A Novel Dialkylamino GFP Chromophore as an Environment-Polarity Sensor Reveals the Role of Twisted Intramolecular Charge Transfer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Compounds 1, 2, and 3
2.2. Steady-State Spectroscopy and Fluorescence Quantum Yield
2.3. Time-Resolved Electronic Spectroscopy and Global Analysis
2.4. Computational Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rational Design and Photophysical Properties of the GFP-Derived Fluorogen
3.2. Theoretical Calculations for Elucidation of the TICT State
3.3. Time-Resolved Spectroscopic Characterization in the Electronic Domain
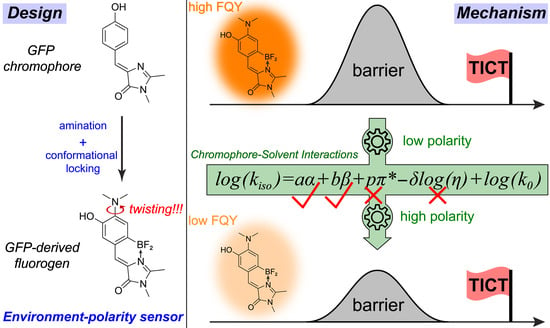
3.4. Multivariable Analysis of Chromophore-Solvent Interactions Regarding TICT
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klymchenko, A.S. Solvatochromic and fluorogenic dyes as environment-sensitive probes: Design and biological applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plamont, M.-A.; Billon-Denis, E.; Maurin, S.; Gauron, C.; Pimenta, F.M.; Specht, C.G.; Shi, J.; Quérard, J.; Pan, B.; Rossignol, J.; et al. Small fluorescence-activating and absorption-shifting tag for tunable protein imaging in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Povarova, N.V.; Zaitseva, S.O.; Baleeva, N.S.; Smirnov, A.Y.; Myasnyanko, I.N.; Zagudaylova, M.B.; Bozhanova, N.G.; Gorbachev, D.A.; Malyshevskaya, K.K.; Gavrikov, A.S.; et al. Red-shifted substrates for fast fluorogen-activating protein based on the GFP-like chromophores. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 9592–9596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, K.P.; Young, A.M.; Palmer, A.E. Fluorescent sensors for measuring metal ions in living systems. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4564–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oscar, B.G.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, Y.; Campbell, R.E.; Fang, C. Excited-state structural dynamics of a dual-emission calmodulin-green fluorescent protein sensor for calcium ion imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10191–10196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, T.-B.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Zhang, X.-X.; Wen, S.-Y.; Yi, H.-B.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.-B. Enhancing the anti-solvatochromic two-photon fluorescence for cirrhosis imaging by forming a hydrogen-bond network. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7473–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, R.; Sung, K. Insights into the unusual dual fluorescence of the ortho-amino analogue of green fluorescent protein chromophore. J. Lumin. 2018, 202, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, Z.R.; Rotkiewicz, K.; Rettig, W. Structural changes accompanying intramolecular electron transfer: Focus on twisted intramolecular charge-transfer states and structures. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 3899–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpulainen, T.; Lang, B.; Rosspeintner, A.; Vauthey, E. Ultrafast elementary photochemical processes of organic molecules in liquid solution. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10826–10939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, J.B.; English, B.P.; Chen, J.; Slaughter, J.P.; Zhang, Z.; Revyakin, A.; Patel, R.; Macklin, J.J.; Normanno, D.; Singer, R.H.; et al. A general method to improve fluorophores for live-cell and single-molecule microscopy. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qiao, Q.; Tian, W.; Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Lang, M.J.; Xu, Z. Aziridinyl fluorophores demonstrate bright fluorescence and superior photostability by effectively inhibiting twisted intramolecular charge transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6960–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G., II; Jackson, W.R.; Halpern, A.M. Medium effects on fluorescence quantum yields and lifetimes for coumarin laser dyes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1980, 72, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Samanta, A. Influence of the structure of the amino group and polarity of the medium on the photophysical behavior of 4-amino-1,8-naphthalimide derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 4763–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppal, V.V.; Melavanki, R.M.; Kusanur, R.A.; Bhavya, P.; Patil, N.R. A role of solvent polarity on bimolecular quenching reactions of 3-acetyl-7-(diethylamino)-2h-chromen-2-one in binary solvent mixtures. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 260, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Jackson, W.R.; Choi, C.Y.; Bergmark, W.R. Solvent effects on emission yield and lifetime for coumarin laser dyes. Requirements for a rotatory decay mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. 