Audiogenic Seizures and Social Deficits: No Aggravation Found in Krushinsky–Molodkina Rats
Abstract
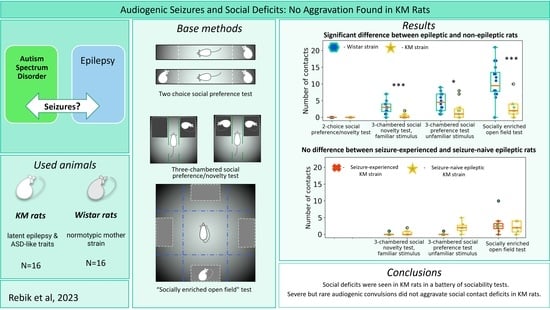
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Elevated Plus Maze
2.3. Sociability Tests
2.3.1. The Two-Choice Test for Social Preference
2.3.2. Socially Enriched Open Field Test
2.3.3. Three-Chambered Social Preference/Social Novelty Test
2.4. Social Dominance Test
2.5. Two-Object Novel Object Recognition
2.6. AGS Provocation
2.7. Automated Tracking
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Elevated Plus Maze
3.2. Different Paradigms of “Social Preference/Social Novelty” Tests
3.2.1. Two Choice Social Preference Test
3.2.2. The “Socially Enriched Open Field Test”
3.2.3. The Social Preference/Social Novelty Test
3.3. Effect of Seizures’ Experience
3.4. Effect of Repetitive Testing
3.5. Two Object Novel Object Recognition Test
3.6. Social Dominance “Tube” Test
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Sun, C.; Zou, M.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Wu, L.; Chen, W.-X. Prevalence of Epilepsy in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Autism 2022, 26, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besag, F. Epilepsy in Patients with Autism: Links, Risks and Treatment Challenges. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadow, K.D.; Perlman, G.; Weber, R.J. Parent-Reported Developmental Regression in Autism: Epilepsy, IQ, Schizophrenia Spectrum Symptoms, and Special Education. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahra, A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, J. Shared Etiology in Autism Spectrum Disorder and Epilepsy with Functional Disability. Behav. Neurol. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks-Kayal, A. Epilepsy and autism spectrum disorders: Are there common developmental mechanisms? Brain Dev. 2010, 32, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Arregui TLlorente, J.; Giménez Minguez, P.; Tønnesen, J.; Peñagarikano, O. Neurobiological Mechanisms of Autism Spectrum Disorder and Epilepsy, Insights from Animal Models//Neuroscience. Pergamon 2020, 445, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; Przewłocki, R. Behavioral alterations in rats prenatally exposed to valproic acid: Animal model of autism. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilby, K.L. A new rat model for vulnerability to epilepsy and autism spectrum disorders. Epilepsia 2008, 49, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Seo, J.S.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, D.; Jung, K.H.; Chu, K.; Lee, S.K.; Jeon, D. Social deficits in the AY-9944 mouse model of atypical absence epilepsy. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 236, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, Z.; Mei, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Hu, S.; Luo, S.; Wang, Q.; Gao, C. The GluN2B-Trp373 NMDA Receptor Variant is Associated with Autism-, Epilepsy-Related Phenotypes and Reduces NMDA Receptor Currents in Rats. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergnes, M.; Marescaux, C.; Boehrer, A.; Depaulis, A. Are rats with genetic absence epilepsy behaviorally impaired? Epilepsy Res. 1991, 9, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkisova, K.Y.; Midzianovskaia, I.S.; Kulikov, M.A. Depressive-like behavioral alterations and c-fos expression in the dopaminergic brain regions in WAG/Rij rats with genetic absence epilepsy. Behav. Brain Res. 2003, 144, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leo, A.; Citraro, R.; Tallarico, M.; Iannone, M.; Fedosova, E.; Nesci, V.; De Sarro, G.; Sarkisova, K.; Russo, E. Cognitive impairment in the WAG/Rij rat absence model is secondary to absence seizures and depressive-like behavior. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 94, 109652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Umeoka, E.H.L.; Cortes de Oliveira, J.A. The Wistar Audiogenic Rat (WAR) Strain and Its Contributions to Epileptology and Related Comorbidities: History and Perspectives. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 71, 250–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, J.; Kumar, U.; Medel-Matus, J.-S.; Shin, D.; Sankar, R.; Mazarati, A. Cytokine-Dependent Bidirectional Connection between Impaired Social Behavior and Susceptibility to Seizures Associated with Maternal Immune Activation in Mice. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 50, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, T.; Veenstra-VanderWeele, J.; Hollander, E.; Kishi, T. Antiepileptic medications in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2014, 44, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebik, A.A.; Riga, V.D.; Smirnov, K.S.; Sysoeva, O.V.; Midzyanovskaya, I.S. Social Behavioral Deficits in Krushinsky-Molodkina Rats, an Animal Model of Audiogenic Epilepsy. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiokhina, A.F.; Rat’kin, A.E.; Fedotova, I.B.; Kuznetsova, L.M.; Kostyna, Z.A.; Sotskaia, M.N.; Chebykina, L.I. A model of audiogenic epilepsy--rats of the Krushinskiĭ-Molodkina strain. Proof of genetic homogeneity. Zhurnal Vyss. Nervn. Deiatelnosti Im. IP Pavlova. 1996, 46, 592–596. [Google Scholar]
