Evidence for Contamination of Silica Microparticles in Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrices Prepared Using Silica-Coated Plastic Tubes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
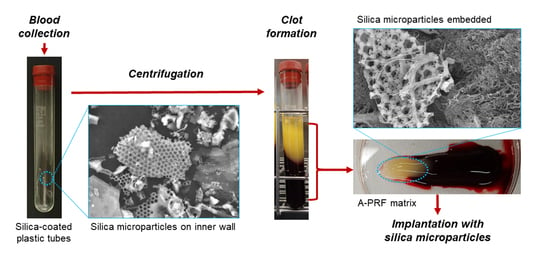
2.1. Preparation of Advanced-PRF (A-PRF) Matrices
2.2. Detachment of Silica Microparticles from the Inner Walls of Tubes or Films
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Examination
2.4. Spectrophotometric Quantification of Detached Silica Microparticles
2.5. Enzymatic Degradation of A-PRF Matrices to Release Silica Microparticles
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbon, S.; Stocco, E.; Macchi, V.; Contran, M.; Grandi, F.; Borean, A.; Parnigotto, P.P.; Porzionato, A.; De Caro, R. Platelet-Rich Fibrin Scaffolds for Cartilage and Tendon Regenerative Medicine: From Bench to Bedside. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawase, T. Platelet-rich plasma and its derivatives as promising bioactive materials for regenerative medicine: basic principles and concepts underlying recent advances. Odontology 2015, 103, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miron, R.J.; Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Bishara, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hernandez, M.; Choukroun, J. Platelet-Rich Fibrin and Soft Tissue Wound Healing: A Systematic Review. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2017, 23, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, P.; Zhai, Z.; Jin, X.; Yang, X.; Qi, Z. Clinical Application of Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery: A Systematic Review. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2018, 42, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumstein, M.A.; Berger, S.; Schober, M.; Boileau, P.; Nyffeler, R.W.; Horn, M.; Dahinden, C.A. Leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) for long-term delivery of growth factor in rotator cuff repair: Review, preliminary results and future directions. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawase, T.; Okuda, K. Comprehensive Quality Control of the Regenerative Therapy Using Platelet Concentrates: The Current Situation and Prospects in Japan. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 6389157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolis, J. Glass surface and blood coagulation. Nature 1956, 178, 805–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukioka, T.; Hiratsuka, T.; Nakamura, M.; Watanabe, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Isobe, K.; Okudera, T.; Okudera, H.; Azuma, A.; Uematsu, K.; et al. An on-site preparable, novel bone-grafting complex consisting of human platelet-rich fibrin and porous particles made of a recombinant collagen-like protein. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 107B, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Del Corso, M.; Diss, A.; Mouhyi, J.; Charrier, J.B. Three-dimensional architecture and cell composition of a Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin clot and membrane. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T. Silica exposure, smoking, silicosis and lung cancer—Complex interactions. Occup. Med. (Oxford, England) 2009, 59, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenland, K.; Ward, E. Silica: A lung carcinogen. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isobe, K.; Suzuki, M.; Watanabe, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kawabata, H.; Nakamura, M.; Okudera, T.; Okudera, H.; Uematsu, K.; et al. Platelet-rich fibrin prepared from stored whole-blood samples. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2017, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawabata, H.; Isobe, K.; Watanabe, T.; Okudera, T.; Nakamura, M.; Suzuki, M.; Ryu, J.; Kitamura, Y.; Okudera, H.; Okuda, K.; et al. Quality Assessment of Platelet-Rich Fibrin-Like Matrix Prepared from Whole Blood Samples after Extended Storage. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Kawase, T.; Horimizu, M.; Okuda, K.; Wolff, L.F.; Yoshie, H. A proposed protocol for the standardized preparation of PRF membranes for clinical use. Biologicals 2012, 40, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Tsukioka, T.; Isobe, K.; Tsujino, T.; Watanabe, T.; Watanabe, T.; Okudera, H.; Nakata, K.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Spectrophotometric determination of platelet counts in platelet-rich plasma. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2018, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIPRO Information for Medical Personnel. Available online: http://med.nipro.co.jp/med_eq_category_detail?id=a1U1000000b1000533AEAQ (accessed on 13 May 2019).
