Figure 1.
Structures of Bioactive steroids bearing nitrile group(s).
Figure 1.
Structures of Bioactive steroids bearing nitrile group(s).
Figure 2.
3D model and percentage distribution of dominant and related biological activities illustrated by the example of dienogest (1), a widely recognized semi-synthetic 19-nortestosterone derivative with unique pharmacological properties. The activities indicated by the numbers are as follows: 1. Menstruation disorders treatment (16.5%), 2. Menopausal disorders treatment (16.3%), 3. Ovulation inhibitor (15.2%), 4. Contraceptive (14.7%), 5. Anti-inflammatory (13.6%), 6. Androgen antagonist (13.3%), and 7. Endometriosis treatment (10.3%). Dienogest is highly selective for the progesterone receptor, exerting a potent progestogenic effect and a moderate anti-gonadotropic effect. It does not possess androgenic, glucocorticoid, or mineralocorticoid activity. Its resemblance to norethisterone is evident in its remarkable endometrial efficacy, which contributes to the stability of the menstrual cycle in women. Dienogest’s robust endometrial efficacy underlies its application in the treatment of endometriosis and provides anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory effects for the management of endometriotic lesions. Nitrile group is marked in blue.
Figure 2.
3D model and percentage distribution of dominant and related biological activities illustrated by the example of dienogest (1), a widely recognized semi-synthetic 19-nortestosterone derivative with unique pharmacological properties. The activities indicated by the numbers are as follows: 1. Menstruation disorders treatment (16.5%), 2. Menopausal disorders treatment (16.3%), 3. Ovulation inhibitor (15.2%), 4. Contraceptive (14.7%), 5. Anti-inflammatory (13.6%), 6. Androgen antagonist (13.3%), and 7. Endometriosis treatment (10.3%). Dienogest is highly selective for the progesterone receptor, exerting a potent progestogenic effect and a moderate anti-gonadotropic effect. It does not possess androgenic, glucocorticoid, or mineralocorticoid activity. Its resemblance to norethisterone is evident in its remarkable endometrial efficacy, which contributes to the stability of the menstrual cycle in women. Dienogest’s robust endometrial efficacy underlies its application in the treatment of endometriosis and provides anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory effects for the management of endometriotic lesions. Nitrile group is marked in blue.
![Biomedicines 11 02698 g002]()
Figure 3.
3D Graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of cyanosteroids (1, 2, 4, and 20) with 92% confidence for the treatment of menstruation disorders and related diseases. These cyanosteroids, featuring a nitrile group, have exhibited noteworthy properties in the treatment of various conditions. They have demonstrated efficacy in addressing menstrual and menopausal disorders, muscular dystrophy, and male reproductive dysfunction and have shown high certainty as potent ovulation inhibitors. These findings have garnered significant attention in the field.
Figure 3.
3D Graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of cyanosteroids (1, 2, 4, and 20) with 92% confidence for the treatment of menstruation disorders and related diseases. These cyanosteroids, featuring a nitrile group, have exhibited noteworthy properties in the treatment of various conditions. They have demonstrated efficacy in addressing menstrual and menopausal disorders, muscular dystrophy, and male reproductive dysfunction and have shown high certainty as potent ovulation inhibitors. These findings have garnered significant attention in the field.
Figure 4.
3D Graph depicting the predicted and calculated anti-inflammatory activity of cyanosteroids (17, 18, and 19) with over 93% confidence. The 6-cyano-steroids (17–19) exhibit remarkable anti-endocrine properties and display robust anti-inflammatory activity. These cyanosteroids not only possess potent anti-inflammatory effects but also demonstrate additional properties as aromatase inhibitors or estrogen antagonists. The high confidence level of over 93% further emphasizes their potential in addressing inflammatory conditions.
Figure 4.
3D Graph depicting the predicted and calculated anti-inflammatory activity of cyanosteroids (17, 18, and 19) with over 93% confidence. The 6-cyano-steroids (17–19) exhibit remarkable anti-endocrine properties and display robust anti-inflammatory activity. These cyanosteroids not only possess potent anti-inflammatory effects but also demonstrate additional properties as aromatase inhibitors or estrogen antagonists. The high confidence level of over 93% further emphasizes their potential in addressing inflammatory conditions.
Figure 5.
3D Graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of cyanosteroid (23) with over 97% confidence for the treatment of heart failure and related diseases. This synthetic cyanosteroid demonstrates an exceptional degree of activity, with over 97% confidence, making it a promising candidate for the treatment of heart failure and atherosclerosis. This compound exhibits a wide range of beneficial properties, acting as a potent cardiotonic agent, exerting antihypertensive effects, and displaying an anti-hyperaldosteronism effect. The combination of these positive qualities in a single drug represents a rare occurrence, further highlighting its potential significance in addressing heart-related conditions.
Figure 5.
3D Graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of cyanosteroid (23) with over 97% confidence for the treatment of heart failure and related diseases. This synthetic cyanosteroid demonstrates an exceptional degree of activity, with over 97% confidence, making it a promising candidate for the treatment of heart failure and atherosclerosis. This compound exhibits a wide range of beneficial properties, acting as a potent cardiotonic agent, exerting antihypertensive effects, and displaying an anti-hyperaldosteronism effect. The combination of these positive qualities in a single drug represents a rare occurrence, further highlighting its potential significance in addressing heart-related conditions.
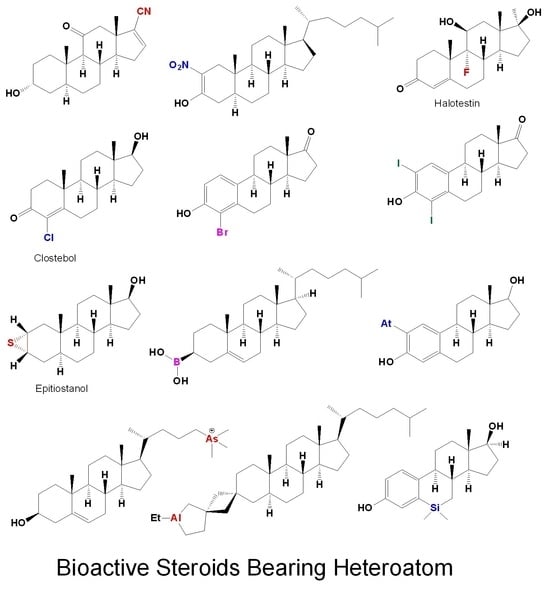
Figure 6.
Bioactive steroids bearing nitrile group(s).
Figure 6.
Bioactive steroids bearing nitrile group(s).
Figure 7.
3D Graph depicting the predicted and calculated activity of cyanosteroids (32, 35, and 36) with over 90% confidence as inhibitors of cholesterol synthesis. Lovastatin and its related metabolites, such as simvastatin, pravastatin, fluvastatin, atorvastatin, and cerivastatin, are well-known inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis. These compounds have been isolated from various sources, including Aspergillus terreus, Monascus species (M. ruber, M. purpureus, M. pilosus, M. vitreus, M. pubigerus, and M. anka), Paecilomyces viridis, Pleurotus ostreatus, and Pencillium citrinum. Cyanosteroids (32, 35, and 36) exhibit robust activity as potent inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis. With their strong inhibitory effects, these compounds hold promise for potential clinical applications in medicine, although further investigation via preliminary trials is warranted.
Figure 7.
3D Graph depicting the predicted and calculated activity of cyanosteroids (32, 35, and 36) with over 90% confidence as inhibitors of cholesterol synthesis. Lovastatin and its related metabolites, such as simvastatin, pravastatin, fluvastatin, atorvastatin, and cerivastatin, are well-known inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis. These compounds have been isolated from various sources, including Aspergillus terreus, Monascus species (M. ruber, M. purpureus, M. pilosus, M. vitreus, M. pubigerus, and M. anka), Paecilomyces viridis, Pleurotus ostreatus, and Pencillium citrinum. Cyanosteroids (32, 35, and 36) exhibit robust activity as potent inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis. With their strong inhibitory effects, these compounds hold promise for potential clinical applications in medicine, although further investigation via preliminary trials is warranted.
Figure 8.
3D Graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of cyanosteroids (38 and 39) with over 91% confidence as 5α-reductase inhibitors. 5α-Reductase inhibitors are widely used in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. These inhibitors encompass diverse azasteroids. Cyanosteroids (38 and 39) also fall into this category of drugs while additionally featuring a nitrile group. The high confidence level, combined with their classification as 5α-reductase inhibitors, positions cyanosteroids (38 and 39) as potential candidates for therapeutic interventions in conditions related to this enzyme’s activity.
Figure 8.
3D Graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of cyanosteroids (38 and 39) with over 91% confidence as 5α-reductase inhibitors. 5α-Reductase inhibitors are widely used in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. These inhibitors encompass diverse azasteroids. Cyanosteroids (38 and 39) also fall into this category of drugs while additionally featuring a nitrile group. The high confidence level, combined with their classification as 5α-reductase inhibitors, positions cyanosteroids (38 and 39) as potential candidates for therapeutic interventions in conditions related to this enzyme’s activity.
Figure 9.
Bioactive steroids bearing nitro group.
Figure 9.
Bioactive steroids bearing nitro group.
Figure 10.
Bioactive steroids bearing nitro group(s).
Figure 10.
Bioactive steroids bearing nitro group(s).
Figure 11.
3D Graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of nitro-steroids (52, 53, and 54) with over 95% confidence as respiratory analeptics. The term analeptic typically refers to respiratory analeptics, which are central nervous system stimulants encompassing a wide range of drugs used for the treatment of conditions such as depression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and respiratory depression. Nitrosteroids, in this case, serve as rare representatives demonstrating such properties.
Figure 11.
3D Graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of nitro-steroids (52, 53, and 54) with over 95% confidence as respiratory analeptics. The term analeptic typically refers to respiratory analeptics, which are central nervous system stimulants encompassing a wide range of drugs used for the treatment of conditions such as depression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and respiratory depression. Nitrosteroids, in this case, serve as rare representatives demonstrating such properties.
Figure 12.
3D Graph presenting the predicted and calculated activity of nitro-steroids (66, 67, 68, and 69) with over 92% confidence as treatments for prostate disease and prostatic (benign) hyperplasia. These nitro-steroids demonstrate potential therapeutic effects specifically targeted toward addressing prostate-related conditions and benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Figure 12.
3D Graph presenting the predicted and calculated activity of nitro-steroids (66, 67, 68, and 69) with over 92% confidence as treatments for prostate disease and prostatic (benign) hyperplasia. These nitro-steroids demonstrate potential therapeutic effects specifically targeted toward addressing prostate-related conditions and benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Figure 15.
Bioactive steroids bearing fluorine atom(s).
Figure 15.
Bioactive steroids bearing fluorine atom(s).
Figure 16.
3D graph presenting the predicted and calculated antiallergic and anti-asthmatic activity of fluorinated steroids (
101,
105,
110, and
112) with over 96% confidence. It is noteworthy that these steroids demonstrate rare and beneficial properties as antiallergic and anti-asthmatic agents. This activity seems to be a dominant characteristic of steroids bearing fluorine atom(s), as multiple steroids within this group exhibit such activity. Further details and specific information can be found in
Table 5.
Figure 16.
