Efficient Portable Urea Biosensor Based on Urease Immobilized Membrane for Monitoring of Physiological Fluids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Parylene Coating of the PTFE Membrane and Urease Immobilization
2.3. Urease Urease Activity Assay
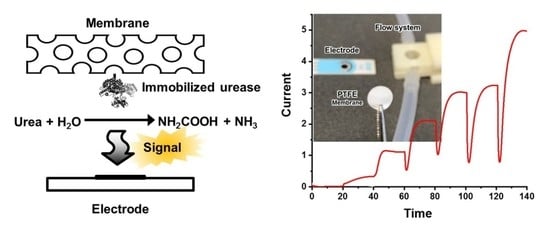
2.4. Urease Configuration of the Flow System and the Urea Biosensor
2.5. Urease Electrochemical Measurements in the Flow Condition
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Immobilization of Urease on the Solid Support
3.2. Analysis of the Urease-Immobilized Membrane Produced by DSS Cross-Linking
3.3. Urea Biosensing Using Urease-Immobilized Membranes
3.4. Repeatability and Interference Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turner, A.; Karube, I.; Wilson, G.S. Biosensors: Fundamentals and Applications; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M. Orientation Control of the Molecular Recognition Layer for Improved Sensitivity: A Review. BioChip J. 2019, 13, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Jung, J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kwon, D.; Kim, B.-G.; Na, H.B.; Lee, H.H. Surface plasmon resonance characteristics of Au nanoparticles layered sensor chip for direct detection of stress hormone conjugated by nanoparticles. BioChip J. 2018, 12, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, X.; Cao, L.; Du, S.; Wang, W.; Yao, S.Q. Competition-Based Universal Photonic Crystal Biosensors by Using Antibody-Antigen Interaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 142, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.K.; Thungon, P.D.; Estrela, P.; Goswami, P. Development of an aptamer-based field effect transistor biosensor for quantitative detection of Plasmodium falciparum glutamate dehydrogenase in serum samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 123, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayorga-Martinez, C.C.; Sofer, Z.K.; Pumera, M. Binary Phosphorene Redox Behavior in Oxidoreductase Enzymatic Systems. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13217–13224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.P. Biosensors: Fundamentals and applications–Historic book now open access. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, P.; Joseph, Y. Enzyme-based biosensors for choline analysis: A. review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosten, A.O. BUN and creatinine. In Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations, 3rd ed.; Butterworths: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, M.; Alegret, S.; del Valle, M. Potentiometric bioelectronic tongue for the analysis of urea and alkaline ions in clinical samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avram, M.; Mittman, N.; Bonomini, L.; Chattopadhyay, J.; Fein, P. Markers for survival in dialysis: A seven-year prospective study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1995, 26, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, V.; Takashima, W.; Kaneto, K. An amperometric urea biosensor based on covalent immobilization of urease onto an electrochemically prepared copolymer poly (N-3-aminopropyl pyrrole-co-pyrrole) film. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3683–3690. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, H.-C.; Doong, R.-A. Simultaneous determination of pH, urea, acetylcholine and heavy metals using array-based enzymatic optical biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Si, S.; Dai, H.; Zhang, C. Piezoelectric urea biosensor based on immobilization of urease onto nanoporous alumina membranes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 3283–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, G.; Sumana, G.; Malhotra, B. Recent developments in urea biosensors. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 44, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervisevic, M.; Dervisevic, E.; Şenel, M. Design of amperometric urea biosensor based on self-assembled monolayer of cystamine/PAMAM-grafted MWCNT/Urease. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervisevic, E.; Dervisevic, M.; Nyangwebah, J.N.; Şenel, M. Development of novel amperometric urea biosensor based on Fc-PAMAM and MWCNT bio-nanocomposite film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, T.; Ganjali, M.R.; Rafiei, F. Trace level and highly selective determination of urea in various real samples based upon voltammetric analysis of diacetylmonoxime-urea reaction product on the carbon nanotube/carbon paste electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 974, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, A.; Biswas, K. Digital Urea Meter for Impedeometric Urea Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Auckland, New Zealand, 20–23 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Moon, B.M.; Seo, Y.B.; Park, C.H.; Park, M.; Sung, G.Y. Fabrication of a Urea Biosensor for Real-Time Dynamic Fluid Measurement. Sensors 2018, 18, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, M.