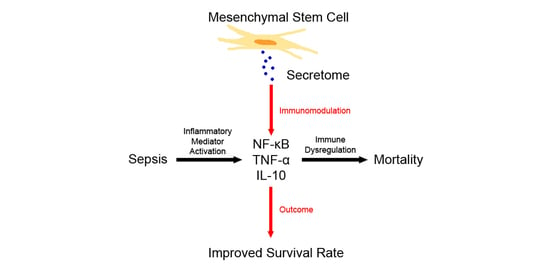
The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome in the Inflammatory Mediators and the Survival Rate of Rat Model of Sepsis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. MSC Isolation, Flow Cytometry and Differentiation Analysis
2.3. Secretome Preparation and Content Analysis
2.4. Examination of Microbial Contamination in Feces
2.5. Sample Size dan Animal Model Procedure
2.6. Survival Rate
2.7. Biomarker Measurement
2.8. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) of Gene Expression
2.9. ELISA of Serum Cytokine Levels
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MSC Characterization and Secretome
3.2. Secretome Content Analysis
3.3. Examination of Microbial Contamination in Feces
3.4. Effect of Secretome on NF-κB
3.5. Effect of Secretome on Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Secretome
3.6. Kaplan-Meier Analysis of Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, L.Y.; Zhou, T.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhou, G.C.; Miao, Z.M.; Shang, M.; He, J.P.; Ding, N.; et al. Duality of Interactions Between TGF-β and TNF-α During Tumor Formation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 810286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussbacher, M.; Salzmann, M.; Brostjan, C.; Hoesel, B.; Schoergenhofer, C.; Datler, H.; Hohensinner, P.; Basílio, J.; Petzelbauer, P.; Assinger, A.; et al. Cell Type-Specific Roles of NF-κB Linking Inflammation and Thrombosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sygitowicz, G.; Sitkiewicz, D. Molecular mechanisms of organ damage in sepsis: An overview. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 24, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadina, M.; Gazaniga, N.; Vian, L.; Furumoto, Y. Small molecules to the rescue: Inhibition of cytokine signaling in immune-mediated diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 85, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-J.; Wang, J.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Kang, J.-Y.; Baek, D.-C.; Kim, G.-H.; Ahn, Y.-C.; Son, C.-G. Ginseng Sprouts Attenuate Mortality and Systemic Inflammation by Modulating TLR4/NF-κB Signaling in an LPS-Induced Mouse Model of Sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhong, Y.; Ali, M.M.; McGuire, F.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M. Role of cytokines as a double-edged sword in sepsis. In Vivo 2013, 27, 669–684. [Google Scholar]
- Georgescu, A.M.; Banescu, C.; Azamfirei, R.; Hutanu, A.; Moldovan, V.; Badea, I.; Voidazan, S.; Dobreanu, M.; Chirtes, I.R.; Azamfirei, L. Evaluation of TNF-α genetic polymorphisms as predictors for sepsis susceptibility and progression. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedeva, C.; Menassa, J.; Puthalakath, H. Sepsis: Inflammation is a necessary evil. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, H.; Ogura, H.; Shimizu, K.; Ikeda, M.; Hirose, T.; Matsuura, H.; Kang, S.; Takahashi, K.; Tanaka, T.; Shimazu, T. The clinical importance of a cytokine network in the acute phase of sepsis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyurkchiev, D.; Bochev, I.; Ivanova-Todorova, E.; Mourdjeva, M.; Oreshkova, T.; Belemezova, K.; Kyurkchiev, S. Secretion of immunoregulatory cytokines by mesenchymal stem cells. World J. Stem Cells 2014, 6, 552–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, W.; Bernhagen, J.; Bucala, R. Cytokines in sepsis: Potent immunoregulators and potential therapeutic targets--an updated view. Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 165974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine Storm. N Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, H.; Chamberlain, T.C.; Mui, A.L.; Little, J.P. Elevated Interleukin-10 Levels in COVID-19: Potentiation of Pro-Inflammatory Responses or Impaired Anti-Inflammatory Action? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 677008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, C.; Scherag, A.; Adhikari, N.K.; Hartog, C.S.; Tsaganos, T.; Schlattmann, P.; Angus, D.C.; Reinhart, K. Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current estimates and limitations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, R.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Phillips, G.; Osborn, T.M.; Townsend, S.; Dellinger, R.P.; Artigas, A.; Schorr, C.; Levy, M.M. Empiric antibiotic treatment reduces mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock from the first hour: Results from a guideline-based performance improvement program. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkhy, H.H.; El-Saed, A.; Alshamrani, M.M.; Alsaedi, A.; Nasser, W.A.; Gammal, A.E.; Aljohany, S.M.; Almunif, S.; Arabi, Y.; Alqahtani, S.; et al. Ten-year resistance trends in pathogens causing healthcare-associated infections; reflection of infection control interventions at a multi-hospital healthcare system in Saudi Arabia, 2007–2016. Antimicrob. Resist Infect. Control 2020, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, L.M.; Nicolau, D.P. Investigational drugs for the treatment of infections caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2018, 27, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Antimicrobial Resistance of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, Hypervirulence-Associated Determinants, and Resistance Mechanisms. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, C.; Cars, O. Antibiotic resistance--problems, progress, and prospects. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1761–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizoso, F.J.; Eiro, N.; Cid, S.; Schneider, J.; Perez-Fernandez, R. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. MedComm 2021, 2, 618–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrawan, S.; Qlintang, S.; Kartika, R.W.; Kurniawati, V.; Lukas, D.V. Severe COVID-19 treatment using hypoxic-mesenchymal stem cell secretome: A case report. In Proceedings of the 1st Tarumanagara International Conference on Medicine and Health (TICMIH 2021), Jakarta, Indonesia, 5–6 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Munoz-Perez, E.; Gonzalez-Pujana, A.; Igartua, M.; Santos-Vizcaino, E.; Hernandez, R.M. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Secretome for the Treatment of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases: Latest Trends in Isolation, Content Optimization and Delivery Avenues. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahandideh, S.; Khatami, S.; Far, A.E.; Kadivar, M. Anti-inflammatory effects of human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells secretome preconditioned with diazoxide, trimetazidine and MG-132 on LPS-induced systemic inflammation mouse model. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Chiu, P.W.Y.; Lam, P.K.; Chin, W.C.; Ng, E.K.W.; Lau, J.Y.W. Secretome from hypoxia-conditioned adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes the healing of gastric mucosal injury in a rodent model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis. Dis. 2018, 1864, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darlan, D.M.; Munir, D.; Jusuf, N.K.; Putra, A.; Ikhsan, R.; Alif, I. In vitro regulation of IL-6 and TGF-ß by mesenchymal stem cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Med. Glas. 2020, 17, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, A.; Widyatmoko, A.; Ibrahim, S.; Amansyah, F.; Amansyah, F.; Berlian, M.A.; Retnaningsih, R.; Pasongka, Z.; Sari, F.E.; Rachmad, B. Case series of the first three severe COVID-19 patients treated with the secretome of hypoxia-mesenchymal stem cells in Indonesia. F1000Research 2021, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, S. The most probable number method and its uses in enumeration, qualification, and validation. J. Valid. Technol. 2010, 16, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Arifin, W.N.; Zahiruddin, W.M. Sample Size Calculation in Animal Studies Using Resource Equation Approach. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 24, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charan, J.; Kantharia, N.D. How to calculate sample size in animal studies? J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2013, 4, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Gong, C.; Fu, J.; Liu, X.; Bi, H.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, D. Evaluation of 2 rat models for sepsis developed by improved cecal ligation/puncture or feces intraperitoneal-injection. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e919054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrum, B.; Anantha, R.V.; Xu, S.X.; Donnelly, M.; Haeryfar, S.M.; McCormick, J.K.; Mele, T. A robust scoring system to evaluate sepsis severity in an animal model. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, C.W.; Kerti, S.J.; Lewis, A.J.; Kennedy, J.; Brant, E.; Griepentrog, J.E.; Zhang, X.; Angus, D.C.; Chang, C.H.; Rosengart, M.R. Murine sepsis phenotypes and differential treatment effects in a randomized trial of prompt antibiotics and fluids. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines for the Use of Animals. Guidelines for the treatment of animals in behavioural research and teaching. Anim. Behav. 2012, 83, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L. Heme oxygenase-1 exerts pro-apoptotic effects on hepatic stellate cells in vitro through regulation of nuclear factor-κB. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Piao, X.; Niu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, C.; Wu, T.; Gu, Q.; Cui, T.; Li, S. Kuijieyuan Decoction Improved Intestinal Barrier Injury of Ulcerative Colitis by Affecting TLR4-Dependent PI3K/AKT/NF-κB Oxidative and Inflammatory Signaling and Gut Microbiota. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, D.C.; van der Poll, T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemura, Y.; Ogura, H.; Takuma, K.; Fujishima, S.; Abe, T.; Kushimoto, S.; Hifumi, T.; Hagiwara, A.; Shiraishi, A.; Otomo, Y.; et al. Japanese Association for Acute Medicine (JAAM) Focused Outcomes Research in Emergency Care in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Sepsis and Trauma (FORECAST) Study Group. Current spectrum of causative pathogens in sepsis: A prospective nationwide cohort study in Japan. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 103, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, T.; Wada, T.; Mizugaki, A.; Oda, Y.; Kayano, K.; Yamakawa, K.; Tanaka, S. Protocol for a Sepsis Model Utilizing Fecal Suspension in Mice: Fecal Suspension Intraperitoneal Injection Model. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 765805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Rodgers, E.; Schoenmann, N.; Raju, R.P. Advances in Rodent Experimental Models of Sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.H.; Han, D.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.W.; Cha, S.M.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Evaluation of the relationship between two different methods for enumeration fecal indicator bacteria: Colony-forming unit and most probable number. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzbacher, M.M.; Sulzbacher, L.M.; Passos, F.R.; Bilibio, B.L.E.; de Oliveira, K.; Althaus, W.F.; Frizzo, M.N.; Ludwig, M.S.; Cruz, I.B.M.D.; Heck, T.G. Adapted Murine Sepsis Score: Improving the Research in Experimental Sepsis Mouse Model. Biomed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5700853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneev, K.V. Mouse Models of Sepsis and Septic Shock. Mol. Biol. 2019, 53, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.J.; Seymour, C.W.; Rosengart, M.R. Current Murine Models of Sepsis. Surg. Infect. 2016, 17, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wan, Q.; Ye, X.; Cheng, Y.; Pathak, J.L.; Li, Z. Cellular hypoxia promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and bone defect healing via STAT3 signaling. Cell. Mol. Biol. Letters. 2019, 24, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, B.; Li, F.; Fang, J.; Xu, L.; Sun, C.; Han, J.; Hua, T.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, X. Hypoxia inducible factor 1α promotes survival of mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxia. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, H.C.; Gamino, V.; Andrusaite, A.T.; Ridgewell, O.J.; McCowan, J.; Shergold, A.L.; Heieis, G.A.; Milling, S.W.F.; Maizels, R.M.; Perona-Wright, G. Tissue-based IL-10 signalling in helminth infection limits IFNγ expression and promotes the intestinal Th2 response. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunna, C.; Mengru, H.; Lei, W.; Weidong, C. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 877, 173090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Jiang, G.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Fang, R.; Bu, X.; Cai, S. TGF-β induces M2-like macrophage polarization via SNAIL-mediated suppression of a pro-inflammatory phenotype. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52294–52306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K. Signaling Cross Talk between TGF-β/Smad and Other Signaling Pathways. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a022137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freudlsperger, C.; Bian, Y.; Wise, S.C.; Burnett, J.; Coupar, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Waes, C.V. TGF-β and NF-κB signal pathway cross-talk is mediated through TAK1 and SMAD7 in a subset of head and neck cancers. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, D.-I.; Lee, A.-H.; Shin, H.-Y.; Song, H.-R.; Park, J.-H.; Kang, T.-B.; Lee, S.-R.; Yang, S.-H. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) in Autoimmune Disease and Current TNF-α Inhibitors in Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senousy, S.R.; Ahmed, A.F.; El-Daly, M.; Khalifa, M.M.A. Cytokines in sepsis: Friend or enemy. J. Adv. Biomed. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 5, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yang, J.; Fang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Candi, E.; Wang, J.; Hua, D.; Shao, C.; Shi, Y. The secretion profile of mesenchymal stem cells and potential applications in treating human diseases. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2022, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Qiu, H.; Xue, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Xie, J. MSC-secreted TGF-β regulates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage M2-like polarization via the Akt/FoxO1 pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, H.N.; Jung, Y.J.; Lee, P.H. Mesenchymal stem cells enhance α-synuclein clearance via M2 microglia polarization in experimental and human parkinsonian disorder. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Mishra, A.K. From Innate Immunity to Inflammation: A Primer on Multiple Facets of NF-κB Signaling in COVID-19. Physiologia 2022, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-N.; Huang, H.