 59.2 ± 1.9 bc | 33.4 ± 3.5 b | 7.0 ± 0.9 a | 3.4 ± 1.5 a | 5.5 ± 3.1 a | 9.0 ± 0.4 a | 39.5 ± 4.8 a |
| Organic Materials | pH | Organic Matter (g/kg) | Available P (mg/kg) | Available K (mg/kg) | Alkeline N (mg/kg) | Cd (mg/kg) | Pb (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 8.87 | 186.7 | 377.2 | 357.1 | 23.7 | 0.22 | 5.17 |
| OF | 7.14 | 463.7 | 49.3 | 106.5 | 127.4 | 0.87 | 39.0 |
| S | 7.43 | 211.1 | 245.5 | 160.5 | 177.6 | 1.12 | 47.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Cai, X.; Li, B.; Zhan, F.; Zu, Y.; He, Y. Organic Materials Promote Rhododendron simsii Growth and Rhizosphere Soil Properties in a Lead–Zinc Mining Wasteland. Plants 2024, 13, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13060891
Chen Y, Li W, Cai X, Li B, Zhan F, Zu Y, He Y. Organic Materials Promote Rhododendron simsii Growth and Rhizosphere Soil Properties in a Lead–Zinc Mining Wasteland. Plants. 2024; 13(6):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13060891
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yunchun, Wei Li, Xinchen Cai, Bo Li, Fangdong Zhan, Yanqun Zu, and Yongmei He. 2024. "Organic Materials Promote Rhododendron simsii Growth and Rhizosphere Soil Properties in a Lead–Zinc Mining Wasteland" Plants 13, no. 6: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13060891
APA StyleChen, Y., Li, W., Cai, X., Li, B., Zhan, F., Zu, Y., & He, Y. (2024). Organic Materials Promote Rhododendron simsii Growth and Rhizosphere Soil Properties in a Lead–Zinc Mining Wasteland. Plants, 13(6), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13060891