Superhydrophobic Coatings as Anti-Icing Systems for Small Aircraft
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Substrates’ Roughness of Substrates
3.2. Application of Coating
- Vertical samples
- Drying at room temperature
- Distance between samples and aerograph = 10 cm
- P = 3 bar; hole size = 1.5 mm
- Horizontal Samples
- Aerograph at 45° wrt the samples
- Drying at 75 °C of each layer of coating for 10 min
- Distance between samples and aerograph = 15 cm
- P = 3 bar; hole size = 1.5 mm;
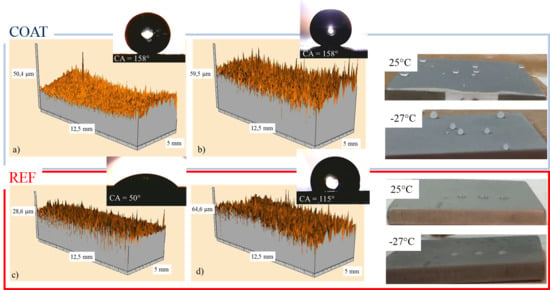
3.3. Contact Angle Measurements
3.4. Surface Free Energy and Work of Adhesion
3.5. 3D samples’ Morphology
3.6. Cutting and Tape Test
3.7. Low Temperature Wettability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kreder, M.J.; Alvarenga, J.; Kim, P.; Aizenberg, J. Design of Anti-Icing Surfaces: Smooth, Textured or Slippery? Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 15003–15039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J. Bio-inspired strategies for anti-icing. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3152–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutzius, T.M.; Jung, S.; Maitra, T.; Eberle, P.; Antonini, C.; Stamatopoulos, C.; Poulikakos, D. Physics of Icing and Rational Design of Surfaces with Extraordinary Icephobicity. Langmuir 2015, 31, 4807–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuler, A.J.; Smith, J.D.; Varanasi, K.K.; Mabry, J.M.; McKinley, G.H.; Cohen, R.E. Relationship between water wettability and ice adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Intefaces 2010, 2, 3100–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golovin, K.; Kobaku, S.; Lee, D.; Di Loreto, E.; Mabry, J.; Tuteja, A. Designing durable icephobic surfaces. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonini, C.; Innocenti, M.; Horn, T.; Marengo, M.; Amirfazli, A. Understanding the effect of superhydrophobic coatings on energy reduction in anti-icing systems. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2011, 67, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.; Yamada, M.; Li, R.; Shang, W.; Otta, S.; Zhong, S.; Ge, L.; Dhinojwala, A.; Conway, K.R.; Bahadur, V.; et al. Dynamics of Ice Nucleation on Water Repellent Surfaces. Langmuir 2012, 28, 3180–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.T.; Hunter, S.R.; Aytug, T. Superhydrophobic materials and coatings: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2015, 78, 086501–086515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, G.; Liu, A. Recent Progress in Preparation and Anti-Icing Applications of Superhydrophobic Coatings. Coatings 2018, 8, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fresnais, J.; Chapel, J.P.; Benyahia, L.; Poncin-Epaillard, F. Plasma-treated superhydrophobic polyethylene surfaces: Fabrication, wetting and dewetting properties. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2009, 23, 447–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikita, M.; Tanaka, K.; Nakamura, T.; Kajiyama, T.; Takahara, A. Super-liquid repellent surfaces prepared by colloidal silica nanoparticles covered with fluoroalkyl groups. Langmuir 2005, 21, 7299–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.T.; Jiang, P. Self-cleaning diffractive macroporous films by doctor blade coating. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12598–12604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, J.; Zhai, L.; Wu, Z.Z.; Cohen, R.E.; Rubner, M.F. Transparent superhydrophobic films based on silica nanoparticles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 7293–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadollahi, S.; Farzaneh, M.; Stafford, L. On the Icephobic Behavior of Organosilicon-Based Surface Structures Developed Through Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Deposition in Nitrogen Plasma. Coatings 2019, 9, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Janjua, Z.A.; Roe, M.; Xu, F.; Turnbull, B.; Choi, K.S.; Hou, X. Super-Hydrophobic/Icephobic Coatings Based on Silica Nanoparticles Modified by Self-Assembled Monolayers. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Jones, A.K.; Sikka, V.K.; Wu, J.; Gao, D. Anti-icing superhydrophobic coatings. Langmuir 2009, 25, 12444–12448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, F.M.; Kustas, A.B.; Williams, T.S.; Hicks, R. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic and Icephobic Coatings by Nanolayered Coating Method. U.S. Patent Application 20190127841 A1, 19 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Furstner, R.; Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C.; Walzel, P. Wetting and self-cleaning properties of artificial superhydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 2005, 21, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscitelli, F.; Tescione, F.; Mazzola, L.; Bruno, G.; Lavorgna, M. On a simplified method to produce hydrophobic coatings for aeronautical applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 472, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4288—Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)–Surface Texture: Profile Method–Rules and Procedures for the Assessment of Surface Texture; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- Young, T. An Essay on the Cohesion of Fluids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1805, 95, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D7490-13 Standard Test Method for Measurement of the Surface Tension of Solid Coatings, Substrates and Pigments using Contact Angle Measurements. American Society for Testing and Materials: Conshohocken, PA, USA, 7 January 2013.