3D graph presenting the predicted and calculated antiallergic and anti-asthmatic activity of fluorinated steroids (
101,
105,
110, and
112) with over 96% confidence. It is noteworthy that these steroids demonstrate rare and beneficial properties as antiallergic and anti-asthmatic agents. This activity seems to be a dominant characteristic of steroids bearing fluorine atom(s), as multiple steroids within this group exhibit such activity. Further details and specific information can be found in
Table 5.
Figure 17.
3D graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activities of steroids bearing fluorine atom(s) (107 and 108) with over 94% confidence for the treatment of gynecological diseases and menopausal disorders.
Figure 17.
3D graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activities of steroids bearing fluorine atom(s) (107 and 108) with over 94% confidence for the treatment of gynecological diseases and menopausal disorders.
Figure 18.
Bioactive steroids bearing chlorine atom(s).
Figure 18.
Bioactive steroids bearing chlorine atom(s).
Figure 19.
3D Graph depicting the predicted and calculated anti-inflammatory activity of steroids containing chlorine atom(s) (127, 129, and 130) with over 95% confidence. This demonstrates the diverse and sometimes unexpected characteristics of chlorinated steroids in terms of their biological activities.
Figure 19.
3D Graph depicting the predicted and calculated anti-inflammatory activity of steroids containing chlorine atom(s) (127, 129, and 130) with over 95% confidence. This demonstrates the diverse and sometimes unexpected characteristics of chlorinated steroids in terms of their biological activities.
Figure 20.
Bioactive steroids bearing bromine atom(s).
Figure 20.
Bioactive steroids bearing bromine atom(s).
Figure 21.
Bioactive steroids bearing iodine atom.
Figure 21.
Bioactive steroids bearing iodine atom.
Figure 22.
3D Graph showing the predicted and calculated activity of steroids bearing iodine atom (154, 158, and 159) with a high degree of confidence as ovulation inhibitors, contraceptives, and climacteric treatments. These iodinated steroids exhibit strong pharmacological properties that have significant potential for various applications in medical practice, particularly in the preservation of women’s health.
Figure 22.
3D Graph showing the predicted and calculated activity of steroids bearing iodine atom (154, 158, and 159) with a high degree of confidence as ovulation inhibitors, contraceptives, and climacteric treatments. These iodinated steroids exhibit strong pharmacological properties that have significant potential for various applications in medical practice, particularly in the preservation of women’s health.
Figure 23.
Bioactive steroids bearing the epithio group.
Figure 23.
Bioactive steroids bearing the epithio group.
Figure 24.
3D graph that depicts the predicted and calculated activity of epithio steroids. Specifically, the graph focuses on compounds numbered 160, 161, 162, 164, 165, and 166. These compounds have been studied for their potential therapeutic applications as antitumor, antitumor breast cancer, and demonstrated estrogen antagonist properties. Based on the graph, these epithio steroids exhibit a high level of confidence, with a maximum prediction accuracy of over 97%. They have shown promising activity in the areas of antitumor effects, specifically in the treatment of breast cancer. Additionally, these steroids have demonstrated properties as estrogen antagonists, suggesting their potential use in blocking the effects of estrogen. The graph provides a visual representation of the relationship between the predicted activity and the calculated activity of these steroids. It allows researchers and scientists to analyze and compare the efficacy of these compounds in different therapeutic areas. This information is valuable in understanding the potential of epithio steroids for their antitumor and estrogen antagonist properties. It can guide further research and development in the field, aiding in the discovery of new treatments and potential drug candidates.
Figure 24.
3D graph that depicts the predicted and calculated activity of epithio steroids. Specifically, the graph focuses on compounds numbered 160, 161, 162, 164, 165, and 166. These compounds have been studied for their potential therapeutic applications as antitumor, antitumor breast cancer, and demonstrated estrogen antagonist properties. Based on the graph, these epithio steroids exhibit a high level of confidence, with a maximum prediction accuracy of over 97%. They have shown promising activity in the areas of antitumor effects, specifically in the treatment of breast cancer. Additionally, these steroids have demonstrated properties as estrogen antagonists, suggesting their potential use in blocking the effects of estrogen. The graph provides a visual representation of the relationship between the predicted activity and the calculated activity of these steroids. It allows researchers and scientists to analyze and compare the efficacy of these compounds in different therapeutic areas. This information is valuable in understanding the potential of epithio steroids for their antitumor and estrogen antagonist properties. It can guide further research and development in the field, aiding in the discovery of new treatments and potential drug candidates.
![Biomedicines 11 02698 g024]()
Figure 25.
Steroids bearing the epithio group.
Figure 25.
Steroids bearing the epithio group.
Figure 26.
3D graph that illustrates the predicted and calculated activity of epithio steroids. Specifically, the graph focuses on compounds numbered 169, 176, and 178. These compounds have been studied for their potential therapeutic applications. The graph shows that these epithio steroids exhibit a high level of confidence, with a maximum prediction accuracy of over 94%. These compounds possess rare properties as both cardiotonic and antiarrhythmic agents. Cardiotonic drugs are used to enhance the performance and improve the contraction of the heart muscles. This leads to improved blood flow to all body tissues, thereby supporting cardiovascular health. On the other hand, antiarrhythmic drugs are medications that help prevent and treat abnormal or irregular heart rhythms. They help restore and maintain a normal rhythm, ensuring the proper functioning of the heart. The fact that these epithio steroids exhibit both cardiotonic and antiarrhythmic properties is noteworthy. It suggests their potential use as dual-function agents for the treatment of cardiovascular conditions.
Figure 26.
3D graph that illustrates the predicted and calculated activity of epithio steroids. Specifically, the graph focuses on compounds numbered 169, 176, and 178. These compounds have been studied for their potential therapeutic applications. The graph shows that these epithio steroids exhibit a high level of confidence, with a maximum prediction accuracy of over 94%. These compounds possess rare properties as both cardiotonic and antiarrhythmic agents. Cardiotonic drugs are used to enhance the performance and improve the contraction of the heart muscles. This leads to improved blood flow to all body tissues, thereby supporting cardiovascular health. On the other hand, antiarrhythmic drugs are medications that help prevent and treat abnormal or irregular heart rhythms. They help restore and maintain a normal rhythm, ensuring the proper functioning of the heart. The fact that these epithio steroids exhibit both cardiotonic and antiarrhythmic properties is noteworthy. It suggests their potential use as dual-function agents for the treatment of cardiovascular conditions.
![Biomedicines 11 02698 g026]()
Figure 27.
Steroids bearing boron atom(s).
Figure 27.
Steroids bearing boron atom(s).
Figure 28.
3D model and percentage distribution of the dominant skin diseases activity on the example of steroid-bearing boron atom (190), which has a wide range of anticancer properties. Where activities are indicated under the numbers: 1. Anti-eczematic (18%), 2. Dermatologic (16%). 3, Anti-psoriatic (14.9%), 4. Antihypertensive (17.9%), 5. Myocardial ischemia treatment (16.8%), and 6. Antineoplastic (16.4%). The boron atom is highlighted in green.
Figure 28.
3D model and percentage distribution of the dominant skin diseases activity on the example of steroid-bearing boron atom (190), which has a wide range of anticancer properties. Where activities are indicated under the numbers: 1. Anti-eczematic (18%), 2. Dermatologic (16%). 3, Anti-psoriatic (14.9%), 4. Antihypertensive (17.9%), 5. Myocardial ischemia treatment (16.8%), and 6. Antineoplastic (16.4%). The boron atom is highlighted in green.
Figure 29.
3D graph illustrates the predicted and calculated activity of steroids bearing a boron atom (192–197). These compounds exhibit a high level of confidence, with a maximum prediction accuracy of over 91%. Notably, these boron-containing steroids demonstrate a unique and rare ability to treat psychosexual dysfunction associated with the treatment of gynecological diseases in women. Psychosexual dysfunction refers to difficulties or disruptions in sexual functioning that may have psychological or emotional origins. The inclusion of boron in these steroids offers a novel approach to addressing psychosexual dysfunction, highlighting their potential in the treatment of gynecological conditions while simultaneously addressing associated sexual issues. This distinctive property sets them apart from other classes of steroids and underscores their significance in providing comprehensive care for women’s health. The 3D graph visually represents the relationship between the predicted activity and the calculated activity of these boron-containing steroids. It offers valuable insights into their potential efficacy in treating psychosexual dysfunction, providing a foundation for further research and clinical exploration in this area. The availability of the 3D plot and the percentage distribution of dominant activity for specific borosteroids offer valuable insights into their efficacy and potential applications. This information guides researchers in exploring the therapeutic potential of these compounds and designing more targeted and effective treatments for various diseases, particularly those related to skin disorders and beyond.
Figure 29.
3D graph illustrates the predicted and calculated activity of steroids bearing a boron atom (192–197). These compounds exhibit a high level of confidence, with a maximum prediction accuracy of over 91%. Notably, these boron-containing steroids demonstrate a unique and rare ability to treat psychosexual dysfunction associated with the treatment of gynecological diseases in women. Psychosexual dysfunction refers to difficulties or disruptions in sexual functioning that may have psychological or emotional origins. The inclusion of boron in these steroids offers a novel approach to addressing psychosexual dysfunction, highlighting their potential in the treatment of gynecological conditions while simultaneously addressing associated sexual issues. This distinctive property sets them apart from other classes of steroids and underscores their significance in providing comprehensive care for women’s health. The 3D graph visually represents the relationship between the predicted activity and the calculated activity of these boron-containing steroids. It offers valuable insights into their potential efficacy in treating psychosexual dysfunction, providing a foundation for further research and clinical exploration in this area. The availability of the 3D plot and the percentage distribution of dominant activity for specific borosteroids offer valuable insights into their efficacy and potential applications. This information guides researchers in exploring the therapeutic potential of these compounds and designing more targeted and effective treatments for various diseases, particularly those related to skin disorders and beyond.
![Biomedicines 11 02698 g029]()
Figure 30.
Steroids bearing an aluminum atom.
Figure 30.
Steroids bearing an aluminum atom.
Figure 31.
3D graph illustrates the predicted and calculated antiprotozoal activity, specifically against Plasmodium sp., of aluminum-containing steroids. The graph focuses on compounds numbered 202, 203, 208, and 209. These compounds have been investigated for their potential as antiprotozoal agents. The graph demonstrates that these aluminum-containing steroids exhibit a high level of confidence, with a maximum prediction accuracy of over 92%. This indicates a strong likelihood that these compounds possess antiprotozoal activity against Plasmodium sp., the protozoan responsible for causing malaria. What makes these aluminum-containing steroids particularly interesting and useful is that they exhibit antiprotozoal activity without the presence of a peroxide group, which is commonly observed in steroids with similar activity. This suggests that the aluminum atom, in combination with the steroid structure, plays a crucial role in their antiprotozoal properties. The 3D graph visually represents the relationship between the predicted activity and the calculated activity of these aluminum-containing steroids. It provides insights into the efficacy of these compounds as antiprotozoal agents against Plasmodium sp.
Figure 31.
