Investigating the Connection between Chronic Periodontitis and Parkinson’s Disease: Findings from a Korean National Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
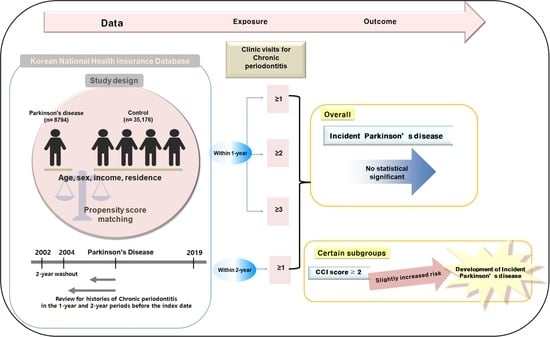
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Patient Selection
2.3. Parkinson’s Disease (Outcome)
2.4. Chronic Periodontitis (Exposure)
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Demographics
3.2. PD Odds Ratios in Relation to CP Histories
3.3. Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pihlstrom, B.L.; Michalowicz, B.S.; Johnson, N.W. Periodontal diseases. Lancet 2005, 366, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Jepsen, S.; Jin, L.; Otomo-Corgel, J. Impact of the global burden of periodontal diseases on health, nutrition and wellbeing of mankind: A call for global action. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeun, Y.-R.; Kwak, Y.S.; Kim, H.-Y. Association Serum Lipid Levels with Periodontal Disease in Korean Adults Over the Age of 50: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2016–2018. Exerc. Sci. 2022, 31, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Kim, H.Y.; Seok, H.; Yeo, C.D.; Kim, Y.S.; Song, J.Y.; Lee, Y.B.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.I.; Lee, T.K.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors of periodontitis among adults with or without diabetes mellitus. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2016, 31, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Korostoff, J.M. Revisiting the Page & Schroeder model: The good, the bad and the unknowns in the periodontal host response 40 years later. Periodontol. 2000 2017, 75, 116–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohangi, G.U.; Singh-Rambirich, S.; Volchansky, A. Periodontal disease: Mechanisms of infection and inflammation and possible impact on miscellaneous systemic diseases and conditions. SADJ 2013, 68, 462, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Page, R.C. The pathobiology of periodontal diseases may affect systemic diseases: Inversion of a paradigm. Ann. Periodontol. 1998, 3, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arigbede, A.O.; Babatope, B.O.; Bamidele, M.K. Periodontitis and systemic diseases: A literature review. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2012, 16, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Yan, X.; Feng, B.; Xu, L. Association of periodontitis and tooth loss with extent of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1243992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nardin, E. The role of inflammatory and immunological mediators in periodontitis and cardiovascular disease. Ann. Periodontol. 2001, 6, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andriankaja, O.M.; Adatorwovor, R.; Kantarci, A.; Hasturk, H.; Shaddox, L.; Levine, M.A. Periodontal Disease, Local and Systemic Inflammation in Puerto Ricans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.S.; Shin, N.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, H.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, Y.S. Correlation between periodontitis and chronic kidney disease in Korean adults. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 32, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentin, D.; Gobin, I.; Maglica, Z. Periodontal Pathogens and Their Links to Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.H.; Moon, S.J.; Kang, M.; Chung, S.J.; Cho, G.J.; Koh, S.B. Incidence of Parkinson’s disease and modifiable risk factors in Korean population: A longitudinal follow-up study of a nationwide cohort. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1094778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeter, C.B.; Rozas, N.S.; Sadowsky, J.M.; Jones, D.J. Parkinson’s Disease Oral Health Module: Interprofessional Coordination of Care. MedEdPORTAL 2018, 14, 10699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozas, N.S.; Sadowsky, J.M.; Jones, D.J.; Jeter, C.B. Incorporating oral health into interprofessional care teams for patients with Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2017, 43, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyra, P.; Machado, V.; Proenca, L.; Domingos, J.; Godinho, C.; Mendes, J.J.; Botelho, J. Parkinson’s Disease, Periodontitis and Patient-Related Outcomes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina 2020, 56, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradeep, A.R.; Singh, S.P.; Martande, S.S.; Raju, A.P.; Rustagi, T.; Suke, D.K.; Naik, S.B. Clinical evaluation of the periodontal health condition and oral health awareness in Parkinson’s disease patients. Gerodontology 2015, 32, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einarsdottir, E.R.; Gunnsteinsdottir, H.; Hallsdottir, M.H.; Sveinsson, S.; Jonsdottir, S.R.; Olafsson, V.G.; Bragason, T.H.; Saemundsson, S.R.; Holbrook, W.P. Dental health of patients with Parkinson’s disease in Iceland. Spec. Care Dent. 2009, 29, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacopino, A.M. Periodontitis and diabetes interrelationships: Role of inflammation. Ann. Periodontol. 2001, 6, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kwon, D.Y.; Choi, M.; Kim, S.; Jung, J.H.; Han, K.; Park, Y.G. Trends in the incidence and prevalence of Parkinson’s disease in Korea: A nationwide, population-based study. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashioka, S.; Inoue, K.; Miyaoka, T.; Hayashida, M.; Wake, R.; Oh-Nishi, A.; Inagaki, M. The Possible Causal Link of Periodontitis to Neuropsychiatric Disorders: More Than Psychosocial Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, T.; Uppoor, A.; Naik, D. Parkinson’s disease and periodontitis—The missing link? A review. Gerodontology 2016, 33, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbe, A.G.; Bock, N.; Derman, S.H.; Felsch, M.; Timmermann, L.; Noack, M.J. Self-assessment of oral health, dental health care and oral health-related quality of life among Parkinson’s disease patients. Gerodontology 2017, 34, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.C.; Sheu, J.J.; Lin, H.C.; Jensen, D.A. Increased risk of parkinsonism following chronic periodontitis: A retrospective cohort study. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1307–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.K.; Wu, Y.T.; Chang, Y.C. Periodontal inflammatory disease is associated with the risk of Parkinson’s disease: A population-based retrospective matched-cohort study. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.G.; Chang, Y.; Lee, J.S.; Song, T.J. Association of Tooth Loss with New-Onset Parkinson’s Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Park. Dis. 2020, 2020, 4760512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowski, J.; Floege, J.; Fliser, D.; Bohm, M.; Marx, N. Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiological Insights and Therapeutic Options. Circulation 2021, 143, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.K.; Huang, J.Y.; Wu, Y.T.; Chang, Y.C. Dental Scaling Decreases the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Nested Case-Control Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2018, 15, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, K.; Qiu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Chen, S.; Xie, W.; Chen, G.; Yang, D. Is There an Association Between Parkinson’s Disease and Periodontitis? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Park. Dis. 2023, 13, 1107–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, E.; Park, J.B.; Park, Y.G. Evaluation of the association between periodontitis and risk of Parkinson’s disease: A nationwide retrospective cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.G.; Kang, H.S.; Lim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.J.; Nam, E.S.; Min, K.W.