- Poletaeva, I.I.; Surina, N.M.; Kostina, Z.A.; Perepelkina, O.V.; Fedotova, I.B. The Krushinsky-Molodkina rat strain: The study of audiogenic epilepsy for 65years. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 71, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbachova, E.L.; Chernigovskaya, E.V.; Glazova, M.V.; Nikitina, L.S. Audiogenic Kindling Activates Expression of Vasopressin in the Hypothalamus of Krushinsky-Molodkina Rats Genetically Prone to Reflex Epilepsy. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2022, 32, e12846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsyba, E.T.; Midzyanovskaya, I.S.; Birioukova, L.M.; Tuomisto, L.M.; van Luijtelaar, G.; Abbasova, K.R. Striatal patchwork of D1-like and D2-like receptors binding densities in rats with genetic audiogenic and absence epilepsies. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surina, N.M.; Fedotova, I.B.; Nikolaev, G.M.; Grechenko, V.V.; Gankovskaya, L.V.; Ogurtsova, A.D.; Poletaeva, I.I. Neuroinflammation in Pathogenesis of Audiogenic Epilepsy: Altered Proinflammatory Cytokine Levels in the Rats of Krushinsky–Molodkina Seizure-Prone Strain. Biochemistry 2023, 88, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvinova, S.A.; Voronina, T.A.; Kudrin, V.S.; Narkevich, V.B.; Surina, N.M.; Poletaeva, I.I.; Fedotova, I.B. The Role of Brain Monoamines in the Formation of Audiogenic Myoclonic Seizures in Krushinsky–Molodkina Rats. Neurochem. J. 2023, 17, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acikgoz, B.; Dalkiran, B.; Dayi, A. An overview of the currency and usefulness of behavioral tests used from past to present to assess anxiety, social behavior and depression in rats and mice. Behav. Process. 2022, 200, 104670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, K.; Fahnestock, M.; Racine, R.J. Kindling and Status Epilepticus Models of Epilepsy: Rewiring the Brain. Prog. Neurobiol. 2004, 73, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, R.; Young, B. Neuroplasticity in Specific Limbic System Circuits May Mediate Specific Kindling Induced Changes in Animal Affect—Implications for Understanding Anxiety Associated with Epilepsy. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 705–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, A.A.; Naumova, A.A.; Dorofeeva, N.A.; Ivlev, A.P.; Glazova, M.V.; Chernigovskaya, E.V. Dynamics of Neurodegeneration in the Hippocampus of Krushinsky-Molodkina Rats Correlates with the Progression of Limbic Seizures. Epilepsy Behav. 2022, 134, 108846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentim-Lima, E.; Oliveira, J.A.C.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Reis, L.C.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Mecawi, A.S. Neuroendocrine Changes in the Hypothalamic-neurohypophysial System in the Wistar Audiogenic Rat (WAR) Strain Submitted to Audiogenic Kindling. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2021, 33, e12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabarin, R.; Netser, S.; Wagner, S. Beyond the Three-Chamber Test: Toward a Multimodal and Objective Assessment of Social Behavior in Rodents. Mol. Autism. 2022, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winslow, J.T. Mouse Social Recognition and Preference. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2003, 22, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, N.; Makinodan, M.; Somayama, N.; Komori, T.; Kishimoto, T.; Nishi, M. Characterization of Behavioral Phenotypes in the BTBR T+ Itpr3tf/J Mouse Model of Autism Spectrum Disorder under Social Housing Conditions Using the Multiple Animal Positioning System. Exp. Anim. 2019, 68, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyokawa, Y.; Kuroda, N.; Takeuchi, Y. The Strain of Unfamiliar Conspecifics Affects Stress Identification in Rats. Behav. Process. 2022, 201, 104714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, M.; Liu, Y.; Xie, S.