1985, 89, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedone, A. Role of solvent on charge transfer in 7-aminocoumarin dyes: New hints from TD-CAM-B3LYP and state specific PCM calculations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 4087–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotkiewicz, K.; Rubaszewska, W. Intramolecular charge transfer state and unusual fluorescence from an upper excited singlet of a nonplanar derivative of p-cyano-N,N-dimethylaniline. J. Lumin. 1982, 27, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettig, W.; Gleiter, R. Dependence of intramolecular rotation in p-cyano-N,N-dialkylanilines on the twist angle. A fluorescence, UV absorption, and photoelectron spectroscopic study. J. Phys. Chem. 1985, 89, 4676–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappoport, D.; Furche, F. Photoinduced intramolecular charge transfer in 4-(dimethyl)aminobenzonitrile—A theoretical perspective. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettig, W. Charge separation in excited states of decoupled systems—TICT compounds and implications regarding the development of new laser dyes and the primary process of vision and photosynthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1986, 25, 971–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loving, G.; Imperiali, B. A versatile amino acid analogue of the solvatochromic fluorophore 4-N,N-dimethylamino-1,8-naphthalimide: A powerful tool for the study of dynamic protein interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13630–13638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, N.; Fan, J.; Xu, F.; Peng, X.; Mu, H.; Wang, J.; Xiong, X. Ratiometric fluorescence imaging of cellular polarity: Decrease in mitochondrial polarity in cancer cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2510–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, P.; Tang, B. Recent progresses in fluorescent probes for detection of polarity. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 427, 213582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, M.S.; Lukyanov, K.A.; Borissova, A.O.; Shamir, J.; Kosenkov, D.; Slipchenko, L.V.; Tolbert, L.M.; Yampolsky, I.V.; Solntsev, K.M. Conformationally locked chromophores as models of excited-state proton transfer in fluorescent proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6025–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, W.; Baranov, M.S.; Baleeva, N.S.; Yampolsky, I.V.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Shamir, A.; Solntsev, K.M.; Fang, C. Unveiling structural motions of a highly fluorescent superphotoacid by locking and fluorinating the GFP chromophore in solution. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 5921–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Tachibana, S.R.; Baleeva, N.S.; Myasnyanko, I.N.; Bogdanov, A.M.; Gavrikov, A.S.; Mishin, A.S.; Malyshevskaya, K.K.; Baranov, M.S.; Fang, C. Developing bright green fluorescent protein (GFP)-like fluorogens for live-cell imaging with nonpolar protein−chromophore interactions. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 8946–8950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würth, C.; Grabolle, M.; Pauli, J.; Spieles, M.; Resch-Genger, U. Relative and absolute determination of fluorescence quantum yields of transparent samples. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1535–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rurack, K.; Spieles, M. Fluorescence quantum yields of a series of red and near-infrared dyes emitting at 600−1000 nm. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Tang, L.; Oscar, B.G.; Zhu, L.; Fang, C. Panoramic portrait of primary molecular events preceding excited state proton transfer in water. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 5484–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.; Zhu, L.; Taylor, M.A.; Wang, Y.; Remington, S.J.; Fang, C. Excited state structural evolution of a GFP single-site mutant tracked by tunable femtosecond-stimulated Raman spectroscopy. Molecules 2018, 23, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snellenburg, J.J.; Laptenok, S.P.; Seger, R.; Mullen, K.M.; van Stokkum, I.H.M. Glotaran: A Java-based graphical user interface for the R-package TIMP. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 49, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Zhu, L.; Baranov, M.S.; Tang, L.; Baleeva, N.S.; Smirnov, A.Y.; Yampolsky, I.V.; Solntsev, K.M.; Fang, C. Photoinduced proton transfer of GFP-inspired fluorescent superphotoacids: Principles and design. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 3804–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Tang, L.; Chen, C. Unveiling coupled electronic and vibrational motions of chromophores in condensed phases. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 151, 200901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Rev. C.