The Impact of Nutritional and Lifestyle Changes on Body Weight, Body Composition and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents during the Pandemic of COVID-19: A Systematic Review
Abstract
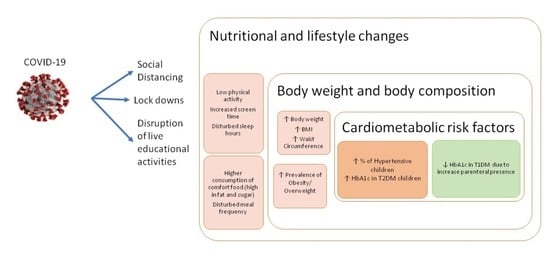
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Selection of Studies and Data Extraction
2.4. Risk of Bias
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
3.2. Main Exposures
3.3. Studies on the Association of Diet and/or Lifestyle Changes on Body Weight/Body Composition
3.4. Studies on the Association of Diet and/or Lifestyle Changes on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO: Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 9 November 2021).
- Ammar, A.; Brach, M.; Trabelsi, K.; Chtourou, H.; Bukhari’s, O.; Masmoudi, L.; Bouaziz, B.; Bentlage, E.; How, D.; Ahmed, M.; et al. Effects of COVID-19 Home Confinement on Eating Behaviour and Physical Activity: Results of the ECLB-COVID19 International Online Survey. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, P.; Luo, M.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J.S.; Xiao, Q.; Luo, J. Fast-food restaurant, unhealthy eating, and childhood obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e12944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baranowski, T.; O’Connor, T.; Johnston, C.; Hughes, S.; Moreno, J.; Chen, T.A.; Meltzer, L.; Baranowski, J. School year versus summer differences in child weight gain: A narrative review. Child. Obes. 2014, 10, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, L.; Gualtieri, P.; Pivari, F.; Soldati, L.; Attinà, A.; Cinelli, G.; Leggeri, C.; Caparello, G.; Barrea, L.; Scerbo, F.; et al. Eating habits and lifestyle changes during COVID-19 lockdown: An Italian survey. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, N.T.; Snethen, J.A.; Greenberg, C.S.; Frenn, M.; Kilanowski, J.F.; Gance-Cleveland, B.; Burke, P.J.; Lewandowski, L. When Pandemics Collide: The Impact of COVID-19 on Childhood Obesity. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2021, 56, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD; WHO. Overweight and Obesity. In Health at a Glance: Asia/Pacific 2020: Measuring Progress Towards Universal Health Coverage; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nogueira-de-Almeida, C.A.; Del Ciampo, L.A.; Ferraz, I.S.; Del Ciampo, I.R.L.; Contini, A.A.; Ued, F.D.V. COVID-19 and obesity in childhood and adolescence: A clinical review. J. Pediatr. 2020, 96, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.T.; Kaelber, D.C.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Blowey, D.; Carroll, A.E.; Daniels, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Dionne, J.M.; Falkner, B.; Flinn, S.K.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20171904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deeb, A.; Attia, S.; Mahmoud, S.; Elhaj, G.; Elfatih, A. Dyslipidemia and Fatty Liver Disease in Overweight and Obese Children. J. Obes. 2018, 2018, 8626818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pulgaron, E.R.; Delamater, A.M. Obesity and type 2 diabetes in children: Epidemiology and treatment. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2014, 14, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Androutsos, O.; Perperidi, M.; Georgiou, C.; Chouliaras, G. Lifestyle Changes and Determinants of Children’s and Adolescents’ Body Weight Increase during the First COVID-19 Lockdown in Greece: The COV-EAT Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Guo, B.; Ao, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Jia, P. Obesity and activity patterns before and during COVID-19 lockdown among youths in China. Clin. Obes. 2020, 10, e12416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.; He, H.; Qiao, L.; Ding, Y.; Ji, S.; Guo, X.; Luo, J.; Luo, Z.; Li, Y.; Pang, H.; et al. Sex differences in changes in BMI and blood pressure in Chinese school-aged children during the COVID-19 quarantine. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 2132–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltoni, G.; Zioutas, M.; Deiana, G.; Biserni, G.B.; Pession, A.; Zucchini, S. Gender differences in weight gain during lockdown due to COVID-19 pandemic in adolescents with obesity. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 2181–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hourani, H.; Alkhatib, B.; Abdullah, M. Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Body Weight, Eating Habits, and Physical Activity of Jordanian Children and Adolescents. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 2021, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujia, R.; Ferro, Y.; Maurotti, S.; Khoory, J.; Gazzaruso, C.; Pujia, A.; Montalcini, T.; Mazza, E. The Effects of COVID-19 on the Eating Habits of Children and Adolescents in Italy: A Pilot Survey Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipolla, C.; Curatola, A.; Ferretti, S.; Giugno, G.; Condemi, C.; Delogu, A.B.; Birritella, L.; Lazzareschi, I. Eating habits and lifestyle in children with obesity during the COVID19 lockdown: A survey in an Italian center. Acta Biomed. 