Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation in Organ Culture: New Insights for Uterine Fibroid Treatment
Abstract
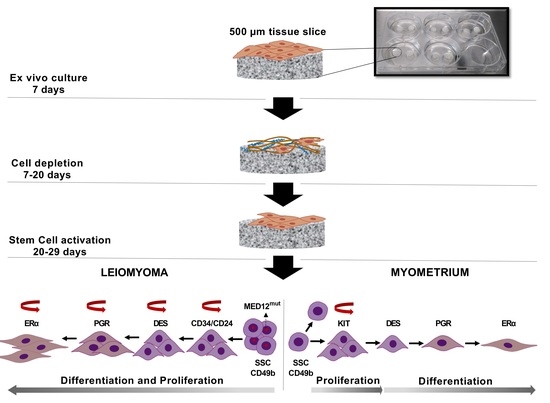
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Sampling
2.2. Tissue Slice Culture
2.3. Nucleic Acid and Protein Isolation
2.4. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.5. MED12 Mutation Detection
2.6. Histological Staining and Immunostaining
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Spontaneous Growth of Myometrial and Leiomyoma Cells
3.2. MED12 Mutation and HMGA2 Expression Were Maintained in Long-Term Cultures
3.3. Differential Expression of Stem Cell and Undifferentiated Cell Markers in Normal and Tumor Slices
3.4. Expression of Ovarian Steroids Receptors Was Induced at Long Incubation Times
3.5. Massive Cell Proliferation in Fibroids Contrast with Few Proliferating Cells in Myometrial Slices
3.6. Differential Expression of IGF Family in Normal and Tumor Slices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stewart, E.A. Uterine Fibroids. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somigliana, E.; Reschini, M.; Bonanni, V.; Busnelli, A.; Piani, L.L.; Vercellini, P. Fibroids and natural fertility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2021, 43, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulun, S.E. Uterine Fibroids. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1344–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, P.; Ono, M.; Moravek, M.; Coon, J.S.; Navarro, A.; Monsivais, D.; Dyson, M.; Druschitz, S.A.; Malpani, S.S.; Serna, V.A.; et al. Human Uterine Leiomyoma Stem/Progenitor Cells Expressing CD34 and CD49b Initiate Tumors In Vivo. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E601–E606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravek, M.; Yin, P.; Coon, J.S.; Ono, M.; Druschitz, S.A.; Malpani, S.S.; Dyson, M.; Rademaker, A.W.; Robins, J.C.; Wei, J.-J.; et al. Paracrine Pathways in Uterine Leiomyoma Stem Cells Involve Insulinlike Growth Factor 2 and Insulin Receptor A. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 1588–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drosch, M.; Schmidt, N.; Markowski, M.N.; Zollner, T.M.; Koch, M.; Bullerdiek, J. The CD24hi smooth muscle subpopulation is the predominant fraction in uterine fibroids. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 20, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehine, M.; Kaasinen, E.; Heinonen, H.-R.; Mäkinen, N.; Kämpjärvi, K.; Sarvilinna, N.; Aavikko, M.; Vähärautio, A.; Pasanen, A.; Bützow, R.; et al. Integrated data analysis reveals uterine leiomyoma subtypes with distinct driver pathways and biomarkers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gattas, G.J.F.; Quade, B.J.; Nowak, R.A.; Morton, C.C. HMGIC Expression in Human Adult and Fetal Tissues and in Uterine Leiomyomata. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 1999, 25, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemke, M.; Meyer, A.; Nezhad, M.H.; Bartnitzke, S.; Drieschner, N.; Frantzen, C.; Schmidt, E.H.; Belge, G.; Bullerdiek, J. Overexpression ofHMGA2in uterine leiomyomas points to its general role for the pathogenesis of the disease. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2009, 48, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, L.J.; Hernández-Beeftink, T.; Salas, A.; Jung, Y.; Reyes, R.; de Oca, F.M.; Hernández, M.; Almeida, T.A. HMGA2 and MED12 alterations frequently co-occur in uterine leiomyomas. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 150, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkinen, N.; Mehine, M.; Tolvanen, J.; Kaasinen, E.; Li, Y.; Lehtonen, H.J.; Gentile, M.; Yan, J.; Enge, M.; Taipale, M.; et al. MED12, the Mediator Complex Subunit 12 Gene, Is Mutated at High Frequency in Uterine Leiomyomas. Science 2011, 334, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäkinen, N.; Heinonen, H.-R.; Moore, S.; Tomlinson, I.P.; Van Der Spuy, Z.M.; Aaltonen, L.A. MED12 exon 2 mutations are common in uterine leiomyomas from South African patients. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 966–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Zou, Y.; Luo, Y.; Guo, J.-B.; Liu, F.-Y.; Zhou, J.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Wan, L.; Huang, O.-P. Prevalence and clinical significance of mediator complex subunit 12 mutations in 362 Han Chinese samples with uterine leiomyoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.; Cheon, K.; Chae, B.; Hwang, H.; Kim, H.-K.; Chung, Y.-J.; Song, J.-Y.; Cho, H.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, M.-R. Analysis of MED12 Mutation in Multiple Uterine Leiomyomas in South Korean patients. Int. J. Med Sci. 2018, 15, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bulun, S.E.; Moravek, M.B.; Yin, P.; Ono, M.; Coon, V.J.S.C.; Dyson, M.T.; Navarro, A.; Marsh, E.E.; Zhao, H.; Maruyama, T.; et al. Uterine Leiomyoma Stem Cells: Linking Progesterone to Growth. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2015, 33, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, A.; Lopez, J.; Reyes, R.; Évora, C.; De Oca, F.M.; Báez, D.; Delgado, A.; Almeida, T.A. Organotypic culture as a research and preclinical model to study uterine leiomyomas. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, T.A.; Quispe-Ricalde, A.; de Oca, F.M.; Foronda, P.; Hernández, M.M. A high-throughput open-array qPCR gene panel to identify housekeeping genes suitable for myometrium and leiomyoma expression analysis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 134, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, A.; Vázquez, P.; Bello, A.R.; Báez, D.; Almeida, T.A. Dual agonist–antagonist effect of ulipristal acetate in human endometrium and myometrium. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 21, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Santana, A.; Marrero-Hernández, S.; Dorta, I.; Hernández, M.; Pinto, F.M.; Báez, D.; Bello, A.R.; Candenas, L.; Almeida, T.A. Altered expression of the tachykinins substance P/neurokinin A/hemokinin-1 and their preferred neurokinin 1/neurokinin 2 receptors in uterine leiomyomata. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klemke, M.; Müller, M.H.; Wosniok, W.; Markowski, M.N.; Nimzyk, R.; Helmke, B.M.; Bullerdiek, J. Correlated Expression of HMGA2 and PLAG1 in Thyroid Tumors, Uterine Leiomyomas and Experimental Models. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Lin, Z.; Reierstad, S.; Wu, J.; Ishikawa, H.; Marsh, E.E.; Innes, J.; Cheng, Y.; Pearson, K.; Coon, J.S.; et al. Transcription Factor KLF11 Integrates Progesterone Receptor Signaling and Proliferation in Uterine Leiomyoma Cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1722–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.T.; Jiang, G.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, J.N. Ki67 is a promising molecular target in the diagnosis of cancer (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 11, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Majumdar, S.; Liu, S.-T. Cell division symmetry control and cancer stem cells. AIMS Mol. Sci. 2020, 7, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, S.J.; Kimble, J. Asymmetric and symmetric stem-cell divisions in development and cancer. Nature 2006, 441, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szotek, P.P.; Chang, H.L.; Zhang, L.; Preffer, F.; Dombkowski, D.; Donahoe, P.K.; Teixeira, J. Adult Mouse Myometrial Label-Retaining Cells Divide in Response to Gonadotropin Stimulation. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzer, G.; Milner, D.J.; Kim, J.U.; Bradley, A.; Capetanaki, Y. Cytoskeletal Control of Myogenesis: A Desmin Null Mutation Blocks the Myogenic Pathway during Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation. Dev. Biol. 1995, 172, 422–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofner, M.; Höllrigl, A.; Puz, S.; Stary, M.; Weitzer, G. Desmin stimulates differentiation of cardiomyocytes and up-regulation of brachyury and nkx2.5. Differentiation 2007, 75, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Maruyama, T.; Masuda, H.; Kajitani, T.; Nagashima, T.; Arase, T.; Ito, M.; Ohta, K.; Uchida, H.; Asada, H.; et al. Side population in human uterine myometrium displays phenotypic and functional characteristics of myometrial stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18700–18705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Gilbert, J.A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, Q.; Ramanujan, K.; Shavlakadze, T.; Eash, J.K.; Scaramozza, A.; Goddeeris, M.M.; et al. An HMGA2-IGF2BP2 Axis Regulates Myoblast Proliferation and Myogenesis. Dev. Cell 2012, 23, 1176–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figarella-Branger, D.; Moreau, H.; Pellissier, J.F.; Bianco, N.; Rougon, G. CD24, a signal-transducing molecule expressed on human B lymphocytes, is a marker for human regenerating muscle. Acta Neuropathol. 1993, 86, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, I.; Kawai, H.; Kawajiri, M.; Fukunaga, H.; Horikiri, T.; Niiyama, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Arimura, K.; Osame, M. Statistically Significant Differences in the Number of CD24 Positive Muscle Fibers and Satellite Cells between Sarcoglycanopathy and Age-Matched Becker Muscular Dystrophy Patients. Intern. Med. 1999, 38, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duex, J.E.; Owens, C.; Chauca-Diaz, A.; Dancik, G.M.; Vanderlinden, L.A.; Ghosh, D.; Leivo, M.Z.; Hansel, D.E.; Theodorescu, D. Nuclear CD24 Drives Tumor Growth and Is Predictive of Poor Patient Prognosis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 4858–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaidi, M.R.; Okada, Y.; Chada, K.K. Misexpression of Full-length HMGA2 Induces Benign Mesenchymal Tumors in Mice. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7453–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schoenmakers, E.F.; Wanschura, S.; Mols, R.; Bullerdiek, J.; Berghe, H.V.D.; Van De Ven, W.J. Recurrent rearrangements in the high mobility group protein gene, HMGI-C, in benign mesenchymal tumours. Nat. Genet. 