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żenkiewicz, M. Methods for the calculation of surface free energy of solids. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2007, 24, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Rudawska, A.; Jacniacka, E. Analysis of Determining SFE Uncertainty with the Owens-Wendt method. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2009, 29, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Models for Surface Free Energy Calculation. Available online: https://www.kruss.de/fileadmin/user_upload/website/literature/kruss-tn306-en.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2019).
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of Solid Surfaces to Wetting by Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S. Simple derivation of Young, Wenzel and Cassie–Baxter equations and its interpretations. arXiv 2008, arXiv:0808.1460. [Google Scholar]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3359–09 Standard Test Methods for Measuring Adhesion by Tape Test; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- Kam, D.H.; Bhattacharya, S.; Mazumder, J. Control of the wetting properties of an AISI 316L stainless steel surface by femtosecond laser induced surface modification. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 105019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Tartaglino, U.; Persson, B.N.J. Influence of Surface Roughness on Superhydrophobicity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 116103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Q.; Lu, C. Size effect of surface roughness to Superhydrophobicity. Procedia IUTAM 2014, 10, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, Y.K.; Chen, Z.; Lin, C.J. Recent Progress on the Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Special Adhesion: From Natural to Biomimetic to Functional. J. Nanoeng. Nanomanuf. 2011, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigoni, S.; de Givenchy, E.T.; Dufay, M.; Guittard, F. Covalent Layer-by-Layer Assembled Superhydrophobic Organic−Inorganic Hybrid Films. Langmuir 2009, 25, 11073–11077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, S.; Farzaneh, M.; Kulinich, S.A. Anti-icing performance of superhydrophobic surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 6264–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


















| Sample ID | Roughness of Uncoated Samples [µm] |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.752 |
| 2 | 0.83 |
| 3 | 0.91 |
| 4 | 1.241 |
| 5 | 1.341 |
| 6 | 1.541 |
| 7 | 4.032 |
| 8 | 4.360 |
| 9 | 4.623 |
| Liquid | Formula | Room T Surface Tension [mN/m] | Dispersive Component [mN/m] | Polar Component [mN/m] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | H2O | 72.8 | 26.4 | 46.4 |
| Diiodomethane | CH2I2 | 50.8 | 50.8 | 0 |
| Formamide | HCONH2 | 57.0 | 22.4 | 34.6 |
| Sample ID | Coating’s Thickness [µm] | Mean Value [µm] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 112.80 | 115.80 | 123.80 | 125.42 | 129.59 | 130.34 | 136.17 | 142.65 | 127 ± 10 |
| 7 | 199.08 | 191.92 | 194.11 | 190.96 | 182.01 | 183.45 | 190 ± 6 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piscitelli, F.; Chiariello, A.; Dabkowski, D.; Corraro, G.; Marra, F.; Di Palma, L. Superhydrophobic Coatings as Anti-Icing Systems for Small Aircraft. Aerospace 2020, 7, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace7010002
Piscitelli F, Chiariello A, Dabkowski D, Corraro G, Marra F, Di Palma L. Superhydrophobic Coatings as Anti-Icing Systems for Small Aircraft. Aerospace. 2020; 7(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace7010002
Chicago/Turabian StylePiscitelli, Filomena, Antonio Chiariello, Dariusz Dabkowski, Gianluca Corraro, Francesco Marra, and Luigi Di Palma. 2020. "Superhydrophobic Coatings as Anti-Icing Systems for Small Aircraft" Aerospace 7, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace7010002
APA StylePiscitelli, F., Chiariello, A., Dabkowski, D., Corraro, G., Marra, F., & Di Palma, L. (2020). Superhydrophobic Coatings as Anti-Icing Systems for Small Aircraft. Aerospace, 7(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace7010002