UBL3 Interacts with Alpha-Synuclein in Cells and the Interaction Is Downregulated by the EGFR Pathway Inhibitor Osimertinib
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Antibodies and Drugs
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
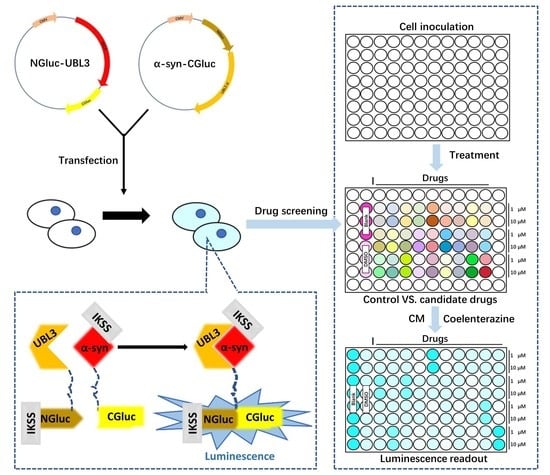
2.4. Plasmids Construction
2.5. Cell Culture and cDNA Transfection
2.6. Cell Treatment
2.7. Sample Preparation and Luciferase Assay
2.8. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Assay
2.9. Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA) Assay
2.10. Co-Immunoprecipitation
2.11. Immunoblot
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. p-S-129 α-syn Was Upregulated in the Substantia Nigra of Ubl3−/− Mice
3.2. UBL3 Interacted with α-syn in Cells
3.3. The Interaction between UBL3 and α-syn in Cells Was Upregulated by the 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinium (MPP+) Exposure
3.4. Interaction between UBL3 and α-syn in Cells Was Significantly Downregulated by Osimertinib
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Downes, B.P.; Saracco, S.A.; Lee, S.S.; Crowell, D.N.; Vierstra, R.D. MUBs, a family of ubiquitin-fold proteins that are plasma membrane-anchored by prenylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 27145–27157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chadwick, B.P.; Kidd, T.; Sgouros, J.; Ish-Horowicz, D.; Frischauf, A.M. Cloning, mapping and expression of UBL3, a novel ubiquitin-like gene. Gene 1999, 233, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageta, H.; Ageta-Ishihara, N.; Hitachi, K.; Karayel, O.; Onouchi, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kahyo, T.; Hatanaka, K.; Ikegami, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; et al. UBL3 modification influences protein sorting to small extracellular vesicles. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Wilson, K.R.; Firth, A.M.; Macri, C.; Schriek, P.; Blum, A.B.; Villar, J.; Wormald, S.; Shambrook, M.; Xu, B.; et al. Ubiquitin-like protein 3 (UBL3) is required for MARCH ubiquitination of major histocompatibility complex class II and CD86. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, Q.M.; Zhang, M.Y.; Yu, Y.H.; Yun, J.P.; Wang, H.Y. Identification of a 7-gene signature that predicts relapse and survival for early stage patients with cervical carcinoma. Med. Oncol. (Northwood Lon. Engl.) 2012, 29, 2911–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Qi, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Guan, Q.; He, J.; Li, M.; Guo, Z.; Yan, H.; Li, P. Identification of Genes Universally Differentially Expressed in Gastric Cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 7326853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Singh, L.C.; Vasudevan, M.; Chattopadhyay, I.; Borthakar, B.B.; Rai, A.K.; Phukan, R.K.; Sharma, J.; Mahanta, J.; Kataki, A.C.; et al. Esophageal Cancer Epigenomics and Integrome Analysis of Genome-Wide Methylation and Expression in High Risk Northeast Indian Population. Omics A J. Integr. Biol. 2015, 19, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yongchun, Z.; Qian, H.; Sanhui, G.; Jie, L.; Hong, Y.; Yanfei, Z.; Guizhen, W.; Yunchao, H.; Guangbiao, Z. Identification of a potential tumor suppressor gene, UBL3, in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, S.; Hagenah, J.; Lincoln, S.; Heckman, M.; Haugarvoll, K.; Lohmann-Hedrich, K.; Kostic, V.; Farrer, M.; Klein, C. alpha-Synuclein and Parkinson disease susceptibility. Neurology 2007, 69, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Fornai, F.; Kwon, H.B.; Yazdani, U.; Atasoy, D.; Liu, X.; Hammer, R.E.; Battaglia, G.; German, D.C.; Castillo, P.E.; et al. Double-knockout mice for alpha- and beta-synucleins: Effect on synaptic functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14966–14971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezey, E.; Dehejia, A.; Harta, G.; Papp, M.I.; Polymeropoulos, M.H.; Brownstein, M.J. Alpha synuclein in neurodegenerative disorders: Murderer or accomplice? Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L. Molecular pathways of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2003, 302, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.Y.; Zhou, C.J.; Zhou, Z.R.; Hong, J.; Che, M.X.; Fu, Q.S.; Song, A.X.; Lin, D.H.; Hu, H.Y. Interaction with synphilin-1 promotes inclusion formation of alpha-synuclein: Mechanistic insights and pathological implication. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2010, 24, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, A.W.; Fauvet, B.; Moniatte, M.; Lashuel, H.A. Alpha-synuclein post-translational modifications as potential biomarkers for Parkinson disease and other synucleinopathies. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2013, 12, 3543–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scudamore, O.; Ciossek, T. Increased Oxidative Stress Exacerbates α-Synuclein Aggregation In Vivo. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 77, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.W.; Margolis, R.L.; Li, X.; Troncoso, J.C.; Lee, M.K.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Ross, C.A. Alpha-synuclein phosphorylation enhances eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusion formation in SH-SY5Y cells. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 5544–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmann, B.M.; Gerez, J.A.; Matečko-Burmann, I.; Campioni, S.; Kumari, P.; Ghosh, D.; Mazur, A.; Aspholm, E.E.; Šulskis, D.; Wawrzyniuk, M.; et al. Regulation of α-synuclein by chaperones in mammalian cells. Nature 2020, 577, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shendelman, S.; Jonason, A.; Martinat, C.; Leete, T.; Abeliovich, A. DJ-1 is a redox-dependent molecular chaperone that inhibits alpha-synuclein aggregate formation. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danzer, K.M.; Kranich, L.R.; Ruf, W.P.; Cagsal-Getkin, O.; Winslow, A.R.; Zhu, L.; Vanderburg, C.R.; McLean, P.J. Exosomal cell-to-cell transmission of alpha synuclein oligomers. Mol. Neurodegener. 2012, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, W.; Wisniewski, J.A.; Ji, H. Hot spot-based design of small-molecule inhibitors for protein-protein interactions. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 2546–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arkin, M.R.; Tang, Y.; Wells, J.A. Small-molecule inhibitors of protein-protein interactions: Progressing toward the reality. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1102–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, G.; Rossmann, M.; Hyvönen, M. Alternative modulation of protein-protein interactions by small molecules. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 35, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savolainen, M.H.; Yan, X.; Myöhänen, T.T.; Huttunen, H.J. Prolyl oligopeptidase enhances α-synuclein dimerization via direct protein-protein interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 5117–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Yao, S.; Yang, Z.X.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.T.; Xu, Z.J.; Zhu, W.L.; et al. Pharmacological characterization of the small molecule 03A10 as an inhibitor of α-synuclein aggregation for Parkinson’s disease treatment. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 1122–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rademacher, D.J. Potential for Therapeutic-Loaded Exosomes to Ameliorate the Pathogenic Effects of α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, N.; Strider, J.; Nolan, W.C.; Yan, S.X.; Galvin, J.E. Curcumin inhibits aggregation of alpha-synuclein. Acta Neuropathol. 2008, 115, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, F.K.; Deep, S. Scutellarin inhibits the uninduced and metal-induced aggregation of α-Synuclein and disaggregates preformed fibrils: Implications for Parkinson’s disease. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 645–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-On, P.; Crews, L.; Koob, A.O.; Mizuno, H.; Adame, A.; Spencer, B.; Masliah, E. Statins reduce neuronal α-synuclein aggregation in in vitro models of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2008, 105, 1656–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavassoly, O.; Del Cid Pellitero, E.; Larroquette, F.; Cai, E.; Thomas, R.A.; Soubannier, V.; Luo, W.; Durcan, T.M.; Fon, E.A. Pharmacological Inhibition of Brain EGFR Activation By a BBB-penetrating Inhibitor, AZD3759, Attenuates α-synuclein Pathology in a Mouse Model of α-Synuclein Propagation. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. NeuroTherapeut. 2021, 18, 979–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Han, S.; Dong, Q.; Cui, M.; Tieu, K. Microglial exosomes facilitate α-synuclein transmission in Parkinson’s disease. Brain A J. Neurol. 2020, 143, 1476–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Adams, K.W.; Fan, Z.; McLean, P.J.; Hyman, B.T. Characterization of oligomer formation of amyloid-β peptide using a split-luciferase complementation assay. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 27081–27091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wille, T.; Blank, K.; Schmidt, C.; Vogt, V.; Gerlach, R.G. Gaussia princeps luciferase as a reporter for transcriptional activity, protein secretion, and protein-protein interactions in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karmacharya, M.B.; Hada, B.; Park, S.R.; Choi, B.H. Low-Intensity Ultrasound Decreases α-Synuclein Aggregation via Attenuation of Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species in MPP(+)-Treated PC12 Cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6235–6244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonsalla, P.K.; Zeevalk, G.D.; German, D.C. Chronic intraventricular administration of 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium as a progressive model of Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2008, 14 (Suppl. 2), S116–S118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giráldez-Pérez, R.; Antolín-Vallespín, M.; Muñoz, M.; Sánchez-Capelo, A. Models of α-synuclein aggregation in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, A.; Lee, H.J.; Suk, J.E.; Jung, J.W.; Kim, K.P.; Lee, S.J. Non-classical exocytosis of alpha-synuclein is sensitive to folding states and promoted under stress conditions. J. Neurochem. 