2021, 92, e2021196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Łuszczki, E.; Bartosiewicz, A.; Pezdan-Śliż, I.; Kuchciak, M.; Jagielski, P.; Oleksy, Ł.; Stolarczyk, A.; Dereń, K. Children’s Eating Habits, Physical Activity, Sleep, and Media Usage before and during COVID-19 Pandemic in Poland. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano, M.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Oses, M.; Arenaza, L.; Amasene, M.; Labayen, I. Changes in lifestyle behaviours during the COVID-19 confinement in Spanish children: A longitudinal analysis from the MUGI project. Pediatr. Obes. 2021, 16, e12731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletzko, B.; Holzapfel, C.; Schneider, U.; Hauner, H. Lifestyle and Body Weight Consequences of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Children: Increasing Disparity. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 77, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minuto, N.; Bassi, M.; Montobbio, C.; Vinci, F.; Mercuri, C.; Perri, F.N.; Cabri, M.; Calevo, M.G.; d’Annunzio, G.; Maghnie, M. The Effect of Lockdown and Physical Activity on Glycemic Control in Italian Children and Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 690222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.P.; Wong, J.S.L.; Selveindran, N.M.; Hong, J.Y.H. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on glycaemic control and lifestyle changes in children and adolescents with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 2021, 73, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Luo, S.; Zheng, X.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S.; Ling, P.; Yue, T.; Xu, W.; Yan, J.; Weng, J. Glycemic control in children and teenagers with type 1 diabetes around lockdown for COVID-19: A continuous glucose monitoring-based observational study. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 1708–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Agha, A.E.; Alharbi, R.S.; Almohammadi, O.A.; Yousef, S.Y.; Sulimani, A.E.; Alaama, R.A. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on glycemic control in children and adolescents. Saudi Med. J. 2021, 42, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, H.; Güneş Kaya, D.; Tarçın, G.; Evliyaoğlu, S.O. Effect of the COVID-19 quarantine on metabolic control in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinker-Shuster, M.; Grossman, E.S.; Yeshayahu, Y. Increased Weight Gain of Children during the COVID-19 Lockdown. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2021, 23, 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Marigliano, M.; Maffeis, C. Glycemic control of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes improved after COVID-19 lockdown in Italy. Acta Diabetol. 2021, 58, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Roso, M.B.; de Carvalho Padilha, P.; Matilla-Escalante, D.C.; Brun, P.; Ulloa, N.; Acevedo-Correa, D.; Arantes Ferreira Peres, W.; Martorell, M.; Rangel Bousquet Carrilho, T.; de Oliveira Cardoso, L.; et al. Changes of Physical Activity and Ultra-Processed Food Consumption in Adolescents from Different Countries during Covid-19 Pandemic: An Observational Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrobelli, A.; Pecoraro, L.; Ferruzzi, A.; Heo, M.; Faith, M.; Zoller, T.; Antoniazzi, F.; Piacentini, G.; Fearnbach, S.N.; Heymsfield, S.B. Effects of COVID-19 Lockdown on Lifestyle Behaviors in Children with Obesity Living in Verona, Italy: A Longitudinal Study. Obesity 2020, 28, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Martínez, A.; Bosque-Prous, M.; González-Casals, H.; Colillas-Malet, E.; Puigcorbé, S.; Esquius, L.; Espelt, A. Social Inequalities in Changes in Diet in Adolescents during Confinement Due to COVID-19 in Spain: The DESKcohort Project. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boone, J.E.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Adair, L.S.; Popkin, B.M. Screen time and physical activity during adolescence: Longitudinal effects on obesity in young adulthood. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2007, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bates, L.C.; Zieff, G.; Stanford, K.; Moore, J.B.; Kerr, Z.Y.; Hanson, E.D.; Barone Gibbs, B.; Kline, C.E.; Stoner, L. COVID-19 Impact on Behaviors across the 24-Hour Day in Children and Adolescents: Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, and Sleep. Children 2020, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paruthi, S.; Brooks, L.J.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Hall, W.A.; Kotagal, S.; Lloyd, R.M.; Malow, B.A.; Maski, K.; Nichols, C.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Recommended Amount of Sleep for Pediatric Populations: A Consensus Statement of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO: Prevalence of Insufficient Physical Activity. Global Health Observatory (GHO) Data. Available online: https://www.who.int/gho/ncd/risk_factors/physical_activity_text/en/ (accessed on 9 November 2021).
