An Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Human Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) Model to Test the Crossing by Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Vectors and Antisense Oligonucleotides
Abstract
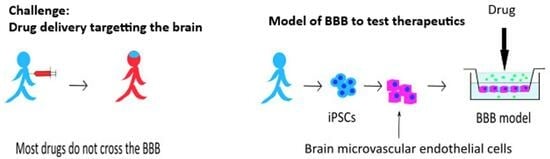
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and iPSC Differentiation to BMECs
2.2. Immunocytochemical Analysis of Tight-Junction Protein
2.3. Flow Cytometry
2.4. TEER Measurements
2.5. Permeability of Fluorescent Tracers
2.6. AAV8 and AAV9 Preparation and Crossing of the BBB
2.7. Assay of BBB Permeability to PMOs
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Characterisation of BMECs Using Immunocytochemistry and Flow Cytometry
3.2. TEER-Based Evaluation of the BBB Models
3.3. Evaluation of Permeability of the BBB Models to Fluorescent Tracers
3.4. Analysis of BBB Model Crossing by AAV8 and AAV9 Vectors and Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Conjugated PMO
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbott, N.J. Blood-brain barrier structure and function and the challenges for CNS drug delivery. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2013, 36, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardridge, W.M. The blood-brain barrier: Bottleneck in brain drug development. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deli, M.A.; Abraham, C.S.; Kataoka, Y.; Niwa, M. Permeability studies on in vitro blood-brain barrier models: Physiology, pathology, and pharmacology. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2005, 25, 59–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, S.; Deli, M.A.; Kawaguchi, H.; Shimizudani, T.; Shimono, T.; Kittel, A.; Tanaka, K.; Niwa, M. A new blood-brain barrier model using primary rat brain endothelial cells, pericytes and astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2009, 54, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernas, M.J.; Cardoso, F.L.; Daley, S.K.; Weinand, M.E.; Campos, A.R.; Ferreira, A.J.; Hoying, J.B.; Witte, M.H.; Brites, D.; Persidsky, Y.; et al. Establishment of primary cultures of human brain microvascular endothelial cells to provide an in vitro cellular model of the blood-brain barrier. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weksler, B.; Romero, I.A.; Couraud, P.O. The hCMEC/D3 cell line as a model of the human blood brain barrier. Fluids Barriers CNS 2013, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biemans, E.; Jäkel, L.; de Waal, R.M.W.; Kuiperij, H.B.; Verbeek, M.M. Limitations of the hCMEC/D3 cell line as a model for Aβ clearance by the human blood-brain barrier. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urich, E.; Lazic, S.E.; Molnos, J.; Wells, I.; Freskgard, P.O. Transcriptional profiling of human brain endothelial cells reveals key properties crucial for predictive in vitro blood-brain barrier models. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippmann, E.S.; Azarin, S.M.; Kay, J.E.; Nessler, R.A.; Wilson, H.K.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Palecek, S.P.; Shusta, E.V. Derivation of blood-brain barrier endothelial cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.I.; Abaci, H.E.; Shuler, M.L. Microfluidic blood-brain barrier model provides in vivo-like barrier properties for drug permeability screening. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czupalla, C.J.; Liebner, S.; Devraj, K. In vitro models of the blood-brain barrier. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1135, 415–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katt, M.E.; Linville, R.M.; Mayo, L.N.; Xu, Z.S.; Searson, P.C. Functional brain-specific microvessels from iPSC-derived human brain microvascular endothelial cells: The role of matrix composition on monolayer formation. Fluids Barriers CNS 2018, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, S.G.; Stebbins, M.J.; Morales, B.S.; Asai, S.W.; Vatine, G.D.; Svendsen, C.N.; Palecek, S.P.; Shusta, E.V. An isogenic blood-brain barrier model comprising brain endothelial cells, astrocytes, and neurons derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. J. Neurochem. 2017, 140, 874–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigenmann, D.E.; Xue, G.; Kim, K.S.; Moses, A.V.; Hamburger, M.; Oufir, M. Comparative study of four immortalized human brain capillary endothelial cell lines, hCMEC/D3, hBMEC, TY10, and BB19, and optimization of culture conditions, for an in vitro blood-brain barrier model for drug permeability studies. Fluids Barriers CNS 2013, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Muñoz, R.J. Gene Therapy, more than ever-a new vision for the journal. Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbot, K.; Tizzano, E.F. The clinical landscape for SMA in a new therapeutic era. Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrpant, C.; Porensky, P.; Zhou, H.; Price, L.; Muntoni, F.; Fletcher, S.; Wilton, S.D.; Burghes, A.H. Improved antisense oligonucleotide design to suppress aberrant SMN2 gene transcript processing: Towards a treatment for spinal muscular atrophy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanpoor, F.; Hammond, S.M.; Abendroth, F.; Hazell, G.; Wood, M.J.A.; Gait, M.J. Identification of a Peptide for Systemic Brain Delivery of a Morpholino Oligonucleotide in Mouse Models of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Nucleic. Acid. Ther. 2017, 27, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, S.M.; Hazell, G.; Shabanpoor, F.; Saleh, A.F.; Bowerman, M.; Sleigh, J.N.; Meijboom, K.E.; Zhou, H.; Muntoni, F.; Talbot, K.; et al. Systemic peptide-mediated oligonucleotide therapy improves long-term survival in spinal muscular atrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10962–10967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foust, K.D.; Nurre, E.; Montgomery, C.L.; Hernandez, A.; Chan, C.M.; Kaspar, B.K. Intravascular AAV9 preferentially targets neonatal neurons and adult astrocytes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, S.; Joussemet, B.; Riviere, C.; Marais, T.; Dubreil, L.; Douar, A.M.; Fyfe, J.; Moullier, P.; Colle, M.A.; Barkats, M. Intravenous administration of self-complementary AAV9 enables transgene delivery to adult motor neurons. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zaidy, S.; Kolb, S.J.; Lowes, L.; Alfano, L.N.; Shell, R.; Church, K.R.; Nagendran, S.; Sproule, D.M.; Feltner, D.E.; Wells, C.; et al. AVXS-101 Gene Replacement Therapy for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: A Comparative Study with a Prospective Natural History Cohort. