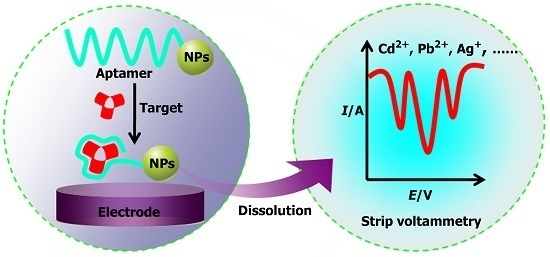
Aptasensors Based on Stripping Voltammetry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Electrochemical Aptasensors
1.2. Electrochemical Stripping Voltammetry
2. Aptasensor Based on Stripping Voltammetry
2.1. Aptasensors for Simultaneous Detection of Small Biomolecules
2.2. Aptasensors for Proteins
2.3. Aptasensors for Cancer Cells and Diseases
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABA | ATP binding aptamer |
| Apt-QDs | aptamer-quantum dots conjugates |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| CBA | cocaine binding aptamer |
| cDNA | complementary DNA |
| CEA | carcinoembryonic antigen |
| CPs | colloidal carbon particles |
| CTIPE | cyclic target-induced primer extension |
| HCR | hybridization chain reaction |
| HER2 | breast cancer marker |
| IgE | human immunoglobulin E |
| IgG | immunoglobulin G |
| MBs | magnetic beads |
| MCF-7 | The number of one type of breast cancer cells |
| MNPs | magnetic nanoparticles |
| MUC1 | human mucin-1 |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PDGF-BB | platelet-derived growth factor |
| PSMs | polystyrene microspheres |
| PSA | prostate-specific antigen |
| QD | quantum dot |
| RCA | rolling circle amplification |
| S. aureus | Staphylococcus aureus |
| SDA | strand-displacement amplification |
| SELEX | systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment |
| SK-BR-3 | HER2-overexpressing breast cancer |
| SPE | screen-printed electrode |
References
- Xu, Y.; Cheng, G.; He, P.; Fang, Y. A review: Electrochemical aptasensors with various detection strategies. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palchetti, I.; Mascini, M. Electrochemical nanomaterial-based nucleic acid aptasensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 3103–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevenot, D.R.; Tóth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical biosensors: Recommended definitions and classification. Pure Appl.Chem. 1999, 71, 2333–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, I.; Zayats, M. Electronic aptamer-based sensors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 6408–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Famulok, M.; Mayer, G. Aptamer modules as sensors and detectors. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarvetnick, N.; Shizuru, J.; Liggitt, D.; Martin, L.; Mclntyre, B.; Gregory, A.; Parslow, T.; Stewart, T. Loss of pancreatic islet tolerance induced by β-cell expression of interferon-γ. Nature 1990, 346, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, D.L.; Joyce, G.F. Selection in vitro of an RNA enzyme that specifically cleaves single-stranded DNA. Nature 1990, 344, 467–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Yigit, M.V.; Mazumdar, D.; Lu, Y. Molecular diagnostic and drug delivery agents based on aptamer-nanomaterial conjugates. Adv. Drug. Delivery. Rev. 2010, 62, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palchetti, I.; Mascini, M. Electrochemical nanomaterial-based nucleic acid aptasensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 3103–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.; Maufort, J.P.; Nie, J.; Stewart, R.; McIntosh, B.E.; Conti, L.R.; Ahmad, K.M.; Soh, H.T.; Thomson, J.A. Development of an efficient targeted cell-SELEX procedure for DNA aptamer reagents. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polonschii, C.; David, S.; Tombelli, S.; Mascini, M.; Gheorghiu, M. A novel low-cost and easy to develop functionalization platform. Case study: Aptamer-based detection of thrombin by surface plasmon resonance. Talanta 2010, 80, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Hu, L.; Liu, Z.; Qi, W.; Zhu, S.; Xu, G. A label-free and signal-on supersandwich fluorescent platform for Hg2+ sensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 793, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Jiang, L.; Shao, Q.; Liu, X.; Marks, R.S.; Ma, J.; Chen, X. Colorimetric detection of mercury ions based on plasmonic nanoparticles. Small 2013, 9, 1467–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, J. Sensitive and rapid screening of T4 polynucleotide kinase activity and inhibition based on coupled exonuclease reaction and graphene oxide platform. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8396–8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Qi, W.; Xu, G. Recent advances in electrochemiluminescence. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3117–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Xu, G. Applications and trends in electrochemiluminescence. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3275–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Qi, W.; Gao, W.; Hanif, S.; Saqib, M.; Xu, G. Label-free signal-on ATP aptasensor based on the remarkable quenching of tris(2,2′-bipyridine)ruthenium(II) electrochemiluminescence by single-walled carbon nanohorn. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 4256–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Cao, Q.; Zhou, M.; Cui, H. A novel homogeneous label-free aptasensor for 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene detection based on an assembly strategy of electrochemiluminescent graphene oxide with gold nanoparticles and aptamer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkoci, A. Electrochemical biosensing with nanoparticles. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. Aptamer/nanoparticle-based sensitive, multiplexed electronic coding of proteins and small biomolecules through a backfilling strategy. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 14261–14265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. Electrochemical analysis of two analytes based on a dual-functional aptamer DNA sequence. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Li, J.; Cheng, W.; Yan, Y.; Tang, R.; Li, Y.; Ju, H.; Ding, S. Electrochemical aptasensor for highly sensitive determination of cocaine using a supramolecular aptamer and rolling circle amplification. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-W.; Nie, J.; Zhang, F.-T.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Zhang, X.-X. Novel homogeneous label-free electrochemical aptasensor based on functional DNA hairpin for target detection. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 9378–9382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Li, H.; Liang, H.; Qiang, W.; Xu, D. Disposable electrochemical aptasensor array by using in situ DNA hybridization inducing silver nanoparticles aggregate for signal amplification. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2775–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Ge, Y.; Lin, J.M. Aptamer based electrochemical assay for the determination of thrombin by using the amplification of the nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Ding, S.; Li, Q.; Yu, T.; Yin, Y.; Ju, H.; Ren, G. A simple electrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive protein detection using cyclic target-induced primer extension. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 36, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbaspour, A.; Norouz-Sarvestani, F.; Noori, A.; Soltani, N. Aptamer-conjugated silver nanoparticles for electrochemical dual-aptamer-based sandwich detection of staphylococcus aureus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jie, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. A novel quantum dot nanocluster as versatile probe for electrochemiluminescence and electrochemical assays of DNA and cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Lei, Y.; Yan, L.; Yu, T.; Li, Q.; Zhang, D.; Ding, S.; Ju, H. A rapid and sensitive aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for direct detection of Escherichia coli O111. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z. Cascade signal amplification strategy for the detection of cancer cells by rolling circle amplification and nanoparticles tagging. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5019–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, W. Cascade signal amplification based on copper nanoparticle-reported rolling circle amplification for ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of the prostate cancer biomarker. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Wu, J.; Ju, H. Label-free signal-on aptasensor for sensitive electrochemical detection of arsenite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, C.; Tang, B. Crystal violet as a G-quadruplex-selective probe for sensitive amperometric sensing of lead. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 11909–11911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Wu, J.; Ju, H. Electrochemical sensing of heavy metal ions with inorganic, organic and bio-materials. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumkov, A.A.; Suprun, E.V.; Shatinina, S.Z.; Lisitsa, A.V.; Shumyantseva, V.V.; Archakov, A.I. Gold and silver nanoparticles for electrochemical detection of cardiac troponin I based on stripping voltammetry. BioNanoScience 2013, 3, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A.; Petrou, P.S.; Kakabakos, S.E. Microfabricated tin-film electrodes for protein and DNA sensing based on stripping voltammetric detection of Cd(II) released from quantum dots labels. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10686–10691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, B.; Chen, G.; Yang, H.; Tang, D. Metal sulfide-functionalized DNA concatamer for ultrasensitive electronic monitoring of ATP using a programmable capillary-based aptasensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanski, M.; Noble, J.; Knight, A.; Porter, R.; Worsley, G. Aptamer-mediated detection of thrombin using silver nanoparticle signal enhancement. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, D. Graphene oxide sheet-mediated silver enhancement for application to electrochemical biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Chandra, P.; Shim, Y.B. Ultrasensitive and selective electrochemical diagnosis of breast cancer based on a hydrazine-Au nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugate. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Wu, Z.; Qiang, W.; Xu, D. Fabrication of streptavidin functionalized silver nanoparticle decorated graphene and its application in disposable electrochemical sensor for immunoglobulin E. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 31, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xiong, E.