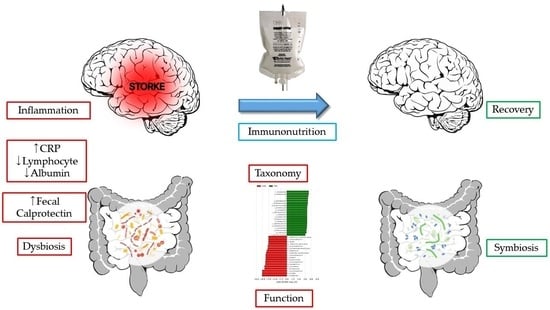
Gut Dysbiosis: A New Avenue for Stroke Prevention and Therapeutics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Demographic Characteristics
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Library Construction and Sequencing
2.5. Sequencing Data Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Alpha Diversity
3.2. Beta Diversity
3.3. Taxonomy Changes
3.4. Biologic Function Changes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jayaraj, R.L.; Azimullah, S.; Beiram, R.; Jalal, F.Y.; Rosenberg, G.A. Neuroinflammation: Friend and foe for ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, A.K.; Hu, B. Brain-gut axis after stroke. Brain Circ. 2018, 4, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrea, L.; Nemeş, S.A.; Szabo, K.; Teleky, B.E.; Vodnar, D.C. Guts Imbalance Imbalances the Brain: A Review of Gut Microbiota Association with Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 813204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanari, M.; Imbriani, P.; Bonsi, P.; Martella, G.; Peppe, A. Beyond the Microbiota: Understanding the Role of the Enteric Nervous System in Parkinson’s Disease from Mice to Human. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovtun, A.S.; Averina, O.V.; Angelova, I.Y.; Yunes, R.A.; Zorkina, Y.A.; Morozova, A.Y.; Pavlichenko, A.V.; Syunyakov, T.S.; Karpenko, O.A.; Kostyuk, G.P.; et al. Alterations of the Composition and Neurometabolic Profile of Human Gut Microbiota in Major Depressive Disorder. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sanmiguel, J.; Schuh, C.M.A.P.; Muñoz-Montesino, C.; Contreras-Kallens, P.; Aguayo, L.G.; Aguayo, S. Complex Interaction between Resident Microbiota and Misfolded Proteins: Role in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Cells 2020, 9, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Su, L.; Zhu, H.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, L.; Qin, C. Gut Microbiota Regulation and Their Implication in the Development of Neurodegenerative Disease. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.A.; Lin, Y.K.; Lai, J.H.; Lo, Y.C.; Yang, Y.S.H.; Ye, S.Y.; Lee, C.J.; Wang, C.C.; Chiang, Y.H.; Tseng, S.H. Maternal Immune Activation Causes Social Behavior Deficits and Hypomyelination in Male Rat Offspring with an Autism-Like Microbiota Profile. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuaish, S.; Al-Otaibi, N.M.; Abujamel, T.S.; Alzahrani, S.A.; Alotaibi, S.M.; AlShawakir, Y.A.; Aabed, K.; El-Ansary, A. Fecal Transplant and Bifidobacterium Treatments Modulate Gut Clostridium Bacteria and Rescue Social Impairment and Hippocampal BDNF Expression in a Rodent Model of Autism. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Editorial of Special Issue “Crosstalk between Depression, Anxiety, and Dementia: Comorbidity in Behavioral Neurology and Neuropsychiatry”. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Exploring the Etiological Links behind Neurodegenerative Diseases: Inflammatory Cytokines and Bioactive Kynurenines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Szabó, Á.; Spekker, E.; Polyák, H.; Tóth, F.; Vécsei, L. Mitochondrial Impairment: A Common Motif in Neuropsychiatric Presentation? The Link to the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic System. Cells 2022, 11, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thayer, J.F.; Sternberg, E.M. Neural aspects of immunomodulation: Focus on the vagus nerve. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwak, M.G.; Chang, S.Y. Gut-Brain Connection: Microbiome, Gut Barrier, and Environmental Sensors. Immun. Netw. 2021, 21, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, T.W. Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Cell 2014, 157, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busnelli, M.; Manzini, S.; Chiesa, G. The Gut Microbiota Affects Host Pathophysiology as an Endocrine Organ: A Focus on Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients 2019, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.A.; Wang, H.X. A Systematic Review of the Interaction Between Gut Microbiota and Host Health from a Symbiotic Perspective. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2019, 1, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, E.C. Nutrition and symbiosis. Nature 1947, 159, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids from Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Lam, S.M.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Niu, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Microbiota Depletion Impairs Thermogenesis of Brown Adipose Tissue and Browning of White Adipose Tissue. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 2720–2737.