3D graph illustrates the predicted and calculated antiprotozoal activity, specifically against Plasmodium sp., of aluminum-containing steroids. The graph focuses on compounds numbered 202, 203, 208, and 209. These compounds have been investigated for their potential as antiprotozoal agents. The graph demonstrates that these aluminum-containing steroids exhibit a high level of confidence, with a maximum prediction accuracy of over 92%. This indicates a strong likelihood that these compounds possess antiprotozoal activity against Plasmodium sp., the protozoan responsible for causing malaria. What makes these aluminum-containing steroids particularly interesting and useful is that they exhibit antiprotozoal activity without the presence of a peroxide group, which is commonly observed in steroids with similar activity. This suggests that the aluminum atom, in combination with the steroid structure, plays a crucial role in their antiprotozoal properties. The 3D graph visually represents the relationship between the predicted activity and the calculated activity of these aluminum-containing steroids. It provides insights into the efficacy of these compounds as antiprotozoal agents against Plasmodium sp.
![Biomedicines 11 02698 g031]()
Figure 32.
Steroids bearing arsenic atoms or arsenosteroids.
Figure 32.
Steroids bearing arsenic atoms or arsenosteroids.
Figure 33.
3D graph illustrates the predicted and calculated antineoplastic activity of steroids bearing arsenic atoms (210–213). These compounds exhibit a high level of confidence, with a maximum prediction accuracy of over 98%.
Figure 33.
3D graph illustrates the predicted and calculated antineoplastic activity of steroids bearing arsenic atoms (210–213). These compounds exhibit a high level of confidence, with a maximum prediction accuracy of over 98%.
Figure 34.
Steroids bearing astatine atoms or astatosteroids.
Figure 34.
Steroids bearing astatine atoms or astatosteroids.
Figure 35.
3D graph represents the predicted and calculated anti-seborrheic and antifungal activity of steroids bearing an astatine atom (216 and 217). The graph demonstrates a high level of confidence, with a maximum prediction accuracy of over 93%. The focus of this graph is specifically on the anti-seborrheic and antifungal properties of astatine-containing steroids. Anti-seborrheic agents are substances that help control seborrheic dermatitis, a common skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and flaky skin. Antifungal agents, on the other hand, combat fungal infections caused by various fungi. By visualizing the predicted and calculated activity in this 3D graph, valuable insights into the potential efficacy of these steroids as anti-seborrheic and antifungal agents can be obtained. This information serves as a foundation for further research and development in the field of dermatology and related medical disciplines. It is worth noting that the exploration of astatosteroids and their biological activities is an ongoing area of investigation. Further studies are required to elucidate their mechanisms of action, evaluate their stability, and assess their potential for therapeutic applications in treating seborrheic dermatitis, fungal infections, and other related conditions.
Figure 35.
3D graph represents the predicted and calculated anti-seborrheic and antifungal activity of steroids bearing an astatine atom (216 and 217). The graph demonstrates a high level of confidence, with a maximum prediction accuracy of over 93%. The focus of this graph is specifically on the anti-seborrheic and antifungal properties of astatine-containing steroids. Anti-seborrheic agents are substances that help control seborrheic dermatitis, a common skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and flaky skin. Antifungal agents, on the other hand, combat fungal infections caused by various fungi. By visualizing the predicted and calculated activity in this 3D graph, valuable insights into the potential efficacy of these steroids as anti-seborrheic and antifungal agents can be obtained. This information serves as a foundation for further research and development in the field of dermatology and related medical disciplines. It is worth noting that the exploration of astatosteroids and their biological activities is an ongoing area of investigation. Further studies are required to elucidate their mechanisms of action, evaluate their stability, and assess their potential for therapeutic applications in treating seborrheic dermatitis, fungal infections, and other related conditions.
![Biomedicines 11 02698 g035]()
Figure 36.
Steroids bearing germanium atoms or germinated steroids.
Figure 36.
Steroids bearing germanium atoms or germinated steroids.
Figure 37.
3D graph represents the predicted and calculated antiacne and dermatologic activity of steroids bearing germanium atom (
227,
228, and
229). The graph demonstrates a high level of confidence, with a maximum prediction accuracy of over 98%. The 3D plot presented in
Figure 37 provides a visual representation of the potential activity of steroids bearing a germanium atom (
227–
229), offering valuable insights into their predicted efficacy. These findings inspire further investigation and potential development of novel therapeutic approaches based on germinated steroids.
Figure 37.
3D graph represents the predicted and calculated antiacne and dermatologic activity of steroids bearing germanium atom (
227,
228, and
229). The graph demonstrates a high level of confidence, with a maximum prediction accuracy of over 98%. The 3D plot presented in
Figure 37 provides a visual representation of the potential activity of steroids bearing a germanium atom (
227–
229), offering valuable insights into their predicted efficacy. These findings inspire further investigation and potential development of novel therapeutic approaches based on germinated steroids.
Figure 38.
Steroids bearing silicon atom(s) or silasteroids.
Figure 38.
Steroids bearing silicon atom(s) or silasteroids.
Figure 39.
3D graph represents the predicted and calculated activity of steroids bearing silicon atoms (
230,
231,
232,
236, and
237) with a maximum of over 99% confidence as ovulation inhibitors, accompanied by contraceptive and antitumor properties. The 3D graph presented in
Figure 39 offers a visual representation of the potential activities of steroids bearing a silicon atom. It serves as a valuable tool for researchers in assessing the biological potential of these compounds and guiding future investigations.
Figure 39.
3D graph represents the predicted and calculated activity of steroids bearing silicon atoms (
230,
231,
232,
236, and
237) with a maximum of over 99% confidence as ovulation inhibitors, accompanied by contraceptive and antitumor properties. The 3D graph presented in
Figure 39 offers a visual representation of the potential activities of steroids bearing a silicon atom. It serves as a valuable tool for researchers in assessing the biological potential of these compounds and guiding future investigations.
Figure 40.
Bioactive Steroids bearing selenium atoms or selenasteroids.
Figure 40.
Bioactive Steroids bearing selenium atoms or selenasteroids.
Figure 41.
Steroids bearing selenium atoms or selenasteroids.
Figure 41.
Steroids bearing selenium atoms or selenasteroids.
Figure 42.
3D graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of steroids bearing a selenium atom (244, 245, and 250) with a maximum confidence level exceeding 93%. These compounds exhibit significant potential for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. The graph provides a visual representation of the activity profiles of these selenium-containing steroids, offering valuable insights into their efficacy and potential therapeutic benefits. The high confidence level indicates the robustness of the predictions and underscores the promise of these compounds in addressing Alzheimer’s disease. Further research and validation studies are necessary to fully evaluate the mechanisms of action and optimize the properties of these steroids for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. However, the 3D graph serves as an informative tool, aiding researchers in assessing the potential of these compounds and guiding future investigations. The study of selenium-containing steroids for Alzheimer’s disease presents an exciting opportunity for the development of novel therapeutic strategies. Continued research in this area holds promise for advancing our understanding of the disease and potentially leading to the discovery of effective treatments.
Figure 42.
3D graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of steroids bearing a selenium atom (244, 245, and 250) with a maximum confidence level exceeding 93%. These compounds exhibit significant potential for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. The graph provides a visual representation of the activity profiles of these selenium-containing steroids, offering valuable insights into their efficacy and potential therapeutic benefits. The high confidence level indicates the robustness of the predictions and underscores the promise of these compounds in addressing Alzheimer’s disease. Further research and validation studies are necessary to fully evaluate the mechanisms of action and optimize the properties of these steroids for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. However, the 3D graph serves as an informative tool, aiding researchers in assessing the potential of these compounds and guiding future investigations. The study of selenium-containing steroids for Alzheimer’s disease presents an exciting opportunity for the development of novel therapeutic strategies. Continued research in this area holds promise for advancing our understanding of the disease and potentially leading to the discovery of effective treatments.
![Biomedicines 11 02698 g042]()
Figure 43.
Steroids bearing tellurium atoms or tellurasteroids.
Figure 43.
Steroids bearing tellurium atoms or tellurasteroids.
Figure 44.
3D graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of steroids bearing tellurium atom (271, 272, 274, 275, and 294) with a maximum of over 96% confidence, which can be used to treat Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other neurodegenerative diseases. The investigation of tellura steroids showcases their diverse range of biological activities and potential applications in various fields, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer therapies. Further research is warranted to elucidate the underlying mechanisms of action and optimize the properties of these compounds for potential clinical use. It is important to note that the specific structure and activity of each compound may vary, and further studies are needed to fully understand their potential therapeutic applications. The presented data serve as a starting point for the exploration of tellura steroids and their potential roles in addressing various diseases and health conditions.
Figure 44.
3D graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of steroids bearing tellurium atom (271, 272, 274, 275, and 294) with a maximum of over 96% confidence, which can be used to treat Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other neurodegenerative diseases. The investigation of tellura steroids showcases their diverse range of biological activities and potential applications in various fields, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer therapies. Further research is warranted to elucidate the underlying mechanisms of action and optimize the properties of these compounds for potential clinical use. It is important to note that the specific structure and activity of each compound may vary, and further studies are needed to fully understand their potential therapeutic applications. The presented data serve as a starting point for the exploration of tellura steroids and their potential roles in addressing various diseases and health conditions.
Figure 45.
Steroids bearing tin atom or organotin steroids.
Figure 45.
Steroids bearing tin atom or organotin steroids.
Figure 46.
3D graph showing the predicted and calculated activity of steroids bearing tin atom (282, 283, 284, and 289) with a maximum of over 99% confidence, demonstrating antitumor activity against pancreatic cancer, prostatic hyperplasia, prostate cancer, and generating anti-metastatic effect. De facto, but all steroids bearing tin atoms show antitumor activity as the dominant effect.
Figure 46.
3D graph showing the predicted and calculated activity of steroids bearing tin atom (282, 283, 284, and 289) with a maximum of over 99% confidence, demonstrating antitumor activity against pancreatic cancer, prostatic hyperplasia, prostate cancer, and generating anti-metastatic effect. De facto, but all steroids bearing tin atoms show antitumor activity as the dominant effect.
Figure 47.
Percentage distribution of the dominant antitumor activity, for example, organotin steroid (292), which possesses a broad range of anticancer properties. The activities are indicated by the following numbers: 1. Antineoplastic (16%): This activity refers to the compound’s ability to inhibit the growth of various types of tumors. 2. Anti-breast cancer (14.8%): This activity specifically targets breast cancer cells, indicating its potential as a therapeutic agent against this malignancy. 3. Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (14.6%): This activity focuses on the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia, a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. 4. Anti-sarcoma cancer (14.6%): This activity highlights the compound’s effectiveness against sarcoma, a cancerous tumor arising from connective tissues. 5. Anti-renal cancer (13.5%): This activity indicates the compound’s potential in combating renal cancer, which originates in the kidneys. 6. Prostate cancer treatment (13.3%): This activity specifically targets prostate cancer cells, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic option for this type of cancer. 7. Anti-pancreatic cancer (13.1%): This activity focuses on the compound’s efficacy against pancreatic cancer, a challenging malignancy with limited treatment options. The percentage distribution of these dominant antitumor activities provides insights into the compound’s efficacy against various types of cancer. These findings suggest that organotin steroid (292) holds promise as a multifunctional anticancer agent capable of targeting different tumor types. Understanding the specific activities and distribution of anticancer properties is crucial in evaluating the potential of organotin steroids as therapeutic agents. Further research and development in this area may uncover opportunities for the design of novel treatments and therapeutic strategies against cancer.
