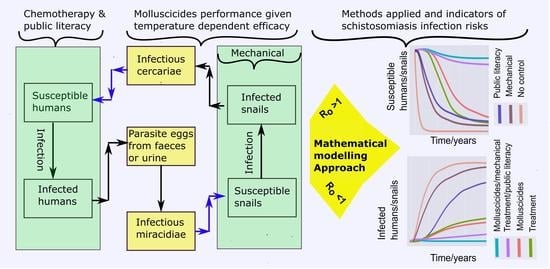
Adapting Strategies for Effective Schistosomiasis Prevention: A Mathematical Modeling Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Schistosomiasis Model Formulation
2.2. Temperature Control
2.3. Reproduction Number
2.4. Steady State
2.5. Parameter Data
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Adenowo, A.F.; Oyinloye, B.E.; Ogunyinka, B.I.; Kappo, A.P. Impact of human schistosomiasis in sub-Saharan Africa. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 19, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO, World Health Organization. Schistosomiasis. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/schistosomiasis (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Wang, L.; Utzinger, J.; Zhou, X.-N. Schistosomiasis control: Experiences and lessons from China. Lancet 2008, 372, 1793–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.; Utzinger, J.; Addiss, D.G. Preventive chemotherapy versus innovative and intensified disease management in neglected tropical diseases: A distinction whose shelf life has expired. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WHO, World Health Organization. Elimination of Schistosomiasis. Sixty-Fifth World Health Assembly, WHA65. 21, Agenda item 13.11. 26 May 2012. Available online: http://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA65/A65_R21-en.pdf (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- French, M.D.; Churcher, T.S.; Gambhir, M.; Fenwick, A.; Webster, J.P.; Kabatereine, N.B.; Basáñez, M.-G. Observed reductions in Schistosoma mansoni transmission from large-scale administration of praziquantel in Uganda: A mathematical modelling study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stothard, J.R.; Chitsulo, L.; Kristensen, T.K.; Utzinger, J. Control of schistosomiasis in sub-Saharan Africa: Progress made, new opportunities and remaining challenges. Parasitology 2009, 136, 1665–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hotez, P.J.; Molyneux, D.H.; Fenwick, A.; Kumaresan, J.; Sachs, S.E.; Sachs, J.D.; Savioli, L. Control of neglected tropical diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- King, C.H.; Bertsch, D. Historical perspective: Snail control to prevent schistosomiasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zacharia, A.; Mushi, V.; Makene, T. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the rate of human schistosomiasis reinfection. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, H. Biological methods for the control of freshwater snails. Parasitol. Today 1990, 6, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolow, S.H.; Huttinger, E.; Jouanard, N.; Hsieh, M.H.; Lafferty, K.D.; Kuris, A.M.; Riveau, G.; Senghor, S.; Thiam, C.; N’Diaye, A.; et al. Reduced transmission of human schistosomiasis after restoration of a native river prawn that preys on the snail intermediate host. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9650–9655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.; Deng, L.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Fan, X. Molluscicides against the snail-intermediate host of Schistosoma: A review. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 3355–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, C.; Sutherland, L.J.; Bertsch, D. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of chemical-based mollusciciding for control of Schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium transmission. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, N.C.; Gurarie, D.; Yoon, N.; Coulibaly, J.T.; Bendavid, E.; Andrews, J.R.; King, C.H. Impact and cost-effectiveness of snail control to achieve disease control targets for schistosomiasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E584–E591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO, World Health Organization. Field Use of Molluscicides in Schistosomiasis Control Programmes: An Operational Manual for Programme Managers; Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolow, S.H.; Wood, C.L.; Jones, I.J.; Lafferty, K.D.; Kuris, A.M.; Hsieh, M.H.; De Leo, G.A. To reduce the global burden of human schistosomiasis, use ‘old fashioned’ snail control. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 34, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiyaka, E.T.; Garira, W. Mathematical analysis of the transmission dynamics of schistosomiasis in the human-snail hosts. J. Biol. Syst. 2009, 17, 397–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xie, D. Control problems of a mathematical model for schistosomiasis transmission dynamics. Nonlinear Dyn. 2010, 63, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abokwara, A.; Madubueze, C.E. The Role of Non-pharmacological Interventions on the Dynamics of Schistosomiasis. J. Math. Fundam. Sci. 2021, 53, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, W.; Trisilowati; Suryanto, A.; Kusumawinahyu, W.M. Mathematical model of schistosomiasis with health education and molluscicide intervention. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1821, 012033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensgaard, A.-S.; Booth, M.; Nikulin, G.; McCreesh, N. Combining process-based and correlative models improves predictions of climate change effects on Schistosoma mansoni transmission in eastern Africa. Geospat. Health 2016, 11, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leo, G.A.; Stensgaard, A.-S.; Sokolow, S.H.; N’goran, E.K.; Chamberlin, A.J.; Yang, G.-J.; Utzinger, J. Schistosomiasis and climate change. BMJ 2020, 371, m4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabo, Z.; Neubauer, T.A.; Tumwebaze, I.; Stelbrink, B.; Breuer, L.; Hammoud, C.; Albrecht, C. Factors controlling the distribution of intermediate host snails of Schistosoma in crater lakes in Uganda: A machine learning approach. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 871735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishel, F.M. Storage Limitation Statements: Temperature–Herbicides: PI123/PI160, 4/2013. EDIS 2013, 4, 123–160. [Google Scholar]
- Ziska, L.H. Increasing minimum daily temperatures are associated with enhanced pesticide use in cultivated soybean along a latitudinal gradient in the mid-western United States. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthies, M.; Beulke, S. Considerations of temperature in the context of the persistence classification in the EU. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2017, 29, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Opinion on a request from EFSA related to the default Q10 value used to describe the temperature effect on transformation rates of pesticides in soil-Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Plant Protection Products and their Residues (PPR Panel). EFSA J. 2008, 6, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECHA. Guidance on Information Requirements and Chemical Safety Assessment; Chapter R.11: PBT/vPvB Assessment; Version 2; Technical Report ECHA-14-G-07-EN; European Chemicals Agency: Helsinki, Finland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- ECHA. Guidance for Information Requirements and Chemical Safety Assessment; Chapter R.7b: Endpoint Specific Guidance; Draft Version 4.0 (Public); European Chemicals Agency: Helsinki, Finland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ronoh, M.; Chirove, F.; Pedro, S.A.; Tchamga, M.S.S.; Madubueze, C.E.; Madubueze, S.C.; Addawe, J.; Mwamtobe, P.M.; Mbra, K.R. Modelling the spread of schistosomiasis in humans with environmental transmission. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 95, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, J.E.T.; Croll, D.; Harrison, W.E.; Utzinger, J.; Freeman, M.C.; Templeton, M.R. The roles of water, sanitation and hygiene in reducing schistosomiasis: A review. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montanari, A.L.; Accorsi, A.; Nasi, M.; Malagoli, D. Effects of a nematode-based molluscicide on survival and antimicrobial peptide expression in Pomacea canaliculata. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2019, 16, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Laidler, K.J.; Chen, H.; Ling, M.; Hencz, L.; Ling, H.Y.; Li, G.; Lin, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, S.; Abyazisani, M.; et al. The development of the Arrhenius equation. J. Chem. Educ. 1984, 61, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.; Tzilivakis, J.; Green, A.; Warner, D. Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB). 2006. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2299/15375 (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Carvalho, S.A.; da Silva, S.O.; Charret, I.D.C. Mathematical modeling of dengue epidemic: Control methods and vaccination strategies. Theory Biosci. 2019, 138, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Commission EC. Technical Guidance Document on Risk Assessment in Support of Commission Directive 93/67/EEC on Risk Assessment for New Notified Substances Part II. In Commission Regulation (EC) No 1488/94 on Risk Assessment for Existing Substances and of Directive 98/8/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council Concerning the Placing of Biocidal Products on the Market; Technical Report EUR 20418 EN/2; European Commission EC: Luxembourg, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann, O.; Heesterbeek, J.A.P.; Metz, J.A.J. On the definition and the computation of the basic reproduction ratio R 0 in models for infectious diseases in heterogeneous populations. J. Math. Biol. 1990, 28, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chavez, C.C.; Feng, Z.; Huang, W. On the computation of R0 and its role on global stability. In Mathematical Approaches for Emerging and Re-Emerging Infection Diseases: An Introduction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; Volume IMA 125, pp. 229–250. [Google Scholar]
- Driessche, P.V.D.; Watmough, J. Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 2002, 180, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.; Jackson, J.; Sitharam, M. Descartes’ rule of signs revisited. Am. Math. Mon. 1998, 105, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulford, A.J.C.; Butterworth, A.E.; Ouma, J.H.; Sturrock, R.F. A statistical approach to schistosome population dynamics and estimation of the life-span of Schistosoma mansoni in man. Parasitology 1995, 110, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colley, D.G.; Bustinduy, A.L.; Secor, W.E.; King, C.H. Human schistosomiasis. Lancet 2014, 383, 2253–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.; Turner, H.; Farrell, S.; Truscott, J. Studies of the transmission dynamics, mathematical model development and the control of schistosome parasites by mass drug administration in human communities. Adv. Parasitol. 2016, 94, 199–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabo, A.; Badawi, H.M.; Bary, B.; Doumbo, O.K. Urinary schistosomiasis among preschool-aged children in Sahelian rural communities in Mali. Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gryseels, B.; Polman, K.; Clerinx, J.; Kestens, L. Human schistosomiasis. Lancet 2006, 368, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, R.M.; Prata, A. Evolution and characteristics of Schistosoma mansoni eggs laid in vitro. J. Parasitol. 1968, 54, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, L.; Grimes, J.E.T.; Templeton, M.R. The effectiveness of water treatment processes against schistosome cercariae: A systematic review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanyi, E.; Afolabi, A.S.; Onyango, N.O. Mathematical modelling and analysis of transmission dynamics and control of schistosomiasis. J. Appl. Math. 2021, 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Eppert, A.; Milner, F.; Minchella, D. Estimation of parameters governing the transmission dynamics of schistosomes. Appl. Math. Lett. 2004, 17, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, S.; Spear, R.C.; Seto, E.; Hubbard, A.; Qiu, D. A multi-group model of Schistosoma japonicum transmission dynamics and control: Model calibration and control prediction. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2005, 10, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangal, T.D.; Paterson, S.; Fenton, A. Predicting the impact of long-term temperature changes on the epidemiology and control of schistosomiasis: A mechanistic model. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soetaert, K.; Petzoldt, T.; Setzer, R.W. Solving differential equations in R: Package deSolve. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2016. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 6 March 2021).