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Li, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, W.; Sun, C.; et al. Alterations of the endocannabinoid system and its therapeutic potential in autism spectrum disorder. Open Biol. 2021, 11, 200306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netser, S.; Meyer, A.; Magalnik, H.; Zylbertal, A.; de la Zerda, S.H.; Briller, M.; Bizer, A.; Grinevich, V.; Wagner, S. Distinct dynamics of social motivation drive differential social behavior in laboratory rat and mouse strains. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, G.P.; de Castro Medeiros, D.; de Oliveira Guarnieri, L.; Mourão FA, G.; Pinto HP, P.; Pereira, G.S.; Moraes, M.F.D. Wistar audiogenic rats display abnormal behavioral traits associated with artificial selection for seizure susceptibility. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 71, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Janke, E.; Bhattarai, J.P.; Wesson, D.W.; Ma, M. Self-Directed Orofacial Grooming Promotes Social Attraction in Mice via Chemosensory Communication. iScience 2022, 25, 104284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang-James, Y.; Yang, L.; Middleton, F.A.; Yang, L.; Patak, J.; Faraone, S.V. Autism-Related Behavioral Phenotypes in an Inbred Rat Substrain. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 269, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirenova, S.D.; Khlebnikova, N.N.; Krupina, N.A. Changes in Sociability and Preference for Social Novelty in Female Rats in Prolonged Social Isolation. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2023, 53, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummer, K.; Klement, S.; Eggart, V.; Mayr, M.J.; Saria, A.; Zernig, G. Conditioned place preference for social interaction in rats: Contribution of sensory components. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöhr, M.; Schwarting, R.K. Ultrasonic communication in rats: Can playback of 50-kHz calls induce approach behavior? PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, A.; McGlone, F. Editorial overview: Affective touch: Neurobiology and function. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2022, 45, 101129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haratizadeh, S.; Parvan, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Shabani, M.; Nozari, M. An overview of modeling and behavioral assessment of autism in the rodent. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2021, 81, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korte, S.M.; De Boer, S.F. A robust animal model of state anxiety: Fear-potentiated behaviour in the elevated plus-maze. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 463, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beery, A.K.; Shambaugh, K.L. Comparative assessment of familiarity/novelty preferences in rodents. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 648830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.Y.; Hu, Z.L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Huang, F.L.; Qiao, X.Q.; Cui, Y.H.; Wan, W.; Wang, X.Q.; Liu, D.; et al. Role of early environmental enrichment on the social dominance tube test at adulthood in the rat. Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 3321–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, T.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Hu, H. Using the tube test to measure social hierarchy in mice. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennaceur, A.; Michalikova, S.; Chazot, P.L. Do rats really express neophobia towards novel objects? Experimental evidence from exposure to novelty and to an object recognition task in an open space and an enclosed space. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 197, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, G.D. Audiogenic seizures in rats of different genetic strains. Zhurn. Vissh. Nervn. Dejat. 1998, 48, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Midzyanovskaya, I.S.; Kuznetsova, G.D.; Vinogradova, L.V.; Shatskova, A.B.; Coenen, A.M.; van Luijtelaar, G. Mixed forms of epilepsy in a subpopulation of WAG/Rij rats. Epilepsy Behav. 2004, 5, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, L.V.; Kuznetsova, G.D.; Coenen, A.M.L. Audiogenic seizures associated with a cortical spreading depression wave suppress spike-wave discharges in rats. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 86, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, L.V. Audiogenic kindling and secondary subcortico-cortical epileptogenesis: Behavioral correlates and electrographic features. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 71, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobe, P.C.; Picchioni, A.L.; Chin, L. Role of brain norepinephrine in audiogenic seizures in the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1973, 184, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, A.; Zhang, H.; Klaminder, J.; Brodin, T.; Andersson, P.L.; Andersson, M. ToxTrac: A fast and robust software for tracking organisms. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkisova, K.Y.; Fedotova, I.B.; Surina, N.M.; Nikolaev, G.M.; Perepelkina, O.V.; Kostina, Z.A.; Poletaeva, I.I. Genetic background contributes to the co-morbidity of anxiety and depression with audiogenic seizure propensity and responses to fluoxetine treatment. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 68, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergaz, Z.; Weinstein-Fudim, L.; Ornoy, A. Genetic and non-genetic animal models for autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Reprod. Toxicol. 2016, 64, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilby, K.L.; O’Brien, T.J. Epilepsy, autism, and neurodevelopment: Kindling a shared vulnerability? Epilepsy Behav. 2013, 26, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Shimada, S. Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumper, S.K.; Ahle, G.M.; Liebman, L.S.; Kellner, C.H. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) in Parkinson’s disease: ECS and dopamine enhancement. J. ECT 2014, 30, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikisch, G.; Mathé, A.A. CSF monoamine metabolites and neuropeptides in depressed patients before and after electroconvulsive therapy. Eur. Psychiatry 2008, 23, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saijo, T.; Takano, A.; Suhara, T.; Arakawa, R.; Okumura, M.; Ichimiya, T.; Ito, H.; Okubo, Y. Effect of electroconvulsive therapy on 5-HT1A receptor binding in patients with depression: A PET study with [11C]WAY 100635. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 13, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, S.; Terao, T.; Hoaki, N.; Wang, Y.; Tsuchiyama, K.; Araki, Y.; Kohno, K. Is serotonergic function associated with the antidepressant effects of modified-electroconvulsive therapy? J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 136, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swartz, C.M. A mechanism of seizure induction by electricity and its clinical implications. J. ECT 2014, 30, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njau, S.; Joshi, S.H.; Espinoza, R.; Leaver, A.M.; Vasavada, M.; Marquina, A.; Woods, R.P.; Narr, K.L. Neurochemical correlates of rapid treatment response to electroconvulsive therapy in patients with major depression. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2017, 42, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, E.; Myers, H.; Saxena, K.; Mitchell-Heggs, R.; Kind, P.; Chattarji, S.; Morris, R.G.M. Experiential modulation of social dominance in a SYNGAP1 rat model of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 54, 7733–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werling, D.M.; Geschwind, D.H. Sex differences in autism spectrum disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, M.; El Rawas, R.; Salti, A.; Klement, S.; Bardo, M.T.; Kemmler, G.; Zernig, G. Reversal of cocaine-conditioned place preference and mesocorticolimbic Zif268 expression by social interaction in rats. Addict. Biol. 2011, 16, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posserud, M.; Hysing, M.; Helland, W.; Gillberg, C.; Lundervold, A.J. Autism traits: The importance of “co-morbid” problems for impairment and contact with services. Data from the Bergen Child Study. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2018, 72, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rebik, A.; Broshevitskaya, N.; Kuzhuget, S.; Aleksandrov, P.; Abbasova, K.; Zaichenko, M.; Midzyanovskaya, I. Audiogenic Seizures and Social Deficits: No Aggravation Found in Krushinsky–Molodkina Rats. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11092566
Rebik A, Broshevitskaya N, Kuzhuget S, Aleksandrov P, Abbasova K, Zaichenko M, Midzyanovskaya I. Audiogenic Seizures and Social Deficits: No Aggravation Found in Krushinsky–Molodkina Rats. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(9):2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11092566
Chicago/Turabian StyleRebik, Anastasiya, Nadezda Broshevitskaya, Syldys Kuzhuget, Pavel Aleksandrov, Kenul Abbasova, Maria Zaichenko, and Inna Midzyanovskaya. 2023. "Audiogenic Seizures and Social Deficits: No Aggravation Found in Krushinsky–Molodkina Rats" Biomedicines 11, no. 9: 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11092566
APA StyleRebik, A., Broshevitskaya, N., Kuzhuget, S., Aleksandrov, P., Abbasova, K., Zaichenko, M., & Midzyanovskaya, I. (2023). Audiogenic Seizures and Social Deficits: No Aggravation Found in Krushinsky–Molodkina Rats. Biomedicines, 11(9), 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11092566