Targeting of Protein Kinase CK2 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Using the Clinical-Grade Synthetic-Peptide CIGB-300
Abstract
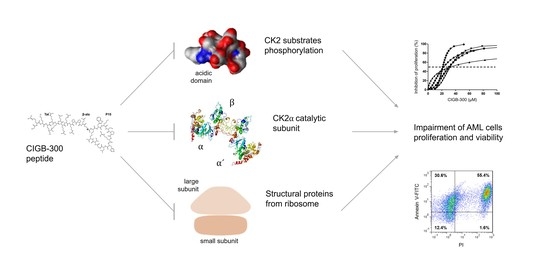
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Patient Samples
2.3. AlamarBlue Assay
2.4. Annexin V/PI Staining
2.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.6. Peptide Internalization and Confocal Microscopy
2.7. Lentiviral Infection
2.8. Pull-Down Experiments
2.9. Western Blot
2.10. Protein Identification by LC-MS/MS
2.11. Phophoproteomic Analysis
2.12. Data Processing and Bioinformatics
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Inhibition of CK2 Impairs AML Cells Proliferation and Viability
3.2. Internalization and Subcellular Distribution of CIGB-300
3.3. Profiling CIGB-300 Interactome in AML Cells
3.4. NPM1 Is Not a Major Target for CIGB-300 in AML Cells
3.5. CIGB-300 Regulates the CK2-Dependent Phosphoproteome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Döhner, H.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Bloomfield, C.D. Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1136–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saultz, J.N.; Garzon, R. Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Concise Review. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilliland, D.G.; Griffin, J.D. The roles of FLT3 in hematopoiesis and leukemia. Blood 2002, 100, 1532–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorentini, A.; Capelli, D.; Saraceni, F.; Menotti, D.; Poloni, A.; Olivieri, A. The Time Has Come for Targeted Therapies for AML: Lights and Shadows. Oncol. Ther. 2020, 8, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kopmar, N.E.; Estey, E.H. New drug approvals in acute myeloid leukemia: An unprecedented paradigm shift. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 17, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cucchi, D.G.J.; Polak, T.B.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Groot, C.A.U.; Cloos, J.; Zweegman, S.; Janssen, J.J.W.M. Two decades of targeted therapies in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2021, 35, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, K.; Minami, Y. Cutting Edge Molecular Therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buontempo, F.; McCubrey, J.A.; Orsini, E.; Ruzzene, M.; Cappellini, A.; Lonetti, A.; Evangelisti, C.; Chiarini, F.; Barata, J.T.; Martelli, A.M. Therapeutic targeting of CK2 in acute and chronic leukemias. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aasebø, E.; Berven, F.S.; Hovland, R.; Døskeland, S.O.; Bruserud, Ø.; Selheim, F.; Hernandez-Valladares, M. The Progression of Acute Myeloid Leukemia from First Diagnosis to Chemoresistant Relapse: A Comparison of Proteomic and Phosphoproteomic Profiles. Cancers 2020, 12, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasebø, E.; Berven, F.S.; Bartaula-Brevik, S.; Stokowy, T.; Hovland, R.; Vaudel, M.; Døskeland, S.O.; Mc Cormack, E.; Batth, T.S.; Olsen, J.V.; et al. Proteome and Phosphoproteome Changes Associated with Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2020, 12, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klink, M.; Rahman, M.; Song, C.; Dhanyamraju, P.; Ehudin, M.; Ding, Y.; Steffens, S.; Bhadauria, P.; Iyer, S.; Aliaga, C.; et al. Mechanistic Basis for In Vivo Therapeutic Efficacy of CK2 Inhibitor CX-4945 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, L.A.; Meggio, F. Protein kinase CK2 (“casein kinase-2”) and its implication in cell division and proliferation. Prog. Cell Cycle Res. 1997, 3, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Villavicencio-Diaz, T.N.; Rabalski, A.J.; Litchfield, D.W. Protein Kinase CK2: Intricate Relationships within Regulatory Cellular Networks. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litchfield, D.W. Protein kinase CK2: Structure, regulation and role in cellular decisions of life and death. Biochem. J. 2003, 369, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, O.; Meggio, F.; Marchiori, F.; Borin, G.; Pinna, L.A. Site specificity of casein kinase-2 (TS) from rat liver cytosol. A study with model peptide substrates. Eur. J. Biochem. 