-P.; Wang, C.-J.; Liu, K.-L.; Lii, C.-K. Sulforaphane inhibits TNF-α-induced adhesion molecule expression through the Rho A/ROCK/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Med. Food. 2014, 17, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Sun, X.; Chen, J.; Liao, X.; He, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Hu, S.; Qiu, C. microRNA-27b shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes prevents sepsis by targeting JMJD3 and downregulating NF-κB signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorrington, M.G.; Fraser, I. NF-κB Signaling in Macrophages: Dynamics, Crosstalk, and Signal Integration. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyawali, B.; Ramakrishna, K.; Dhamoon, A.S. Sepsis: The evolution in definition, pathophysiology, and management. SAGE Open Med. 2019, 7, 2050312119835043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-J.; Zhao, J.-W.; Zhang, D.-H.; Zheng, A.-H.; Wu, G.-Q. Immunotherapy of Cancer by Targeting Regulatory T cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 104, 108469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Huang, S.-Y.; Sun, J.-H.; Zhang, H.-C.; Cai, Q.-L.; Gao, C.; Li, L.; Cao, J.; Xu, F.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: Mechanisms, diagnosis and current treatment options. Mil. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, I.J.; Sjaastad, F.V.; Griffith, T.S.; Badovinac, V.P. Sepsis-Induced T Cell Immunoparalysis: The Ins and Outs of Impaired T Cell Immunity. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomino, A.; Tsuda, M.; Aoki, R.; Kajita, Y.; Hashiba, M.; Terajima, T.; Kano, H.; Takeyama, N. Increased PD-1 Expression and Altered T Cell Repertoire Diversity Predict Mortality in Patients with Septic Shock: A Preliminary Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, C.B.; Beckmann, N.; Salyer, C.E.; Hanschen, M.; Crisologo, P.A.; Caldwell, C.C. Potential Targets to Mitigate Trauma- or Sepsis-Induced Immune Suppression. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 622601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.T.; Beckmann, N.; Winer, L.K.; Kim, Y.; Goetzman, H.S.; Veile, R.E.; Gulbins, E.; Goodman, M.D.; Nomellini, V.; Caldwell, C.C. Amitriptyline Treatment Mitigates Sepsis-Induced Tumor Necrosis Factor Expression and Coagulopathy. Shock 2019, 51, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-P.; Chu, C.-M.; Liu, P.-H.; Leu, S.-W.; Lin, S.-W.; Hu, H.-C.; Kao, K.-C.; Li, L.-F.; Yu, C.-C. Increased Production of Interleukin-10 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha in Stimulated Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells after Inhibition of S100A12. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yan, B. Research on the effect of cytokine concentration on the immune level and survival conditions of elderly patients with sepsis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, T.H.S.; Britton, G.J.; Hill, E.V.; Verhagen, J.; Burton, B.R.; Wraith, D.C. Regulation of adaptive immunity; the role of interleukin-10. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Molecules | Normoxic MSC Secretome Value ± SE (pg/mL) | Hypoxic MSC Secretome Value ± SE (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| IL-10 | 150.61 ± 15.32 | 269.57 ± 38.39 *** |
| TGF-β | 73.53 ± 7.15 | 138.15 ± 6.12 *** |
| TNF-α | 3.55 ± 0.59 | 4.93 ± 1.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sari, M.I.; Jusuf, N.K.; Munir, D.; Putra, A.; Bisri, T.; Ilyas, S.; Farhat, F.; Muhar, A.M.; Rusda, M.; Amin, M.M. The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome in the Inflammatory Mediators and the Survival Rate of Rat Model of Sepsis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082325
Sari MI, Jusuf NK, Munir D, Putra A, Bisri T, Ilyas S, Farhat F, Muhar AM, Rusda M, Amin MM. The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome in the Inflammatory Mediators and the Survival Rate of Rat Model of Sepsis. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(8):2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082325
Chicago/Turabian StyleSari, Mutiara Indah, Nelva Karmila Jusuf, Delfitri Munir, Agung Putra, Tatang Bisri, Syafruddin Ilyas, Farhat Farhat, Adi Muradi Muhar, Muhammad Rusda, and Mustafa Mahmud Amin. 2023. "The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome in the Inflammatory Mediators and the Survival Rate of Rat Model of Sepsis" Biomedicines 11, no. 8: 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082325
APA StyleSari, M. I., Jusuf, N. K., Munir, D., Putra, A., Bisri, T., Ilyas, S., Farhat, F., Muhar, A. M., Rusda, M., & Amin, M. M. (2023). The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome in the Inflammatory Mediators and the Survival Rate of Rat Model of Sepsis. Biomedicines, 11(8), 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082325