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, W.; Helms, V.; McCammon, J.A.; Langhoff, P.W. Shedding light on the dark and weakly fluorescent states of green fluorescent proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6177–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altoè, P.; Bernardi, F.; Garavelli, M.; Orlandi, G.; Negri, F. Solvent effects on the vibrational activity and photodynamics of the green fluorescent protein chromophore: A quantum-chemical study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3952–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, D.; Tahara, T.; Meech, S.R. Excited-state dynamics in the green fluorescent protein chromophore. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.A.; Zhu, L.; Rozanov, N.D.; Stout, K.T.; Chen, C.; Fang, C. Delayed vibrational modulation of the solvated GFP chromophore into a conical intersection. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 9728–9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, S.A.; Chen, C.; Tang, L.; Zhu, L.; Baleeva, N.S.; Myasnyanko, I.N.; Baranov, M.S.; Fang, C. Shedding light on ultrafast ring-twisting pathways of halogenated GFP chromophores from the excited to ground state. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 14636–14648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, M. GFP: From jellyfish to the Nobel prize and beyond. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, G. (Ed.) Fluorescent Proteins I: From Understanding to Design; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 11, p. 268. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Tang, L. Mapping structural dynamics of proteins with femtosecond stimulated Raman spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2020, 71, 239–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Baranov, M.S.; Zhu, L.; Baleeva, N.S.; Smirnov, A.Y.; Zaitseva, S.; Yampolsky, I.V.; Solntsev, K.M.; Fang, C. Designing redder and brighter fluorophores by synergistic tuning of ground and excited states. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 2537–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Fang, C. Devising efficient red-shifting strategies for bioimaging: A generalizable donor-acceptor fluorophore prototype. Chem. Asian J. 2020, 15, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, C. Solvatochromic dyes as solvent polarity indicators. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 2319–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, M.S.; Solntsev, K.M.; Baleeva, N.S.; Mishin, A.S.; Lukyanov, S.A.; Lukyanov, K.A.; Yampolsky, I.V. Red-shifted fluorescent aminated derivatives of a conformationally locked GFP chromophore. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 13234–13241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamlet, M.J.; Abboud, J.-L.M.; Abraham, M.H.; Taft, R.W. Linear solvation energy relationships. 23. A comprehensive collection of the solvatochromic parameters, π*, α, and β, and some methods for simplifying the generalized solvatochromic equation. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baleeva, N.S.; Zaitseva, S.O.; Gorbachev, D.A.; Smirnov, A.Y.; Zagudaylova, M.B.; Baranov, M.S. The role of N-substituents in radiationless deactivation of aminated derivatives of a locked GFP chromophore. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 5219–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Fang, C. Nitration of tyrosine channels photoenergy through a conical intersection in water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 4915–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iikura, H.; Tsuneda, T.; Yanai, T.; Hirao, K. A long-range correction scheme for generalized-gradient-approximation exchange functionals. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 3540–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrdanz, M.A.; Martins, K.M.; Herbert, J.M. A long-range-corrected density functional that performs well for both ground-state properties and time-dependent density functional theory excitation energies, including charge-transfer excited states. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 054112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maroncelli, M.; Fleming, G.R. Picosecond solvation dynamics of coumarin 153: The importance of molecular aspects of solvation. J. Chem. Phys. 1987, 86, 6221–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Lustres, J.L.; Rodriguez-Prieto, F.; Mosquera, M.; Senyushkina, T.A.; Ernsting, N.P.; Kovalenko, S.A. Ultrafast proton transfer to solvent: Molecularity and intermediates from solvation- and diffusion-controlled regimes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 5408–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Fang, C. Uncovering the hidden excited state toward fluorescence of an intracellular pH indicator. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 4969–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Stokkum, I.H.M.; Larsen, D.S.; van Grondelle, R. Global and target analysis of time-resolved spectra. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1657, 82–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krueger, T.D.; Boulanger, S.A.; Zhu, L.; Tang, L.; Fang, C. Discovering a rotational barrier within a charge-transfer state of a photoexcited chromophore in solution. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 7, 024901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solntsev, K.M.; Poizat, O.; Dong, J.; Rehault, J.; Lou, Y.; Burda, C.; Tolbert, L.M. Meta and para effects in the ultrafast excited-state dynamics of the green fluorescent protein chromophores. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 2700–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tutol, J.N.; Tang, L.; Zhu, L.; Ong, W.S.Y.; Dodani, S.; Fang, C. Excitation ratiometric chloride sensing in a standalone yellow fluorescent protein is powered by the interplay between proton transfer and conformational reorganization. Chem. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digman, M.A.; Caiolfa, V.R.; Zamai, M.; Gratton, E. The phasor approach to fluorescence lifetime imaging analysis. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, L14–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranjit, S.; Malacrida, L.; Jameson, D.M.; Gratton, E. Fit-free analysis of fluorescence lifetime imaging data using the phasor approach. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1979–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinenko, K.L.; Webber, N.M.; Meech, S.R. Internal conversion in the chromophore of the green fluorescent protein: Temperature dependence and isoviscosity analysis. J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 107, 2616–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramers, H.A. Brownian motion in a field of force and the diffusion model of chemical reactions. Physica 1940, 7, 284–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettig, W.; Fritz, R.; Braun, D. Combination of pressure and temperature dependent measurements: A simple access to intrinsic thermal activation energies. J. Phys. Chem. A 1997, 101, 6830–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, H. Solvent-fluctuation control of solution reactions and its manifestation in protein functions. In Advances in Chemical Physics: Electron Transfer—From Isolated Molecules to Biomolecules. Part 2; Prigogine, I., Rice, S.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; Volume 107, pp. 601–646. [Google Scholar]
- Amdursky, N.; Erez, Y.; Huppert, D. Molecular rotors: What lies behind the high sensitivity of the thioflavin-T fluorescent marker. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romei, M.G.; Lin, C.-Y.; Mathews, I.I.; Boxer, S.G. Electrostatic control of photoisomerization pathways in proteins. Science 2020, 367, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozhanova, N.G.; Baranov, M.S.; Baleeva, N.S.; Gavrikov, A.S.; Mishin, A.S. Red-shifted aminated derivatives of GFP chromophore for live-cell protein labeling with lipocalins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Solvent | (ns) | (108 s−1) | (108 s−1) | (108 s−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H2O | 0.78 | 12.90 | 12.65 | 0.25 |
| 2 | MeOH | 0.54 | 18.55 | 17.43 | 1.12 |
| 3 | EtOH | 1.05 | 9.50 | 8.31 | 1.19 |
| 4 | 2-PrOH | 1.32 | 7.56 | 6.32 | 1.24 |
| 5 | ACN | 1.38 | 7.25 | 6.10 | 1.15 |
| 6 | DMF | 1.85 | 5.39 | 4.59 | 0.80 |
| 7 | acetone | 2.23 | 4.48 | 3.15 | 1.33 |
| 8 | DCM | 4.24 | 2.36 | 0.88 | 1.48 |
| 9 | EtOAc | 9.94 | 1.01 | 0.54 | 0.47 |
| 10 | dioxane | 3.72 | 2.69 | 1.10 | 1.59 |
| 11 | toluene | 6.10 | 1.64 | 0.50 | 1.14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Boulanger, S.A.; Sokolov, A.I.; Baranov, M.S.; Fang, C. A Novel Dialkylamino GFP Chromophore as an Environment-Polarity Sensor Reveals the Role of Twisted Intramolecular Charge Transfer. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080234
Chen C, Boulanger SA, Sokolov AI, Baranov MS, Fang C. A Novel Dialkylamino GFP Chromophore as an Environment-Polarity Sensor Reveals the Role of Twisted Intramolecular Charge Transfer. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(8):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080234
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Cheng, Sean A. Boulanger, Anatolii I. Sokolov, Mikhail S. Baranov, and Chong Fang. 2021. "A Novel Dialkylamino GFP Chromophore as an Environment-Polarity Sensor Reveals the Role of Twisted Intramolecular Charge Transfer" Chemosensors 9, no. 8: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080234
APA StyleChen, C., Boulanger, S. A., Sokolov, A. I., Baranov, M. S., & Fang, C. (2021). A Novel Dialkylamino GFP Chromophore as an Environment-Polarity Sensor Reveals the Role of Twisted Intramolecular Charge Transfer. Chemosensors, 9(8), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080234