1986, 160, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, M.; Sarno, S.; Cesaro, L.; Nakamura, H.; Pinna, L.A. Extraordinary pleiotropy of protein kinase CK2 revealed by weblogo phosphoproteome analysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Bioenergy 2009, 1793, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, O.; Meggio, F.; Draetta, G.; Pinna, L.A. The consensus sequences for cdc2 kinase and for casein kinase-2 are mutually incompatible A study with peptides derived from the β-subunit of casein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1992, 301, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meggio, F.; Pinna, L.A. One-thousand-and-one substrates of protein kinase CK2? FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2003, 17, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castello, J.; Ragnauth, A.; Friedman, E.; Rebholz, H. CK2—An Emerging Target for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- St-Denis, N.A.; Litchfield, D.W. Protein kinase CK2 in health and disease: From birth to death: The role of protein kinase CK2 in the regulation of cell proliferation and survival. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2009, 66, 1817–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trembley, J.; Wang, G.; Unger, G.; Slaton, J.; Ahmed, K. Protein kinase CK2 in health and disease: CK2: A key player in cancer biology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2009, 66, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.S.; Eom, J.I.; Cheong, J.-W.; Choi, A.J.; Lee, J.K.; Yang, W.I.; Min, Y.H. Protein Kinase CK2α as an Unfavorable Prognostic Marker and Novel Therapeutic Target in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piazza, F.; Manni, S.; Ruzzene, M.; Pinna, L.A.; Gurrieri, C.; Semenzato, G. Protein kinase CK2 in hematologic malignancies: Reliance on a pivotal cell survival regulator by oncogenic signaling pathways. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prins, R.C.; Burke, R.T.; Tyner, J.W.; Druker, B.; Loriaux, M.M.; E Spurgeon, S. CX-4945, a selective inhibitor of casein kinase-2 (CK2), exhibits anti-tumor activity in hematologic malignancies including enhanced activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia when combined with fludarabine and inhibitors of the B-cell receptor pathway. Leukemia 2013, 27, 2094–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zakharia, K.; Miyabe, K.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Moser, C.D.; Borad, M.J.; Roberts, L.R. Preclinical In Vitro and In Vivo Evidence of an Antitumor Effect of CX-4945, a Casein Kinase II Inhibitor, in Cholangiocarcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, S.E.; Baladrón, I.; Valenzuela, C.; Perera, Y. CIGB-300: A peptide-based drug that impairs the Protein Kinase CK2-mediated phosphorylation. Semin. Oncol. 2018, 45, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Drygin, D.; Streiner, N.; Chua, P.; Pierre, F.; O’Brien, S.E.; Bliesath, J.; Omori, M.; Huser, N.; Ho, C.; et al. CX-4945, an Orally Bioavailable Selective Inhibitor of Protein Kinase CK2, Inhibits Prosurvival and Angiogenic Signaling and Exhibits Antitumor Efficacy. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 10288–10298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marschke, R.F.; Borad, M.J.; McFarland, R.W.; Alvarez, R.H.; Lim, J.K.; Padgett, C.S.; Von Hoff, D.D.; O’Brien, S.E.; Northfelt, D.W. Findings from the phase I clinical trials of CX-4945, an orally available inhibitor of CK. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borad, M.J.; Bai, L.-Y.; Chen, M.-H.; Hubbard, J.M.; Mody, K.; Rha, S.Y.; Richards, D.A.; Davis, S.L.; Soong, J.; Huang, C.-E.C.