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, N.Y.; et al. Changes in the Incidence Rates of Gastrointestinal Diseases Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic in South Korea: A Long-Term Perspective. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, H.S.; Lim, H.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, N.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, E.S. Possible Incidental Parkinson’s Disease following Asthma: A Nested Case-Control Study in Korea. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.J.; Byun, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, N.Y.; Park, H.R.; Choi, H.G. Longitudinal follow-up study of the association between statin use and chronic periodontitis using national health screening cohort of Korean population. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.J.; Kang, H.S.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Bang, W.J.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, N.Y.; Hong, S.; Lee, H.K. Risk for Esophageal Cancer Based on Lifestyle Factors-Smoking, Alcohol Consumption, and Body Mass Index: Insight from a South Korean Population Study in a Low-Incidence Area. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, H.G.; Lim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.J.; Nam, E.S.; Min, K.W.; Park, H.Y.; et al. Comparison of the Concordance of Cardiometabolic Diseases and Physical and Laboratory Examination Findings between Monozygotic and Dizygotic Korean Adult Twins: A Cross-Sectional Study Using KoGES HTS Data. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization; the International Association for the Study of Obesity and the International Obesity Task Force. The Asia-Pacific Perspective: Redefining Obesity and Its Treatment; Health Communications Australia Pty Limited: Sydney, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, H.; Li, B.; Couris, C.M.; Fushimi, K.; Graham, P.; Hider, P.; Januel, J.-M.; Sundararajan, V. Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Dalton, J.E. A unified approach to measuring the effect size between two groups using SAS. In SAS Global Forum 2012: Statistics and Data Analysis; SAS: Bucharest, Romania, 2012; pp. 335–2012. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, P.C. Balance diagnostics for comparing the distribution of baseline covariates between treatment groups in propensity-score matched samples. Stat. Med. 2009, 28, 3083–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Roosaar, A.; Axell, T.; Ye, W. Tobacco Use, Oral Health, and Risk of Parkinson’s Disease. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 185, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botelho, J.; Machado, V.; Mendes, J.J.; Mascarenhas, P. Causal Association between Periodontitis and Parkinson’s Disease: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Genes 2021, 12, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, A.; Hönekopp, J. Heterogeneity of Research Results: A New Perspective From Which to Assess and Promote Progress in Psychological Science. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2021, 16, 174569162096419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, G.E.; Kim, S.M.; Han, K.; Kim, N.H.; Chung, H.S.; Kim, J.W.; Han, B.; Cho, S.J.; Yu, J.H.; Park, Y.G.; et al. Metabolic syndrome and risk of Parkinson disease: A nationwide cohort study. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.J.; Kang, H.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, N.Y.; Choi, H.G.; Lim, H. Chronic Periodontitis and the Potential Likelihood of Gastric Cancer: A Nested Case-Control Study in the Korean Population Utilizing a National Health Sample Cohort. Cancers 2023, 15, 3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Kiprowska, M.; Kansara, T.; Kansara, P.; Li, P. Neuroinflammation: A Distal Consequence of Periodontitis. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 101, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehui, W.; Mengting, Z.; Pengfei, L.; Yuanyin, W.; Jianguang, X.; Tao, W. Elucidation of common molecular diagnostic biomarkers between chronic periodontitis and Parkinson’s disease via bioinformatics analyses. J. Periodontal Res. 2023, 58, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Characteristics | Total Participants | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PD | Control | Standardized Difference | |
| Age (y), n (%) | 0.00 | ||
| 40–64 | 1676 (19.06) | 1676 (19.06) | |
| 65–85+ | 7118 (80.94) | 7118 (80.94) | |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.00 | ||
| Male | 4204 (47.81) | 16,816 (47.81) | |
| Female | 4590 (52.19) | 18,360 (52.19) | |
| Income, n (%) | 0.00 | ||
| 1 (lowest) | 1624 (18.47) | 6496 (18.47) | |
| 2 | 952 (10.83) | 3808 (10.83) | |
| 3 | 1172 (13.33) | 4688 (13.33) | |
| 4 | 1691 (19.23) | 6764 (19.23) | |
| 5 (highest) | 3355 (38.15) | 13,420 (38.15) | |
| Region of residence, n (%) | 0.00 | ||
| Urban | 3326 (37.82) | 13,304 (37.82) | |
| Rural | 5468 (62.18) | 21,872 (62.18) | |
| Obesity, n (%) | 0.01 | ||
| Underweight | 318 (3.62) | 1283 (3.65) | |
| Normal | 3098 (35.23) | 12,521 (35.60) | |
| Overweight | 2308 (26.25) | 9289 (26.41) | |
| Obese I and Obese II | 3070 (34.91) | 3070 (34.91) | |
| Smoking status, n (%) | 0.09 | ||
| Nonsmoker | 6765 (76.93) | 25,888 (73.60) | |
| Past smoker | 1200 (13.65) | 5142 (14.62) | |
| Current smoker | 829 (9.43) | 4146 (11.79) | |
| Alcohol consumption, n (%) | 0.10 | ||
| <1 time a week | 6243 (70.99) | 23,295 (66.22) | |
| ≥1 time a week | 2551 (29.01) | 11,881 (33.78) | |
| Systolic blood pressure (n, %) | 0.00 | ||
| <120 mmHg | 2122 (24.13) | 8156 (23.19) | |
| 120–139 mmHg | 3967 (45.11) | 17,428 (49.55) | |
| ≥140 mmHg | 2705 (30.76) | 9592 (27.27) | |
| Diastolic blood pressure (n, %) | 0.11 | ||
| <80 mmHg | 3651 (41.52) | 16,604 (47.20) | |
| 80–89 mmHg | 3090 (35.14) | 12,529 (35.62) | |
| ≥90 mmHg | 2053 (23.35) | 6043 (17.18) | |
| Fasting blood glucose (n, %) | 0.11 | ||
| <100 mg/dL | 4613 (52.46) | 20,128 (57.22) | |
| 100–125 mg/dL | 2918 (33.18) | 11,078 (31.49) | |
| ≥126 mg/dL | 1263 (14.36) | 3970 (11.29) | |
| Total cholesterol (n, %) | 0.05 | ||
| <200 mg/dL | 5169 (58.78) | 19,833 (56.38) | |
| 200–239 mg/dL | 2501 (28.44) | 10,815 (30.75) | |
| ≥240 mg/dL | 1124 (12.78) | 4528 (12.87) | |
| CCI score (n, %) | 0.29 | ||
| 0 | 2649 (30.12) | 16,827 (47.84) | |
| 1 | 2030 (23.08) | 6867 (19.52) | |
| ≥2 | 4115 (46.79) | 11,482 (32.64) | |
| The number of CP treatments (Mean, SD) | |||
| within 1 year | 1.75 (3.98) | 1.81 (3.52) | 0.01 |
| within 2 years | 3.61 (7.05) | 3.62 (6.10) | 0.01 |
| N of PD | N of Control | Odd Ratios for PD (95% Confidence Interval) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Exposure/Total, %) | (Exposure/Total, %) | Crude † | p | Model 1 †‡ | p | Model 2 †§ | p | |
| Total (n = 43,970) | ||||||||
| No CP | 7380/8794 (83.9%) | 29,689/35,176 (84.4%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 1414/8794 (16.1%) | 5487/35,176 (15.6%) | 1.04 (0.97–1.11) | 0.265 | 1.03 (0.97–1.10) | 0.323 | 1.04 (0.98–1.11) | 0.228 |
| Age < 65 years old (n = 8380) | ||||||||
| No CP | 1374/1676 (82%) | 5445/6704 (81.2%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 302/1676 (18%) | 1259/6704 (18.8%) | 0.95 (0.83–1.09) | 0.474 | 0.95 (0.83–1.09) | 0.461 | 0.94 (0.82–1.09) | 0.416 |
| Age ≥ 65 years old (n = 35,590) | ||||||||
| No CP | 6006/7118 (84.4%) | 24,244/28,472 (85.2%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 1112/7118 (15.6%) | 4228/28,472 (14.9%) | 1.06 (0.99–1.14) | 0.103 | 1.07 (1.00–1.15) | 0.061 | 1.07 (0.99–1.15) | 0.086 |