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 111. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, L.; Jin, S.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Lv, Z.Y.; Xin, C.Q.; Tan, C.C.; Zhao, M.K.; Wang, L.; Liu, J. AAV vectors applied to the treatment of CNS disorders: Clinical status and challenges. J. Control. Release 2023, 355, 458–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatine, G.D.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Barriga, B.K.; Svendsen, S.; Salim, A.; Garcia, L.; Garcia, V.J.; Ho, R.; Yucer, N.; Qian, T.; et al. Modeling Psychomotor Retardation using iPSCs from MCT8-Deficient Patients Indicates a Prominent Role for the Blood-Brain Barrier. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 20, 831–843.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippmann, E.S.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Azarin, S.M.; Palecek, S.P.; Shusta, E.V. A retinoic acid-enhanced, multicellular human blood-brain barrier model derived from stem cell sources. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.B.; Dayton, R.D.; Henning, P.P.; Cain, C.D.; Zhao, L.R.; Schrott, L.M.; Orchard, E.A.; Knight, D.S.; Klein, R.L. Expansive Gene Transfer in the Rat CNS Rapidly Produces Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Relevant Sequelae When TDP-43 is Overexpressed. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 2064–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehay, B.; Dalkara, D.; Dovero, S.; Li, Q.; Bezard, E. Systemic scAAV9 variant mediates brain transduction in newborn rhesus macaques. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, E.H.; Marinelli, N.A.; Shi, Y.; McClatchey, P.M.; Balotin, K.M.; Gullett, D.R.; Hagerla, K.A.; Bowman, A.B.; Ess, K.C.; Wikswo, J.P.; et al. A Simplified, Fully Defined Differentiation Scheme for Producing Blood-Brain Barrier Endothelial Cells from Human iPSCs. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 12, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crone, C.; Olesen, S.P. Electrical resistance of brain microvascular endothelium. Brain Res. 1982, 241, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, A.M.; Jones, H.C.; Abbott, N.J. Electrical resistance across the blood-brain barrier in anaesthetized rats: A developmental study. J. Physiol. 1990, 429, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Q.R.; Rapoport, S.I. Cerebrovascular permeability coefficients to sodium, potassium, and chloride. J. Neurochem. 1986, 46, 1732–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollmann, E.K.; Bailey, A.K.; Potharazu, A.V.; Neely, M.D.; Bowman, A.B.; Lippmann, E.S. Accelerated differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells to blood-brain barrier endothelial cells. Fluids Barriers CNS 2017, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, J.R.; Fletcher, C.V.; Podany, A.T.; Dyavar, S.R.; Scarsi, K.K.; Pais, G.M.; Scheetz, M.H.; Avedissian, S.N. A novel 4-cell in-vitro blood-brain barrier model and its characterization by confocal microscopy and TEER measurement. J. Neurosci. Meth. 2023, 392, 109867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Page, S.; Al-Ahmad, A.J. Isogenic blood-brain barrier models based on patient-derived stem cells display inter-individual differences in cell maturation and functionality. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ahmad, A.J. Comparative study of expression and activity of glucose transporters between stem cell-derived brain microvascular endothelial cells and hCMEC/D3 cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2017, 313, C421–C429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Su, X.J.; Sorenson, C.M.; Sheibani, N. Tissue-specific distributions of alternatively spliced human PECAM-1 isoforms. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart C 2003, 284, H1008–H1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredsson, F.P.; Rising, A.C.; Mandel, R.J. AAV9: A potential blood-brain barrier buster. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, S.F.; Andrews, A.M.; Lutton, E.M.; Mu, D.; Hudry, E.; Hyman, B.T.; Maguire, C.A.; Ramirez, S.H. Trafficking of adeno-associated virus vectors across a model of the blood-brain barrier; a comparative study of transcytosis and transduction using primary human brain endothelial cells. J. Neurochem. 2017, 140, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.Y.; McCarty, D.M. Crossing the blood-brain-barrier with viral vectors. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 21, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Diao, Y. Crossing the blood-brain barrier with AAV vectors. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selvakumaran, J.; Ursu, S.; Bowerman, M.; Lu-Nguyen, N.; Wood, M.J.; Malerba, A.; Yáñez-Muñoz, R.J. An Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Human Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) Model to Test the Crossing by Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Vectors and Antisense Oligonucleotides. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102700
Selvakumaran J, Ursu S, Bowerman M, Lu-Nguyen N, Wood MJ, Malerba A, Yáñez-Muñoz RJ. An Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Human Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) Model to Test the Crossing by Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Vectors and Antisense Oligonucleotides. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(10):2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102700
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelvakumaran, Jamuna, Simona Ursu, Melissa Bowerman, Ngoc Lu-Nguyen, Matthew J. Wood, Alberto Malerba, and Rafael J. Yáñez-Muñoz. 2023. "An Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Human Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) Model to Test the Crossing by Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Vectors and Antisense Oligonucleotides" Biomedicines 11, no. 10: 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102700
APA StyleSelvakumaran, J., Ursu, S., Bowerman, M., Lu-Nguyen, N., Wood, M. J., Malerba, A., & Yáñez-Muñoz, R. J. (2023). An Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Human Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) Model to Test the Crossing by Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Vectors and Antisense Oligonucleotides. Biomedicines, 11(10), 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102700