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J. Nanomaterials as signal amplification elements in DNA-based electrochemical sensing. Nano Today 2014, 9, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhu, Z.; Lei, J.; Geng, Y.; Ju, H. Sub-femtomolar electrochemical detection of DNA using surface circular strand-replacement polymerization and gold nanoparticle catalyzed silver deposition for signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, F.; White, R.J.; Zuo, X.; Patterson, A.; Xiao, Y.; Kang, D.; Gong, X.; Plaxco, K.W.; Heeger, A.J. An electrochemical supersandwich assay for sensitive and selective DNA detection in complex matrices. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14346–14348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusinek, C.A.; Bange, A.; Warren, M.; Kang, W.; Nahan, K.; Papautsky, I.; Heineman, W.R. Bare and polymer-coated indium tin oxide as working electrodes for manganese cathodic stripping voltammetry. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4221–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, G.; Beni, V. Stripping voltammetry at micro-interface arrays: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 769, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omanović, D.; Garnier, C.; Gibbon–Walsh, K.; Pižeta, I. Electroanalysis in environmental monitoring: Tracking trace metals—A mini review. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 61, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, S.; Chang, J.; Zhou, G.; Chen, J. Nanomaterial-enabled rapid detection of water contaminants. Small 2015, 11, 5336–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Nanoparticle-based electrochemical bioassays of proteins. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Hu, L.; Han, S.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, G. Electrodes with extremely high hydrogen overvoltages as substrate electrodes for stripping analysis based on bismuth-coated electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2012, 738, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, F.; Gao, F.; Wang, X.; Xie, L.; Gao, F.; Wang, Q. Determination of lead(II) by adsorptive stripping voltammetry using a glassy carbon electrode modified with β-cyclodextrin and chemically reduced graphene oxide composite. Microchimica. Acta 2016, 183, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosolina, S.M.; Chambers, J.Q.; Lee, C.W.; Xue, Z.-L. Direct determination of cadmium and lead in pharmaceutical ingredients using anodic stripping voltammetry in aqueous and DMSO/water solutions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 893, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, S.; Dai, W.; Li, C.; Du, D.; Shen, X. Submonolayer deposition on glassy carbon electrode for anodic stripping voltammetry: An ultra sensitive method for antimony in tap water. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2015, 210, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.; Gu, T.; Ma, Y.; Chen, C.; Tan, Y.; Xie, Q.; Yao, S. Enhanced cathodic preconcentration of As(0) at Au and Pt electrodes for anodic stripping voltammetry analysis of As(III) and As(V). J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 11400–11409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Pei, X.; Bange, A.; Haynes, E.N.; Heineman, W.R.; Papautsky, I. Copper-based electrochemical sensor with palladium electrode for cathodic stripping voltammetry of manganese. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 12070–12077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laglera, L.M.; Santos-Echeandía, J.; Caprara, S.; Monticelli, D. Quantification of Iron in seawater at the low picomolar range based on optimization of bromate/ammonia/dihydroxynaphtalene system by catalytic adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetry. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2486–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mirceski, V.; Hocevar, S.B.; Ogorevc, B.; Gulaboski, R.; Drangov, I. Diagnostics of anodic stripping mechanisms under square-wave voltammetry conditions using bismuth film substrates. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4429–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, E.; Maity, S.K.; Patra, S.; Madhuri, R.; Sharma, P.K. A metronidazole-probe sensor based on imprinted biocompatible nanofilm for rapid and sensitive detection of anaerobic protozoan. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 32881–32893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.; Roy, E.; Madhuri, R.; Sharma, P.K. Nano-iniferter based imprinted sensor for ultra trace level detection of prostate-specific antigen in both men and women. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ge, L.; Guo, B.; Yan, M.; Hao, N.; Xu, L. Homogeneously ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of adenosine triphosphate based on multiple signal amplification strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 58, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.-L. Determinationation of kanamycin by square-wave cathodic adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2009, 44, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.-Y.; Mi, X.-N.; Zhao, W.-W.; Xu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. CdS Nanoparticles functionalized colloidal carbon particles: Preparation, characterization and application for electrochemical detection of thrombin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3654–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, B.