- Atkin, A.J.; Sharp, S.J.; Corder, K.; van Sluijs, E.M. Prevalence and correlates of screen time in youth: An international perspective. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 47, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grosso, G.; Galvano, F. Mediterranean diet adherence in children and adolescents in southern European countries. NFS J. 2016, 3, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Identity | Country | Study Design | Participants (N) | Age Range (Years) | Diet Assessment | Lifestyle Assessment | Anthropometry and Body Composition Assessment | Outcome in Diet and Lifestyle | Outcome in Body Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Androutsos et al., 2021 [14] | Greece | Cross sectional Online survey | 397 | 2–18 | Questionnaire for the dietary habits of parents and children | Questionnaire on Sleep duration Screen time and Physical activity | Self-reported weight and height | ↑ sleep duration ↑ screen time ↓ physical activity ↓ fast food ↑ fruit and vegetables ↑ breakfast | ↑ Body weight in 35% of the participants |
| Yang et al., 2020 [15] | China | Retrospective study | 10,082 | 16–18 | N/A | Physical activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) long form | Self-reported weight and Height BMI | ↓ physical activity frequency and intensity ↑ screen time | ↑ BMI ↑ % Overweight/Obesity |
| Qiu et al., 2021 [16] | China | Cohort study | 445 | 7–12 | Questionnaire on diet | Questionnaires on lifestyle | Measured weight and Height | N/A | ↑ % Overweight/Obesity |
| Maltoni et al., 2021 [17] | Italy | Cross sectional | 51 | 10–18 | Questionnaire on nutrition | Physical activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) sort form | Measured weight and Height Waist circumference | ↑ Sedentary behavior ↓ Physical activity | ↑ BMI ↑ Waist circumference ↑ Weight ↑ Weight/height ratio |
| Al Hourani et al., 2021 [18] | Jordan | Cross sectional | 477 | 6–17 | FFQ | Questionnaire on Screen time and Physical activity | Self-reported weight and height BMI for age Z scores | ↑ Screen time ↑ Sedentary ↑Dietary intake | ↑ BMI for age Z score ↑ Body Weight |
| Pujia et al., 2021 [19] | Italy | Cross sectional Online survey | 439 | 5–14 | Questionnaire on eating habits | Questionnaire on physical activity | Self-reported weight and height BMI | ↑ Comfort food intake (chocolate, sweet snacks, and deserts ↑ pizza and bakery products ↓ sweetened beverages and candies ↑ sedentary lifestyle in adolescents | ↑ Body Weight in 59.7% of the participants ↑ BMI |
| Cipolla et al., 2021 [20] | Italy | Cross sectional Telephone interview | 64 | 8–18 | Questionnaire on eating habits | Questionnaire on physical activity | Measured weight and height | ↑ pizza and bakery products ↑ sedentary lifestyle ↑ Screen time | ↑ BMI |
| Łuszczki et al., 2021 [21] | Poland | Cross sectional | 1016 | 6–15 | FFQ-6 | Sleep quality and durationScreen timeSelf-reported physical activity | Measured weight and height BMI | ↓ Sleep duration ↑ Sleep quality ↓ Physical activity ↑ Screen time ↓ fruit juices, carbonated sugar sweetened/diet drinks, meats ↓ canned food, fast f ood, snacks ↑ protein intake ↑ sweets | Non-significant changes |
| Medrano et al., 2020 [22] | Spain | Longitudinal cohort study (MUGI project) | 291 | 8–16 | Adherence to Mediterranean diet (KIDMED) | Physical Activity and screen time during leisure were assessed by “The Youth Activity Profile” questionnaire (YAP) | Measured Height and Weight BMI Body Composition (BIA) Waist circumference | ↓ Physical activity ↑ Screen time ↑ KIDMED score | Non-significant changes |
| Koletzko et al., 2021 [23] | Germany | Cross sectional Online survey | 1000 parents with at least 1 child<14 y living in the same household | 0–14 | Questionnaire on diet habits | Questionnaire on Physical activity | Self-reported weight gain | ↑ Fruit and Vegetables ↑ Carbohydrates ↑ Salty/sweet snacks ↑ Soft drinks ↓ Physical activity ↑ cooking at home | ↑ Body weight in 9% of the children |