Figure 47.
Percentage distribution of the dominant antitumor activity, for example, organotin steroid (292), which possesses a broad range of anticancer properties. The activities are indicated by the following numbers: 1. Antineoplastic (16%): This activity refers to the compound’s ability to inhibit the growth of various types of tumors. 2. Anti-breast cancer (14.8%): This activity specifically targets breast cancer cells, indicating its potential as a therapeutic agent against this malignancy. 3. Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (14.6%): This activity focuses on the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia, a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. 4. Anti-sarcoma cancer (14.6%): This activity highlights the compound’s effectiveness against sarcoma, a cancerous tumor arising from connective tissues. 5. Anti-renal cancer (13.5%): This activity indicates the compound’s potential in combating renal cancer, which originates in the kidneys. 6. Prostate cancer treatment (13.3%): This activity specifically targets prostate cancer cells, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic option for this type of cancer. 7. Anti-pancreatic cancer (13.1%): This activity focuses on the compound’s efficacy against pancreatic cancer, a challenging malignancy with limited treatment options. The percentage distribution of these dominant antitumor activities provides insights into the compound’s efficacy against various types of cancer. These findings suggest that organotin steroid (292) holds promise as a multifunctional anticancer agent capable of targeting different tumor types. Understanding the specific activities and distribution of anticancer properties is crucial in evaluating the potential of organotin steroids as therapeutic agents. Further research and development in this area may uncover opportunities for the design of novel treatments and therapeutic strategies against cancer.
![Biomedicines 11 02698 g047]()
Figure 48.
Structures of ferrocene steroid conjugates.
Figure 48.
Structures of ferrocene steroid conjugates.
Figure 49.
Bioactive ferrocene steroid conjugates.
Figure 49.
Bioactive ferrocene steroid conjugates.
Figure 50.
3D graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of ferrocene steroid conjugates (311, 317, 320, and 321) with a maximum of over 96% confidence as a strong anti-breast cancer drug. In materials science, ferrocene steroid conjugates have been explored for their potential in developing functional materials, such as sensors and molecular switches. The combination of the redox-active ferrocene unit with the structural versatility of steroids opens possibilities for designing materials with tailored properties and responsive behavior. Furthermore, ferrocene steroid conjugates have shown promise in catalysis, where the unique electronic properties of ferrocene can influence the reactivity and selectivity of the conjugates. These conjugates can serve as catalysts or catalytic precursors in various transformations, offering new synthetic pathways and opportunities for sustainable and efficient chemical processes. The study of ferrocene steroid conjugates represents an interdisciplinary field at the intersection of chemistry and biology. The exploration of their properties and applications provides valuable insights into the synergistic effects arising from the combination of ferrocene and steroid motifs.
Figure 50.
3D graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of ferrocene steroid conjugates (311, 317, 320, and 321) with a maximum of over 96% confidence as a strong anti-breast cancer drug. In materials science, ferrocene steroid conjugates have been explored for their potential in developing functional materials, such as sensors and molecular switches. The combination of the redox-active ferrocene unit with the structural versatility of steroids opens possibilities for designing materials with tailored properties and responsive behavior. Furthermore, ferrocene steroid conjugates have shown promise in catalysis, where the unique electronic properties of ferrocene can influence the reactivity and selectivity of the conjugates. These conjugates can serve as catalysts or catalytic precursors in various transformations, offering new synthetic pathways and opportunities for sustainable and efficient chemical processes. The study of ferrocene steroid conjugates represents an interdisciplinary field at the intersection of chemistry and biology. The exploration of their properties and applications provides valuable insights into the synergistic effects arising from the combination of ferrocene and steroid motifs.
![Biomedicines 11 02698 g050]()
Figure 51.
Structures of titanocene steroid conjugates.
Figure 51.
Structures of titanocene steroid conjugates.
Figure 52.
Density functional theory calculated structures of titanocene steroid conjugates. (A = 332, B = 338 and C = 339).
Figure 52.
Density functional theory calculated structures of titanocene steroid conjugates. (A = 332, B = 338 and C = 339).
Figure 53.
3D graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of titanocene steroid conjugate (338) with a high confidence level of over 99%. The graph indicates that this conjugate exhibits strong antineoplastic activity and shows potential as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of prostatic hyperplasia and proliferative diseases.
Figure 53.
3D graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of titanocene steroid conjugate (338) with a high confidence level of over 99%. The graph indicates that this conjugate exhibits strong antineoplastic activity and shows potential as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of prostatic hyperplasia and proliferative diseases.
Figure 54.
3D model and percentage distribution of the dominant antitumor activity for the titanocene steroid conjugate (338). The graph depicts the distribution of activities as follows: 1, Antineoplastic (23.5%); 2, Toxic (22.5%); 3, Antineoplastic, alkylator (16.1%); 4, Proliferative diseases treatment (12.8%), 5, Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (12.7%), and 6, Apoptosis agonist (12.5%). These percentages represent the relative contribution of each activity to the overall biological profile of the titanocene steroid conjugate (338). The titanium atom is highlighted in yellow, and the chlorine atoms in green.
Figure 54.
3D model and percentage distribution of the dominant antitumor activity for the titanocene steroid conjugate (338). The graph depicts the distribution of activities as follows: 1, Antineoplastic (23.5%); 2, Toxic (22.5%); 3, Antineoplastic, alkylator (16.1%); 4, Proliferative diseases treatment (12.8%), 5, Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (12.7%), and 6, Apoptosis agonist (12.5%). These percentages represent the relative contribution of each activity to the overall biological profile of the titanocene steroid conjugate (338). The titanium atom is highlighted in yellow, and the chlorine atoms in green.
Table 1.
Biological activities of cyanosteroids (
1–
23) [
41].
Table 1.
Biological activities of cyanosteroids (
1–
23) [
41].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 1 | Menstruation disorders treatment (0.962) | Antineoplastic (0.821) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.954) | Anti-inflammatory (0.793) |
| Ovulation inhibitor (0.888) | Diuretic (0.781) |
| Contraceptive (0.861) | Endometriosis treatment (0.604) |
| Androgen antagonist (0.777) | Psychosexual dysfunction treatment (0.567) |
| 2 | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.929) | Antineoplastic (0.839) |
| Contraceptive (0.859) | Respiratory analeptic (0.830) |
| Ovulation inhibitor (0.829) | Psychosexual dysfunction treatment (0.514) |
| Menstruation disorders treatment (0.776) | Prostate cancer treatment (0.500) |
| 3 | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.754) | Antineoplastic (0.813) |
| Ovulation inhibitor (0.692) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.589) |
| 4 | Menstruation disorders treatment (0.980) | Antineoplastic (0.852) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.965) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.840) |
| Contraceptive (0.857) | Anti-inflammatory (0.826) |
| 5 | Hair growth stimulant (0.875) | Antineoplastic (0.768) |
| Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.833) | Immunosuppressant (0.739) |
| 6 | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.875) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.745) |
| 7 | Cytoprotectant (0.963) | Antineoplastic (melanoma) (0.831) |
| Apoptosis agonist (0.937) | Antineoplastic (pancreatic cancer) (0.777) |
| Chemopreventive (0.900) | Antineoplastic (solid tumors (0.747) |
| 8 | Lipid metabolism regulator (0.965) | Anti-secretoric (0.958) |
| Steroid synthesis inhibitor (0.808) | Antineoplastic (0.909) |
| 9 | Antineoplastic (0.913) | Steroid synthesis inhibitor (0.800) |
| Apoptosis agonist (0.813) | Lipid metabolism regulator (0.750) |
| 10 | Androgen antagonist (0.958) | Antineoplastic (0.874) |
| Steroid synthesis inhibitor (0.829) | Prostate cancer treatment (0.809) |
| 11 | Androgen antagonist (0.987) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.909) |
| Steroid synthesis inhibitor (0.773) | Contraceptive (0.875) |
| Estrogen antagonist (0.750) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.865) |
| 12 | Antineoplastic (0.787) | Anti-inflammatory (0.682) |
| 13 | Antineoplastic (0.811) | Anti-inflammatory (0.731) |
| 14 | 5-Alpha-reductase inhibitor (0.841) | Anesthetic general (0.796) |
| 15 | Antineoplastic (0.849) | Anti-inflammatory (0.752) |
| 16 | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.896) | Antineoplastic (0.870) |
| 17 | Anti-inflammatory (0.938) | Antineoplastic (0.898) |
| Aromatase inhibitor (0.818) | Estrogen antagonist (0.723) |
| 18 | Anti-inflammatory (0.963) | Estrogen antagonist (0.727) |
| Antineoplastic (0.894) | Aromatase inhibitor (0.739) |
| 19 | Anti-inflammatory (0.934) | Estrogen antagonist (0.807) |
| Antineoplastic (0.904) | Aromatase inhibitor (0.785) |
| 20 | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.925) | Anesthetic general (0.825) |
| Contraceptive female (0.789) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.756) |
| 21 | Anti-inflammatory (0.863) | Hair growth stimulant (0.914) |
| Estrogen antagonist (0.816) | Contraceptive (0.912) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.813) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.844) |
| 22 | Antineoplastic (0.868) | Hair growth stimulant (0.784) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.833) | Respiratory analeptic (0.750) |
| Contraceptive (0.770) | Hypogonadism treatment (0.700) |
| 23 | Heart failure treatment (0.968) | Anti-hyperaldosteronism (0.963) |
| Diuretic (0.967) | Antihypertensive (0.930) |
| Cardiotonic (0.933) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.755) |
Table 2.
Biological activities of cyanosteroids (
24–
51) [
41].
Table 2.
