Change in Pediatric Health Care Spending and Drug Utilization during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differences in the Incidence of Communicable Respiratory Diseases between 2019 and 2020
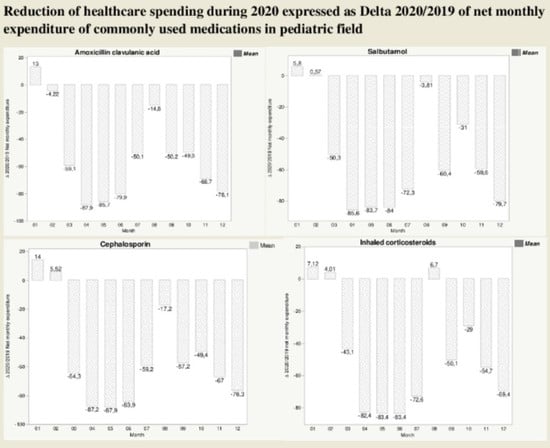
3.2. Differences in Net Expenditure of Common Pediatric Drugs between 2019 and 2020
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization Press Conference. The World Health Organization (WHO) Has Officially Named the Disease Caused by the Novel Coronavirus as COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergen-cies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 11 February 2020).
- Jefferson, T.; Del Mar, C.B.; Dooley, L.; Ferroni, E.; Al-Ansary, L.A.; Bawazeer, G.A.; van Driel, M.L.; Nair, S.; Jones, M.A.; Thorning, S. Physical interventions to interrupt or reduce the spread of respiratory viruses: Systematic review. BMJ 2009, 339, b3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacIntyre, C.R.; Cauchemez, S.; Dwyer, D.E.; Seale, H.; Cheung, P.; Browne, G.; Fasher, M.; Wood, J.; Gao, Z.; Booy, R.; et al. Face Mask Use and Control of Respiratory Virus Transmission in Households. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decreto del Presidente del Consiglio dei Ministri. 9 March 2020. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2020/03/09/20A01558/sg (accessed on 28 October 2020).
- Remuzzi, A.; Remuzzi, G. COVID-19 and Italy: What next? Lancet 2020, 395, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Task Force COVID-19 del Dipartimento Malattie Infettive e Servizio di Informatica, Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Epidemia COVID-19, Aggiornamento nazionale: 18 settembre 2020. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/coronavirus/bollettino/Bollettino-sorveglianza-integrata-COVID-19_23-aprile-2020.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- Decreto del Presidente del Consiglio dei Ministri. 24 October 2020. Available online: www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2020/10/25/20A05861/sg (accessed on 24 October 2020).
- Santi, L.; Golinelli, D.; Tampieri, A.; Farina, G.; Greco, M.; Rosa, S.; Beleffi, M.; Biavati, B.; Campinoti, F.; Guerrini, S.; et al. Non-COVID-19 patients in times of pandemic: Emergency department visits, hospitalizations and cause-specific mortality in Northern Italy. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubrano, R.; Villani, A.; Berrettini, S.; Caione, P.; Chiara, A.; Costantino, A.; Formigari, R.; Franzoni, E.; Gattinara, G.C.; Giustardi, A.; et al. Point of view of the Italians pediatric scientific societies about the pediatric care during the COVID-19 lockdown: What has changed and future prospects for restarting. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2020, 46, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raucci, U.; Musolino, A.M.; Di Lallo, D.; Piga, S.; Barbieri, M.A.; Pisani, M.; Rossi, F.P.; Reale, A.; degli Atti, M.L.C.; Villani, A.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the Emergency Department of a tertiary children’s hospital. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pines, J.M.; Zocchi, M.S.; Black, B.S.; Carlson, J.N.; Celedon, P.; Moghtaderi, A.; Venkat, A.; US Acute Care Solutions Research Group. Characterizing pediatric emergency department visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 41, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, J.; Rakkar, J.; KAu, A.; Fuhrman, D.; Clark, R.; Horvat, C. Trends in US Pediatric Hospital Admissions in 2020 Compared with the Decade Before the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2037227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Brusselen, D.; De Troeyer, K.; Ter Haar, E.; Vander Auwera, A.; Poschet, K.; Van Nuijs, S.; Bael, A.; Stobbelaar, K.; Verhulst, S.; Van Herendael, B.; et al. Bronchiolitis in COVID-19 times: A nearly absent disease? Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotulo, G.A.; Percivale, B.; Molteni, M.; Naim, A.; Brisca, G.; Piccotti, E.; Castagnola, E. The impact of COVID-19 lockdown on infectious diseases epidemiology: The experience of a tertiary Italian Pediatric Emergency Department. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 43, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baraldi, E.; Lanari, M.; Manzoni, P.; Rossi, G.A.; Vandini, S.; Rimini, A.; Romagnoli, C.; Colonna, P.; Biondi, A.; Biban, P.; et al. Inter-society consensus document on treatment and prevention of bronchiolitis in newborns and infants. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2014, 40, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention (2020 Update). Available online: http://ginasthma.org (accessed on 12 November 2021).