- Andrade, G.; Bertsch, D.J.; Gazzinelli, A.; King, C.H. Decline in infection-related morbidities following drug-mediated reductions in the intensity of Schistosoma infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thétiot-Laurent, S.A.-L.; Boissier, J.; Robert, A.; Meunier, B. Schistosomiasis chemotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7936–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, C.L.; Osakunor, D.N.; Downs, J.A.; Kayuni, S.; Stothard, J.R.; Lamberton, P.H.; Reinhard-Rupp, J.; Rollinson, D. Schistosomiasis control: Leave no age group behind. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, N.C.; Bezerra, F.S.M.; Colley, D.G.; Fleming, F.M.; Homeida, M.; Kabatereine, N.; Kabole, F.M.; King, C.H.; Mafe, M.A.; Midzi, N.; et al. Review of 2022 WHO guidelines on the control and elimination of schistosomiasis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, e327–e335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satayathum, S.A.; King, C.; Muchiri, E.M.; Ouma, J.H.; Whalen, C.C. Factors affecting infection or reinfection with Schistosoma haematobium in coastal Kenya: Survival analysis during a nine-year, school-based treatment program. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, W. Progress of research on molluscicidal effect of nereistoxin pesticide. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 2012, 19, 482. [Google Scholar]
- Seligman, P.F.; Maguire, R.J.; Lee, R.F.; Hinga, K.R.; Valkirs, A.O.; Stang, P.M. Persistence and fate of tributyltin in aquatic ecosystems. In Organotin; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 20, pp. 429–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolow, S.H.; Wood, C.L.; Jones, I.J.; Swartz, S.J.; Lopez, M.; Hsieh, M.H.; Lafferty, K.D.; Kuris, A.M.; Rickards, C.; De Leo, G.A. Global assessment of schistosomiasis control over the past century shows targeting the snail intermediate host works best. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sprecher, S.L.; Getsinger, K.D. Zebra Mussel Chemical Control Guide; ERDC/EL TR-00-1; U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2000; 114p. [Google Scholar]
- Zayed, K.M.; Guo, Y.-H.; Lv, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.-N. Molluscicidal and antioxidant activities of silver nanoparticles on the multi-species of snail intermediate hosts of schistosomiasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, G.D.; Mills, G.A.; Gravell, A.; Jones, L.; Townsend, I.; Cameron, D.G.; Fones, G.R. Review of the molluscicide metaldehyde in the environment. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2017, 3, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gohar, A.A.; Maatooq, G.T.; Gadara, S.R.; Aboelmaaty, W.S.; El-Shazly, A.M. Molluscicidal activity of the methanol extract of Callistemon viminalis (Sol. ex Gaertner) G. Don ex Loudon fruits, bark and leaves against Biomphalaria alexandrina snails. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 505. [Google Scholar]



| Intermediate Hosts | Schistosoma Parasite Forms |
|---|---|
| Susceptible snails | Free-living miracidia |
| Infected snails | Free-living cercaria |
| Parameter | Definition | Baseline Value | Values Range/Day | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human recruitment rate | 4127 | 254–8000 | [18,49] | |
| Snail recruitment rate | 200 | 200 | [18] | |
| Initial age of infection in children | 730 d | d | [33,46] | |
| The human death rate due to infection | 0.0039 | 0.0039 | [50] | |
| Natural death rate of human | 0.00004025 | 0.0000384–0.0000421 | [18,41] | |
| ρ | Proportion of stool/urine per person | 115 g | 70–160 g | [51] |
| Number of egg parasites in stool/urine | 262 g−1 | 10–513 g−1 | [51] | |
| Miracidia emergence rate | 0.00232 | 0.00232 | [52] | |