-E.; et al. Silmitasertib (CX-4945) in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin as first-line treatment for patients with locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma: A phase Ib/II study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea, S.E.; Reyes, O.; Puchades, Y.; Mendoza, O.; Vispo, N.; Torrens, I.; Santos, A.; Silva, R.; Acevedo, B.; López, E.; et al. Antitumor Effect of a Novel Proapoptotic Peptide that Impairs the Phosphorylation by the Protein Kinase 2 (Casein Kinase 2). Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7127–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perera, Y.; Farina, H.G.; Gil, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Benavent, F.; Castellanos, L.; Gómez, R.E.; Acevedo, B.E.; Alonso, D.F.; Perea, S.E. Anticancer peptide CIGB-300 binds to nucleophosmin/B23, impairs its CK2-mediated phosphorylation, and leads to apoptosis through its nucleolar disassembly activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perera, Y.; Costales, H.C.; Diaz, Y.; Reyes, O.; Farina, H.G.; Mendez, L.; Gómez, R.E.; Acevedo, B.E.; Gomez, D.E.; Alonso, D.F.; et al. Sensitivity of tumor cells towards CIGB-300 anticancer peptide relies on its nucleolar localization. J. Pept. Sci. Off. Publ. Eur. Pept. Soc. 2012, 18, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, Y.; Ramos, Y.; Padrón, G.; Caballero, E.; Guirola, O.; Caligiuri, L.G.; Lorenzo, N.; Gottardo, F.; Farina, H.G.; Filhol, O.; et al. CIGB-300 anticancer peptide regulates the protein kinase CK2-dependent phosphoproteome. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 470, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, Y.; Melão, A.; Ramón, A.C.; Vázquez, D.; Ribeiro, D.; Perea, S.E.; Barata, J.T. Clinical-Grade Peptide-Based Inhibition of CK2 Blocks Viability and Proliferation of T-ALL Cells and Counteracts IL-7 Stimulation and Stromal Support. Cancers 2020, 12, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, Y.; Farina, H.G.; Hernández, I.; Mendoza, O.; Serrano, J.M.; Reyes, O.; Gómez, D.E.; Gómez, R.E.; Acevedo, B.E.; Alonso, D.F.; et al. Systemic administration of a peptide that impairs the protein kinase (CK2) phosphorylation reduces solid tumor growth in mice. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 122, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, S.E.; Reyes, O.; Baladrón, I.; Perera, Y.; Farina, H.; Gil, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Bacardí, D.; Marcelo, J.L.; Cosme, K.; et al. CIGB-300, a novel proapoptotic peptide that impairs the CK2 phosphorylation and exhibits anticancer properties both in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 316, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solares, A.M.; Santana, A.; Baladrón, I.; Valenzuela, C.; González, C.A.; Díaz, A.; Castillo, D.; Ramos, T.; Gómez, R.; Alonso, D.F.; et al. Safety and preliminary efficacy data of a novel Casein Kinase 2 (CK2) peptide inhibitor administered intralesionally at four dose levels in patients with cervical malignancies. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soriano-García, J.L.; López-Díaz, A.; Solares-Asteasuainzarra, M.; Baladrón-Castrillo, I.; Batista-Albuerne, N.; García-García, I.; González-Méndez, L.; Perera-Negrín, Y.; Valenzuela-Silva, C.M.; Pedro, A.P.; et al. Pharmacological and safety evaluation of CIGB-300, a casein kinase 2 inhibitor peptide, administered intralesionally to patients with cervical cancer stage IB2/II. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2013, 1, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarduy, M.R.; García, I.; Coca, M.A.; Perera, A.; Torres, L.A.; Valenzuela, C.M.; Baladrón, I.; Solares, M.; Reyes, V.; Hernández, I.; et al. Optimizing CIGB-300 intralesional delivery in locally advanced cervical cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Diegues, R.; de la Torre-Santos, A. Phase I Study of CIGB-300 Administered Intravenously in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Solid Tumors. Arch. Med. 2018, 1, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, H.; Li, D.; Zhou, Y.; Landesman-Bollag, E.; Zhang, G.; Anderson, N.M.; Tang, K.C.; Roderick, J.E.; Kelliher, M.A.; Seldin, D.C.; et