Biological activities of cyanosteroids (
24–
51) [
41].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 24 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.942) | Muscular dystrophy treatment (0.927) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.876) | Respiratory analeptic (0.907) |
| Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.854) | Neuroprotector (0.904) |
| Contraceptive (0.725) | Oxytocic (0.755) |
| 25 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.835) | Antineoplastic (0.779) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.658) | Dementia treatment (0.624) |
| Contraceptive (0.649) | Prostate cancer treatment (0.603) |
| 26 | Anesthetic general (0.913) | Cholesterol antagonist (0.936) |
| Anesthetic (0.792) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.879) |
| 27 | Cholesterol antagonist (0.707) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.843) |
| Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.618) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.813) |
| 28 | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.826) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.779) |
| Cholesterol antagonist (0.786) | Contraceptive (0.719) |
| 29 | Anti-inflammatory (0.846) | Contraceptive (0.796) |
| Antineoplastic (0.833) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.682) |
| 30 | Cholesterol antagonist (0.840) | Antineoplastic (0.869) |
| Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.706) | Spasmolytic, urinary (0.857) |
| Transcription factor NF kappa B inhibitor (0.687) | Anti-inflammatory (0.840) |
| 31 | Anti-osteoporotic (0.814) | Antineoplastic (0.780) |
| Hypolipemic (0.711) | Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.609) |
| 32 | Cholesterol antagonist (0.903) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.700) |
| Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.743) | Cytoprotectant (0.699) |
| 33 | Antineoplastic (0.878) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.872) |
| Apoptosis agonist (0.699) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.715) |
| 34 | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.932) | Diuretic (0.788) |
| 35 | Cholesterol synthesis inhibitor (0.911) | Anesthetic general (0.913) |
| Atherosclerosis treatment (0.908) | Respiratory analeptic (0.898) |
| 36 | Cholesterol synthesis inhibitor (0.932) | Anesthetic general (0.889) |
| Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.838) | Respiratory analeptic (0.831) |
| 37 | Antineoplastic (0.845) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.835) |
| Cytoprotectant (0.764) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.814) |
| 38 | Inhibitor 5α-reductase type II (0.921) | Psychotropic (0.952) |
| Anxiolytic (0.909) | Antidepressant (0.914) |
| 39 | Inhibitor 5α-reductase type II (0.933) | Psychotropic (0.943) |
| Anxiolytic (0.911) | Antidepressant (0.908) |
| 40 | Contraceptive (0.977) | Antineoplastic (0.910) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.872) | Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.666) |
| 41 | Anti-inflammatory (0.837) | Contraceptive (0.803) |
| 42 | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.874) | Antineoplastic (0.864) |
| 43 | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.886) | Antineoplastic (0.871) |
| 44 | Antineoplastic (sarcoma) (0.808) | Anti-inflammatory (0.845) |
| 45 | Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.885) | Apoptosis agonist (0.710) |
| 46 | Antineoplastic (0.894) | Apoptosis agonist (0.788) |
| 47 | Lipid metabolism regulator (0.748) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.682) |
| 48 | Antineoplastic (0.847) | Apoptosis agonist (0.810) |
| 49 | Antineoplastic (0.843) | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.817) |
| 50 | Antineoplastic (0.879) | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.865) |
| 51 | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.878) | Antineoplastic (0.849) |
| Hypolipemic (0.735) | Apoptosis agonist (0.820) |
| Atherosclerosis treatment (0.544) | Prostate cancer treatment (0.585) |
| Cholesterol synthesis inhibitor (0.524) | Cytoprotectant (0.584) |
Table 3.
Biological activities of nitro-steroids (
52–
72) [
110].
Table 3.
Biological activities of nitro-steroids (
52–
72) [
110].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 52 | Respiratory analeptic (0.951) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.908) |
| Anesthetic general (0.929) | Analeptic (0.847) |
| Anesthetic (0.815) | Dermatologic (0.747) |
| 53 | Respiratory analeptic (0.962) | Analeptic (0.873) |
| Anesthetic general (0.917) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.845) |
| 54 | Respiratory analeptic (0.953) | Analeptic (0.865) |
| Anesthetic general (0.951) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.839) |
| 55 | Antifungal (0.893) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.841) |
| Anti-inflammatory (0.751) | Muscular dystrophy treatment (0.813) |
| 56 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.872) | Antineoplastic (0.818) |
| Respiratory analeptic (0.809) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.660) |
| 57 | Antineoplastic (0.870) | Contraceptive (0.695) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.651) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.646) |
| 58 | Antineoplastic (0.792) | Anesthetic general (0.882) |
| Acute neurologic disorders treatment (0.761) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.772) |
| 59 | Neuroprotector (0.810) | Respiratory analeptic (0.789) |
| Acute neurologic disorders treatment (0.791) | Anesthetic general (0.753) |
| 60 | Antineoplastic (0.797) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.885) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.703) | Anesthetic general (0.750) |
| 61 | Antineoplastic (0.862) | Dermatologic (0.716) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.784) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.675) |
| 62 | Respiratory analeptic (0.882) | Antineoplastic (0.790) |
| Analeptic (0.768) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.740) |
| 63 | Anesthetic general (0.865) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.750) |
| Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.805) | Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.665) |
| 64 | Inhibitor 5a-reductase (0.971) | Respiratory analeptic (0.964) |
| Spasmolytic, Papaverin-like (0.667) | Analeptic (0.884) |
| 65 | Inhibitor 5a-reductase (0.933) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.920) |
| Spasmolytic, Papaverin-like (0.623) | Antineoplastic (0.764) |
| Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.704) | Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.714) |
| 66 | Prostate disorders treatment (0.959) | Inhibitor 5a-reductase (0.911) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.785) | Respiratory analeptic (0.703) |
| Antineoplastic (0.764) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.689) |
| 67 | Prostate disorders treatment (0.976) | Inhibitor 5a-reductase (0.889) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.895) | Dermatologic (0.785) |
| 68 | Prostate disorders treatment (0.946) | Inhibitor 5a-reductase (0.876) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.883) | Dermatologic (0.791) |
| 69 | Prostate disorders treatment (0.915) | Dermatologic (0.766) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.753) |
| 70 | Respiratory analeptic (0.918) | Dermatologic (0.741) |
| Anesthetic general (0.839) | Anti-psoriatic (0.652) |
| 71 | Respiratory analeptic (0.880) | Anti-eczematic (0.791) |
| Anesthetic general (0.812) | Dermatologic (0.753) |
| 72 | Respiratory analeptic (0.929) | Anesthetic general (0.919) |
| Analeptic (0.833) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.819) |
Table 4.
Biological activities of nitro-steroids (
73–
100) [
110].
Table 4.
Biological activities of nitro-steroids (
73–
100) [
110].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 73 | Anti-eczematic (0.814) | Antineoplastic (0.709) |
| Dermatologic (0.736) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.708) |
| 74 | Antineoplastic (0.799) | Respiratory analeptic (0.748) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.715) | Antiallergic (0.681) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.645) | Dermatologic (0.646) |
| 75 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.819) | Neuroprotector (0.807) |
| Analeptic (0.706) | Acute neurologic disorders treatment (0.727) |
| 76 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.811) | Neuroprotector (0.810) |
| Analeptic (0.723) | Acute neurologic disorders treatment (0.707) |
| 77 | Antineoplastic (0.906) | Respiratory analeptic (0.860)
Analeptic (0.726) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.883) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.736) |
| 78 | 4-Methyl sterol oxidase (0.925) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.887) |
| Neuroprotector (0.708) | Antineoplastic (0.870) |
| Immunosuppressant (0.648) | Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.768) |
| 79 | 4-Methyl sterol oxidase (0.914) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.892) |
| Neuroprotector (0.742) | Antineoplastic (0.843) |
| 80 | Prostate disorders treatment (0.976) | 4-Methyl sterol oxidase (0.909) |
| Antineoplastic (0.922) | Neuroprotector (0.723) |
| 81 | Antineoplastic (0.890) | Anti-inflammatory (0.755) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.809) | Antifungal (0.753) |
| 82 | Respiratory analeptic (0.883) | Anti-eczematic (0.831) |
| 83 | Respiratory analeptic (0.877) | Anti-eczematic (0.829) |
| 84 | Prostate disorders treatment (0.812) | Dermatologic (0.793) |
| 85 | Respiratory analeptic (0.905) | Anti-eczematic (0.836) |
| Analeptic (0.838) | Dermatologic (0.756) |
| 86 | Respiratory analeptic (0.976) | Antineoplastic (0.898) |
| Analeptic (0.900) | Anti-secretoric (0.880) |
| 87 | Antineoplastic (0.903) | Respiratory analeptic (0.881) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.868) | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.871) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.726) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.721) |
| 88 | Respiratory analeptic (0.928) | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.889) |
| Neuroprotector (0.916) | Muscular dystrophy treatment (0.882) |
| Antineoplastic (0.904) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.866) |
| 89 | Muscular dystrophy treatment (0.940) | Respiratory analeptic (0.921) |
| Ovulation inhibitor (0.812) | Antineoplastic (0.909) |
| Hypogonadism treatment (0.746) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.863) |
| 90 | Antineoplastic (0.905) | Respiratory analeptic (0.886) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.702) | Analeptic (0.765) |
| 91 | Anti-eczematic (0.831) | Dermatologic (0.709) |
| 92 | Respiratory analeptic (0.953) | Anesthetic general (0.919) |
| Analeptic (0.858) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.892) |
| 94 | Gonadotropin inhibitor (0.932) | Muscular dystrophy treatment (0.891) |
| Ovulation inhibitor (0.886) | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.879) |
| 95 | Respiratory analeptic (0.980) | Anti-inflammatory (0.930) |
| Anti-secretoric (0.937) | Antiallergic (0.827) |
| 96 | Respiratory analeptic (0.965) | Anti-inflammatory (0.944) |
| Anti-secretoric (0.934) | Antiallergic (0.864) |
| 97 | Anesthetic general (0.905) | Respiratory analeptic (0.782) |
| 98 | Cardiotonic (0.890) | Anesthetic general (0.707) |
| 99 | Anesthetic general (0.880) | Respiratory analeptic (0.868) |
| 100 | Anesthetic general (0.869) | Respiratory analeptic (0.851) |
Table 6.
Biological activities of steroids bearing chlorine atom (
117–
130) [
151,
175].
Table 6.
Biological activities of steroids bearing chlorine atom (
117–
130) [
151,
175].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 117 | Anti-seborrheic (0.931) | Respiratory analeptic (0.796) |
| Growth stimulant (0.923) | Endometriosis treatment (0.770) |
| 118 | Anti-seborrheic (0.936) | Antineoplastic (0.888) |
| Growth stimulant (0.900) | Respiratory analeptic (0.828) |
| 119 | Anti-seborrheic (0.941) | Antineoplastic (0.893) |
| Growth stimulant (0.873) | Anti-inflammatory (0.868) |
| 120 | Anti-seborrheic (0.909) | Antineoplastic (0.888) |
| Growth stimulant (0.886) | Anti-inflammatory (0.806) |
| 121 | Respiratory analeptic (0.925) | Anti-inflammatory (0.871) |
| Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.914) | Antiallergic (0.747) |
| 122 | Respiratory analeptic (0.925) | Anti-inflammatory (0.871) |
| Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.914) | Antiallergic (0.747) |
| 123 | Gynecological disorders treatment (0.959) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.887) |
| Antineoplastic (0.947) | Lipid metabolism regulator (0.828) |
| Growth stimulant (0.848) | Antidepressant (0.833) |
| 124 | Anesthetic general (0.951) | Anti-inflammatory (0.863) |
| Respiratory analeptic (0.764) | Antineoplastic (0.821) |
| Antiallergic (0.734) | Antipruritic (0.797) |
| 125 | Anti-inflammatory (0.888) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.844) |
| Anti-asthmatic (0.847) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.614) |
| 126 | Antineoplastic (0.818) | Anesthetic general (0.769) |
| 127 | Anti-inflammatory (0.979) | Antiarthritic (0.926) |
| Anti-asthmatic (0.957) | Antipruritic, allergic (0.832) |
| Antiallergic (0.907) | Rheumatoid arthritis treatment (0.607) |
| 128 | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.926) | Neuroprotector (0.872) |
| Anesthetic general (0.913) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.817) |
| Respiratory analeptic (0.897) | Immunosuppressant (0.755) |
| 129 | Anti-inflammatory (0.956) | Antiallergic (0.904) |
| Antineoplastic (0.906) | Antipruritic, allergic (0.741) |
| Respiratory analeptic (0.816) | |
| 130 | Anti-inflammatory (0.955) | Immunosuppressant (0.812) |
| Antiallergic (0.920) | Anti-asthmatic (0.795) |
Table 7.
Biological activities of steroids bearing bromine atom(s) (
131–
142) [
175].
Table 7.