| Men (n = 21,020) | ||||||||
| No CP | 3459/4204 (82.3%) | 13,986/16,816 (83.2%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 745/4204 (17.7%) | 2830/16,816 (16.8%) | 1.06 (0.97–1.16) | 0.169 | 1.08 (0.99–1.18) | 0.094 | 1.07 (0.98–1.18) | 0.122 |
| Women (n = 22,950) | ||||||||
| No CP | 3921/4590 (85.4%) | 15,703/18,360 (85.5%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 669/4590 (14.6%) | 2657/18,360 (14.5%) | 1.01 (0.92–1.11) | 0.858 | 1.01 (0.92–1.10) | 0.878 | 1.00 (0.91–1.10) | 0.987 |
| Low income (n = 18,740) | ||||||||
| No CP | 3186/3748 (85%) | 12,812/14,992 (85.5%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 562/3748 (15%) | 2180/14,992 (14.5%) | 1.04 (0.94–1.15) | 0.479 | 1.04 (0.94–1.16) | 0.397 | 1.04 (0.93–1.15) | 0.508 |
| High income (n = 25,230) | ||||||||
| No CP | 4194/5046 (83.1%) | 16,877/20,184 (83.6%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 852/5046 (16.9%) | 3307/20,184 (16.4%) | 1.04 (0.95–1.13) | 0.388 | 1.04 (0.96–1.14) | 0.306 | 1.04 (0.96–1.13) | 0.372 |
| Urban residents (n = 16,630) | ||||||||
| No CP | 2741/3326 (82.4%) | 10,913/13,304 (82%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 585/3326 (17.6%) | 2391/13,304 (18%) | 0.97 (0.88–1.08) | 0.608 | 0.99 (0.89–1.09) | 0.819 | 0.98 (0.89–1.09) | 0.745 |
| Rural residents (n = 27,340) | ||||||||
| No CP | 4639/5468 (84.8%) | 18,776/21,872 (85.8%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 829/5468 (15.2%) | 3096/21,872 (14.2%) | 1.08 (1.00–1.18) | 0.058 | 1.09 (1.00–1.18) | 0.050 * | 1.08 (0.99–1.17) | 0.078 |
| Underweight (n = 1617) | ||||||||
| No CP | 284/318 (89.3%) | 1152/1299 (88.7%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 34/318 (10.7%) | 147/1299 (11.3%) | 0.94 (0.63–1.39) | 0.752 | 0.92 (0.62–1.37) | 0.677 | 0.94 (0.63–1.40) | 0.753 |
| Normal weight (n = 15,612) | ||||||||
| No CP | 2595/3098 (83.8%) | 10,655/12,514 (85.1%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 503/3098 (16.2%) | 1859/12,514 (14.9%) | 1.11 (1.00–1.24) | 0.055 | 1.12 (1.00–1.25) | 0.042 * | 1.11 (1.00–1.24) | 0.056 |
| Overweight (n = 11,480) | ||||||||
| No CP | 1930/2308 (83.6%) | 7652/9172 (83.4%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 378/2308 (16.4%) | 1520/9172 (16.6%) | 0.99 (0.87–1.12) | 0.823 | 1.00 (0.88–1.13) | 0.953 | 1.00 (0.88–1.13) | 0.981 |
| Obese (n = 15,261) | ||||||||
| No CP | 2571/3070 (83.8%) | 10,230/12,191 (83.9%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 499/3070 (16.3%) | 1961/12,191 (16.1%) | 1.01 (0.91–1.13) | 0.820 | 1.02 (0.92–1.14) | 0.708 | 1.00 (0.90–1.12) | 0.965 |
| Non-smoker (n = 32,525) | ||||||||
| No CP | 5723/6765 (84.6%) | 21,834/25,760 (84.8%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 1042/6765 (15.4%) | 3926/25,760 (15.2%) | 1.01 (0.94–1.09) | 0.741 | 1.01 (0.93–1.08) | 0.877 | 1.00 (0.93–1.08) | 0.988 |
| Past smoker and current smoker (n = 11,445) | ||||||||
| No CP | 1657/2029 (81.7%) | 7855/9416 (83.4%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 372/2029 (18.3%) | 1561/9416 (16.6%) | 1.13 (1.00–1.28) | 0.056 | 1.15 (1.02–1.31) | 0.027 * | 1.15 (1.01–1.31) | 0.031 * |
| Alcohol consumption < 1 time a week (n = 29,626) | ||||||||
| No CP | 1657/2029 (81.7%) | 7855/9416 (83.4%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 372/2029 (18.3%) | 1561/9416 (16.6%) | 1.10 (1.02–1.18) | 0.018 * | 1.09 (1.01–1.18) | 0.026 * | 1.08 (1.00–1.17) | 0.044 * |
| Alcohol consumption ≥ 1 time a week (n = 14,344) | ||||||||
| No CP | 2141/2551 (83.9%) | 9785/11,793 (83%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 410/2551 (16.1%) | 2008/11,793 (17%) | 0.93 (0.83–1.05) | 0.243 | 0.95 (0.84–1.06) | 0.362 | 0.94 (0.83–1.06) | 0.292 |
| SBP < 140 mmHg and DBP < 90 mmHg (n = 30,124) | ||||||||