al. CK2 inhibitor CX-4945 destabilizes NOTCH1 and synergizes with JQ1 against human T-acute lymphoblastic leukemic cells. Haematologica 2016, 102, e17–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tubi, L.Q.; Nunes, S.C.; Brancalion, A.; Breatta, E.D.; Manni, S.; Mandato, E.; Zaffino, F.; Macaccaro, P.; Carrino, M.; Gianesin, K.; et al. Protein kinase CK2 regulates AKT, NF-κB and STAT3 activation, stem cell viability and proliferation in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubi, L.Q.; Gurrieri, C.; Brancalion, A.; Bonaldi, L.; Bertorelle, R.; Manni, S.; Pavan, L.; Lessi, F.; Zambello, R.; Trentin, L.; et al. Inhibition of protein kinase CK2 with the clinical-grade small ATP-competitive compound CX-4945 or by RNA interference unveils its role in acute myeloid leukemia cell survival, p53-dependent apoptosis and daunorubicin-induced cytotoxicity. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martins, L.R.; Perera, Y.; Lucio, P.; da Silva, M.G.; Perea, S.E.; Barata, J.T. Targeting chronic lymphocytic leukemia using CIGB-300, a clinical-stage CK2-specific cell-permeable peptide inhibitor. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Doherty, U.; Swiggard, W.J.; Malim, M.H. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Spinoculation Enhances Infection through Virus Binding. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10074–10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lachmann, A.; Ma’Ayan, A. KEA: Kinase enrichment analysis. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Arighi, C.N.; Ross, K.E.; Ren, J.; Julie, C.; Chen, S.-C.; Wang, Q.; Cowart, J.; Vijay-Shanker, K.; Wu, C.H. iPTMnet: An integrated resource for protein post-translational modification network discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, M.; Rodríguez-Ulloa, A.; Besada, V.; Ramón, A.C.; Pérez, G.V.; Ramos, Y.; Guirola, O.; González, L.J.; Zettl, K.; Wiśniewski, J.R.; et al. Phosphoproteomic Landscape of AML Cells Treated with the ATP-Competitive CK2 Inhibitor CX-4945. Cells 2021, 10, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Mann, M. Consecutive Proteolytic Digestion in an Enzyme Reactor Increases Depth of Proteomic and Phosphoproteomic Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2631–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.; Hein, M.; Luber, C.A.; Paron, I.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Accurate Proteome-wide Label-free Quantification by Delayed Normalization and Maximal Peptide Ratio Extraction, Termed MaxLFQ. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 2513–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linding, R.; Jensen, L.J.; Pasculescu, A.; Olhovsky, M.; Colwill, K.; Bork, P.; Yaffe, M.B.; Pawson, T. NetworKIN: A resource for exploring cellular phosphorylation networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 36, D695–D699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bian, Y.; Ye, M.; Wang, C.; Cheng, K.; Song, C.; Dong, M.; Pan, Y.; Qin, H.; Zou, H. Global Screening of CK2 Kinase Substrates by an Integrated Phosphoproteomics Workflow. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Cho, B.S.; Kim, H.-J. New agents in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood Res. 2020, 55, S14–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzzene, M.; Pinna, L.A. Addiction to protein kinase CK2: A common denominator of diverse cancer cells? Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Proteins Proteom. 2010, 1804, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.A.; Alkan, S. Acute Leukemias and Myelodysplastic Syndromes. In Clinical Laboratory Medicine, 2nd ed.; McClatchey, K.D., Ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002; p. 909. [Google Scholar]