Biological activities of steroids bearing bromine atom(s) (
131–
142) [
175].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 131 | Antineoplastic (0.886) | Anti-inflammatory (0.819) |
| Prostate cancer treatment (0.674) | Antibacterial (0.786) |
| 132 | Antineoplastic (0.902) | Anti-inflammatory (0.710) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.673) | Cystic fibrosis treatment (0.555) |
| 133 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.887) | Antineoplastic (0.833) |
| Contraceptive (0.609) | Prostate cancer treatment (0.694) |
| 134 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.859) | Antineoplastic (0.848) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.691) | Prostate cancer treatment (0.561) |
| 135 | Anti-inflammatory (0.895) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.801) |
| Respiratory analeptic (0.875) | Contraceptive (0.745) |
| 136 | Anti-inflammatory (0.879) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.783) |
| Antineoplastic (0.816) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.655) |
| 137 | Apoptosis agonist (0.752) | Antinociceptive (0.734) |
| Antineoplastic (0.751) | Cytoprotectant (0.682) |
| 138 | Antineoplastic (0.891) | Angiogenesis inhibitor (0.945) |
| Apoptosis agonist (0.785) | Antiviral (Influenza) (0.567) |
| 139 | Antiviral (Influenza) (0.888) | Apoptosis agonist (0.775) |
| Antibacterial (0.856) | Antineoplastic (0.757) |
| 140 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.793) | Antineoplastic (0.751) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.579) | Cystic fibrosis treatment (0.740) |
| 141 | Antineoplastic (0.785) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.742) |
| Genital warts treatment (0.759) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.618) |
| 142 | Apoptosis agonist (0.869) | Anti-inflammatory (0.853) |
| Antineoplastic (0.852) | Antiallergic (0.665) |
Table 8.
Biological activities of steroids bearing iodine atom (
143–
159) [
175].
Table 8.
Biological activities of steroids bearing iodine atom (
143–
159) [
175].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 143 | Antineoplastic (0.906) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.840) |
| Prostate cancer treatment (0.712) | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.757) |
| 144 | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.877) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.814) |
| Antineoplastic (0.823) | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.754) |
| 145 | Respiratory analeptic (0.947) | Antineoplastic (0.855) |
| Diuretic (0.813) | Apoptosis agonist (0.780) |
| 146 | Respiratory analeptic (0.895) | Contraceptive (0.796) |
| Antineoplastic (0.820) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.651) |
| 147 | Respiratory analeptic (0.980) | Anti-inflammatory (0.924) |
| Anti-secretoric (0.932) | Antineoplastic (0.915) |
| 148 | Anti-inflammatory (0.910) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.724) |
| Anti-secretoric (0.828) | Contraceptive (0.656) |
| 149 | Antineoplastic (0.924) | Respiratory analeptic (0.791) |
| Prostate cancer treatment (0.710) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.738) |
| 150 | Antineoplastic (0.905) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.726) |
| Prostate cancer treatment (0.608) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.643) |
| 151 | Antineoplastic (0.883) | Antileukemic (0.599) |
| 152 | Respiratory analeptic (0.952) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.913) |
| Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.927) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.721) |
| 153 | Alopecia treatment (0.864) | Anti-osteoporotic (0.793) |
| Antineoplastic (0.847) | Anti-secretoric (0.729) |
| 154 | Contraceptive (0.908) | Antineoplastic (0.883) |
| Ovulation inhibitor (0.885) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.712) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.677) | Apoptosis agonist (0.606) |
| 155 | Antineoplastic (0.846) | Anti-eczematic (0.817) |
| Prostate cancer treatment (0.675) | Anti-psoriatic (0.621) |
| 156 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.833) | Antineoplastic (0.812) |
| Respiratory analeptic (0.803) | Apoptosis agonist (0.647) |
| 157 | Antineoplastic (0.827) | Cardiotonic (0.723) |
| Prostate cancer treatment (0.775) | Antiarrhythmic (0.568) |
| 158 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.903) | Antineoplastic (0.860) |
| Contraceptive (0.835) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.804) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.692) | Prostate cancer treatment (0.719) |
| 159 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.958) | Antineoplastic (0.889) |
| Contraceptive (0.878) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.876) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.752) | Prostate cancer treatment (0.769) |
Table 10.
Biological activities of steroids bearing epithio group (
178–
189) [
110].
Table 10.
Biological activities of steroids bearing epithio group (
178–
189) [
110].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 178 | Cardiotonic (0.936) | Antineoplastic (0.912) |
| Antipruritic (0.787) | Anti-secretoric (0.857) |
| 179 | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.865) | Hepatic disorders treatment (0.792) |
| Cholesterol antagonist (0.858) | Hepatoprotectant (0.762) |
| 180 | Hypolipemic (0.805) | Antineoplastic (0.828) |
| Cholesterol antagonist (0.754) | Apoptosis agonist (0.785) |
| Atherosclerosis treatment (0.657) | |
| 181 | Aromatase inhibitor (0.884) | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.896) |
| Antineoplastic (0.806) | |
| 182 | Aromatase inhibitor (0.854) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.750) |
| Antineoplastic (0.746) | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.720) |
| 183 | Cholesterol antagonist (0.916) | Respiratory analeptic (0.903) |
| Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.836) | Anesthetic general (0.858) |
| 184 | Neuroprotector (0.916) | Cholesterol antagonist (0.893) |
| Cardiotonic (0.788) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.771) |
| 185 | Muscular dystrophy treatment (0.873) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.872) |
| Acute neurologic disorders treatment (0.849) | Cholesterol antagonist (0.817) |
| 186 | Cholesterol synthesis inhibitor (0.834) | Hepatoprotectant (0.859) |
| Cholesterol antagonist (0.824) | Hepatic disorders treatment (0.762) |
| 187 | Anti-secretoric (0.823) | Antineoplastic (0.781) |
| Anti-osteoporotic (0.665) | Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.666) |
| 188 | Anti-seborrheic (0.924) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.775) |
| Anti-eczematic (0.797) | Estrogen antagonist (0.670) |
| 189 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.830) | Cholesterol antagonist (0.734) |
Table 11.
Biological activities of steroids bearing boron atom(s) (
190–
201) [
260].
Table 11.
Biological activities of steroids bearing boron atom(s) (
190–
201) [
260].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 190 | Anti-eczematic (0.804) | Antihypertensive (0.798) |
| Dermatologic (0.716) | Myocardial ischemia treatment (0.751) |
| Anti-psoriatic (0.665) | Antineoplastic (0.735) |
| 191 | Anti-eczematic (0.796) | Antineoplastic (0.796) |
| Dermatologic (0.767) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.756) |
| 192 | Antineoplastic (0.910) | Gynecological disorders treatment (0.866) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.713) | Psychosexual dysfunction treatment (0.821) |
| 193 | Antineoplastic (0.883) | Gynecological disorders treatment (0.849) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.695) | Psychosexual dysfunction treatment (0.817) |
| 194 | Antineoplastic (0.844) | Psychosexual dysfunction treatment (0.756) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.631) | Gynecological disorders treatment (0.693) |
| 195 | Antineoplastic (0.870) | Psychosexual dysfunction treatment (0.772) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.647) | Gynecological disorders treatment (0.714) |
| 196 | Antineoplastic (0.866) | Psychosexual dysfunction treatment (0.754) |
| Antimetastatic (0.614) | Gynecological disorders treatment (0.631) |
| 197 | Antineoplastic (0.817) | Psychosexual dysfunction treatment (0.759) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.652) | Gynecological disorders treatment (0.707) |
| 198 | Antineoplastic (0.682) | Radiosensitizer (0.521) |
| Antineoplastic (lymphocytic leukemia) (0.526) |
| 199 | Antineoplastic (0.881) | Neuroprotector (0.870) |
| Apoptosis agonist (0.742) | Chemosensitizer (0.755) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.712) | Radiosensitizer (0.738) |
| 200 | Antineoplastic (0.762) | Radiosensitizer (0.587)
Chemosensitizer (0.525) |
| Antineoplastic (renal cancer) (0.574) |
| Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.524) |
| Prostate cancer treatment (0.513) |
| Antineoplastic (pancreatic cancer) (0.512) |
| 201 | Genital warts treatment (0.894) | Antineoplastic (0.849) |
| Rhinitis treatment (0.662) | Apoptosis agonist (0.639) |
| Macular degeneration treatment (0.597) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.555) |
Table 12.
Biological activities of steroids bearing aluminum atom (
202–
209) [
284].
Table 12.
Biological activities of steroids bearing aluminum atom (
202–
209) [
284].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 202 | Antiprotozoal (Plasmodium) (0.906) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.787) |
| Antifungal (0.825) | Hypolipemic (0.753) |
| Antibacterial (0.758) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.602) |
| 203 | Antiprotozoal (Plasmodium) (0.906) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.787) |
| Antifungal (0.825) | Hypolipemic (0.753) |
| Antibacterial (0.758) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.602) |
| 204 | Antiprotozoal (Plasmodium) (0.910) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.741) |
| Antifungal (0.818) | Hypolipemic (0.675) |
| Antibacterial (0.722) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.580) |
| 205 | Antiprotozoal (Plasmodium) (0.924) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.817) |
| Cytoprotectant (0.751) | Hypolipemic (0.735) |
| Biliary tract disorders treatment (0.744) | Cholesterol synthesis inhibitor (0.601) |
| 206 | Antiprotozoal (Plasmodium) (0.908) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.881) |
| Biliary tract disorders treatment (0.713) | Hypolipemic (0.691) |
| Anti-psoriatic (0.695) | Myasthenia Gravis treatment (0.584) |
| 207 | Antiprotozoal (Plasmodium) (0.909) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.899) |
| Biliary tract disorders treatment (0.726) | Hypolipemic (0.776) |
| Anti-psoriatic (0.717) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.584) |
| 208 | Antiprotozoal (Plasmodium) (0.911) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.907) |
| Cytoprotectant (0.704) | Hypolipemic (0.748) |
| Anti-psoriatic (0.700) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.599) |
| 209 | Antiprotozoal (Plasmodium) (0.910) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.895) |
| Cytoprotectant (0.728) | Hypolipemic (0.738) |
| Anti-psoriatic (0.697) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.595) |
Table 13.
Biological activities of steroids bearing arsenic atom (
210–
215) [
260].
Table 13.
Biological activities of steroids bearing arsenic atom (
210–
215) [
260].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 210 | Antineoplastic (0.983) | Antiviral (0.866) |
| Antiprotozoal (0.941) | |
| 211 | Antineoplastic (0.982) | Antiviral (0.882) |
| Antiprotozoal (0.947) | |
| 212 | Antineoplastic (0.985) | Antiviral (0.939) |
| Apoptosis agonist (0.755) | Anti-inflammatory (0.629) |
| 213 | Antineoplastic (0.984) | Antiprotozoal (0.946) |
| Apoptosis agonist (0.716) | Antiviral (0.927) |
| 214 | Antineoplastic (0.870) | Dermatologic (0.818) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.641) | Anti-inflammatory (0.517) |
| 215 | Antineoplastic (0.844) | Contraceptive (0.625) |
| Apoptosis agonist (0.574) | Gynecological disorders treatment (0.604) |
Table 14.
Biological activities of steroids bearing astatine atom (
216–
220) [
260].
Table 14.