1995, 10, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello, J.B.H.; Barros-Filho, M.C.; Abreu, F.B.; Cirilo, P.D.R.; Domingues, M.A.C.; Pontes, A.; Rogatto, S.R. MicroRNAs involved in the HMGA2 deregulation and its co-occurrence with MED12 mutation in uterine leiomyoma. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 24, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Chen, G.; He, Q.; Liu, M.; Gao, K.; Cai, B.; Qu, J.; Lin, S.; Geng, A.; Li, S.; et al. An HMGA2-p62-ERα axis regulates uterine leiomyomas proliferation. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 10966–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qiang, W.; Griffin, B.B.; Gao, T.; Chakravarti, D.; Bulun, S.; Kim, J.J.; Wei, J.-J. HMGA2-mediated tumorigenesis through angiogenesis in leiomyoma. Fertil. Steril. 2020, 114, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unachukwu, U.; Chada, K.; D’Armiento, J. High Mobility Group AT-Hook 2 (HMGA2) Oncogenicity in Mesenchymal and Epithelial Neoplasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, H. HMGA2 involvement in uterine leiomyomas development through angiogenesis activation. Fertil. Steril. 2020, 114, 974–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turiello, R.; Pinto, A.; Morello, S. CD73: A Promising Biomarker in Cancer Patients. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 609931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.; Segars, J.; Catherino, W.H. Integrin β1 regulates leiomyoma cytoskeletal integrity and growth. Matrix Biol. 2012, 31, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, R.; Liao, C.; Zhang, Q. Hypoxia-Driven Effects in Cancer: Characterization, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2021, 10, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Ii, M.; Saito, T.; Terai, Y.; Tabata, Y.; Ohmichi, M.; Asahi, M. Establishment of a novel mouse xenograft model of human uterine leiomyoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasajima, J.; Mizukami, Y.; Sugiyama, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Kawamoto, T.; Koizumi, K.; Fujii, R.; Motomura, W.; Sato, K.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Transplanting Normal Vascular Proangiogenic Cells to Tumor-Bearing Mice Triggers Vascular Remodeling and Reduces Hypoxia in Tumors. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6283–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serna, V.A.; Wu, X.; Qiang, W.; Thomas, J.; Blumenfeld, M.L.; Kurita, T. Cellular kinetics of MED12-mutant uterine leiomyoma growth and regression in vivo. Endocrine-Related Cancer 2018, 25, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennesch, M.A.; Picard, D. Minireview: Tipping the Balance: Ligand-Independent Activation of Steroid Receptors. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grissom, E.M.; Daniel, J. Evidence for Ligand-Independent Activation of Hippocampal Estrogen Receptor-α by IGF-1 in Hippocampus of Ovariectomized Rats. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 3149–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Saile, K.; Swartz, C.D.; He, H.; Zheng, X.; Kissling, G.E.; Di, X.; Lucas, S.; Robboy, S.J.; Dixon, D. Differential Expression of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) and IGF-I Pathway Activation in Human Uterine Leiomyomas. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkioka, E.; Msaouel, P.; Philippou, A.; Vlaghogiannis, N.I.; Vogkou, C.T.; Margiolis, A.; Koutsilieris, M. The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Signaling Pathways in Uterine Leiomyoma. In Vivo 2015, 29, 637–649. [Google Scholar]
- Allard, J.B.; Duan, C. IGF-Binding Proteins: Why Do They Exist and Why Are There So Many? Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salas, A.; Beltrán-Flores, S.; Évora, C.; Reyes, R.; Montes de Oca, F.; Delgado, A.; Almeida, T.A. Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation in Organ Culture: New Insights for Uterine Fibroid Treatment. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071542
Salas A, Beltrán-Flores S, Évora C, Reyes R, Montes de Oca F, Delgado A, Almeida TA. Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation in Organ Culture: New Insights for Uterine Fibroid Treatment. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(7):1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071542
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalas, Ana, Silvia Beltrán-Flores, Carmen Évora, Ricardo Reyes, Francisco Montes de Oca, Araceli Delgado, and Teresa A. Almeida. 2022. "Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation in Organ Culture: New Insights for Uterine Fibroid Treatment" Biomedicines 10, no. 7: 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071542
APA StyleSalas, A., Beltrán-Flores, S., Évora, C., Reyes, R., Montes de Oca, F., Delgado, A., & Almeida, T. A. (2022). Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation in Organ Culture: New Insights for Uterine Fibroid Treatment. Biomedicines, 10(7), 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071542