“Green” Three-Electrode Sensors Fabricated by Injection-Moulding for On-Site Stripping Voltammetric Determination of Trace In(III) and Tl(I)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
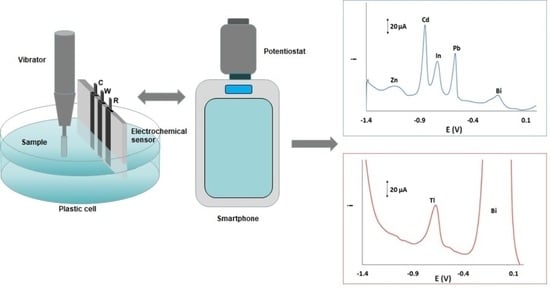
2.2. Fabrication of the Sensor
2.3. Instrumentation and Experimental Set-Up
2.4. Experimental Procedure
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cobelo-García, A.; Filella, M.; Croot, P.; Frazzoli, C.; Du Laing, G.; Ospina-Alvarez, N.; Rauch, S.; Salaun, P.; Schäfer, J.; Zimmermann, S. COST action TD1407: Network on technology-critical elements (NOTICE)—from environmental processes to human health threats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 15188–15194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cobelo-García, A.; Filella, M. Electroanalytical techniques for the quantification of technology-critical elements in environmental samples. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 3, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuss, P.; Blengini, G.A. Towards better monitoring of technology critical elements in Europe: Coupling of natural and anthropogenic cycles. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu-Olayan, A.H.; Thomas, Β.V. Bourgeoning impact of the technology critical elements in the marine environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technology Critical Elements and Their Relevance to the Global Environment Facility. The Scientific and Technical Advisory Panel, UN. 2020. Available online: https://stapgef.org/sites/default/files/2021-02/TCEs%20and%20their%20Relevance%20to%20the%20GEF_web.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- White, S.J.O.; Shine, J.P. Exposure Potential and Health Impacts of Indium and Gallium, Metals Critical to Emerging Electronics and Energy Technologies. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2016, 3, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Chen, L.H. Toxicity of antimony, gallium, and indium toward a teleost model and a native fish species of semiconductor manufacturing districts of Taiwan. J. Elem. 2017, 23, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.H.; Han, J.-H.; Cho, H.-W.; Kang, M. Studies on the Toxicity and Distribution of Indium Compounds According to Particle Size in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Toxicol. Res. 2014, 30, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toxicological Review of Thallium and Compounds, EPA. 2009. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/toxreviews/1012tr.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Cvjetko, P.; Cvjetko, I.; Pavlica, M. Thallium Toxicity in Humans. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2010, 61, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peter, A.J.; Viraraghavan, T. Thallium: A review of public health and environmental concerns. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska-Czapla, M.; Grygoyć, K. Speciation and Fractionation of Less-Studied Technology-Critical Elements (Nb, Ta, Ga, In, Ge, Tl, Te): A Review. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, M.; Rodushkin, I. A concise guide for the determination of less-studied technology-critical elements (Nb, Ta, Ga, In, Ge, Te) by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in environmental samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2018, 141, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honeychurch, K.C. Recent Developments in the Stripping Voltammetric Determination of Indium. World J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 1, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ariño, C.; Serrano, N.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M.; Esteban, M. Voltammetric determination of metal ions beyond mercury electrodes. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 990, 11–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A. Tin film sensor with on-chip three-electrode configuration for voltammetric determination of trace Tl(I) in strong acidic media. Talanta 2014, 125, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martos, L.M.; Jost, C.L. Sequential determination of five heavy metal ions in Brazilian phosphate fertilizers and surface waters by stripping voltammetry. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 6535–6546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, J.; Tyszczuk-Rotko, K.; Rotko, M. Voltammetric screen-printed carbon sensor modified with multiwalled carbon nanotubes and bismuth film for trace analysis of thallium(I), Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2019, 55, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Shan, Y.; Ma, J.; Xie, L.; Du, X. Simultaneous Determination of Indium and Thallium Ions by Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Using Antimony Film Electrode. Sensor Lett. 2009, 7, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopha, H.; Baldrianova, L.; Tesarova, E.; Hocevar, S.B.; Svancara, I.; Ogorevc, B.; Vytras, K. Insights into the simultaneous chronopotentiometric stripping measurement of indium(III), thallium(I) and zinc(II) in acidic medium at the in situ prepared antimony film carbon paste electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 7929–7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrowski, A.; Putek, M.; Zarebski, J. Antimony Film Electrode Prepared In Situ in Hydrogen Potassium Tartrate in Anodic Stripping Voltammetric Trace Detection of Cd(II), Pb(II), Zn(II), Tl(I), In(III) and Cu(II). Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A.; Goddard, N.J.; Fielden, P.R.; Baldock, S.J. Determination of Pb(II) by sequential injection/stripping analysis at all-plastic electrochemical fluidic cells with integrated composite electrodes. Talanta 2016, 153, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidi, S.; Chrysostomou, A.; Economou, A.; Kokkinos, C.; Fielden, P.R.; Baldock, S.J.; Goddard, N.J. Disposable Injection Molded Conductive Electrodes Modified with Antimony Film for the Electrochemical Determination of Trace Pb(II) and Cd(II). Sensors 2019, 19, 4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Partheni, B.; Svarnias, K.; Economou, A.; Kokkinos, C.; Fielden, P.R.; Baldock, S.J.; Goddard, N.J. Voltammetric Determination of Trace Heavy Metals by Sequential-injection Analysis at Plastic Fluidic Chips with Integrated Carbon Fiber-based Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalambous, A.; Economou, A. A study on the utility of bismuth-film electrodes for the determination of In(III) in the presence of Pb(II) and Cd(II) by square wave anodic stripping voltammetry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 547, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, C.; Raptis, I.; Economou, A.; Speliotis, T. Determination of Trace Tl(I) by Anodic Stripping Voltammetry on Novel Disposable Microfabricated Bismuth-Film Sensors. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 2359–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadara, R.O.; Tothill, I.E. Resolving the copper interference effect on the stripping chronopotentiometric response of lead(II) obtained at bismuth film screen-printed electrode. Talanta 2005, 66, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| In(III) | Tl(I) | |
|---|---|---|
| Supporting electrolyte | 0.10 mol L−1 acetate buffer (pH 4.5) + 2.0 × 10−5 mol L−1 K4(Fe(CN)6] + 0.80 mol L−1 KBr | 0.10 mol L−1 acetate buffer (pH 4.5) + 2.0 × 10−5 mol L−1 EDTA |
| Deposition potential (V) | −1.40 | |
| Bi(III) concentration (mg L−1) | 0.50 | 10 |
| Deposition time (s) | 240 | |
| SW frequency (Hz) | 25 | |
| SW pulse height (mV) | 25 | |
| SW step (mV) | 4 | |
| Cleaning time (s) | 30 | |
| Cleaning potential (V) | +0.20 | |
| In(III) | Tl(I) | |
|---|---|---|
| Linear range (μg L−1) | 3.6–100 | 4.4–100 |
| Slope (μA μg−1 L) | 1.02 | 0.37 |
| Intercept (μA) | 0.86 | 0.43 |
| Coefficient of determination | 0.987 | 0.998 |
| % RSDb * | 14.3% | 12.1% |
| % RSDw ** | 5.3% | 5.6% |
| LOD (μg L−1) *** | 1.2 | 1.5 |
| LOQ (μg L−1) *** | 3.6 | 4.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pitsou, M.; Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A.; Fielden, P.R.; Baldock, S.J.; Goddard, N.J. “Green” Three-Electrode Sensors Fabricated by Injection-Moulding for On-Site Stripping Voltammetric Determination of Trace In(III) and Tl(I). Chemosensors 2021, 9, 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9110310
Pitsou M, Kokkinos C, Economou A, Fielden PR, Baldock SJ, Goddard NJ. “Green” Three-Electrode Sensors Fabricated by Injection-Moulding for On-Site Stripping Voltammetric Determination of Trace In(III) and Tl(I). Chemosensors. 2021; 9(11):310. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9110310
Chicago/Turabian StylePitsou, Maria, Christos Kokkinos, Anastasios Economou, Peter R. Fielden, Sara J. Baldock, and Nickolas J. Goddard. 2021. "“Green” Three-Electrode Sensors Fabricated by Injection-Moulding for On-Site Stripping Voltammetric Determination of Trace In(III) and Tl(I)" Chemosensors 9, no. 11: 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9110310
APA StylePitsou, M., Kokkinos, C., Economou, A., Fielden, P. R., Baldock, S. J., & Goddard, N. J. (2021). “Green” Three-Electrode Sensors Fabricated by Injection-Moulding for On-Site Stripping Voltammetric Determination of Trace In(III) and Tl(I). Chemosensors, 9(11), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9110310