Biological activities of steroids bearing astatine atom (
216–
220) [
260].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 216 | Anti-seborrheic (0.936) | Alopecia treatment (0.923) |
| Growth stimulant (0.805) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.920) |
| Antifungal (0.789) | Anti-secretoric (0.884) |
| 217 | Anti-seborrheic (0.934) | Alopecia treatment (0.913) |
| Growth stimulant (0.703) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.901) |
| Antifungal (0.689) | Anti-secretoric (0.836) |
| 218 | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.912) | Antineoplastic (0.839) |
| Anti-secretoric (0.837) | Bone diseases treatment (0.777) |
| 219 | Respiratory analeptic (0.976) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.967) |
| Anesthetic general (0.924) | Hypolipemic (0.785) |
| Antineoplastic (0.824) | Bone diseases treatment (0.796) |
| 220 | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.927) | Anti-eczematic (0.825) |
| Antineoplastic (0.834) | Dermatologic (0.805) |
| Hypolipemic (0.740) | Anti-psoriatic (0.685) |
Table 15.
Biological activities of steroids bearing germanium atom (
221–
229) [
260].
Table 15.
Biological activities of steroids bearing germanium atom (
221–
229) [
260].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 221 | Respiratory analeptic (0.870) | Antineoplastic (0.860) |
| Anesthetic (0.738) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.806) |
| 222 | Respiratory analeptic (0.874) | Antineoplastic (0.852) |
| Anesthetic general (0.856) | Cytoprotectant (0.714) |
| 223 | Antineoplastic (0.957) | Antiacne (0.939) |
| Respiratory analeptic (0.779) | Dermatologic (0.928) |
| 224 | Antineoplastic (0.961) | Antiacne (0.952) |
| Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.793) | Dermatologic (0.935) |
| Respiratory analeptic (0.785) | Anti-seborrheic (0.830) |
| 225 | Antineoplastic (0.960) | Antiacne (0.951) |
| Anesthetic general (0.841) | Dermatologic (0.940) |
| Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.770) | Anti-eczematic (0.695) |
| 226 | Antineoplastic (0.964) | Antiacne (0.960) |
| Anesthetic general (0.915) | Dermatologic (0.948) |
| Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.896) | Anti-eczematic (0.735) |
| 227 | Antiacne (0.970) | Antineoplastic (0.969) |
| Dermatologic (0.955) | Anesthetic general (0.816) |
| Anti-seborrheic (0.691) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.738) |
| 228 | Antiacne (0.980) | Antineoplastic (0.974) |
| Dermatologic (0.972) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.768) |
| Anti-seborrheic (0.831) | Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.651) |
| 229 | Anti-seborrheic (0.918) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.847) |
| Dermatologic (0.776) | Antineoplastic (0.821) |
| Antiacne (0.613) | Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.606) |
Table 16.
Biological activities of steroids bearing silicone atom(s) (
230–
241) [
260].
Table 16.
Biological activities of steroids bearing silicone atom(s) (
230–
241) [
260].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 230 | Antineoplastic (0.992) | Psychotropic (0.879) |
| Contraceptive (0.879) | Anxiolytic (0.762) |
| Ovulation inhibitor (0.872) | Neurodegenerative diseases treatment (0.587) |
| 231 | Antineoplastic (0.985) | Psychotropic (0.815) |
| Contraceptive (0.841) | Anxiolytic (0.754) |
| Ovulation inhibitor (0.812) | Neurodegenerative diseases treatment (0.725) |
| 232 | Antineoplastic (0.995) | Psychotropic (0.827) |
| 5 Hydroxytryptamine 2A antagonist (0.765) | Anxiolytic (0.806) |
| 5 Hydroxytryptamine 2 antagonist (0.588) | |
| 233 | Antineoplastic (0.994) | Psychotropic (0.834) |
| 5 Hydroxytryptamine 2A antagonist (0.740) | Anxiolytic (0.823) |
| 234 | Antineoplastic (0.973) | Psychotropic (0.702) |
| Apoptosis agonist (0.887) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.618) |
| 235 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.926) | Psychotropic (0.846) |
| Contraceptive (0.880) | Anxiolytic (0.742) |
| 236 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.859) | Antineoplastic (0.871) |
| Contraceptive (0.799) | Hypolipemic (0.818) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.686) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.690) |
| 237 | Antineoplastic (0.977) | Hypolipemic (0.634) |
| Apoptosis agonist (0.616) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.606) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.613) | Contraceptive (0.575) |
| 238 | Antineoplastic (0.943) | Antiarthritic (0.927) |
| Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.728) | Hypolipemic (0.751) |
| Skeletal muscle relaxant (0.673) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.688) |
| 239 | Antineoplastic (0.905) | Anti-inflammatory (0.755) |
| Contraceptive (0.813) | Antifungal (0.748) |
| Dermatologic (0.773) | Hypolipemic (0.752) |
| 240 | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.917) | Antineoplastic (0.883) |
| Immunosuppressant (0.776) | Antiprotozoal (Leishmania) (0.858) |
| Antipruritic (0.771) | Respiratory analeptic (0.800) |
| 241 | Antineoplastic (0.899) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.796) |
| Anabolic (0.878) | Anti-inflammatory (0.750) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.605) | Respiratory analeptic (0.728) |
Table 17.
Biological activities of steroids bearing selenium atom (
242–
267) [
260].
Table 17.
Biological activities of steroids bearing selenium atom (
242–
267) [
260].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 242 | Antineoplastic (0.894) | Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.702) |
| Chemoprotective (0.775) | Anti-psoriatic (0.691) |
| 243 | Antineoplastic (0.913) | Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.794) |
| Chemoprotective (0.816) | Cerebrovascular disorders treatment (0.774) |
| 244 | Cerebrovascular disorders treatment (0.869) | Psychosexual dysfunction treatment (0.791) |
| Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.833) | Neurodegenerative diseases treatment (0.775) |
| 245 | Antineoplastic (0.938) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.756) |
| Chemoprotective (0.809) | Cerebrovascular disorders treatment (0.732) |
| Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.778) | Vascular (peripheral) disease treatment (0.689) |
| 246 | Antineoplastic (0.846) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.841) |
| Chemoprotective (0.786) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.791) |
| 247 | Anti-inflammatory (0.940) | Antineoplastic (0.897) |
| Antiallergic (0.790) | Anticarcinogenic (0.778) |
| 248 | Anti-inflammatory (0.959) | Antiallergic (0.843) |
| Respiratory analeptic (0.870) | Anti-asthmatic (0.757) |
| 249 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.918) | Anti-inflammatory (0.738) |
| Antineoplastic (0.876) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.726) |
| 250 | Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.783) | Antineoplastic (0.899) |
| Ovulation inhibitor (0.757) | Membrane permeability inhibitor (0.788) |
| Chemoprotective (0.740) | Cytochrome P450 inhibitor (0.559) |
| 251 | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.905) | Antineoplastic (0.858) |
| Anesthetic general (0.901) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.855) |
| 252 | Antineoplastic (0.926) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.877) |
| Chemoprotective (0.780) | Anti-inflammatory (0,865) |
| 253 | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.908) | Anti-eczematic (0.825) |
| Antineoplastic (0.882) | Dermatologic (0.799) |
| 254 | Respiratory analeptic (0.963) | Chemopreventive (0.916) |
| Anesthetic general (0.946) | Antineoplastic (0.884) |
| Wound healing agent (0.880) | Anticarcinogenic (0.753) |
| 255 | Respiratory analeptic (0.971) | Chemopreventive (0.923) |
| Anesthetic general (0.910) | Antineoplastic (0.856) |
| Wound healing agent (0.817) | Anticarcinogenic (0.804) |
| 256 | Anti-inflammatory (0.950) | Antineoplastic (0.818) |
| Antiallergic (0.793) | Cell adhesion molecule inhibitor (0.745) |
| 257 | Anti-inflammatory (0.936) | Antineoplastic (0.813) |
| Antiallergic (0.682) | Cell adhesion molecule inhibitor (0.752) |
| 258 | Choleretic (0.909) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.905) |
| Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.856) | Anesthetic general (0.903) |
| Hepatoprotectant (0.829) | Antineoplastic (0.849) |
| 259 | Anti-inflammatory (0.907) | Respiratory analeptic (0.861) |
| Inflammatory Bowel disease treatment (0.750) | Antineoplastic (0.855) |
| 260 | Chemopreventive (0.936) | Anticarcinogenic (0.815) |
| Antineoplastic (0.918) | Prostate cancer treatment (0.795) |
| 261 | Antineoplastic (0.951) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.704) |
| Chemoprotective (0.844) | Antihypertensive (0.649) |
| 262 | Antineoplastic (0.935) | Anti-inflammatory (0.918) |
| Chemoprotective (0.804) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.826) |
| 263 | Hypolipemic (0.995) | Antioxidant (0.973) |
| Atherosclerosis treatment (0.991) | Antineoplastic (0.852) |
| Lipoprotein disorders treatment (0.982) | Chemoprotective (0.748) |
| 264 | Antineoplastic (0.922) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.902) |
| Chemopreventive (0.914) | Hypolipemic (0.899) |
| 265 | Antineoplastic (0.918) | Hypolipemic (0.913) |
| Chemopreventive (0.894) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.884) |
| Anticarcinogenic (0.801) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.822) |
| 266 | Hypolipemic (0.996) | Antioxidant (0.978) |
| Atherosclerosis treatment (0.995) | Antineoplastic (0.904) |
| Lipoprotein disorders treatment (0.991) | Chemoprotective (0.823) |
| Antiarthritic (0.979) | Anticarcinogenic (0.795) |
| 267 | Hypolipemic (0.995) | Antioxidant (0.970) |
| Atherosclerosis treatment (0.989) | Antineoplastic (0.850) |
| Lipoprotein disorders treatment (0.980) | Chemoprotective (0.785) |
Table 18.
Biological activities of steroids bearing tellurium atom (
268–
280) [
260].
Table 18.