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Huang, S.; Xu, W.; Chen, L.; Su, J.; Ni, H.; Feng, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, Q. Compound K attenuates hyperglycemia by enhancing glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion through activating TGR5 via the remodeling of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. J. Ginseng. Res. 2022, 46, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Li, H.; Anjum, K.; Zhong, X.; Miao, S.; Zheng, G.; Liu, W.; Li, L. Dual Role of Indoles Derived from Intestinal Microbiota on Human Health. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 903526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L.J.; Esterhazy, D.; Kim, S.H.; Lemetre, C.; Aguilar, R.R.; Gordon, E.A.; Pickard, A.J.; Cross, J.R.; Emiliano, A.B.; Han, S.M.; et al. Commensal bacteria make GPCR ligands that mimic human signalling molecules. Nature 2017, 549, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominique, M.; Lucas, N.; Legrand, R.; Bouleté, I.M.; Bôle-Feysot, C.; Deroissart, C.; Léon, F.; Nobis, S.; do Rego, J.C.; Lambert, G.; et al. Effects of Bacterial CLPB Protein Fragments on Food Intake and PYY Secretion. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, X.; Liotta, A.S.; Shiloach, J.; Gutierrez, J.C.; Wang, H.; Ochani, M.; Ochani, K.; Yang, H.; Rabin, A.; LeRoith, D.; et al. New melanocortin-like peptide of E. coli can suppress inflammation via the mammalian melanocortin-1 receptor (MC1R): Possible endocrine-like function for microbes of the gut. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2017, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Dong, X.; Zou, X. Akkermansia muciniphila as a Next-Generation Probiotic in Modulating Human Metabolic Homeostasis and Disease Progression: A Role Mediated by Gut-Liver-Brain Axes? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, L.M.T. Gut Bacteria and Neurotransmitters. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, C.C.; Skaar, E.P. Nutritional immunity: The battle for nutrient metals at the host-pathogen interface. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukic, A.; Bakiri, L.; Wagner, E.F.; Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E. Calprotectin: From biomarker to biological function. Gut 2021, 70, 1978–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.P.; Kim, W.J. Fecal Calprotectin Is Increased in Stroke. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koszewicz, M.; Jaroch, J.; Brzecka, A.; Ejma, M.; Budrewicz, S.; Mikhaleva, L.M.; Muresanu, C.; Schield, P.; Somasundaram, S.G.; Kirkland, C.E.; et al. Dysbiosis is one of the risk factor for stroke and cognitive impairment and potential target for treatment. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 164, 105277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blekhman, R.; Tang, K.; Archie, E.A.; Barreiro, L.B.; Johnson, Z.P.; Wilson, M.E.; Kohn, J.; Yuan, M.L.; Gesquiere, L.; Grieneisen, L.E.; et al. Common methods for fecal sample storage in field studies yield consistent signatures of individual identity in microbiome sequencing data. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, C.; Kim, W.J.; Moon, J.; Moon, S.Y.; Kim, W.; Hu, H.J.; Min, J. Differences in the gut microbiome composition of Korean children and adult samples based on different DNA isolation kits. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Tsompana, M.; Ruscitto, A.; Sharma, A.; Genco, R.; Sun, Y.; Buck, M.J. An accurate and efficient experimental approach for characterization of the complex oral microbiota. Microbiome 2015, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, W.E.; Dehner, C.; Kim, W.J.; Pagovich, O.; Aguiar, C.L.; Yu, A.T.; Roth, A.S.; Vieira, S.M.; Kriegel, C.; Adeniyi, O.; et al. Pathogenic Autoreactive T and B Cells Cross-React with Mimotopes Expressed by a Common Human Gut Commensal to Trigger Autoimmunity. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 100–113.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, A.L.; Julious, S.A.; Cooper, C.L.; Campbell, M.J. Estimating the sample size for a pilot randomised trial to minimise the overall trial sample size for the external pilot and main trial for a continuous outcome variable. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2016, 25, 1057–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kers, J.G.; Saccenti, E. The Power of Microbiome Studies: Some Considerations on Which Alpha and Beta Metrics to Use and How to Report Results. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 796025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante, A.; García-Berrocoso, T.; Rodriguez, N.; Llombart, V.; Ribó, M.; Molina, C.; Montaner, J. Ischemic stroke outcome: A review of the influence of post-stroke complications within the different scenarios of stroke care. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 29, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajti, J.; Szok, D.; Csáti, A.; Szabó, Á.; Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Exploring Novel Therapeutic Targets in the Common Pathogenic Factors in Migraine and Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, P.M.; Ca, J.; Kandi, V.; Reddy, M.K.; Harikrishna, G.V.; Reddy, K.; Jp, R.; Reddy, A.N.; Narang, J. Connecting the Dots: The Interplay Between Stroke and the Gut-Brain Axis. Cureus 2023, 15, e37324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Y.; Guo, Z.N.; Yang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Jin, H. Gut-brain axis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies for ischemic stroke through immune functions. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1081347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peh, A.; O’Donnell, J.A.; Broughton, B.R.S.; Marques, F.Z. Gut Microbiota and Their Metabolites in Stroke: A Double-Edged Sword. Stroke 2022, 53, 1788–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Liao, S.X.; He, Y.; Wang, S.; Xia, G.H.; Liu, F.T.; Zhu, J.J.; You, C.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, L.; et al. Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota with Reduced Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Level in Patients with Large-Artery Atherosclerotic Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haak, B.W.; Westendorp, W.F.; van Engelen, T.S.R.; Brands, X.; Brouwer, M.C.; Vermeij, J.D.; Hugenholtz, F.; Verhoeven, A.; Derks, R.J.; Giera, M.; et al. Disruptions of Anaerobic Gut Bacteria Are Associated with Stroke and Post-stroke Infection: A Prospective Case-Control Study. Transl. Stroke Res. 2021, 12, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Gu, M.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Acute Ischemic Stroke Associated With 3-Month Unfavorable Outcome. Front. Neurol. 2022, 12, 799222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nergiz, S.; Ozturk, U. The Effect of Prognostic Nutritional Index on Infection in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. Medicina 2023, 59, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuz, A.A.; Hasenberg, A.; Hermann, D.M.; Gunzer, M.; Singh, V. Ischemic stroke and concomitant gastrointestinal complications- a fatal combination for patient recovery. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1037330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, Y.J. Vitamin A: A key coordinator of host-microbe interactions in the intestine. BMB Rep. 2023, 56, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyák, H.; Galla, Z.; Nánási, N.; Cseh, E.K.; Rajda, C.; Veres, G.; Spekker, E.; Szabó, Á.; Klivényi, P.; Tanaka, M.; et al. The Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic System Is Suppressed in Cuprizone-Induced Model of Demyelination Simulating Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashige, T.G.; Zygielk, E.M.; Drennan, C.L.; Nolan, E.M. Nickel Sequestration by the Host-Defense Protein Human Calprotectin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8828–8836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Li, S.; Dong, Q.; Hu, W. Impact of Early High-protein Diet on Neurofunctional Recovery in Rats with Ischemic Stroke. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 2235–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.O.; Park, H.; Chun, M.; Kim, H.S. Immunomodulatory effects of high-protein diet with resveratrol supplementation on radiation-induced acute-phase inflammation in rats. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, R.; Smoliner, C.; Jäger, M.; Warnecke, T.; Leischker, A.H.; Dziewas, R.; DGEM Steering Committee. Guideline clinical nutrition in patients with stroke. Exp. Transl. Stroke Med. 2013, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Immunonutrition. BMJ 2003, 327, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, O.; Barbul, A. Immunonutrition: Role in Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martí, I.; Líndez, A.A.; Reith, W. Arginine-dependent immune responses. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 5303–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Jeon, S.M.; Silwal, P.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, C.R.; Chung, C.; Han, J.E.; et al. Arginine-mediated gut microbiome remodeling promotes host pulmonary immune defense against nontuberculous mycobacterial infection. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2073132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.F.; Pan, M.X.; Tang, J.C.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, H.B.; Liu, R.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, Z.F.; et al. Arginine is neuroprotective through suppressing HIF-1α/LDHA-mediated inflammatory response after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol. Brain 2020, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newsholme, P. Why is L-glutamine metabolism important to cells of the immune system in health, postinjury, surgery or infection? J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2515S–2522S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.L.; Li, Y.F.; Shan, H.M.; Wang, L.P.; Yuan, F.; Ma, Y.Y.; Li, W.L.; He, T.T.; Wang, Y.Y.; Qu, M.J.; et al. L-glutamine protects mouse brain from ischemic injury via up-regulating heat shock protein 70. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 1030–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, S.; Alalwan, T.A.; Alaali, Z.; Alnashaba, T.; Gasparri, C.; Infantino, V.; Hammad, L.; Riva, A.; Petrangolini, G.; Allegrini, P.; et al. The Role of Glutamine in the Complex Interaction between Gut Microbiota and Health: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, S.; Svahn, S.L.; Johansson, M.E. Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Immune Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Hu, X.; Zhang, W.; Leak, R.K.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, J. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids enhance cerebral angiogenesis and provide long-term protection after stroke. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 68, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menni, C.; Zierer, J.; Pallister, T.; Jackson, M.A.; Long, T.; Mohney, R.P.; Steves, C.J.; Spector, T.D.; Valdes, A.M. Omega-3 fatty acids correlate with gut microbiome diversity and production of N-carbamylglutamate in middle aged and elderly women. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polcz, M.E.; Barbul, A. The Role of Vitamin A in Wound Healing. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2019, 34, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadri, A.; Sjahrir, H.; Juwita Sembiring, R.; Ichwan, M. Combination of vitamin A and D supplementation for ischemic stroke: Effects on interleukin-1ß and clinical outcome. Med. Glas. 2020, 17, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Xiong, X.Q.; Yang, T.; Cui, T.; Hou, N.L.; Lai, X.; Liu, S.; Guo, M.; Liang, X.H.; et al. Effect of vitamin A supplementation on gut microbiota in children with autism spectrum disorders—A pilot study. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elste, V.; Troesch, B.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Weber, P. Emerging Evidence on Neutrophil Motility Supporting Its Usefulness to Define Vitamin C Intake Requirements. Nutrients 2017, 9, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazan, S.; Dave, S.; Papoutsis, A.J.; Deshpande, N.; Howell, M.C., Jr.; Martin, L.M. Vitamin C improves gut Bifidobacteria in humans. Future Microbiol. 2022; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris-Blanco, K.C.; Chokkalla, A.K.; Kim, T.; Bhatula, S.; Bertogliat, M.J.; Gaillard, A.B.; Vemuganti, R. High-Dose Vitamin C Prevents Secondary Brain Damage After Stroke via Epigenetic Reprogramming of Neuroprotective Genes. Transl. Stroke Res. 2022, 13, 1017–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.H.; Sermersheim, M.; Li, H.; Lee, P.H.U.; Steinberg, S.M.; Ma, J. Zinc in Wound Healing Modulation. Nutrients 2017, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, L.; Wang, P.; Liang, J. Zinc improves neurological recovery by promoting angiogenesis via the astrocyte-mediated HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway in experimental stroke. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 1790–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.M.; Pinna, C.; Biagi, G.; Stefanelli, C.; Maia, M.R.G.; Matos, E.; Segundo, M.A.; Fonseca, A.J.M.; Cabrita, A.R.J. Supplemental selenium source on gut health: Insights on fecal microbiome and fermentation products of growing puppies. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Simani, L.; Abedi, S.; Pakdaman, H. Is Selenium Supplementation Beneficial in Acute Ischemic Stroke? Neurologist 2021, 27, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| CON (n = 26) | STR (n = 25) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 58.6 ± 14.1 | 60.8 ± 15.2 | 0.579 |
| Sex (M/F) | 16/10 | 14/11 | 0.663 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.4 ± 3.5 | 23.7 ± 3.4 | 0.808 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| DM (number) | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| Hypertension (number) | 8 | 13 | 0.159 |
| CAD (number) | 0 | 2 | 0.235 |
| Medication | |||
| PPI (number) | 0 | 0 | NA |
| NSAID (number) | 0 | 0 | NA |
| ABX (number) | 0 | 25 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.P.; Kim, D.; Kim, W.J. Gut Dysbiosis: A New Avenue for Stroke Prevention and Therapeutics. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11092352
Park SY, Lee SP, Kim D, Kim WJ. Gut Dysbiosis: A New Avenue for Stroke Prevention and Therapeutics. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(9):2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11092352
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Shin Young, Sang Pyung Lee, Dongin Kim, and Woo Jin Kim. 2023. "Gut Dysbiosis: A New Avenue for Stroke Prevention and Therapeutics" Biomedicines 11, no. 9: 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11092352
APA StylePark, S. Y., Lee, S. P., Kim, D., & Kim, W. J. (2023). Gut Dysbiosis: A New Avenue for Stroke Prevention and Therapeutics. Biomedicines, 11(9), 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11092352