| No CP | 4728/5669 (83.4%) | 20,524/24,455 (83.9%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 941/5669 (16.6%) | 3931/24,455 (16.1%) | 1.04 (0.96–1.12) | 0.330 | 1.04 (0.97–1.13) | 0.272 | 1.04 (0.96–1.12) | 0.361 |
| SBP ≥ 140 mmHg or DBP ≥ 90 mmHg (n = 13,846) | ||||||||
| No CP | 2652/3125 (84.9%) | 9165/10,721 (85.5%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 473/3125 (15.1%) | 1556/10,721 (14.5%) | 1.05 (0.94–1.17) | 0.387 | 1.05 (0.94–1.17) | 0.405 | 1.04 (0.93–1.17) | 0.460 |
| Fasting blood glucose < 100 mg/dL (n = 24,375) | ||||||||
| No CP | 3880/4613 (84.1%) | 16,680/19,762 (84.4%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 733/4613 (15.9%) | 3082/19,762 (15.6%) | 1.02 (0.94–1.12) | 0.619 | 1.03 (0.94–1.13) | 0.499 | 1.03 (0.94–1.13) | 0.476 |
| Fasting blood glucose ≥ 100 mg/dL (n = 19,595) | ||||||||
| No CP | 3500/4181 (83.7%) | 13,009/15,414 (84.4%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 681/4181 (16.3%) | 2405/15,414 (15.6%) | 1.05 (0.96–1.15) | 0.281 | 1.06 (0.96–1.16) | 0.238 | 1.04 (0.95–1.14) | 0.414 |
| Total cholesterol < 200 mg/dL (n = 25,115) | ||||||||
| No CP | 4316/5169 (83.5%) | 16,848/19,946 (84.5%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 853/5169 (16.5%) | 3098/19,946 (15.5%) | 1.07 (0.99–1.17) | 0.088 | 1.08 (0.99–1.17) | 0.079 | 1.08 (0.99–1.17) | 0.091 |
| Total cholesterol ≥ 200 mg/dL (n = 18,855) | ||||||||
| No CP | 3064/3625 (84.5%) | 12,841/15,230 (84.3%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 561/3625 (15.5%) | 2389/15,230 (15.7%) | 0.98 (0.89–1.09) | 0.755 | 1.00 (0.90–1.10) | 0.960 | 0.98 (0.89–1.09) | 0.741 |
| CCI scores = 0 (n = 19,476) | ||||||||
| No CP | 2245/2649 (84.8%) | 14,105/16,824 (83.8%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 404/2649 (15.3%) | 2719/16,824 (16.2%) | 0.93 (0.83–1.05) | 0.235 | 0.92 (0.82–1.03) | 0.137 | 0.92 (0.82–1.03) | 0.131 |
| CCI score = 1 (n = 8885) | ||||||||
| No CP | 1709/2030 (84.2%) | 5796/6855 (84.6%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 321/2030 (15.8%) | 1059/6855 (15.5%) | 1.03 (0.90–1.18) | 0.689 | 1.01 (0.88–1.16) | 0.874 | 1.01 (0.88–1.16) | 0.874 |
| CCI score ≥ 2 (n = 15,612) | ||||||||
| No CP | 3426/4115 (83.3%) | 9788/11,497 (85.1%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CP ≥ 1 | 689/4115 (16.7%) | 1709/11,497 (14.9%) | 1.15 (1.05–1.27) | 0.004 * | 1.14 (1.04–1.26) | 0.008 * | 1.14 (1.04–1.26) | 0.008 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, N.-E.; Yoo, D.M.; Han, K.M.; Kang, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Bang, W.J.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, N.Y.; Park, H.Y.; et al. Investigating the Connection between Chronic Periodontitis and Parkinson’s Disease: Findings from a Korean National Cohort Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040792
Lee N-E, Yoo DM, Han KM, Kang HS, Kim JH, Kim J-H, Bang WJ, Choi HG, Kim NY, Park HY, et al. Investigating the Connection between Chronic Periodontitis and Parkinson’s Disease: Findings from a Korean National Cohort Study. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(4):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040792
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Na-Eun, Dae Myoung Yoo, Kyeong Min Han, Ho Suk Kang, Ji Hee Kim, Joo-Hee Kim, Woo Jin Bang, Hyo Geun Choi, Nan Young Kim, Ha Young Park, and et al. 2024. "Investigating the Connection between Chronic Periodontitis and Parkinson’s Disease: Findings from a Korean National Cohort Study" Biomedicines 12, no. 4: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040792
APA StyleLee, N. -E., Yoo, D. M., Han, K. M., Kang, H. S., Kim, J. H., Kim, J. -H., Bang, W. J., Choi, H. G., Kim, N. Y., Park, H. Y., & Kwon, M. J. (2024). Investigating the Connection between Chronic Periodontitis and Parkinson’s Disease: Findings from a Korean National Cohort Study. Biomedicines, 12(4), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040792