Biological activities of steroids bearing tellurium atom (
268–
280) [
260].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 268 | Antioxidant (0.956) | Neurodegenerative disease treatment (0.897) |
| Anti-inflammatory (0.936) | Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.877) |
| Antineoplastic (0.935) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.873) |
| Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.815) | Antiparkinsonian (0.868) |
| 269 | Antioxidant (0.946) | Neurodegenerative diseases treatment (0.871) |
| Anti-inflammatory (0.930) | Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.863) |
| Antineoplastic (0.930) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.861) |
| Anesthetic general (0.879) | Antiparkinsonian (0.833) |
| 270 | Antiprotozoal (Plasmodium) (0.818) | Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.757) |
| Antiprotozoal (0.801) | Neurodegenerative diseases treatment (0.735) |
| Antioxidant (0.774) | Antiparkinsonian (0.730) |
| Ovulation inhibitor (0.625) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.670) |
| 271 | Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.966) | Antineoplastic (0.828) |
| Antioxidant (0.965) | Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.678) |
| Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.889) | Antineoplastic (pancreatic cancer) (0.522) |
| Atherosclerosis treatment (0.703) | Prostate cancer treatment (0.501) |
| 272 | Antiparkinsonian (0.946) | Antioxidant (0.966) |
| Neurodegenerative diseases treatment (0.945) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.964) |
| Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.928) | Anti-inflammatory (0.955) |
| 273 | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.958) | Antineoplastic (0.871) |
| Anti-inflammatory (0.913) | Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.838) |
| Atherosclerosis treatment (0.890) | Antioxidant (0.807) |
| Respiratory analeptic (0.885) | Neurodegenerative diseases treatment (0.801) |
| 274 | Antiparkinsonian (0.955) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.977) |
| Neurodegenerative diseases treatment (0.954) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.956) |
| Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.940) | Antioxidant (0.963) |
| Antineoplastic (0.932) | Anti-hyperlipoproteinemic (0.811) |
| 275 | Anti-inflammatory (0.926) | Neurodegenerative diseases treatment (0.877) |
| Antioxidant (0.922) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.869) |
| Atherosclerosis treatment (0.908) | Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.868) |
| Antineoplastic (0.895) | Antiparkinsonian (0.848) |
| 276 | Respiratory analeptic (0.959) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.876) |
| Anesthetic general (0.937) | Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.828) |
| Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.909) | Neurodegenerative diseases treatment (0.808) |
| 277 | Anti-inflammatory (0.911) | Antioxidant (0.878) |
| Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.886) | Anesthetic general (0.863) |
| Atherosclerosis treatment (0.883) | Antineoplastic (0.862) |
| 278 | Respiratory analeptic (0.933) | Atherosclerosis treatment (0.838) |
| Anesthetic general (0.921) | Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.821) |
| Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.902) | Neurodegenerative diseases treatment (0.796) |
| 279 | Anti-inflammatory (0.918) | Antioxidant (0.894) |
| Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.892) | Anesthetic general (0.859) |
| Atherosclerosis treatment (0.843) | Antineoplastic (0.834) |
| 280 | Anti-inflammatory (0.928) | Neurodegenerative diseases treatment (0.888) |
| Antioxidant (0.926) | Antineoplastic (0.884) |
| Atherosclerosis treatment (0.910) | Alzheimer’s disease treatment (0.877) |
| Anesthetic general (0.894) | Antiparkinsonian (0.872) |
Table 19.
Biological activities of steroids bearing tin atom (
281–
298) [
358].
Table 19.
Biological activities of steroids bearing tin atom (
281–
298) [
358].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 281 | Antineoplastic (0.905) | Anti-inflammatory (0.640) |
| Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.866) | Dementia treatment (0.519) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.832) | |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.766) | |
| 282 | Antineoplastic (0.996) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.721) |
| Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.825) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.647) |
| 283 | Antineoplastic (0.946) | Postmenopausal disorders treatment (0.677) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.843) | Gynecological disorders treatment (0.553) |
| Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.780) | Contraceptive (0.509) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.748) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.505) |
| 284 | Antineoplastic (0.996) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.689) |
| Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.777) | Genital warts treatment (0.538) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.582) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.532) |
| 285 | Antineoplastic (0.887) | Choleretic (0.895) |
| Antimetastatic (0.776) | Biliary tract disorders treatment (0.825) |
| Antibacterial (0.677) | Hepatic disorders treatment (0.716) |
| 286 | Antineoplastic (0.890) | Choleretic (0.894) |
| Antimetastatic (0.781) | Hepatic disorders treatment (0.734) |
| 287 | Antineoplastic (0.823) | Choleretic (0.895) |
| Antimetastatic (0.775) | Hepatic disorders treatment (0.707) |
| 288 | Antineoplastic (0.848) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0. 895) |
| Antimetastatic (0.710) | Cholesterol synthesis inhibitor (0.645) |
| Antibacterial (0.685) | Antifungal (0.649) |
| 289 | Antineoplastic (0.921) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.907) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.753) | Respiratory analeptic (0.847) |
| Antimetastatic (0.748) | Anti-eczematic (0.822) |
| Antineoplastic (pancreatic cancer) (0.702) | Anesthetic general (0.804) |
| Prostate cancer treatment (0.700) | Dermatologic (0.747) |
| Antibacterial (0.573) | Cholesterol synthesis inhibitor (0.627) |
| 290 | Antineoplastic (0.909) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.906) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.833) | Anti-eczematic (0.830) |
| Antimetastatic (0.740) | Dermatologic (0.736) |
| 291 | Antineoplastic (0.904) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.901) |
| Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.881) | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.716) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.780) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.663) |
| 292 | Antineoplastic (0.906) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.840) |
| Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.837) | Dermatologic (0.674) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.827) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.666) |
| Antineoplastic (sarcoma) (0.824) | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.650) |
| Antineoplastic (renal cancer) (0.762) | Respiratory analeptic (0.651) |
| Prostate cancer treatment (0.750) | Bone diseases treatment (0.641) |
| Antineoplastic (pancreatic cancer) (0.741) | |
| 293 | Antineoplastic (0.841) | Anesthetic general (0.850) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.841) | Immunosuppressant (0.725) |
| 294 | Anti-inflammatory (0.917) | Antineoplastic (0.828) |
| Anesthetic general (0.872) | Muscular dystrophy treatment (0.784) |
| 295 | Anti-inflammatory (0.920) | Allergic conjunctivitis treatment (0.765) |
| Antineoplastic (0.761) | Antiallergic (0.760) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.701) | Antipruritic, allergic (0.710) |
| 296 | Anti-eczematic (0.807) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.683) |
| Anti-osteoporotic (0.612) | Cytoprotectant (0.683) |
| 297 | Antineoplastic (0.874) | Anti-eczematic (0.707) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.734) | Anti-inflammatory (0.622) |
| Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.712) | Anti-secretoric (0.580) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.718) | Antibacterial (0.544) |
| 298 | Antineoplastic (0.704) | Anti-eczematic (0.630) |
| Antibacterial (0.566) | Dermatologic (0.532) |
Table 20.
Biological activities of ferrocene steroid conjugates (
299–
332) [
370].
Table 20.
Biological activities of ferrocene steroid conjugates (
299–
332) [
370].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 299 | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.847) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.656) |
| 300 | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.909) | Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.909) |
| Prostate disorders treatment (0.626) | Antineoplastic (0.880) |
| 301 | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.831) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.714) |
| 302 | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.794) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.596) |
| 303 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.748) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.703) |
| 304 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.748) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.703) |
| 305 | Prostate disorders treatment (0.755) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.588) |
| 306 | Anti-inflammatory (0.876) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.725)
Growth stimulant (0.581) |
| Allergic conjunctivitis treatment (0.765) |
| Antiallergic (0.690) |
| 307 | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.731) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.648) |
| 308 | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.826) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.712) |
| 309 | Anti-inflammatory (0.788) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.763) |
| Allergic conjunctivitis treatment (0.680) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.639) |
| 310 | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.795) | Muscular dystrophy treatment (0.719) |
| Ovulation inhibitor (0.770) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.629) |
| 311 | Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.969) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.867) |
| Antineoplastic (0.930) | Contraceptive (0.635) |
| 312 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.880) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.697) |
| Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.714) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.668) |
| 313 | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.809) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.680) |
| 314 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.909) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.653) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.651) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.625) |
| 315 | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.900) | Prostate disorders treatment (0.662) |
| Ovulation inhibitor (0.702) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.648) |
| 316 | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.911) | Dementia treatment (0.647) |
| Cardiotonic (0.845) | Respiratory analeptic (0.661) |
| 317 | Antineoplastic (0.832) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.758)
Choleretic (0.677) |
| Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.819) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.518) |
| 318 | Antineoplastic (0.837) | Anesthetic general (0.831)
Respiratory analeptic (0.785) |
| Cytoprotectant (0.684) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.585) |
| 319 | Antineoplastic (0.944) | Anti-psoriatic (0.910) |
| Apoptosis agonist (0.879) | Anti-osteoporotic (0.899) |
| Proliferative disease treatment (0.637) | Antiparkinsonian, rigidity relieving (0.568) |
| 320 | Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.819) | Genital warts treatment (0.656) |
| Antineoplastic (0.774) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.594) |
| 321 | Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.818) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.638) |
| Antineoplastic (0.782) | Steroid synthesis inhibitor (0.533) |
| 322 | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.920) | Respiratory analeptic (0.854) |
| Antineoplastic (0.837); | Anesthetic general (0.694) |
| Proliferative disease treatment (0.638) | Cholesterol synthesis inhibitor (0.636) |
| 323 | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.885) | Respiratory analeptic (0.860) |
| Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.819) | Anesthetic general (0.846) |
| 324 | Anti-inflammatory (0.718) | HCV IRES inhibitor (0.669) |
| 325 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.728) | HCV IRES inhibitor (0.712) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.625) | Anti-osteoporotic (0.619) |
| 326 | Ovulation inhibitor (0.775) | HCV IRES inhibitor (0.766) |
| Menopausal disorders treatment (0.715) | Anti-osteoporotic (0.708) |
| 327 | Glutaconyl-CoA decarboxylase inhibitor (0.637) | Glyceryl-ether monooxygenase inhibitor (0.545) |
| 328 | Gestagen antagonist (0.598) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.526) |
| 329 | Glutaconyl-CoA decarboxylase inhibitor (0.655) | Estrogen alpha receptor agonist (0.626) |
| 330 | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.942) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.862) |
| 331 | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.942) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.862) |
| 332 | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.938) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.859) |
Table 21.
Biological activities of titanocene steroid conjugates (
332–
339) [
370].
Table 21.
Biological activities of titanocene steroid conjugates (
332–
339) [
370].
| No. | Dominated Biological Activity (Pa) * | Additional Predicted Activities (Pa) * |
|---|
| 332 | Antineoplastic (0.996) | Dermatologic (0.638) |
| Antineoplastic, alkylator (0.878) | Anti-eczematic (0.553) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.740) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.527) |
| 333 | Antineoplastic (0.996) | Ovulation inhibitor (0.668) |
| Antineoplastic, alkylator (0.823) | Dermatologic (0.583) |
| Antineoplastic (breast cancer) (0.740) | Menopausal disorders treatment (0.525) |
| 334 | Antineoplastic (0.996) | Dermatologic (0.531) |
| Alkylator (0.895) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.527) |
| Antineoplastic, alkylator (0.775) | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.500) |
| 335 | Antineoplastic (0.996) | Dermatologic (0.531) |
| Alkylator (0.895) | Erythropoiesis stimulant (0.527) |
| Antineoplastic, alkylator (0.775) | Male reproductive dysfunction treatment (0.500) |
| 336 | Antineoplastic (0.995) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.881) |
| Toxic (0.948) | Hypolipemic (0.643) |
| Antineoplastic, alkylator (0.583) | Cholesterol synthesis inhibitor (0.622) |
| Apoptosis agonist (0.529) | Immunosuppressant (0.593) |
| 337 | Antineoplastic (0.995) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.881) |
| Toxic (0.948) | Hypolipemic (0.643) |
| Antineoplastic, alkylator (0.583) | Cholesterol synthesis inhibitor (0.622) |
| Apoptosis agonist (0.529) | Immunosuppressant (0.593) |
| 338 | Antineoplastic (0.996) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.802)
Cholesterol synthesis inhibitor (0.594)
Hypolipemic (0.558) |
| Toxic (0.952) |
| Antineoplastic, alkylator (0.681) |
| Proliferative disease treatment (0.542) |
| Prostatic (benign) hyperplasia treatment (0.537) |
| Apoptosis agonist (0.529) |
| 339 | Antineoplastic (0.996) | Anti-hypercholesterolemic (0.643) |
| Proliferative disease treatment (0.579) | Cholesterol synthesis inhibitor (0.550) |