| Identity | Country | Study Design | Participants (N) | Age Range (Years) | Diet Assessment | Lifestyle Assessment | Cardiometabolic Risk Factors | Outcome in Diet and Lifestyle | Outcome in Cardiometabolic Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qiu et al., 2021 [16] | China | Cohort study | 445 | 7–12 | Questionnaire on diet | Questionnaires on lifestyle | Blood pressure measured | N/A | ↑% with Elevated Blood pressure |
| Maltoni et al., 2021 [17] | Italy | Cross sectional | 51 | 10–18 | Questionnaire on nutrition | Physical activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) sort form | Blood pressure | ↑ Sedentary behavior ↓ Physical activity | ↓% with Elevated blood pressure |
| Minuto et al., 2021 [24] | Italy | Retrospective observational cohort study | 202 101 (0–18) with T1DM | 6–39 | N/A | Self-reported physical activity | GCM for glucose monitoring HbA1c | ↓ Physical activity | Improved glycemic control |
| Peng Cheng et al., 2021 [25] | Malaysia | Cross sectional | 123 (93 patients with T1DM and 30 with T2DM) | 0–18 | Standardized questionnaire for diet and lifestyle | Standardized questionnaire for lifestyle Physical activity assessment with PAQ-C for children and PAQ-A for older children; | HbA1c | ↓ meal frequency (skipping breakfast) ↓ physical activity ↑ screen time ↑ sleep duration | ↑ HbA1c in T2DM and pubertal adolescents ↓ HbA1c in pre-pubertal T1DM children ↑ Weight and BMI SDS in T1DM ↓ Weight and BMI SDS in T2DM |
| Wu et al., 2021 [26] | China | Observational study Telephone interview | 43 with T1DM | 0–18 | Questionnaire for dietary intake | Questionnaire for, physical exercise, sleep habits and emotions | GCM for glucose monitoring HbA1c | ↑ number of snacks, ↑ sleep duration ↑ time for diabetes management ↓ physical activity | No significant changes |
| Al Agha et al., 2021 [27] | Saudi Arabia | Cross sectional study | 150 with T1DM | 2–18 | Questionnaire for dietary habits | Questionnaire for physical activity and mood | Blood pressure (systolic and diastolic) HbA1c CGM | ↓ physical activity ↑ consumption of carbohydrates and fast food ↓ mood | ↑ HbA1c ↑ BMI↑ Blood pressure |
| Turan et al., 2021 [28] | Turkey | Cross sectional | 100 with T1DM | 3–18 | Questionnaire on snack and meal frequency, CHO consumption | Physical Activity Questionnaire-A (PAQ-A) or Physical Activity Questionnaire-C (PAQ-C) | HbA1c BMI | ↑ consumption of carbohydrates Delayed sleep times | ↑ HbA1c ↓ No of hypoglycaemic events |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karatzi, K.; Poulia, K.-A.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Zampelas, A. The Impact of Nutritional and Lifestyle Changes on Body Weight, Body Composition and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents during the Pandemic of COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Children 2021, 8, 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121130
Karatzi K, Poulia K-A, Papakonstantinou E, Zampelas A. The Impact of Nutritional and Lifestyle Changes on Body Weight, Body Composition and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents during the Pandemic of COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Children. 2021; 8(12):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121130
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaratzi, Kalliopi, Kalliopi-Anna Poulia, Emilia Papakonstantinou, and Antonis Zampelas. 2021. "The Impact of Nutritional and Lifestyle Changes on Body Weight, Body Composition and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents during the Pandemic of COVID-19: A Systematic Review" Children 8, no. 12: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121130
APA StyleKaratzi, K., Poulia, K. -A., Papakonstantinou, E., & Zampelas, A. (2021). The Impact of Nutritional and Lifestyle Changes on Body Weight, Body Composition and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents during the Pandemic of COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Children, 8(12), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121130