- Rabalski, A.J.; Gyenis, L.; Litchfield, D.W. Molecular Pathways: Emergence of Protein Kinase CK2 (CSNK2) as a Potential Target to Inhibit Survival and DNA Damage Response and Repair Pathways in Cancer Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2840–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spiliotis, E.T.; Kinoshita, M.; Nelson, W.J. A Mitotic Septin Scaffold Required for Mammalian Chromosome Congression and Segregation. Science 2005, 307, 1781–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.; Ding, X.; Chen, F.; Liu, M.; Shen, S.; Gu, X.; Yu, L. The phosphorylation of SEPT2 on Ser218 by casein kinase 2 is important to hepatoma carcinoma cell proliferation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 325, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M. The MCM Complex: Its Role in DNA Replication and Implications for Cancer Therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2005, 5, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, T.; Ficarro, S.B.; Jiang, W. Essential Role of Phosphorylation of MCM2 by Cdc7/Dbf4 in the Initiation of DNA Replication in Mammalian Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 4459–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasof, G.M.; Goyal, L.; White, E. Btf, a Novel Death-Promoting Transcriptional Repressor That Interacts with Bcl-2-Related Proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 4390–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mou, S.-J.; Yang, P.-F.; Liu, Y.-P.; Xu, N.; Jiang, W.-W.; Yue, W.-J. BCLAF1 promotes cell proliferation, invasion and drug-resistance though targeting lncRNA NEAT1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Life Sci. 2020, 242, 117177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.S.Y.; Kranzusch, P.J.; Cate, J.H.D. eIF3 targets cell-proliferation messenger RNAs for translational activation or repression. Nature 2015, 522, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.; Bernstein, D.A.; Mumbach, M.R.; Jovanovic, M.; Herbst, R.H.; León-Ricardo, B.X.; Engreitz, J.M.; Guttman, M.; Satija, R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Transcriptome-wide Mapping Reveals Widespread Dynamic-Regulated Pseudouridylation of ncRNA and mRNA. Cell 2014, 159, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Box, J.K.; Paquet, N.; Adams, M.N.; Boucher, D.; Bolderson, E.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Richard, D.J. Nucleophosmin: From structure and function to disease development. BMC Mol. Biol. 2016, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| HL-60 Cells | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK2 Substrates | Sequence Window (31 Amino Acids) | Occupancy | ||
| Protein | Gene Name | Phosphosite | Treated–Control | |
| Q8NE71 | ABCF1 | S140 | KTKGGNVFAALIQDQSEEEEEEEKHPPKPAK | −0.26934 2 |
| O00203 | AP3B1 | S276 | KEGDELEDNGKNFYESDDDQKEKTDKKKKPY | −0.42700 |
| Q9NYF8 | BCLAF1 | S397 | DYFSDKESGKQKFNDSEGDDTEETEDYRQFR | −0.29015 1 |
| Q8N6N3 | C1orf52 | S158 | AKKARLLPEGEETLESDDEKDEHTSKKRKVE | −0.36448 |
| Q9GZR7 | DDX24 | S82 | SLFSKEAPKRKAQAVSEEEEEEEGKSSSPKK | −0.32842 |
| O60832 | DKC1 | S485 | KKKSKKDKKAKAGLESGAEPGDGDSDTTKKK | −0.37766 |
| O60832 | DKC1 | S494 | AKAGLESGAEPGDGDSDTTKKKKKKKKAKEV | −0.33120 1 |
| Q99613 | EIF3C | S39 | TKPVGGNYGKQPLLLSEDEEDTKRVVRSAKD | −0.27378 2 |
| Q04637 | EIF4G1 | S1198 | REAALPPVSPLKAALSEEELEKKSKAIIEEY | −0.27602 |
| Q5T1M5 | FKBP15 | S346 | IPFKSGEPALRTKSNSLSEQLAINTSPDAVK | −0.25002 |
| Q9BW71 | HIRIP3 | S196 | APGKASVSRKQAREESEESEAEPVQRTAKKV | −0.28420 |
| Q9BW71 | HIRIP3 | S199 | KASVSRKQAREESEESEAEPVQRTAKKVEGN | −0.26487 |
| P17096 | HMGA1 | S44 | PRKQPPVSPGTALVGSQKEPSEVPTPKRPRG | −0.31768 |
| Q9Y2U8 | LEMD3 | S144 | PAAGSKVLLGFSSDESDVEASPRDQAGGGGR | −0.32523 |
| P07948 | LYN | S13 | ___MGCIKSKGKDSLSDDGVDLKTQPVRNTE | −0.39875 |
| P20645 | M6PR | S267 | PAAYRGVGDDQLGEESEERDDHLLPM_____ | −0.25999 |
| P49736 | MCM2 | S41 | SSPGRSSRRTDALTSSPGRDLPPFEDESEGL | −0.42099 2 |
| Q99733 | NAP1L4 | S125 | ITGDVEPTDAESEWHSENEEEEKLAGDMKSK | −0.33982 |
| P19338 | NCL | S580 | NARSQPSKTLFVKGLSEDTTEETLKESFDGS | −0.56758 |
| Q9Y266 | NUDC | T145 | AQLKNGSLDSPGKQDTEEDEEEDEKDKGKLK | −0.65068 |