- Bradley, J.S.; Byington, C.L.; Shah, S.S.; Alverson, B.; Carter, E.R.; Harrison, C.; Kaplan, S.L.; Mace, S.E.; McCracken, G.H.; Moore, M.R.; et al. The Management of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Infants and Children Older Than 3 Months of Age: Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, e25–e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, M.; Clark, J.; Coote, N.; Fletcher, P.; Harnden, A.; Mckean, M.; Thomson, A.; British Thoracic Society Standards of Care Committee. British Thoracic Society guidelines for the management of community acquired pneumonia in children: Update 2011. Thorax 2011, 66 (Suppl. S2), ii1–ii23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gates, A.; Gates, M.; Vandermeer, B.; Johnson, C.; Hartling, L.; Johnson, D.W.; Klassen, T.P. Glucocorticoids for croup in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 8, CD001955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiq, S.; Grainger, J. The diagnosis and management of acute otitis media: American Academy of Pediatrics Guidelines 2013. Arch. Dis. Child.-Educ. Pract. Ed. 2015, 100, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantell, R.H. Pharyngitis: Diagnosis and Management. Pediatr. Rev. 1981, 3, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isoldi, S.; Mallardo, S.; Marcellino, A.; Bloise, S.; Dilillo, A.; Iorfida, D.; Testa, A.; Del Giudice, E.; Martucci, V.; Sanseviero, M.; et al. The comprehensive clinic, laboratory, and instrumental evaluation of children with COVID-19: A 6-months prospective study. J. Med Virol. 2021, 93, 3122–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloise, S.; Marcellino, A.; Testa, A.; Dilillo, A.; Mallardo, S.; Isoldi, S.; Martucci, V.; Sanseviero, M.T.; Del Giudice, E.; Iorfida, D.; et al. Serum IgG levels in children 6 months after SARS-CoV-2 infection and comparison with adults. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 3335–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, D.K.; Foley, D.A.; Minney-Smith, C.A.; Martin, A.C.; Mace, A.O.; Sikazwe, C.T.; Le, H.; Levy, A.; Blyth, C.C.; Moore, H.C. The impact of COVID-19 public health measures on detections of influenza and respiratory syncytial virus in children during the 2020 Australian winter. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 28, ciaa1475. [Google Scholar]
- Polcwiartek, L.B.; Polcwiartek, C.; Andersen, M.P.; Østergaard, L.; Broccia, M.D.; Gislason, G.H.; Køber, L.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Schou, M.; Fosbøl, E.; et al. Consequences of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) lockdown on infection-related hospitalizations among the pediatric population in Denmark. Eur. J. Pediatrics 2021, 180, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matera, L.; Nenna, R.; Rizzo, V.; Morini, F.A.; Banderali, G.; Calvani, M.; Calvi, M.; Cozzi, G.; Fabiani, E.; Falsaperla, R.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic Impact on Pediatric Emergency Rooms: A Multicenter Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiapinotto, S.; Sarria, E.E.; Mocelin, H.T.; Lima, J.A.; Mattiello, R.; Fischer, G.B. Impact of non-pharmacological initiatives for COVID-19 on hospital admissions due to pediatric acute respiratory illnesses. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2021, 39, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.S.; Baggio, D.M.; Fascina, L.P.; Prado, C.D. Impact of social isolation due to COVID-19 on the seasonality of pediatric respiratory diseases. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viganò, M.; Mantovani, L.; Cozzolino, P.; Harari, S. Correction to: Treat all COVID 19-positive patients, but do not forget those negative with chronic diseases. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2020, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blecker, S.; Jones, S.A.; Petrilli, C.M.; Admon, A.J.; Weerahandi, H.; Francois, F.; Horwitz, L.I. Hospitalizations for Chronic Disease and Acute Conditions in the Time of COVID-19. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, N.G.; Custovic, A.; Deschildre, A.; Mathioudakis, A.G.; Phipatanakul, W.; Wong, G.; Xepapadaki, P.; Agache, I.; Bacharier, L.; Bonini, M.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 on Pediatric Asthma: Practice Adjustments and Disease Burden. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 2592–2599.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guijon, O.L.; Morphew, T.; Ehwerhemuepha, L.; Galant, S.P. Evaluating the impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on asthma morbidity: A comprehensive analysis of potential influencing factors. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 127, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Zviedrite, N.; Uzicanin, A. Effectiveness of workplace social distancing measures in reducing influenza transmission: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Figueroa, G.P.; Ojo, O. The effectiveness of alcohol-based gel for hand sanitising in infection control. Br. J. Nurs. 2018, 27, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, A.E.; Murray, G.F.; Perez, V.; Coulborn, R.M.; Davis, B.M.; Uddin, M.; Shay, D.; Waterman, S.H.; Monto, A.S. Mask use, hand hygiene, and seasonal influenza-like illness among young adults: A randomized intervention trial. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cowling, B.J.; Chan, K.-H.; Fang, V.J.; Cheng, C.K.; Fung, R.O.; Wai, W.; Sin, J.; Seto, W.H.; Yung, R.; Chu, D.W.; et al. Facemasks and Hand Hygiene to Prevent Influenza Transmission in Households. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacIntyre, C.R.; Chughtai, A.A. A rapid systematic review of the efficacy of face masks and respirators against coronaviruses and other respiratory transmissible viruses for the community, healthcare workers and sick patients. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2020, 108, 103629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, R.; Dana, T.; Jungbauer, R.; Weeks, C.; McDonagh, M.S. Masks for Prevention of Respiratory Virus Infections, Including SARS-CoV-2, in Health Care and Community Settings: A Living Rapid Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pan, L.; Tang, S.; Ji, J.; Shi, X. Mask use during COVID-19: A risk adjusted strategy. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngonghala, C.N.; Iboi, E.; Eikenberry, S.; Scotch, M.; MacIntyre, C.R.; Bonds, M.H.; Gumel, A.B. Mathematical assessment of the impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions on curtailing the 2019 novel Coronavirus. Math. Biosci. 2020, 325, 108364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, T.; Foxlee, R.; Del Mar, C.; Dooley, L.; Ferroni, E.; Hewak, B.; Prabhala, A. Interventions for the interruption or reduction of the spread of respiratory viruses. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, 4, CD006207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach, L.J.; Straney, L.; Gelbart, B.; Alexander, J.; Franklin, D.; Beca, J.; Whitty, J.A.; Ganu, S.; Wilkins, B.; Slater, A.; et al. Burden of disease and change in practice in critically ill infants with bronchiolitis. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonova, E.N.; Rycroft, C.E.; Ambrose, C.S.; Heikkinen, T.; Principi, N. Burden of paediatric influenza in Western Europe: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lubrano, R.; Bloise, S.; Testa, A.; Marcellino, A.; Dilillo, A.; Mallardo, S.; Isoldi, S.; Martucci, V.; Sanseviero, M.; Del Giudice, E.; et al. Assessment of Respiratory Function in Infants and Young Children Wearing Face Masks during the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e210414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenah, E.; Chao, D.L.; Matrajt, L.; Halloran, M.E.; Longini, I.M., Jr. The Global Transmission and Control of Influenza. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esposito, S.; Principi, N. To mask or not to mask children to overcome COVID-19. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 179, 1267–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manisalidis, I.; Stavropoulou, E.; Stavropoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poole, S.; Brendish, N.J.; Tanner, A.R.; Clark, T.W. Physical distancing in schools for SARS-CoV-2 and the resurgence of rhinovi-rus. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, e92–e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fegert, J.M.; Vitiello, B.; Plener, P.L.; Clemens, V. Challenges and burden of the Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic for child and adolescent mental health: A narrative review to highlight clinical and research needs in the acute phase and the long return to normality. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2020, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Roy, D.; Sinha, K.; Parveen, S.; Sharma, G.; Joshi, G. Impact of COVID-19 and lockdown on mental health of children and adolescents: A narrative review with recommendations. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 293, 113429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Shao, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Miao, J.; Yang, X.; Zhu, G. An investigation of mental health status of children and adolescents in china during the outbreak of COVID-19. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 275, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubrano, R.; Bloise, S.; Marcellino, A.; Ciolli, C.P.; Testa, A.; De Luca, E.; Dilillo, A.; Mallardo, S.; Isoldi, S.; Martucci, V.; et al. Effects of N95 Mask Use on Pulmonary Function in Children. J. Pediatr. 2021, 237, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubrano, R.; Bloise, S.; Marcellino, A.; Ciolli, C.P.; Testa, A.; De Luca, E.; Dilillo, A.; Mallardo, S.; Isoldi, S.; Martucci, V.; et al. Assessment of respiratory function in children wearing a N95 mask with or without an exhalation valve: Data compared. Data Brief 2021, 39, 107550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, M.; Rutherford, G.W. Facial Masking for Covid-19—Potential for “Variolation” as We Await a Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Months | 2019 Median (IQR) | 2020 Median (IQR) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 2.5 (0–6.25) | 2 (0–7) | 0.80 |
| February | 3 (1–8) | 2 (0–6) | 0.34 |
| Start of first lockdown | |||
| March | 1 (0–2) | 0 (0–1) | 0.0136 |
| April | 0.5 (0–3.25) | 0 (0–0) | 0.0010 |
| May | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–0) | 0.0065 |
| End of first lockdown | |||
| June | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0.418 |
| July | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0.557 |
| August | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 1 |
| September | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0.483 |
| October | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–0) | 0.192 |
| Start of second lockdown | |||
| November | 0 (0–3.25) | 0 (0–0) | 0.0079 |
| December | 1 (0–2.5) | 0 (0–0) | 0.0019 |
| Months | 2019 Median (IQR) | 2020 Median (IQR) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 8.5 (4–15.5) | 6 (1.75–18.25) | 0.45 |
| February | 5.5 (2–16.5) | 5 (1.75–17.25) | 0.70 |
| Start of first lockdown | |||
| March | 7 (2.75–13.25) | 0 (0–4.25) | 0.0006 |
| April | 6 (3.75–11.25) | 0.5 (0–2) | <0.0001 |
| May | 5 (2–9.25) | 1 (0–2.25) | <0.0001 |
| End of first lockdown | |||
| June | 2.5 (1–6.5) | 0 (0–2) | 0.0002 |
| July | 1 (0–4) | 0 (0–2) | 0.1253 |
| August | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–0) | 0.1652 |
| September | 2 (0–4.25) | 0 (0–2) | 0.0235 |
| October | 4 (0–6) | 1 (0–4) | 0.060 |
| Start of second lockdown | |||
| November | 2 (1–8.5) | 0.5 (0–3.75) | 0.0295 |
| December | 4 (1–9.25) | 0 (0–2.25) | 0.0005 |
| Months | 2019 Median (IQR) | 2020 Median (IQR) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 14 (3–23.5) | 16.5 (8–28) | 0.39 |
| February | 14.5 (5.75–23) | 12 (6–25.25) | 0.86 |
| Start of first lockdown | |||
| March | 8 (5–20.75) | 2 (0.75–4.25) | <0.0001 |
| April | 8.5 (5.75–15.25) | 0 (0–0) | <0.0001 |
| May | 5 (2–13) | 0 (0–1) | <0.0001 |
| End of first lockdown | |||
| June | 3.5 (1–7.25) | 0 (0–0) | <0.0001 |
| July | 2 (0–4) | 0 (0–0) | 0.0002 |
| August | 0 (0–1.25) | 0 (0–0) | 0.049 |