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. Aptamer/quantum dot-based simultaneous electrochemical detection of multiple small molecules. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 688, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.-J. Simultaneous detection of tumor cell apoptosis regulators Bcl-2 and Bax through a dual-signal-marked electrochemical immunosensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7674–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Liu, L.; Xu, A.; Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; Chen, C.; Xie, Q. Ultrasensitive immunoassay of proteins based on gold label/silver staining, galvanic replacement reaction enlargement, and in situ microliter-droplet anodic stripping voltammetry. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 2855–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.A.; Wang, J.; Kawde, A.-N.; Xiang, Y.; Gothelf, K.V.; Collins, G. Quantum-dot/aptamer-based ultrasensitive multi-analyte electrochemical biosensor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2228–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Chang, Z.; Xing, R.; Chen, M.; Wang, Q.; He, P.; Fang, Y. An electrochemical aptasensor for detection of thrombin based on target protein-induced strand displacement. Electroanalysis 2008, 20, 2113–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fan, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, G. Detection of breast cancer cells specially and accurately by an electrochemical method. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2686–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Xie, M.; Bash, R.; Chen, J.J.L.; Wang, J. Ultrasensitive label-free aptamer-based electronic detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 9054–9056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suprun, E.; Shumyantseva, V.; Bulko, T.; Rachmetova, S.; Rad’ko, S.; Bodoev, N.; Archakov, A. Au-nanoparticles as an electrochemical sensing platform for aptamer–thrombin interaction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suprun, E.; Shumyantseva, V.; Rakhmetova, S.; Voronina, S.; Radko, S.; Bodoev, N.; Archakov, A. Label-free electrochemical thrombin aptasensor based on Ag nanoparticles modified electrode. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ji, J.; Liu, Y.; Kong, J.; Liu, B. An aptamer-based biosensor for sensitive thrombin detection. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Wang, L.; Shao, Y.; Wang, J.; Engelhard, M.H.; Lin, Y. Functionalized graphene oxide as a nanocarrier in a multienzyme labeling amplification strategy for ultrasensitive electrochemical immunoassay of phosphorylated p53 (S392). Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, D.; Zou, Z.; Shin, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Engelhard, M.H.; Liu, J.; Aksay, I.A.; Lin, Y. Sensitive immunosensor for cancer biomarker based on dual signal amplification strategy of graphene sheets and multienzyme functionalized carbon nanospheres. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2989–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xu, M.; Huang, H.; Zhou, J.; Abdel-Halimb, E.S.; Zhang, J.-R.; Zhu, J.-J. Aptamer-quantum dots conjugates-based ultrasensitive competitive electrochemical cytosensor for the detection of tumor cell. Talanta 2011, 85, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Tan, T.; Fu, J.-J.; Zheng, T.; Zhu, J.-J. A novel aptamer-based competition strategy for ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of leukemia cells. Analyst 2013, 138, 6323–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xu, S.; He, Z.; Deng, A.; Zhu, J.-J. Supersandwich cytosensor for selective and ultrasensitive detection of cancer cells using aptamer-DNA concatamer-quantum dots probes. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3385–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Fan, C. Isothermal amplification of nucleic acids. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12491–12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.A.; Cui, C.H.; Bose, S.; Guo, D.G.; Shen, C.; Wong, W.P.; Halvorsen, K.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Teo, G.S.L.; Phillips, J.A.; et al. Bioinspired multivalent DNA network for capture and release of cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19626–19631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Yang, C.-Y.; Sun, R.-L.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Kao, W.-C.; Yang, P.-C. Rapid single cell detection of Staphylococcus aureus by aptamer-conjugated gold nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, W.; Wu, D.; Xu, G.; Nsabimana, J.; Nsabimana, A. Aptasensors Based on Stripping Voltammetry. Chemosensors 2016, 4, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors4030012
Qi W, Wu D, Xu G, Nsabimana J, Nsabimana A. Aptasensors Based on Stripping Voltammetry. Chemosensors. 2016; 4(3):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors4030012
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Wenjing, Di Wu, Guobao Xu, Jacques Nsabimana, and Anaclet Nsabimana. 2016. "Aptasensors Based on Stripping Voltammetry" Chemosensors 4, no. 3: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors4030012
APA StyleQi, W., Wu, D., Xu, G., Nsabimana, J., & Nsabimana, A. (2016). Aptasensors Based on Stripping Voltammetry. Chemosensors, 4(3), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors4030012