The Interplay of Adipokines and Pancreatic Beta Cells in Metabolic Regulation and Diabetes
Abstract
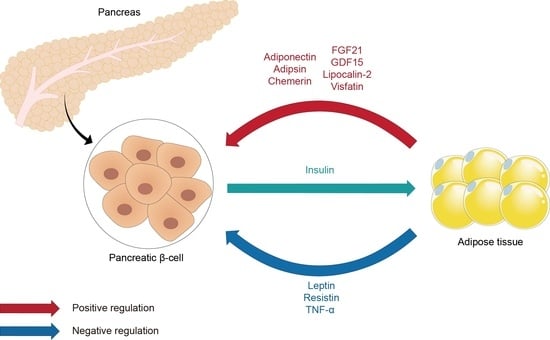
:1. Introduction
2. Beta Cell and Diabetes
2.1. Diabetes and Diabetes-Related Complications
2.2. Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion (GSIS)
2.3. Beta Cell Compensation and Development of Type 2 Diabetes
3. Leptin
4. Adiponectin
5. Apelin
6. Resistin
7. Visfatin
8. Other Adipokines
8.1. Adipsin
8.2. Lipocalin-2
8.3. Chemerin
8.4. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21)
8.5. Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF15)
8.6. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α)
9. Conclusions
10. Methodology
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taylor, E.B. The complex role of adipokines in obesity, inflammation, and autoimmunity. Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 731–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas Lima, L.C.; Braga, V.A.; do Socorro de Franca Silva, M.; Cruz, J.C.; Sousa Santos, S.H.; de Oliveira Monteiro, M.M.; Balarini, C.M. Adipokines, diabetes and atherosclerosis: An inflammatory association. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roep, B.O.; Thomaidou, S.; van Tienhoven, R.; Zaldumbide, A. Type 1 diabetes mellitus as a disease of the beta-cell (do not blame the immune system?). Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudish, L.I.; Reusch, J.E.; Sussel, L. beta Cell dysfunction during progression of metabolic syndrome to type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4001–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, T.J.; Habener, J.F. The adipoinsular axis: Effects of leptin on pancreatic beta-cells. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 278, E1–E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Magkos, F.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Kang, E.S. Effects of leptin and adiponectin on pancreatic beta-cell function. Metabolism 2011, 60, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, V.A.; Malide, D.; Zarnowski, M.J.; Taylor, S.I.; Cushman, S.W. Insulin stimulates both leptin secretion and production by rat white adipose tissue. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 4463–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.; Asakawa, A.; Amitani, H.; Inui, A. Stimulation of leptin secretion by insulin. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, S543–S548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.K.; Bae, K.H.; Lee, S.C.; Oh, K.J. The Latest Insights into Adipokines in Diabetes. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46 (Suppl. 1), S19–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaborators, G.B.D.D. Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2023, 402, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentki, M.; Matschinsky, F.M.; Madiraju, S.R. Metabolic signaling in fuel-induced insulin secretion. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 162–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.E.; Newgard, C.B. Mechanisms controlling pancreatic islet cell function in insulin secretion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, F.M.; Lloyd, M.; Haythorne, E.A. Glucokinase activity in diabetes: Too much of a good thing? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 34, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, K.; James, C.; Hussain, K. Pancreatic beta-cell KATP channels: Hypoglycaemia and hyperglycaemia. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2010, 11, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentki, M.; Nolan, C.J. Islet beta cell failure in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1802–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cohrs, C.M.; Stertmann, J.; Bozsak, R.; Speier, S. Human beta cell mass and function in diabetes: Recent advances in knowledge and technologies to understand disease pathogenesis. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysham, C.; Shubrook, J. Beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes: Mechanisms, markers, and clinical implications. Postgrad. Med. 2020, 132, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, G.C.; Gaglia, J.; Bonner-Weir, S. Inadequate beta-cell mass is essential for the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorena, K.; Jachimowicz-Duda, O.; Slezak, D.; Robakowska, M.; Mrugacz, M. Adipokines and Obesity. Potential Link to Metabolic Disorders and Chronic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recinella, L.; Orlando, G.; Ferrante, C.; Chiavaroli, A.; Brunetti, L.; Leone, S. Adipokines: New Potential Therapeutic Target for Obesity and Metabolic, Rheumatic, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 578966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppari, R.; Ichinose, M.; Lee, C.E.; Pullen, A.E.; Kenny, C.D.; McGovern, R.A.; Tang, V.; Liu, S.M.; Ludwig, T.; Chua, S.C., Jr.; et al. The hypothalamic arcuate nucleus: A key site for mediating leptin’s effects on glucose homeostasis and locomotor activity. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, L.; Kellerer, M.; Capp, E.; Haring, H.U. Leptin stimulates glucose transport and glycogen synthesis in C2C12 myotubes: Evidence for a P13-kinase mediated effect. Diabetologia 1997, 40, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceddia, R.B.; Lopes, G.; Souza, H.M.; Borba-Murad, G.R.; William, W.N., Jr.; Bazotte, R.B.; Curi, R. Acute effects of leptin on glucose metabolism of in situ rat perfused livers and isolated hepatocytes. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1999, 23, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.; Fernandez-Galaz, C.; Fernandez-Agullo, T.; Arribas, C.; Andres, A.; Ros, M.; Carrascosa, J.M. Leptin impairs insulin signaling in rat adipocytes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorbaek, C.; Uotani, S.; da Silva, B.; Flier, J.S. Divergent signaling capacities of the long and short isoforms of the leptin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 32686–32695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, T.J.; Heller, R.S.; Habener, J.F. Leptin receptors expressed on pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 224, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emilsson, V.; Liu, Y.L.; Cawthorne, M.A.; Morton, N.M.; Davenport, M. Expression of the functional leptin receptor mRNA in pancreatic islets and direct inhibitory action of leptin on insulin secretion. Diabetes 1997, 46, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitout, V.; Rouault, C.; Guerre-Millo, M.; Briaud, I.; Reach, G. Inhibition of insulin secretion by leptin in normal rodent islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, R.N.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, R.M.; Hurley, J.D.; Smith, D.M.; Ghatei, M.A.; Withers, D.J.; Gardiner, J.V.; Bailey, C.J.; Bloom, S.R. Leptin rapidly suppresses insulin release from insulinoma cells, rat and human islets and, in vivo, in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruhbeck, G. Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin. Biochem. J. 2006, 393, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieffer, T.J.; Heller, R.S.; Leech, C.A.; Holz, G.G.; Habener, J.F. Leptin suppression of insulin secretion by the activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 1997, 46, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seufert, J.; Kieffer, T.J.; Leech, C.A.; Holz, G.G.; Moritz, W.; Ricordi, C.; Habener, J.F. Leptin suppression of insulin secretion and gene expression in human pancreatic islets: Implications for the development of adipogenic diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.E.; Thomas, S.; Digby, J.E.; Dunmore, S.J. Glucose induces and leptin decreases expression of uncoupling protein-2 mRNA in human islets. FEBS Lett. 2002, 513, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Ryu, S.Y.; Yu, W.J.; Han, Y.E.; Ji, Y.S.; Oh, K.; Sohn, J.W.; Lim, A.; Jeon, J.P.; Lee, H.; et al. Leptin promotes K(ATP) channel trafficking by AMPK signaling in pancreatic beta-cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12673–12678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Kryukova, Y.N.; Shyng, S.L. Leptin regulates KATP channel trafficking in pancreatic beta-cells by a signaling mechanism involving AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 34098–34109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, V.A.; Yang, Z.; Dell’Acqua, M.L.; Shyng, S.L. AKAP79/150 coordinates leptin-induced PKA signaling to regulate K(ATP) channel trafficking in pancreatic beta-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.; Hardy, S.C.; Irving, A.J.; Ashford, M.L. Leptin activation of ATP-sensitive K+ (KATP) channels in rat CRI-G1 insulinoma cells involves disruption of the actin cytoskeleton. J. Physiol. 2000, 527 Pt 1, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Ho, W.K.; Jeon, J.H. AMPK regulates K(ATP) channel trafficking via PTEN inhibition in leptin-treated pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 440, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane, V.A.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; ElSheikh, A.; Dunford, J.; Kievit, P.; Fortin, D.A.; Shyng, S.L. Leptin modulates pancreatic beta-cell membrane potential through Src kinase-mediated phosphorylation of NMDA receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 17281–17297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehnen, P.; Laubner, K.; Raile, K.; Schofl, C.; Jakob, F.; Pilz, I.; Path, G.; Seufert, J. Protein phosphatase 1 (PP-1)-dependent inhibition of insulin secretion by leptin in INS-1 pancreatic beta-cells and human pancreatic islets. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 1800–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, E.; Marroqui, L.; Batista, T.M.; Caballero-Garrido, E.; Carneiro, E.M.; Boschero, A.C.; Nadal, A.; Quesada, I. The clock gene Rev-erbalpha regulates pancreatic beta-cell function: Modulation by leptin and high-fat diet. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Fu, R.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y.S.; Pan, J.R.; Liu, J.L.; Luo, H.S.; Yin, J.D.; Li, D.F.; Cui, S. LIM-homeodomain transcription factor Isl-1 mediates the effect of leptin on insulin secretion in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 12395–12405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimabukuro, M.