| Natural death rate of IHs | 0.01110 | 0.004–0.0182 | [52] | |
| Natural death rate of parasite eggs | 0.07193 | 0.001–0.14286 | [44,46,49] | |
| Natural death rate of miracidia | 0.49165 | 0.0833–0.9 | [46,49] | |
| Nautral death rate of cercaria | 0.002605 | 0.00104–0.00417 | [52] | |
| Number of miracidia released per egg | 500 | 500 | [52] | |
| β1 | Cercaria-human infection rate | 0.0750 | 0.028–0.122 | [52] |
| β2 | Miracidia-snail infection rate | 0.001235 | 0.000127–0.615 | [52] |
| Cercaria shedding rate | 2.6 | 2.6 | [19,49] | |
| δ2 | Snail death rate due to infection | 0.026 | 0.002–0.05 | [52] |
| Parasite egg carrying capacity | 100,000 | 100,000 | Estimated | |
| Co | Saturation coefficient for miracidia infectivity | 1,000,000 | Estimated | |
| Mo | Saturation coefficient for cercaria infectivity | 1,000,000 | [19] | |
| limitation of miracidia the growth velocity | 0.25 | 0.2–0.3 | [18,19] | |
| Effective rates of control strategies | 0.5 | 0–1 | Varied | |
| Chemical-induced death rates | 0.5 | 0–1 | Varied |
| Parameter | ρ | |||||||||
| +0.8338 | +0.0451 | +0.0195 | −0.0089 | −0.7899 | +0.7725 | +0.7545 | +0.5504 | −0.8636 | −0.7537 | |
| Parameter | β1 | β2 | δ2 | Co | Mo | |||||
| −0.5777 | +0.8186 | +0.7607 | +0.7928 | +0.8005 | −0.6731 | −0.7799 | −0.8032 | −0.0481 | −0.8303 |
| 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ( | 10,000 | 1947 | 1390 | 1139 | 988 | 884 | 808 | 748 | 700 | 660 | 643 |
| () | 10,000 | 9900 | 9600 | 9100 | 8400 | 7500 | 6400 | 5100 | 3600 | 1900 | 975 |
| () | 10,000 | 9950 | 9798 | 9539 | 9165 | 8660 | 8000 | 7141 | 6000 | 4359 | 3122 |
| () | 10,000 | 295 | 138 | 86.9 | 61.6 | 46.8 | 37.2 | 30.6 | 25.7 | 22.0 | 20.5 |
| () | 10,000 | 1928 | 1334 | 1036 | 830 | 663 | 517 | 382 | 252 | 125 | 62.7 |
| () | 10,000 | 294 | 136 | 82.9 | 56.5 | 40.5 | 29.8 | 21.8 | 15.4 | 9.6 | 6.401 |
| () | 10,000 | 57.4 | 19.3 | 9.9 | 6.1 | 4.1 | 3.0 | 2.3 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.3 |
| () | 10,000 | 1937 | 1362 | 1086 | 905 | 766 | 646 | 534 | 420 | 288 | 201 |
| () | 10,000 | 292 | 133 | 79.1 | 51.7 | 35.1 | 23.8 | 15.6 | 9.3 | 4.2 | 1.9 |
| () | 10,000 | 9850 | 9406 | 8681 | 7699 | 6495 | 5120 | 3642 | 2160 | 828 | 304 |
| () | 10,000 | 292 | 133 | 79.1 | 51.7 | 35.1 | 23.8 | 15.6 | 9.3 | 4.2 | 1.9 |
| () | 10,000 | 9850 | 9406 | 8681 | 7699 | 6495 | 5120 | 3642 | 2160 | 828 | 304 |
| () | 10,000 | 57.1 | 18.8 | 9.4 | 5.6 | 3.6 | 2.4 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 0.63 | 0.41 |
| () | 10,000 | 291 | 130 | 75.5 | 47.4 | 30.4 | 19.1 | 11.1 | 5.5 | 1.8 | 0.62 |
| () | 10,000 | 56.6 | 18.1 | 8.6 | 4.7 | 2.7 | 1.5 | 0.83 | 0.39 | 0.12 | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tabo, Z.; Kalinda, C.; Breuer, L.; Albrecht, C. Adapting Strategies for Effective Schistosomiasis Prevention: A Mathematical Modeling Approach. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2609. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11122609
Tabo Z, Kalinda C, Breuer L, Albrecht C. Adapting Strategies for Effective Schistosomiasis Prevention: A Mathematical Modeling Approach. Mathematics. 2023; 11(12):2609. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11122609
Chicago/Turabian StyleTabo, Zadoki, Chester Kalinda, Lutz Breuer, and Christian Albrecht. 2023. "Adapting Strategies for Effective Schistosomiasis Prevention: A Mathematical Modeling Approach" Mathematics 11, no. 12: 2609. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11122609
APA StyleTabo, Z., Kalinda, C., Breuer, L., & Albrecht, C. (2023). Adapting Strategies for Effective Schistosomiasis Prevention: A Mathematical Modeling Approach. Mathematics, 11(12), 2609. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11122609