Magnesium, Little Known But Possibly Relevant: A Link between NASH and Related Comorbidities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: An Overview
1.2. Nutritional Imbalances in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Potential Role of Magnesium
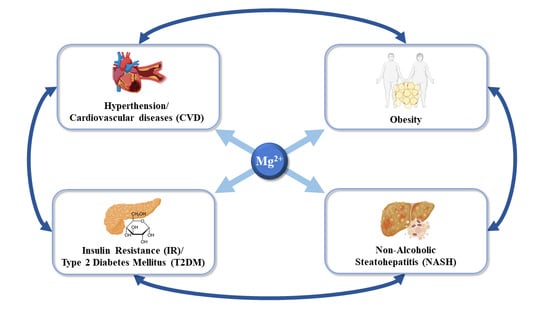
2. Magnesium and Systemic Complications during Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
2.1. Magnesium in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Cancer
2.2. Magnesium in Overweight and Obesity
2.3. Magnesium in Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
2.4. Magnesium in Hypertension and Cardiovascular Diseases (CVD)
3. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marra, F.; Lotersztajn, S. Pathophysiology of NASH: Perspectives for a targeted treatment. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 5250–5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, J.; Ouro, A.; Ala-Ibanibo, L.; Presa, N.; Delgado, T.C.; Martínez-Chantar, M.L. Sphingolipids in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma: Ceramide turnover. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Epidemiology and Natural History of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2012, 2, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertot, L.C.; Adams, L.A. Trends in hepatocellular carcinoma due to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.-W.; Ting, Y.-W.; Chan, W.-K. Epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-related hepatocellular carcinoma and its implications. JGH Open Open Access J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: Consider the population. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 47, S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, J.; Nuñez-García, M.; Fernández-Tussy, P.; Barbier-Torres, L.; Fernández-Ramos, D.; Gómez-Santos, B.; Buqué, X.; Lopitz-Otsoa, F.; Goikoetxea-Usandizaga, N.; Serrano-Macia, M.; et al. Targeting Hepatic Glutaminase 1 Ameliorates Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Restoring Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein Triglyceride Assembly. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, D.H.; Forbes, J.M.; Angus, P.W.; Herath, C.B. Development and Progression of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Role of Advanced Glycation End Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, S.L. Reversibility of hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis—Is it all hype? Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 4, 236–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbay, A.; Friedman, S.; Gores, G.J. Apoptosis: The Nexus of Liver Injury and Fibrosis. Hepatology 2004, 39, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbay, A.; Feldstein, A.E.; Higuchi, H.; Werneburg, N.; Grambihler, A.; Bronk, S.F.; Gores, G.J. Kupffer Cell Engulfment of Apoptotic Bodies Stimulates Death Ligand and Cytokine Expression. Hepatology 2003, 38, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mederacke, I.; Hsu, C.C.; Troeger, J.S.; Huebener, P.; Mu, X.; Dapito, D.H.; Pradere, J.; Schwabe, R.F. Fate-tracing reveals hepatic stellate cells as dominant contributors to liver fibrosis independent of its etiology. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hallsworth, K.; Adams, L.A. Lifestyle modification in NAFLD/NASH: Facts and figures. JHEP Rep. Innov. Hepatol. 2019, 1, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paglialunga, S.; Dehn, C.A. Clinical assessment of hepatic de novo lipogenesis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greger, J.L.; Baligar, P.; Abernathy, R.P.; Bennett, O.A.; Peterson, T. Calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, copper, and manganese balance in adolescent females. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1978, 31, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ervin, R.B.; Wang, C.-Y.; Wright, J.D.; Kennedy-Stephenson, J. Dietary intake of selected minerals for the United States population: 1999–2000. Adv. Data 2004, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Aikawa, J.K. Magnesium: Its Biologic Significance; CRC Series on Cations of Biological Significance; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1981; Volume 1, ISBN 084935871X. [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan, R. Magnesium metabolism and its disorders. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2003, 24, 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Dudley, S.C., Jr. Magnesium, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Cardiovascular Disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 907. [Google Scholar]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J.; Galioto, A.; Ferlisi, A.; Cani, C.; Malfa, L.; Pineo, A.; Busardo’, A.; Paolisso, G. Role of magnesium in insulin action, diabetes and cardio-metabolic syndrome X. Mol. Asp. Med. 2003, 24, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, M.; Di Bella, G.; Brucato, V.; D’Angelo, D.; Damiani, P.; Monteverde, A.; Belvedere, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Serum ionized magnesium in diabetic older persons. Metabolism 2014, 63, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosique-Esteban, N.