| P11940 | PABPC1 | T319 | GIDDERLRKEFSPFGTITSAKVMMEGGRSKG | −0.29314 |
| Q13177 | PAK2 | T169 | TPALNAKGTEAPAVVTEEEDDDEETAPPVIA | −0.29629 |
| Q9H307 | PNN | S381 | MEEETEVRESEKQQDSQPEEVMDVLEMVENV | −0.29978 |
| P41236 | PPP1R2 | S121 | AAEGLEPKYRIQEQESSGEEDSDLSPEEREK | −0.41242 2 |
| P41236 | PPP1R2 | S122 | AEGLEPKYRIQEQESSGEEDSDLSPEEREKK | −0.41242 2 |
| Q15019 | SEPTIN2 | S218 | IEEHNIKIYHLPDAESDEDEDFKEQTRLLKA | −0.26771 1, 2 |
| Q05519 | SRSF11 | S464 | SPKTKECSVEKGTGDSLRESKVNGDDHHEED | −0.33007 |
| P50502 | ST13 | S75 | KPDSKVEEDLKADEPSSEESDLEIDKEGVIE | −0.28517 |
| P16949 | STMN1 | S63 | EEIQKKLEAAEERRKSHEAEVLKQLAEKREH | −0.33565 2 |
| Q9Y2W1 | THRAP3 | S211 | NQGDEAKEQTFSGGTSQDTKASESSKPWPDA | −0.29138 |
| P42166 | TMPO | S66 | PPLPAGTNSKGPPDFSSDEEREPTPVLGSGA | −0.48358 |
| P42166 | TMPO | S67 | PLPAGTNSKGPPDFSSDEEREPTPVLGSGAA | −0.48358 |
| P11388 | TOP2A | S1106 | KEAQQKVPDEEENEESDNEKETEKSDSVTDS | −0.28536 |
| P12956 | XRCC6 | S520 | DLTLPKVEAMNKRLGSLVDEFKELVYPPDYN | −0.37632 |
| OCI-AML3 Cells | ||||
| CK2 substrates | Sequence Window (31 Amino Acids) | Occupancy | ||
| Protein | Gene Name | Phosphosite | Treated–Control | |
| Q9NYF8 | BCLAF1 | S397 | DYFSDKESGKQKFNDSEGDDTEETEDYRQFR | −0.30557 1 |
| P38398 | BRCA1 | S1164 | TPDDLLDDGEIKEDTSFAENDIKESSAVFSK | −0.39325 |
| Q5SW79 | CEP170 | S1112 | PTRTSLLRRARLGEASDSELADADKASVASE | −0.43657 |
| O60832 | DKC1 | S494 | AKAGLESGAEPGDGDSDTTKKKKKKKKAKEV | −0.29482 1 |
| O60841 | EIF5B | S214 | GQKKNQKNKPGPNIESGNEDDDASFKIKTVA | −0.28682 |
| P07910 | HNRNPC | S220 | EKEQSKQAVEMKNDKSEEEQSSSSVKKDETN | −0.46978 |
| P07910 | HNRNPC | S225 | KQAVEMKNDKSEEEQSSSSVKKDETNVKMES | −0.45974 |
| P49736 | MCM2 | S13 | ___MAESSESFTMASSPAQRRRGNDPLTSSP | −0.40609 2 |
| P49736 | MCM2 | S139 | AGRGLGRMRRGLLYDSDEEDEERPARKRRQV | −0.34224 2 |
| Q99733 | NAP1L4 | S7 | _________MADHSFSDGVPSDSVEAAKNAS | −0.27194 |
| O00567 | NOP56 | S520 | KPKKKKSFSKEELMSSDLEETAGSTSIPKRK | −0.37049 |
| Q15019 | SEPTIN2 | S218 | IEEHNIKIYHLPDAESDEDEDFKEQTRLLKA | −0.42615 1, 2 |
| Q05519 | SRSF11 | S433 | VKVTRDYDEEEQGYDSEKEKKEEKKPIETGS | −0.37940 |
| Q8TCJ2 | STT3B | S499 | LGDDMKRENPPVEDSSDEDDKRNQGNLYDKA | −0.34446 |
| P11388 | TOP2A | S1247 | EKKNKKKIKNENTEGSPQEDGVELEGLKQRL | −0.33514 |
| Q02880 | TOP2B | S1550 | TTPKGKGRGAKKRKASGSENEGDYNPGRKTS | −0.29360 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosales, M.; Pérez, G.V.; Ramón, A.C.; Cruz, Y.; Rodríguez-Ulloa, A.; Besada, V.; Ramos, Y.; Vázquez-Blomquist, D.; Caballero, E.; Aguilar, D.; et al. Targeting of Protein Kinase CK2 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Using the Clinical-Grade Synthetic-Peptide CIGB-300. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070766
Rosales M, Pérez GV, Ramón AC, Cruz Y, Rodríguez-Ulloa A, Besada V, Ramos Y, Vázquez-Blomquist D, Caballero E, Aguilar D, et al. Targeting of Protein Kinase CK2 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Using the Clinical-Grade Synthetic-Peptide CIGB-300. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(7):766. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070766
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosales, Mauro, George V. Pérez, Ailyn C. Ramón, Yiliam Cruz, Arielis Rodríguez-Ulloa, Vladimir Besada, Yassel Ramos, Dania Vázquez-Blomquist, Evelin Caballero, Daylen Aguilar, and et al. 2021. "Targeting of Protein Kinase CK2 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Using the Clinical-Grade Synthetic-Peptide CIGB-300" Biomedicines 9, no. 7: 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070766
APA StyleRosales, M., Pérez, G. V., Ramón, A. C., Cruz, Y., Rodríguez-Ulloa, A., Besada, V., Ramos, Y., Vázquez-Blomquist, D., Caballero, E., Aguilar, D., González, L. J., Zettl, K., Wiśniewski, J. R., Yang, K., Perera, Y., & Perea, S. E. (2021). Targeting of Protein Kinase CK2 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Using the Clinical-Grade Synthetic-Peptide CIGB-300. Biomedicines, 9(7), 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070766