| September | 2 (0–3.25) | 0 (0–2) | 0.055 |
| October | 4.5 (1–10) | 2 (0–3) | 0.052 |
| Start of second lockdown | |||
| November | 5 (2–15) | 1 (0–2) | 0.0002 |
| December | 6 (4–16.5) | 0.74 (0–4.25) | <0.0001 |
| Months | 2019 Median (IQR) | 2020 Median (IQR) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 2.5 (1–14.5) | 4 (1.75–12) | 0.70 |
| February | 4 (2–14.25) | 2.5 (0–10.25) | 0.29 |
| Start of first lockdown | |||
| March | 4 (1–11) | 0 (0–3) | 0.0005 |
| April | 2.5 (0.75–5.25) | 0 (0–0) | <0.0001 |
| May | 1.5 (0.75–4) | 0 (0–0) | <0.0001 |
| End of first lockdown | |||
| June | 1 (0–2) | 0 (0–0) | <0.0021 |
| July | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–0) | 0.123 |
| August | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–0.25) | 0.370 |
| September | 1 (0–4) | 0 (0–1) | 0.0058 |
| October | 3 (0–8.5) | 1 (0–3) | 0.0185 |
| Start of second lockdown | |||
| November | 2 (0–10) | 0 (0–2) | 0.0053 |
| December | 2.5 (1–7) | 0.5 (0–3) | 0.0118 |
| Months | 2019 Median (IQR) | 2020 Median (IQR) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 10 (6–20.5) | 10.5 (5–21) | 0.98 |
| February | 15.5 (7.75–24.75) | 10 (5.5–20.75) | 0.24 |
| Start of first lockdown | |||
| March | 12.5 (6.75–25.75) | 3 (0–5) | <0.0001 |
| April | 8 (4–15.25) | 0 (0–1.25) | <0.0001 |
| May | 8.5 (4–12.75) | 0 (0–1) | <0.0001 |
| End of first lockdown | |||
| June | 5 (2.75–10.25) | 0.5 (0–2) | <0.0001 |
| July | 7.5 (3–16.25) | 3.5 (1–8) | 0.0274 |
| August | 4 (2–7.25) | 4 (0–8.25) | 0.49 |
| September | 3.5 (1.75–8.25) | 1 (0–3.25) | 0.0204 |
| October | 6.5 (2–11.25) | 3 (0–5.25) | 0.044 |
| Start of second lockdown | |||
| November | 7 (2.75–14.5) | 2 (0–4.25) | 0.0063 |
| December | 9 (4.75–15) | 2 (0–5.5) | <0.0001 |
| Months | 2019 Median (IQR) | 2020 Median (IQR) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 25.5 (18–47) | 26 (14.25–60.75) | 0.97 |
| February | 29 (17.75–36.5) | 19 (7.5–44) | 0.29 |
| Start of first lockdown | |||
| March | 29 (14–41.25) | 3.5 (0–6.25) | <0.0001 |
| April | 28 (10.75–43.25) | 0 (0–3.25) | <0.0001 |
| May | 18.5 (7–32) | 1 (0–4.25) | <0.0001 |
| End of first lockdown | |||
| June | 14.5 (4.75–27.25) | 1 (0–2.25) | <0.0001 |
| July | 9 (2.75–15.75) | 1 (0–2.25) | <0.0001 |
| August | 4 (1.5–12) | 2.5 (0–6.25) | 0.14 |
| September | 10.5 (3–16.5) | 2 (0–5.25) | 0.0010 |
| October | 16 (5.75–30.5) | 4 (1.75–12) | 0.0014 |
| Start of second lockdown | |||
| November | 17.5 (5.75–31.5) | 3 (1.75–12.25) | 0.0003 |
| December | 20 (9–36.75) | 2 (0.75–12) | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lubrano, R.; Del Giudice, E.; Marcellino, A.; Ventriglia, F.; Dilillo, A.; De Luca, E.; Mallardo, S.; Isoldi, S.; Martucci, V.; Sanseviero, M.; et al. Change in Pediatric Health Care Spending and Drug Utilization during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Children 2021, 8, 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121183
Lubrano R, Del Giudice E, Marcellino A, Ventriglia F, Dilillo A, De Luca E, Mallardo S, Isoldi S, Martucci V, Sanseviero M, et al. Change in Pediatric Health Care Spending and Drug Utilization during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Children. 2021; 8(12):1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121183
Chicago/Turabian StyleLubrano, Riccardo, Emanuela Del Giudice, Alessia Marcellino, Flavia Ventriglia, Anna Dilillo, Enrica De Luca, Saverio Mallardo, Sara Isoldi, Vanessa Martucci, Mariateresa Sanseviero, and et al. 2021. "Change in Pediatric Health Care Spending and Drug Utilization during the COVID-19 Pandemic" Children 8, no. 12: 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121183
APA StyleLubrano, R., Del Giudice, E., Marcellino, A., Ventriglia, F., Dilillo, A., De Luca, E., Mallardo, S., Isoldi, S., Martucci, V., Sanseviero, M., Iorfida, D., Malvaso, C., Cerimoniale, G., Ragni, G., Grandinetti, A. L., Arenare, L., & Bloise, S. (2021). Change in Pediatric Health Care Spending and Drug Utilization during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Children, 8(12), 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121183