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Pyun, J.C.; Sung, G.Y. Parylene-Coated Polytetrafluoroethylene-Membrane-Based Portable Urea Sensor for Real-Time Monitoring of Urea in Peritoneal Dialysate. Sensors 2019, 19, 4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Yoon, S.; Ahn, J.; Yang, D.; Tian, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes for the immobilization of enzyme in glucose biosensors. Electrochem. Commun. 2003, 5, 800–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delvaux, M.; Demoustier-Champagne, S. Immobilisation of glucose oxidase within metallic nanotubes arrays for application to enzyme biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putzbach, W.; Ronkainen, N.J. Immobilization techniques in the fabrication of nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors: A review. Sensors 2013, 13, 4811–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucca, P.; Sanjust, E. Inorganic materials as supports for covalent enzyme immobilization: Methods and mechanisms. Molecules 2014, 19, 14139–14194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, O.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Torres, R.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Glutaraldehyde in bio-catalysts design: A useful crosslinker and a versatile tool in enzyme immobilization. Rsc Adv. 2014, 4, 1583–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvaro, G.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Blanco, R.M.; Guisán, J.M. Immobilization-stabilization of Penicillin G acylase fromEscherichia coli. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1990, 26, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, N.S.; Reisler, E.; Houk, K. Quantitative evaluation of the lengths of homobifunctional protein cross-linking reagents used as molecular rulers. Protein Sci. 2001, 10, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieniarz, C.; Husain, M.; Barnes, G.; King, C.A.; Welch, C.J. Extended length heterobifunctional coupling agents for protein conjugations. Bioconjug. Chem. 1996, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Nishi, H.; Hamana, H.; Sekioka, N.; Xiuyun, W.; Uchiyama, S. Bioelectrochemical conversion of urea to nitrogen using aminated carbon electrode. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, S96–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabla, P.K. Renal function in diabetic nephropathy. World J. Diabetes 2010, 1, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Cheng, N.L.; Hsu, Y.J.; Halperin, M.L. Intrafamilial phenotype variability in patients with Gitelman syndrome having the same mutations in their thiazide-sensitive sodium/chloride cotransporter. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 43, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, G.; Leal-Khouri, S. Significance of low serum urea nitrogen concentrations. Clin. Chem. 1989, 35, 639–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C. Urea and the clinical value of measuring blood urea concentration. Acutecaretesting Org. 2016, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Twardowski, Z. Influence of different automated peritoneal dialysis schedules on solute and water removal. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 1998, 13 (Suppl. S6), 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Abbreviation | Expansion |
|---|---|
| GA | glutaraldehyde |
| PTFE | polytetrafluoroethylene |
| DSG | disuccinimidyl glutarate |
| DSS | disuccinimidyl suberate |
| BS(PEG)5 | bis-N-succinimidyl-(pentaethylene glycol) ester |
| PDMS | polydimethylsiloxane |
| Parylene-A | amine-functionalized poly (p-xylylene) |
| OD | optical density |
| LOD | limit of detection |
| RDS | relative standard deviation |
| Urease Immobilizing Substrate | Cross-Linker | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silk fibroin | GA | - | [20] |
| Porous PTFE | GA | 4 mM | [21] |
| Porous PTFE | DSS | 1.1 mM | This work |
| Factor | Performance |
|---|---|
| LOD | 1.1 mM (PBS) 1.2 mM (human serum) |
| Sensitivity | 3.4 mA M−1 cm−2 (PBS) 1.6 mA M−1 cm−2 (human serum) |
| Dynamic range | 1.1–20 mM (PBS) 1.2–20 mM (human serum) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.Y.; Sung, G.Y.; Park, M. Efficient Portable Urea Biosensor Based on Urease Immobilized Membrane for Monitoring of Physiological Fluids. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120596
Kim JY, Sung GY, Park M. Efficient Portable Urea Biosensor Based on Urease Immobilized Membrane for Monitoring of Physiological Fluids. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(12):596. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120596
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jee Young, Gun Yong Sung, and Min Park. 2020. "Efficient Portable Urea Biosensor Based on Urease Immobilized Membrane for Monitoring of Physiological Fluids" Biomedicines 8, no. 12: 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120596
APA StyleKim, J. Y., Sung, G. Y., & Park, M. (2020). Efficient Portable Urea Biosensor Based on Urease Immobilized Membrane for Monitoring of Physiological Fluids. Biomedicines, 8(12), 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120596