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhou, Y.T.; Newgard, C.B.; Unger, R.H. Protection against lipoapoptosis of beta cells through leptin-dependent maintenance of Bcl-2 expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9558–9561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.E.; Dunmore, S.J. Leptin decreases apoptosis and alters BCL-2: Bax ratio in clonal rodent pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2007, 23, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maedler, K.; Schulthess, F.T.; Bielman, C.; Berney, T.; Bonny, C.; Prentki, M.; Donath, M.Y.; Roduit, R. Glucose and leptin induce apoptosis in human beta-cells and impair glucose-stimulated insulin secretion through activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinases. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maedler, K.; Sergeev, P.; Ehses, J.A.; Mathe, Z.; Bosco, D.; Berney, T.; Dayer, J.M.; Reinecke, M.; Halban, P.A.; Donath, M.Y. Leptin modulates beta cell expression of IL-1 receptor antagonist and release of IL-1beta in human islets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8138–8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Yamamoto, Y.; Munesue, S.; Motoyoshi, S.; Saito, H.; Win, M.T.; Watanabe, T.; Tsuneyama, K.; Yamamoto, H. Induction of receptor for advanced glycation end products by insufficient leptin action triggers pancreatic beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes. Genes Cells 2013, 18, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covey, S.D.; Wideman, R.D.; McDonald, C.; Unniappan, S.; Huynh, F.; Asadi, A.; Speck, M.; Webber, T.; Chua, S.C.; Kieffer, T.J. The pancreatic beta cell is a key site for mediating the effects of leptin on glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morioka, T.; Asilmaz, E.; Hu, J.; Dishinger, J.F.; Kurpad, A.J.; Elias, C.F.; Li, H.; Elmquist, J.K.; Kennedy, R.T.; Kulkarni, R.N. Disruption of leptin receptor expression in the pancreas directly affects beta cell growth and function in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2860–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetboun, M.; Abitbol, G.; Rozenberg, K.; Rozenfeld, H.; Deutsch, A.; Sampson, S.R.; Rosenzweig, T. Maintenance of redox state and pancreatic beta-cell function: Role of leptin and adiponectin. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 1966–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyren, R.; Chang, C.L.; Lindstrom, P.; Barmina, A.; Vorrsjo, E.; Ali, Y.; Juntti-Berggren, L.; Bensadoun, A.; Young, S.G.; Olivecrona, T.; et al. Localization of lipoprotein lipase and GPIHBP1 in mouse pancreas: Effects of diet and leptin deficiency. BMC Physiol. 2012, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Ahn, I.S.; Kim, D.S. Central infusion of leptin improves insulin resistance and suppresses beta-cell function, but not beta-cell mass, primarily through the sympathetic nervous system in a type 2 diabetic rat model. Life Sci. 2010, 86, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujikawa, T.; Chuang, J.C.; Sakata, I.; Ramadori, G.; Coppari, R. Leptin therapy improves insulin-deficient type 1 diabetes by CNS-dependent mechanisms in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17391–17396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquenne, M.; Folgueira, C.; Bourouh, C.; Millet, M.; Silva, A.; Clasadonte, J.; Imbernon, M.; Fernandois, D.; Martinez-Corral, I.; Kusumakshi, S.; et al. Leptin brain entry via a tanycytic LepR-EGFR shuttle controls lipid metabolism and pancreas function. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1071–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, P.E.; Williams, S.; Fogliano, M.; Baldini, G.; Lodish, H.F. A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26746–26749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.; Liang, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. AdipoQ is a novel adipose-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 10697–10703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Okubo, K.; Shimomura, I.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Matsubara, K. cDNA cloning and expression of a novel adipose specific collagen-like factor, apM1 (AdiPose Most abundant Gene transcript 1). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 221, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, Y.; Tobe, T.; Choi-Miura, N.H.; Mazda, T.; Tomita, M. Isolation and characterization of GBP28, a novel gelatin-binding protein purified from human plasma. J. Biochem. 1996, 120, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, Y.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Takahashi, M.; Maeda, K.; Miyagawa, J.; Hotta, K.; Shimomura, I.; Nakamura, T.; Miyaoka, K.; et al. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 257, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cnop, M.; Havel, P.J.; Utzschneider, K.M.; Carr, D.B.; Sinha, M.K.; Boyko, E.J.; Retzlaff, B.M.; Knopp, R.H.; Brunzell, J.D.; Kahn, S.E. Relationship of adiponectin to body fat distribution, insulin sensitivity and plasma lipoproteins: Evidence for independent roles of age and sex. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrila, A.; Chan, J.L.; Yiannakouris, N.; Kontogianni, M.; Miller, L.C.; Orlova, C.; Mantzoros, C.S. Serum adiponectin levels are inversely associated with overall and central fat distribution but are not directly regulated by acute fasting or leptin administration in humans: Cross-sectional and interventional studies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 4823–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajvani, U.B.; Du, X.; Combs, T.P.; Berg, A.H.; Rajala, M.W.; Schulthess, T.; Engel, J.; Brownlee, M.; Scherer, P.E. Structure-function studies of the adipocyte-secreted hormone Acrp30/adiponectin. Implications fpr metabolic regulation and bioactivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9073–9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Yokomizo, T.; Kita, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Hara, K.; Tsunoda, M.; et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 2003, 423, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharroubi, I.; Rasschaert, J.; Eizirik, D.L.; Cnop, M. Expression of adiponectin receptors in pancreatic beta cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 312, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzell, M.S.; Nogueiras, R.; Dieguez, C.; Ahren, B. Dual action of adiponectin on insulin secretion in insulin-resistant mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 321, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Ohara-Imaizumi, M.; Kubota, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Eto, K.; Kanno, T.; Kubota, T.; Wakui, M.; Nagai, R.; Noda, M.; et al. Adiponectin induces insulin secretion in vitro and in vivo at a low glucose concentration. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Ye, L.; Tang, J.; Gu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hong, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Globular adiponectin augments insulin secretion from pancreatic islet beta cells at high glucose concentrations. Endocrine 2006, 30, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patane, G.; Caporarello, N.; Marchetti, P.; Parrino, C.; Sudano, D.; Marselli, L.; Vigneri, R.; Frittitta, L. Adiponectin increases glucose-induced insulin secretion through the activation of lipid oxidation. Acta Diabetol. 2013, 50, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munhoz, A.C.; Serna, J.D.C.; Vilas-Boas, E.A.; Caldeira da Silva, C.C.; Santos, T.G.; Mosele, F.C.; Felisbino, S.L.; Martins, V.R.; Kowaltowski, A.J. Adiponectin reverses beta-Cell damage and impaired insulin secretion induced by obesity. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, J.R.; Keating, D.J.; Chen, C.; Parkington, H.C. Adiponectin increases insulin content and cell proliferation in MIN6 cells via PPARgamma-dependent and PPARgamma-independent mechanisms. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huypens, P.; Moens, K.; Heimberg, H.; Ling, Z.; Pipeleers, D.; Van de Casteele, M. Adiponectin-mediated stimulation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in pancreatic beta cells. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Chen, L.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Yang, N.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Hou, X. Adiponectin reduces glucotoxicity-induced apoptosis of INS-1 rat insulin-secreting cells on a microfluidic chip. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2009, 217, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Qiao, J.; Li, N.; Qiao, S. AMPK alpha1 mediates the protective effect of adiponectin against insulin resistance in INS-1 pancreatic beta cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2019, 37, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesekara, N.; Krishnamurthy, M.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Suhail, A.; Sweeney, G.; Wheeler, M.B. Adiponectin-induced ERK and Akt phosphorylation protects against pancreatic beta cell apoptosis and increases insulin gene expression and secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33623–33631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.E.; Conner, A.C.; Digby, J.E.; Ward, K.L.; Ramanjaneya, M.; Randeva, H.S.; Dunmore, S.J. Regulation of beta-cell viability and gene expression by distinct agonist fragments of adiponectin. Peptides 2010, 31, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Holland, W.L.; Gordillo, R.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q.A.; Shao, M.; Morley, T.S.; Gupta, R.K.; Stahl, A.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin is essential for lipid homeostasis and survival under insulin deficiency and promotes beta-cell regeneration. eLife 2014, 3, e03851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q.A.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin-mediated antilipotoxic effects in regenerating pancreatic islets. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; Su, Y.X.; Deng, H.C. Adiponectin-induced inhibition of intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways protects pancreatic beta-cells against apoptosis. Horm. Metab. Res. 2013, 45, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Su, Y.X.; Deng, H.C. Lipoapoptosis pathways in pancreatic beta-cells and the anti-apoptosis mechanisms of adiponectin. Horm. Metab. Res. 2014, 46, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, A.H.; Kawakubo, M.; Trigo, E.; Kjos, S.L.; Buchanan, T.A. Declining beta-cell compensation for insulin resistance in Hispanic women with recent gestational diabetes mellitus: Association with changes in weight, adiponectin, and C-reactive protein. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, M.; Battista, M.C.; Doyon, M.; Menard, J.; Ardilouze, J.L.; Perron, P.; Hivert, M.F. Lower adiponectin levels at first trimester of pregnancy are associated with increased insulin resistance and higher risk of developing gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retnakaran, R.; Hanley, A.J.; Raif, N.; Hirning, C.R.; Connelly, P.W.; Sermer, M.; Kahn, S.E.; Zinman, B. Adiponectin and beta cell dysfunction in gestational diabetes: Pathophysiological implications. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retnakaran, R.; Qi, Y.; Connelly, P.W.; Sermer, M.; Hanley, A.J.; Zinman, B. Low adiponectin concentration during pregnancy predicts postpartum insulin resistance, beta cell dysfunction and fasting glycaemia. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Wattez, J.S.; Lee, S.; Nguyen, A.; Schaack, J.; Hay, W.W., Jr.; Shao, J. Adiponectin Deficiency Impairs Maternal Metabolic Adaptation to Pregnancy in Mice. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Saget, S.; Lu, C.; Hay, W.W., Jr.; Karsenty, G.; Shao, J. Adiponectin Promotes Maternal beta-Cell Expansion Through Placental Lactogen Expression. Diabetes 2021, 70, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatemoto, K.; Hosoya, M.; Habata, Y.; Fujii, R.; Kakegawa, T.; Zou, M.X.; Kawamata, Y.; Fukusumi, S.; Hinuma, S.; Kitada, C.; et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide ligand for the human APJ receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 251, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinz, M.J.; Davenport, A.P. Emerging roles of apelin in biology and medicine. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 107, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Sun, W.; Chen, X. The Role of Apelin/Apelin Receptor in Energy Metabolism and Water Homeostasis: A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 632886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Masri, B.; Daviaud, D.; Gesta, S.; Guigne, C.; Mazzucotelli, A.; Castan-Laurell, I.; Tack, I.; Knibiehler, B.; Carpene, C.; et al. Apelin, a newly identified adipokine up-regulated by insulin and obesity. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 1764–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daviaud, D.; Boucher, J.; Gesta, S.; Dray, C.; Guigne, C.; Quilliot, D.; Ayav, A.; Ziegler, O.; Carpene, C.; Saulnier-Blache, J.S.; et al. TNFalpha up-regulates apelin expression in human and mouse adipose tissue. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 1528–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorhede Winzell, M.; Magnusson, C.; Ahren, B. The apj receptor is expressed in pancreatic islets and its ligand, apelin, inhibits insulin secretion in mice. Regul. Pept. 2005, 131, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Yu, P.; Pan, H.; Li, P.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J. Apelin inhibits insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells by activation of PI3-kinase-phosphodiesterase 3B. Endocr. Res. 2009, 34, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Englander, E.W.; Gomez, G.A.; Rastellini, C.; Quertermous, T.; Kundu, R.K.; Greeley, G.H., Jr. Pancreatic Islet APJ Deletion Reduces Islet Density and Glucose Tolerance in Mice. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 2451–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.R.; Zhang, N.K.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, H.H. Overexpression of apelin in Wharton’ jelly mesenchymal stem cell reverses insulin resistance and promotes pancreatic beta cell proliferation in type 2 diabetic rats. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steppan, C.M.; Bailey, S.T.; Bhat, S.; Brown, E.J.; Banerjee, R.R.; Wright, C.M.; Patel, H.R.; Ahima, R.S.; Lazar, M.A. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 2001, 409, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, D.B.; Sewter, C.P.; Klenk, E.S.; Segal, D.G.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Considine, R.V.; O’Rahilly, S. Resistin/Fizz3 expression in relation to obesity and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma action in humans. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2199–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaev, I.; Smith, U. Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes are not related to resistin expression in human fat cells or skeletal muscle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 285, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.Z.; Huang, Q.; Xu, A.; McLenithan, J.C.; Eisen, J.A.; Shuldiner, A.R.; Alkan, S.; Gong, D.W. Comparative studies of resistin expression and phylogenomics in human and mouse. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 310, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.E.; Onyango, D.J.; Dunmore, S.J. Resistin down-regulates insulin receptor expression, and modulates cell viability in rodent pancreatic beta-cells. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 3273–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.L.; Zhao, D.Y.