- Madl, A.K.; Donovan, E.P.; Gaffney, S.H.; McKinley, M.A.; Moody, E.C.; Henshaw, J.L.; Paustenbach, D.J. State-of-the-science review of the occupational health hazards of crystalline silica in abrasive blasting operations and related requirements for respiratory protection. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B Crit. Rev. 2008, 11, 548–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becton Dickinson Vacutainer Brand SST Tubes Containing Silica and Gel, Material Safety Data Sheet. Available online: http://catalog.bd.com/ecat/msds/d01/vs60313.pdf (accessed on 13 May 2019).
- Mannello, F.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Meschiari, C.A.; Tonti, G.A. Differences in both matrix metalloproteinase 9 concentration and zymographic profile between plasma and serum with clot activators are due to the presence of amorphous silica or silicate salts in blood collection devices. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 374, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cement Concrete & Aggregates Australia. Amorphous Silica Properties, Characterisation and Uses. Available online: https://www.ccaa.com.au/imis_prod/documents/TECH_NOTE_79_-_Amorphous_Silica.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2019).
- Ashworth, C.T.; Adams, G. Blood specific gravity studies: Relationship of specific gravity of whole blood to specific gravity of plasma, red blood cell count, hematocrit, and hemoglobin as indicators of hemoconcentration. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1941, 26, 1934–1939. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, C.A.; Elsaesser, A.; Arkusz, J.; Smok, A.; Palus, J.; Lesniak, A.; Salvati, A.; Hanrahan, J.P.; Jong, W.H.; Dziubaltowska, E.; et al. Reproducible comet assay of amorphous silica nanoparticles detects no genotoxicity. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3069–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewamatawong, T.; Kawamura, N.; Okajima, M.; Sawada, M.; Morita, T.; Shimada, A. Acute pulmonary toxicity caused by exposure to colloidal silica: particle size dependent pathological changes in mice. Toxicol. Pathol. 2005, 33, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaka, T.; Nakayama, M.; Nakamura, K.; Ishimiya, M.; Furusawa, E.; Ogasawara, K. Effect of silica particle size on macrophage inflammatory responses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merget, R.; Bauer, T.; Kupper, H.U.; Philippou, S.; Bauer, H.D.; Breitstadt, R.; Bruening, T. Health hazards due to the inhalation of amorphous silica. Arch. Toxicol. 2002, 75, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandberg, W.J.; Lag, M.; Holme, J.A.; Friede, B.; Gualtieri, M.; Kruszewski, M.; Schwarze, P.E.; Skuland, T.; Refsnes, M. Comparison of non-crystalline silica nanoparticles in IL-1beta release from macrophages. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2012, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, S.M. Safety issues associated with platelet-rich fibrin method. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2007, 103, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Neotube | Vacuette | Venoject II | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material of tube | plastic (PET) | plastic (PET) | plastic (PET) |
| Silica types | amorphous | not disclosed | not disclosed |
| Object coated | inner-wall surface | inner-wall surface | film |
| Additives | not disclosed | not disclosed | thrombin |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsujino, T.; Takahashi, A.; Yamaguchi, S.; Watanabe, T.; Isobe, K.; Kitamura, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Nakata, K.; Kawase, T. Evidence for Contamination of Silica Microparticles in Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrices Prepared Using Silica-Coated Plastic Tubes. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines7020045
Tsujino T, Takahashi A, Yamaguchi S, Watanabe T, Isobe K, Kitamura Y, Tanaka T, Nakata K, Kawase T. Evidence for Contamination of Silica Microparticles in Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrices Prepared Using Silica-Coated Plastic Tubes. Biomedicines. 2019; 7(2):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines7020045
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsujino, Tetsuhiro, Akira Takahashi, Sadahiro Yamaguchi, Taisuke Watanabe, Kazushige Isobe, Yutaka Kitamura, Takaaki Tanaka, Koh Nakata, and Tomoyuki Kawase. 2019. "Evidence for Contamination of Silica Microparticles in Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrices Prepared Using Silica-Coated Plastic Tubes" Biomedicines 7, no. 2: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines7020045
APA StyleTsujino, T., Takahashi, A., Yamaguchi, S., Watanabe, T., Isobe, K., Kitamura, Y., Tanaka, T., Nakata, K., & Kawase, T. (2019). Evidence for Contamination of Silica Microparticles in Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrices Prepared Using Silica-Coated Plastic Tubes. Biomedicines, 7(2), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines7020045