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Hernández-Alonso, P.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Dietary Magnesium and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review with Emphasis in Epidemiological Studies. Nutrients 2018, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Zhu, X.; Fan, L.; Kabagambe, E.K.; Song, Y.; Tao, M.; Zhong, X.; Hou, L.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Liu, J.; et al. Magnesium intake and mortality due to liver diseases: Results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Cohort. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, H.; Mao, Y. Magnesium and liver disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayssiguier, Y.; Chevalier, F.; Bonnet, M.; Kopp, J.; Durlach, J. Influence of magnesium deficiency on liver collagen after carbon tetrachloride or ethanol administration to rats. J. Nutr. 1985, 115, 1656–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, A.; Scarpa, A. Mg2+ control of respiration in isolated rat liver mitochondria. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 12849–12856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, Y.; Ohno, S.; Akita, Y.; Kawasaki, H.; Suzuki, K. Enzymatic properties of a novel phorbol ester receptor/protein kinase, nPKC. J. Biochem. 1989, 106, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malpuech-Brugère, C.; Nowacki, W.; Daveau, M.; Gueux, E.; Linard, C.; Rock, E.; Lebreton, J.; Mazur, A.; Rayssiguier, Y. Inflammatory response following acute magnesium deficiency in the rat. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1501, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paik, Y.H.; Yoon, Y.J.; Lee, H.C.; Jung, M.K.; Kang, S.H.; Chung, S.I.; Kim, J.K.; Cho, J.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Han, K.H. Antifibrotic effects of magnesium lithospermate B on hepatic stellate cells and thioacetamide-induced cirrhotic rats. Exp. Mol. Med. 2011, 43, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, D.N.; Banik, S.; Rypma, R.S. Role of divalent metal cations in ATP hydrolysis catalyzed by the hepatitis C virus NS3 helicase: Magnesium provides a bridge for ATP to fuel unwinding. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 365, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blaszczyk, U.; Duda-Chodak, A. Magnesium: Its role in nutrition and carcinogenesis. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2013, 64, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zou, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhu, X.; Jia, Q.; Wang, L.; Yan, R. Inhibitory effect of magnesium cantharidate on human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cell proliferation by blocking MAPK signaling pathway. Chin. J. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 33, 347–351. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, M.; Brenner, D.A. Clinical syndromes of alcoholic liver disease. Dig. Dis. 2005, 23, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, M.; Ishii, H. Role of mitochondria in alcoholic liver injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiskirchen, R.; Tacke, F. Cellular and molecular functions of hepatic stellate cells in inflammatory responses and liver immunology. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2014, 3, 344–363. [Google Scholar]
- Poikolainen, K.; Alho, H. Magnesium treatment in alcoholics: A randomized clinical trial. Subst. Abus. Treat. Prev. Policy 2008, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hruby, A.; Hu, F.B. The Epidemiology of Obesity: A Big Picture. Pharmacoeconomics 2015, 33, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo-Sanchez, P.; Bril, F.; Maximos, M.; Lomonaco, R.; Biernacki, D.; Orsak, B.; Subbarayan, S.; Webb, A.; Hecht, J.; Cusi, K. High Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Normal Plasma Aminotransferase Levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamnani, G.; Rukadikar, C.; Gupta, V.; Singh, S.; Tiwari, S.; Bhartiy, S.; Sharma, P. Serum magnesium in relation with obesity. Natl. J. Physiol. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Gutiérrez, A.; Sánchez-Pimienta, T.G.; Carriquiry, A.; da Costa, T.H.M.; Ariza, A.C. Higher dietary magnesium intake is associated with lower body mass index, waist circumference and serum glucose in Mexican adults. Nutr. J. 2018, 17, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Moran, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Oral magnesium supplementation improves the metabolic profile of metabolically obese, normal-weight individuals: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, F.H. Magnesium, inflammation, and obesity in chronic disease. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurstjens, S.; van Diepen, J.A.; Overmars-Bos, C.; Alkema, W.; Bindels, R.J.M.; Ashcroft, F.M.; Tack, C.J.J.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; de Baaij, J.H.F. Magnesium deficiency prevents high-fat-diet-induced obesity in mice. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2030–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Leeuw, I.H.; van Gaal, L.; Vanroelen, W. Magnesium and obesity: Effects of treatment on magnesium and other parameters. Magnesium 1987, 6, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Simental-Mendía, M.; Sahebkar, A.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Effect of magnesium supplementation on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 73, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed-Ali, V.; Pinkney, J.H.; Coppack, S.W. Adipose tissue as an endocrine and paracrine organ. Int. J. Obes. 1998, 22, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devaux, S.; Adrian, M.; Laurant, P.; Berthelot, A.; Quignard-Boulangé, A. Dietary magnesium intake alters age-related changes in rat adipose tissue cellularity. Magnes. Res. 2016, 29, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, A.S.; Tousoulis, D. The molecular mechanisms of obesity paradox. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes—Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walti, M.K.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Walczyk, T.; Spinas, G.A.; Hurrell, R.F. Measurement of magnesium absorption and retention in type 2 diabetic patients with the use of stable isotopes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McNair, P.; Christensen, M.S.; Christiansen, C.; Madsbad, S.; Transbøl, I. Renal hypomagnesaemia in human diabetes mellitus: Its relation to glucose homeostasis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1982, 12, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mather, H.M.; Levin, G.E. Magnesium status in diabetes. Lancet 1979, 1, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gommers, L.M.M.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J.M.; de Baaij, J.H.F. Hypomagnesemia in Type 2 Diabetes: A Vicious Circle? Diabetes 2016, 65, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tin, A.; Grams, M.E.; Maruthur, N.M.; Astor, B.C.; Couper, D.; Mosley, T.H.; Selvin, E.; Coresh, J.; Kao, W.H.L. Results from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study suggest that low serum magnesium is associated with incident kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutierrez-Rodelo, C.; Roura-Guiberna, A.; Olivares-Reyes, J.A. Molecular Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance: An Update. Gac. Med. Mex. 2017, 153, 214–228. [Google Scholar]
- Kostov, K. Effects of Magnesium Deficiency on Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: Focusing on the Processes of Insulin Secretion and Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium and aging. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, R.; Wang, H.; Liang, F. Mechanisms Linking Inflammation to Insulin Resistance. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 508409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeel, F.R.; Balon, E.; Scott, S.; Nadler, J.L. Magnesium deficiency and glucose metabolism in rat adipocytes. Metabolism 1996, 45, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, H.; Garg, R. Effect of magnesium supplementation on type 2 diabetes associated cardiovascular risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. Off. J. Br. Diet. Assoc. 2017, 30, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Shankar, R.; Singh, G.P. Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Hypertension: A Cross-Sectional Study in Urban Varanasi. Int. J. Hypertens. 2017, 2017, 5491838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruan, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Z.; Sun, S.; Kowal, P.; Shi, Y.; Wu, F. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) and associated risk factors among older adults in six low-and middle-income countries: Results from SAGE Wave 1. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Virani, S.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Delling, F.N.; Deo, R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 137, e67–e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, W.; McGovern, A.; Coyle, R.; Han, T.S.; Sharma, P.; Correa, A.; Ferreira, F.; de Lusignan, S. Incidence and prevalence of cardiovascular disease in English primary care: A cross-sectional and follow-up study of the Royal College of General Practitioners (RCGP) Research and Surveillance Centre (RSC). BMJ Open 2018, 8, e020282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dibaba, D.T.; Xun, P.; Song, Y.; Rosanoff, A.; Shechter, M.; He, K. The effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure in individuals with insulin resistance, prediabetes, or noncommunicable chronic diseases: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawano, Y.; Matsuoka, H.; Takishita, S.; Omae, T. Effects of magnesium supplementation in hypertensive patients: Assessment by office, home, and ambulatory blood pressures. Hypertension 1998, 32, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.; Odelola, O.A.; Rangaswami, J.; Amanullah, A. A review of nutritional factors in hypertension management. Int. J. Hypertens. 