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, C.M.; Ji, C.B.; Chen, X.H.; Liu, F.; Guo, X.R. Resistin induces rat insulinoma cell RINm5F apoptosis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 36, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, M.; Okada, T.; Ozawa, K.; Yada, T. Resistin induces insulin resistance in pancreatic islets to impair glucose-induced insulin release. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 353, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Hong, S.M.; Sung, S.R.; Jung, H.K. Long-term effects of central leptin and resistin on body weight, insulin resistance, and beta-cell function and mass by the modulation of hypothalamic leptin and insulin signaling. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuhara, A.; Matsuda, M.; Nishizawa, M.; Segawa, K.; Tanaka, M.; Kishimoto, K.; Matsuki, Y.; Murakami, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Murakami, H.; et al. Visfatin: A protein secreted by visceral fat that mimics the effects of insulin. Science 2005, 307, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Bermejo, A.; Chico-Julia, B.; Fernandez-Balsells, M.; Recasens, M.; Esteve, E.; Casamitjana, R.; Ricart, W.; Fernandez-Real, J.M. Serum visfatin increases with progressive beta-cell deterioration. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2871–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revollo, J.R.; Korner, A.; Mills, K.F.; Satoh, A.; Wang, T.; Garten, A.; Dasgupta, B.; Sasaki, Y.; Wolberger, C.; Townsend, R.R.; et al. Nampt/PBEF/Visfatin regulates insulin secretion in beta cells as a systemic NAD biosynthetic enzyme. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.E.; Onyango, D.J.; Ramanjaneya, M.; Conner, A.C.; Patel, S.T.; Dunmore, S.J.; Randeva, H.S. Visfatin regulates insulin secretion, insulin receptor signalling and mRNA expression of diabetes-related genes in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 44, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Dong, W.; Qian, L.; Wu, J.; Peng, Y. Visfatin inhibits apoptosis of pancreatic beta-cell line, MIN6, via the mitogen-activated protein kinase/phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 47, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinnler, R.; Gorski, T.; Stolz, K.; Schuster, S.; Garten, A.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; Engelse, M.A.; de Koning, E.J.; Korner, A.; Kiess, W.; et al. The adipocytokine Nampt and its product NMN have no effect on beta-cell survival but potentiate glucose stimulated insulin secretion. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Kang, S.; Moon, N.R.; Park, S. Central visfatin potentiates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and beta-cell mass without increasing serum visfatin levels in diabetic rats. Cytokine 2014, 65, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayers, S.R.; Beavil, R.L.; Fine, N.H.F.; Huang, G.C.; Choudhary, P.; Pacholarz, K.J.; Barran, P.E.; Butterworth, S.; Mills, C.E.; Cruickshank, J.K.; et al. Structure-functional changes in eNAMPT at high concentrations mediate mouse and human beta cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, K.S.; Min, H.Y.; Johnson, D.; Chaplinsky, R.J.; Flier, J.S.; Hunt, C.R.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipsin: A circulating serine protease homolog secreted by adipose tissue and sciatic nerve. Science 1987, 237, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, B.S.; Cook, K.S.; Yaglom, J.; Groves, D.L.; Volanakis, J.E.; Damm, D.; White, T.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipsin and complement factor D activity: An immune-related defect in obesity. Science 1989, 244, 1483–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.T.; Damm, D.; Hancock, N.; Rosen, B.S.; Lowell, B.B.; Usher, P.; Flier, J.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Human adipsin is identical to complement factor D and is expressed at high levels in adipose tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 9210–9213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ma, M.; Ippolito, G.C.; Schroeder, H.W., Jr.; Carroll, M.C.; Volanakis, J.E. Complement activation in factor D-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 14577–14582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, J.C.; Ljubicic, S.; Leibiger, B.; Kern, M.; Leibiger, I.B.; Moede, T.; Kelly, M.E.; Chatterjee Bhowmick, D.; Murano, I.; Cohen, P.; et al. Adipsin is an adipokine that improves beta cell function in diabetes. Cell 2014, 158, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Banoy, N.; Guseh, J.S.; Li, G.; Rubio-Navarro, A.; Chen, T.; Poirier, B.; Putzel, G.; Rosselot, C.; Pabon, M.A.; Camporez, J.P.; et al. Adipsin preserves beta cells in diabetic mice and associates with protection from type 2 diabetes in humans. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Rajala, M.W.; Berger, J.P.; Moller, D.E.; Barzilai, N.; Scherer, P.E. Hyperglycemia-induced production of acute phase reactants in adipose tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 42077–42083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratchmarova, I.; Kalume, D.E.; Blagoev, B.; Scherer, P.E.; Podtelejnikov, A.V.; Molina, H.; Bickel, P.E.; Andersen, J.S.; Fernandez, M.M.; Bunkenborg, J.; et al. A proteomic approach for identification of secreted proteins during the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes to adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2002, 1, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lam, K.S.; Kraegen, E.W.; Sweeney, G.; Zhang, J.; Tso, A.W.; Chow, W.S.; Wat, N.M.; Xu, J.Y.; Hoo, R.L.; et al. Lipocalin-2 is an inflammatory marker closely associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and hyperglycemia in humans. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.W.; Yang, Q.; Mody, N.; Graham, T.E.; Hsu, C.H.; Xu, Z.; Houstis, N.E.; Kahn, B.B.; Rosen, E.D. The adipokine lipocalin 2 is regulated by obesity and promotes insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 2533–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosialou, I.; Shikhel, S.; Luo, N.; Petropoulou, P.I.; Panitsas, K.; Bisikirska, B.; Rothman, N.J.; Tenta, R.; Cariou, B.; Wargny, M.; et al. Lipocalin-2 counteracts metabolic dysregulation in obesity and diabetes. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20191261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goralski, K.B.; McCarthy, T.C.; Hanniman, E.A.; Zabel, B.A.; Butcher, E.C.; Parlee, S.D.; Muruganandan, S.; Sinal, C.J. Chemerin, a novel adipokine that regulates adipogenesis and adipocyte metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 28175–28188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechler, C.; Feder, S.; Haberl, E.M.; Aslanidis, C. Chemerin Isoforms and Activity in Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Okimura, Y.; Iguchi, G.; Nishizawa, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Suda, K.; Kitazawa, R.; Fujimoto, W.; Takahashi, K.; Zolotaryov, F.N.; et al. Chemerin regulates beta-cell function in mice. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, R.; Ge, Q.; Yue, L.; Ma, D.; Khattab, F.; Xie, W.; Cui, Y.; Gilon, P.; Zhao, X.; et al. Chemerin as an Inducer of beta Cell Proliferation Mediates Mitochondrial Homeostasis and Promotes beta Cell Mass Expansion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonenkov, A.; Shiyanova, T.L.; Koester, A.; Ford, A.M.; Micanovic, R.; Galbreath, E.J.; Sandusky, G.E.; Hammond, L.J.; Moyers, J.S.; Owens, R.A.; et al. FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Nakatake, Y.; Konishi, M.; Itoh, N. Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gene Struct. Expr. 2000, 1492, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camporez, J.P.G.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Petersen, M.C.; Pesta, D.; Guigni, B.A.; Serr, J.; Zhang, D.; Kahn, M.; Samuel, V.T.; Jurczak, M.J. Cellular mechanisms by which FGF21 improves insulin sensitivity in male mice. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3099–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, F.M.; Maratos-Flier, E. Understanding the Physiology of FGF21. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Tian, H.; Lam, K.S.L.; Lin, S.; Hoo, R.C.L.; Konishi, M.; Itoh, N.; Wang, Y.; Bornstein, S.R.; Xu, A.; et al. Adiponectin Mediates the Metabolic Effects of FGF21 on Glucose Homeostasis and Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muise, E.S.; Azzolina, B.; Kuo, D.W.; El-Sherbeini, M.; Tan, Y.; Yuan, X.; Mu, J.; Thompson, J.R.; Berger, J.P.; Wong, K.K. Adipose fibroblast growth factor 21 is up-regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and altered metabolic states. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qiang, L.; Farmer, S.R. Identification of a domain within peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ regulating expression of a group of genes containing fibroblast growth factor 21 that are selectively repressed by SIRT1 in adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wente, W.; Efanov, A.M.; Brenner, M.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Koster, A.; Sandusky, G.E.; Sewing, S.; Treinies, I.; Zitzer, H.; Gromada, J. Fibroblast growth factor-21 improves pancreatic β-cell function and survival by activation of extracellular signal–regulated kinase 1/2 and Akt signaling pathways. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Feng, J.; Wei, T.; Zhang, L.; Lang, S.; Yang, K.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Sterr, M.; Lickert, H.; et al. Pancreatic alpha cell glucagon–liver FGF21 axis regulates beta cell regeneration in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Alvarez-Guaita, A.; Melvin, A.; Rimmington, D.; Dattilo, A.; Miedzybrodzka, E.L.; Cimino, I.; Maurin, A.-C.; Roberts, G.P.; Meek, C.L.; et al. GDF15 Provides an Endocrine Signal of Nutritional Stress in Mice and Humans. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 707–718.e708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Day, E.A.; Townsend, L.K.; Djordjevic, D.; Jørgensen, S.B.; Steinberg, G.R. GDF15: Emerging biology and therapeutic applications for obesity and cardiometabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, A.P.; Chen, M.; Taskar, P.; Rimmington, D.; Patel, S.; Tadross, J.A.; Cimino, I.; Yang, M.; Welsh, P.; Virtue, S.; et al. GDF15 mediates the effects of metformin on body weight and energy balance. Nature 2020, 578, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Townsend, L.K.; Desormeaux, G.J.; Frangos, S.M.; Batchuluun, B.; Dumont, L.; Kuhre, R.E.; Ahmadi, E.; Hu, S.; Rebalka, I.A.; et al. GDF15 promotes weight loss by enhancing energy expenditure in muscle. Nature 2023, 619, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Recarte, D.; Barroso, E.; Gumà, A.; Pizarro-Delgado, J.; Peña, L.; Ruart, M.; Palomer, X.; Wahli, W.; Vázquez-Carrera, M. GDF15 mediates the metabolic effects of PPARβ/δ by activating AMPK. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Mulya, A.; Nieuwoudt, S.; Vandanmagsar, B.; McDowell, R.; Heintz, E.C.; Zunica, E.R.; Collier, J.J.; Bozadjieva-Kramer, N.; Seeley, R.J. GDF15 Mediates the Effect of Skeletal Muscle Contraction on Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 2023, 72, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertpatipanpong, P.; Lee, J.; Kim, I.; Eling, T.; Oh, S.Y.; Seong, J.K.; Baek, S.J. The anti-diabetic effects of NAG-1/GDF15 on HFD/STZ-induced mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Shargill, N.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-α: Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993, 259, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Arner, P.; Caro, J.F.; Atkinson, R.L.; Spiegelman, B.M. Increased adipose tissue expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 2409–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Rehman, K.; Liaqat, A. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha: Role in Development of Insulin Resistance and Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Kim, K.-H. TNF-α inhibits glucose-induced insulin secretion in a pancreatic β-cell line (INS-1). FEBS Lett. 1995, 377, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, L.A.; Thomas, H.E.; Ming, L.; Grell RIMA DARWICHE, M.; Volodin, L.; Kay, T.W. Tumor necrosis factor-α-activated cell death pathways in NIT-1 insulinoma cells and primary pancreatic β cells. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 3219–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, T.L.; Zanni, M.V.; Johnsen, S.; Rasheed, S.; Makimura, H.; Lee, H.; Khor, V.K.; Ahima, R.S.; Grinspoon, S.K. TNF-α antagonism with etanercept decreases glucose and increases the proportion of high molecular weight adiponectin in obese subjects with features of the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E146–E150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koulmanda, M.; Bhasin, M.; Awdeh, Z.; Qipo, A.; Fan, Z.; Hanidziar, D.; Putheti, P.; Shi, H.; Csizuadia, E.; Libermann, T.A.; et al. The Role of TNF-α in Mice with Type 1- and 2- Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.D.; Tisch, R.; Singer, S.M.; Cao, Z.A.; Liblau, R.S.; Schreiber, R.D.; McDevitt, H.O. Effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha on insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in NOD mice. I. The early development of autoimmunity and the diabetogenic process. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Adipokine | Effect | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adiponectin | Insulin secretion | ↑ | [69,70,71,72,73] |
| Beta cell proliferation | ↑ | [53,88] | |
| Beta cell apoptosis | ↓ | [75,76,77,82] | |
| Adipsin | Insulin secretion | ↑ | [118] |
| Beta cell apoptosis | ↓ | [119] | |
| Beta cell dedifferentiation | ↓ | [119] | |
| Apelin | Insulin secretion | ↓/↑ | [95,97] |
| Beta cell proliferation | ↑ | [97] | |
| Chemerin | Insulin secretion | ↑ | [127] |
| Beta cell proliferation | ↑ | [128] | |
| FGF21 | Insulin secretion | ↑ | [136] |
| Insulin sensitivity | ↑ | [133] | |
| Beta cell regeneration | ↑ | [137] | |
| GDF15 | Insulin secretion | ↑ | [142] |
| Insulin resistance | ↓ | [143,144] | |
| Leptin | Insulin secretion | ↓ | [34,35,37,38,39,40,43,45] |
| Beta cell proliferation | ↓ | [53] | |
| Beta cell apoptosis | ↓/↑ | [46,47,48,49] | |
| Lipocalin-2 | Insulin secretion | ↑ | [124] |
| Beta cell proliferation | ↑ | [124] | |
| Resistin | Insulin secretion | ↓ | [104] |
| Beta cell apoptosis | ↑ | [103] | |
| TNF-α | Insulin secretion | ↓ | [148,149] |
| Insulin resistance | ↑ | [145,146,147,150,151] | |
| Visfatin | Insulin secretion | ↑ | [107,109,111,112] |
| Beta cell proliferation | ↑ | [110] | |
| Beta cell apoptosis | ↓ | [110] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Oh, C.-M.; Kim, H. The Interplay of Adipokines and Pancreatic Beta Cells in Metabolic Regulation and Diabetes. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11092589
Kim J, Oh C-M, Kim H. The Interplay of Adipokines and Pancreatic Beta Cells in Metabolic Regulation and Diabetes. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(9):2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11092589
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Joon, Chang-Myung Oh, and Hyeongseok Kim. 2023. "The Interplay of Adipokines and Pancreatic Beta Cells in Metabolic Regulation and Diabetes" Biomedicines 11, no. 9: 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11092589
APA StyleKim, J., Oh, C. -M., & Kim, H. (2023). The Interplay of Adipokines and Pancreatic Beta Cells in Metabolic Regulation and Diabetes. Biomedicines, 11(9), 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11092589