2010, 113, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fussi, N.; Höllerhage, M.; Chakroun, T.; Nykänen, N.P.; Rösler, T.W.; Koeglsperger, T.; Wurst, W.; Behrends, C.; Höglinger, G.U. Exosomal secretion of α-synuclein as protective mechanism after upstream blockage of macroautophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, K.; Iwatsubo, T. Extracellular α-synuclein levels are regulated by neuronal activity. Mol. Neurodegener. 2018, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welchman, R.L.; Gordon, C.; Mayer, R.J. Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins as multifunctional signals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotharius, J.; O’Malley, K.L. The parkinsonism-inducing drug 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium triggers intracellular dopamine oxidation. A novel mechanism of toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 38581–38588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.Y.; Jeon, H.; Kim, H.; Koo, S.; Kim, S. Sophora flavescens Aiton Decreases MPP(+)-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in SH-SY5Y Cells. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grünewald, A.; Kumar, K.R.; Sue, C.M. New insights into the complex role of mitochondria in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 177, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Poon, W.S.; Lu, G.; Wang, A.; Meng, H.; Feng, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, S. Alpha-synuclein knockdown attenuates MPP+ induced mitochondrial dysfunction of SH-SY5Y cells. Brain Res. 2009, 1292, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Sun, W.L.; Shen, J.; Wei, M.; Chen, B.; Qi, Y.J.; Xu, C.S. LncRNA-UCA1 promotes PD development by upregulating SNCA. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 7908–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.S.; Gilligan, D.; Pacey, S. Treatment approaches for EGFR-inhibitor-resistant patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e447–e459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.S.; Koppula, S.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, D.K. Analysis of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Related Gene Expression Changes in a Cellular and Animal Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gill, S.S.; Patel, N.K.; Hotton, G.R.; O’Sullivan, K.; McCarter, R.; Bunnage, M.; Brooks, D.J.; Svendsen, C.N.; Heywood, P. Direct brain infusion of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in Parkinson disease. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Xue, L.; Bai, X.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Xie, A. Association between epidermal growth factor receptor gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 736, 135273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, B.; Royzen, M. Recent Development of Prodrugs of Gemcitabine. Genes 2022, 13, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, N.M.; Fernandes, P.A.; Ramos, M.J. Understanding ribonucleotide reductase inactivation by gemcitabine. Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany) 2007, 13, 8507–8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamura, A.; Muraoka-Hirayama, S.; Sakurai, K. Loss of Mitochondrial DNA by Gemcitabine Triggers Mitophagy and Cell Death. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estaun-Panzano, J.; Arotcarena, M.L.; Bezard, E. Monitoring α-synuclein aggregation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 176, 105966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| NGluc-UBL3∆5 | For 5′-TAAACGCGTGGTACCTCTAGAGTCG-3′ |
| Rev 5′-ATTACTCTCTCCAGTCTTCTCACGATTCC-3′ | |
| 3xFlag-UBL3∆5 | For 5′-TAAGAATTCTGCAGATATCCATCACAC-3′ |
| Rev 5′-ATTACTCTCTCCAGTCTTCTCACGATTCC-3′ | |
| XhoI-α-syn-XbaI | For 5′-GCACTCGAGGCCACCATGGATG-3′ |
| Rev 5′-GCCTCTAGATTA GGCTTCAGGTTCGTAGTC-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; Hasan, M.M.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Waliullah, A.S.M.; Ping, Y.; Zhang, C.; Oyama, S.; Mimi, M.A.; Tomochika, Y.; et al. UBL3 Interacts with Alpha-Synuclein in Cells and the Interaction Is Downregulated by the EGFR Pathway Inhibitor Osimertinib. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061685
Chen B, Hasan MM, Zhang H, Zhai Q, Waliullah ASM, Ping Y, Zhang C, Oyama S, Mimi MA, Tomochika Y, et al. UBL3 Interacts with Alpha-Synuclein in Cells and the Interaction Is Downregulated by the EGFR Pathway Inhibitor Osimertinib. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(6):1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061685
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Bin, Md. Mahmudul Hasan, Hengsen Zhang, Qing Zhai, A. S. M. Waliullah, Yashuang Ping, Chi Zhang, Soho Oyama, Mst. Afsana Mimi, Yuna Tomochika, and et al. 2023. "UBL3 Interacts with Alpha-Synuclein in Cells and the Interaction Is Downregulated by the EGFR Pathway Inhibitor Osimertinib" Biomedicines 11, no. 6: 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061685
APA StyleChen, B., Hasan, M. M., Zhang, H., Zhai, Q., Waliullah, A. S. M., Ping, Y., Zhang, C., Oyama, S., Mimi, M. A., Tomochika, Y., Nagashima, Y., Nakamura, T., Kahyo, T., Ogawa, K., Kaneda, D., Yoshida, M., & Setou, M. (2023). UBL3 Interacts with Alpha-Synuclein in Cells and the Interaction Is Downregulated by the EGFR Pathway Inhibitor Osimertinib. Biomedicines, 11(6), 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061685