2013, 2013, 698940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangvoraphonkchai, K.; Davenport, A. Magnesium and Cardiovascular Disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efstratiadis, G.; Sarigianni, M.; Gougourelas, I. Hypomagnesemia and cardiovascular system. Hippokratia 2006, 10, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Resnick, L.M.; Militianu, D.; Cunnings, A.J.; Pipe, J.G.; Evelhoch, J.L.; Soulen, R.L. Direct magnetic resonance determination of aortic distensibility in essential hypertension: Relation to age, abdominal visceral fat, and in situ intracellular free magnesium. Hypertension 1997, 30, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Gobbo, L.C.; Song, Y.; Poirier, P.; Dewailly, E.; Elin, R.J.; Egeland, G.M. Low serum magnesium concentrations are associated with a high prevalence of premature ventricular complexes in obese adults with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2012, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DiNicolantonio, J.J.; Liu, J.; O’Keefe, J.H. Magnesium for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. Open Heart 2018, 5, e000775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbagallo, M.; Gupta, R.K.; Resnick, L.M. Cellular ions in NIDDM: Relation of calcium to hyperglycemia and cardiac mass. Diabetes Care 1996, 19, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, M. The role of magnesium in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2011, 13, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayssiguier, Y.; Gueux, E.; Bussière, L.; Durlach, J.; Mazur, A. Dietary magnesium affects susceptibility of lipoproteins and tissues to peroxidation in rats. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1993, 12, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berra-Romani, R.; Guzmán-Silva, A.; Vargaz-Guadarrama, A.; Flores-Alonso, J.C.; Alonso-Romero, J.; Treviño, S.; Sánchez-Gómez, J.; Coyotl-Santiago, N.; García-Carrasco, M.; Moccia, F. Type 2 Diabetes Alters Intracellular Ca(2+) Handling in Native Endothelium of Excised Rat Aorta. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gröber, U.; Schmidt, J.; Kisters, K. Magnesium in Prevention and Therapy. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8199–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Ketteler, M. Magnesium basics. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, i3–i14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolisek, M.; Zsurka, G.; Samaj, J.; Weghuber, J.; Schweyen, R.J.; Schweigel, M. Mrs2p is an essential component of the major electrophoretic Mg2+ influx system in mitochondria. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goytain, A.; Quamme, G.A. Identification and characterization of a novel mammalian Mg2+ transporter with channel-like properties. BMC Genom. 2005, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schlingmann, K.P.; Waldegger, S.; Konrad, M.; Chubanov, V.; Gudermann, T. TRPM6 and TRPM7-Gatekeepers of human magnesium metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2007, 1772, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.S.; Kozlov, G.; Fakih, R.; Funato, Y.; Miki, H.; Gehring, K. The cyclic nucleotide-binding homology domain of the integral membrane protein CNNM mediates dimerization and is required for Mg(2+) efflux activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 19998–20007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuda-Lennikov, M.; Biancalana, M.; Zou, J.; Ravell, J.C.; Zheng, L.; Kanellopoulou, C.; Jiang, P.; Notarangelo, G.; Jing, H.; Masutani, E.; et al. Magnesium transporter 1 (MAGT1) deficiency causes selective defects in N-linked glycosylation and expression of immune-response genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 13638–13656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramoto, T.; Kuwamura, M.; Tokuda, S.; Izawa, T.; Nakane, Y.; Kitada, K.; Akao, M.; Guénet, J.-L.; Serikawa, T. A mutation in the gene encoding mitochondrial Mg2+ channel MRS2 results in demyelination in the rat. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleig, A.; Schweigel-Röntgen, M.; Kolisek, M. Solute carrier family SLC41: What do we really know about it? Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Membr. Transp. Signal. 2013, 2, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simón, J.; Delgado, T.C.; Martinez-Cruz, L.A.; Martínez-Chantar, M.L. Magnesium, Little Known But Possibly Relevant: A Link between NASH and Related Comorbidities. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020125
Simón J, Delgado TC, Martinez-Cruz LA, Martínez-Chantar ML. Magnesium, Little Known But Possibly Relevant: A Link between NASH and Related Comorbidities. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(2):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020125
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimón, Jorge, Teresa Cardoso Delgado, Luis Alfonso Martinez-Cruz, and Maria Luz Martínez-Chantar. 2021. "Magnesium, Little Known But Possibly Relevant: A Link between NASH and Related Comorbidities" Biomedicines 9, no. 2: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020125
APA StyleSimón, J., Delgado, T. C., Martinez-Cruz, L. A., & Martínez-Chantar, M. L. (2021). Magnesium, Little Known But Possibly Relevant: A Link between NASH and Related Comorbidities. Biomedicines, 9(2), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020125