Genetic Polymorphisms of ACE1 Rs4646994 Associated with Lung Cancer in Patients with Pulmonary Nodules: A Case–Control Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Conformity
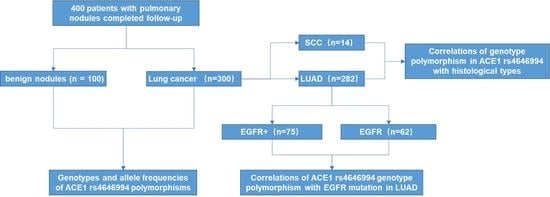
2.2. Case and Control
2.3. Genotyping
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristic of Study Subjects
3.2. Correlations of Allele and Genotype Frequencies of ACE1 rs4646994 Polymorphism with Risk of Lung Cancer in Pulmonary Nodules
3.3. Correlations of Allele and Genotype Frequencies of ACE1 rs4646994 Polymorphism with Histological Types of SCC and LUAD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| CI | confidence intervals |
| LUAD | adenocarcinoma |
| NSCLC | non-small-cell lung cancer |
| OR | odds ratios |
| SCC | squamous-cell carcinoma |
| SCLC | small-cell lung cancer |
| SNPs | single-nucleotide polymorphisms |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varoli, F.; Vergani, C.; Caminiti, R.; Francese, M.; Gerosa, C.; Bongini, M.; Roviaro, G. Management of solitary pulmonary nodule. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2008, 33, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beasley, M.B.; Chirieac, L.R.; Dacic, S.; Duhig, E.; Flieder, D.B.; et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, A.A.; Solomon, B.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Gainor, J.F.; Heist, R.S. Lung cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, K. Pulmonary Nodules. JAMA 2021, 326, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, N.; Kim, K.H.; Jeong, B.H.; Lee, K.; Kim, H.; Kwon, O.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Cho, J.; Lee, H.Y.; Um, S.W. The Impact of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor on the Natural Course of Concurrent Subsolid Nodules in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 54, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, L.; Rosell, R.; Cardona, A.F.; Martin, C.; Zatarain-Barron, Z.L.; Arrieta, O. Lung cancer in never smokers: The role of different risk factors other than tobacco smoking. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 148, 102895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurria, A.; Kris, M.G. Management of lung cancer in older adults. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2003, 53, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.E.B.; Leitao, L.P.C.; Andrade, R.B.; Modesto, A.A.C.; Fernandes, B.M.; Burbano, R.M.R.; Assumpcao, P.P.; Fernandes, M.R.; Guerreiro, J.F.; Santos, S.; et al. UGT1A1 Gene Polymorphism Contributes as a Risk Factor for Lung Cancer: A Pilot Study with Patients from the Amazon. Genes 2022, 13, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cui, Z.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Lv, X.; Yang, Z.; Gao, M.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, B.; et al. LncRNA NEAT1 polymorphisms and lung cancer susceptibility in a Chinese Northeast Han Population: A case-control study. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Classen, V.; Helmig, S. XRCC1 polymorphism and lung cancer risk. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 8, 761–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Yang, D.; Ji, B.; Li, J. Angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion gene polymorphism and lung cancer risk: A meta-analysis. J. Renin. Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2015, 16, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, P.J.; Lam, L. Evaluating the Patient With a Pulmonary Nodule: A Review. JAMA 2022, 327, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saengsiwaritt, W.; Jittikoon, J.; Chaikledkaew, U.; Udomsinprasert, W. Genetic polymorphisms of ACE1, ACE2, and TMPRSS2 associated with COVID-19 severity: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieder, M.J.; Taylor, S.L.; Clark, A.G.; Nickerson, D.A. Sequence variation in the human angiotensin converting enzyme. Nat. Genet. 1999, 22, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.; Albaiceta, G.M.; Garcia-Clemente, M.; Lopez-Larrea, C.; Amado-Rodriguez, L.; Lopez-Alonso, I.; Hermida, T.; Enriquez, A.I.; Herrero, P.; Melon, S.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzymes (ACE, ACE2) gene variants and COVID-19 outcome. Gene 2020, 762, 145102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Abbas, M.; Verma, S.; Khan, F.H.; Raza, S.T.; Siddiqi, Z.; Ahmad, I.; Mahdi, F. Impact of I/D polymorphism of angiotensin-converting enzyme 1 (ACE1) gene on the severity of COVID-19 patients. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 91, 104801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanghe, J.R.; Speeckaert, M.M.; De Buyzere, M.L. COVID-19 infections are also affected by human ACE1 D/I polymorphism. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 1125–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehoe, P.G. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and Alzheimer s disease? J. Renin. Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2003, 4, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellon, R.; Hamdi, H.K. Demystifying the ACE polymorphism: From genetics to biology. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed-Tabatabaei, F.A.; Oostra, B.A.; Isaacs, A.; van Duijn, C.M.; Witteman, J.C. ACE polymorphisms. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, V.; Goswami, B. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE). Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 524, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmorzynski, S.; Szudy-Szczyrek, A.; Popek-Marciniec, S.; Korszen-Pilecka, I.; Wojcierowska-Litwin, M.; Luterek, M.; Chocholska, S.; Styk, W.; Swiderska-Kolacz, G.; Januszewska, J.; et al. ACE Insertion/Deletion Polymorphism (rs4646994) Is Associated with the Increased Risk of Multiple Myeloma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Kaur, G.; Pathak, T.; Banerjee, I. Systematic review and meta-analysis of human genetic variants contributing to COVID-19 susceptibility and severity. Gene 2022, 844, 146790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradzadegan, A.; Vaisi-Raygani, A.; Nikzamir, A.; Rahimi, Z. Angiotensin converting enzyme insertion/deletion (I/D) (rs4646994) and Vegf polymorphism (+405G/C; rs2010963) in type II diabetic patients: Association with the risk of coronary artery disease. J. Renin. Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2015, 16, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toumazis, I.; Bastani, M.; Han, S.S.; Plevritis, S.K. Risk-Based lung cancer screening: A systematic review. Lung Cancer 2020, 147, 154–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sears, C.R.; Rivera, M.P. Age, Sex, Smoking, and Race: Is Progress Being Made in Lung Cancer Screening Eligibility? Chest 2021, 160, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.L.; Shi, Y.; Fung, K.Z.; Ngo, S.; Elicker, B.M.; Brown, J.K.; Hiatt, R.A.; Tang, V.L.; Walter, L.C. Age, comorbidity, life expectancy, and pulmonary nodule follow-up in older veterans. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Case (n = 300) | Control (n = 100) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, n (%) | 0.862 a | ||
| Male | 135 (45%) | 44 (44%) | |
| Female | 165 (55%) | 56 (56%) | |
| Age (years) | |||
| Median (p25–p75%) | 57.00 (49.00–64.00) | 55.00 (48.25–61.00) | 0.038 b* |
| Histology | |||
| Squamous Cell Carcinoma | 14 (5.3%) | - | |
| Adencarcinoma | 282 (93.4%) | - | NA |
| Small Cell Carcinoma | 2 (0.6%) | - | |
| Malt | 2 (0.6%) | - | |
| EGFR Mutation-positive | 1.000 c | ||
| Yes | 75 (52.1%) | 1 (50%) | |
| No | 69 (47.9%) | 1 (50%) |
| Genotype/Allele | Case (n = 300) | Control (n = 100) | p-Value a | OR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II | 121 | 41 | Reference | ||
| ID | 132 | 53 | 0.474 | 0.839 | 0.519–1.356 |
| DD | 47 | 6 | 0.031 | 2.760 | 1.095–6.953 |
| DD vs. ID + II | 0.014 | 3.035 | 1.252–7.356 | ||
| I allele | 374 | 135 | Reference | ||
| D allele | 226 | 65 | 0.167 | 1.271 | 0.904–1.786 |
| Genotype/ | SCC | LUAD | Control | p-Value a† | OR † | 95%CI † | p-Value a‡ | OR ‡ | 95%CI ‡ | p-Value a§ | OR § | 95%CI § |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allele | (n = 14) | (n = 282) | (n = 100) | |||||||||
| II | 7 (50%) | 112 (39.7%) | 41 (41%) | Reference | Reference | Reference | ||||||
| ID | 6 (42.9%) | 126 (44.7%) | 53 (53%) | 0.153 | 0.354 | 0.085–1.469 | 0.593 | 0.876 | 0.540–1.422 | 0.363 | 1.751 | 0.524–5.857 |
| DD | 1 (7.1%) | 44 (14.6%) | 6 (6%) | 0.499 | 0.367 | 0.020–6.708 | 0.032 | 2.756 | 1.090–6.968 | 0.492 | 2.169 | 0.239–19.728 |
| DD vs. ID + II | 0.783 | 0.679 | 0.043–10.709 | 0.016 | 2.963 | 1.219–7.199 | 0.647 | 1.649 | 0.194–14.040 | |||
| I allele | 20 (71.4%) | 350 (62.1%) | 135 | Reference | Reference | Reference | ||||||
| D allele | 8 (28.6%) | 214 (37.9%) | 65 | 0.696 | 0.845 | 0.362–1.972 | 0.139 | 1.279 | 0.919–1.821 | 0.330 | 1.551 | 0.642–3.748 |
| Genotype/Allele | EGFR+ (n = 75) | EGFR (n = 62) | p-Value a | OR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II | 32 (42.7%) | 22 (35.5%) | Reference | ||
| ID | 37 (49.3%) | 26 (41.9%) | 0.894 | 1.054 | 0.490–2.264 |
| DD | 6 (8.0%) | 14 (22.6%) | 0.044 | 0.312 | 0.101–0.968 |
| DD vs. ID + II | 69 (57.3%) | 48 (64.5%) | 0.027 | 0.304 | 0.105–0.875 |
| I allele | 101 (67.3%) | 70 (56.5%) | Reference | ||
| D allele | 49 (32.7%) | 54 (43.5%) | 0.065 | 0.628 | 0.383–1.029 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, R.; Sang, S.; Teng, J.; Zhong, H.; Li, H.; Han, B. Genetic Polymorphisms of ACE1 Rs4646994 Associated with Lung Cancer in Patients with Pulmonary Nodules: A Case–Control Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061549
Qiao R, Sang S, Teng J, Zhong H, Li H, Han B. Genetic Polymorphisms of ACE1 Rs4646994 Associated with Lung Cancer in Patients with Pulmonary Nodules: A Case–Control Study. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(6):1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061549
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Rong, Siyao Sang, Jiajun Teng, Hua Zhong, Hui Li, and Baohui Han. 2023. "Genetic Polymorphisms of ACE1 Rs4646994 Associated with Lung Cancer in Patients with Pulmonary Nodules: A Case–Control Study" Biomedicines 11, no. 6: 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061549
APA StyleQiao, R., Sang, S., Teng, J., Zhong, H., Li, H., & Han, B. (2023). Genetic Polymorphisms of ACE1 Rs4646994 Associated with Lung Cancer in Patients with Pulmonary Nodules: A Case–Control Study. Biomedicines, 11(6), 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061549