The Efficacy of Phenolic Compound Extraction from Potato Peel Waste
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. CSE
2.3. IUAE
2.4. DUAE
2.5. Measurement of TPC in Potato Peel Extracts
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
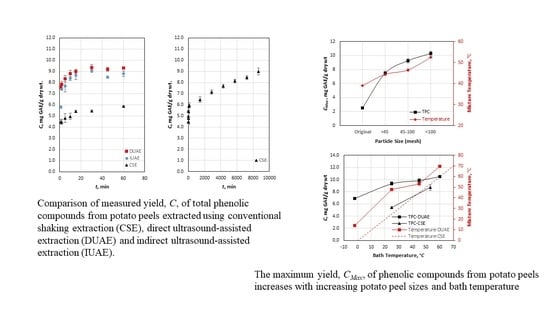
3.1. Yield Curves of Selected Methods
3.2. Modeling of the Yield Curves
3.3. Efficacies of the Extracting Methods
3.4. Factors Affecting CMax
3.4.1. Effects of Particle Size
3.4.2. Effects of Bath Temperature
3.4.3. Effects of the Solvent-to-Particle Ratio
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calcio Gaudino, E.; Colletti, A.; Grillo, G.; Tabasso, S.; Cravotto, G. Emerging Processing Technologies for the Recovery of Valuable Bioactive Compounds from Potato Peels. Foods 2020, 9, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, H.; Riciputi, Y.; Capanoglu, E.; Caboni, M.F.; Verardo, V. Phenolic Compounds in the Potato and Its Byproducts: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, B.; Tiwari, B.K.; Hossain, M.B.; Rai, D.K.; Brunton, N.P. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of polyphenols from potato peels: Profiling and kinetic modelling. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.; Singh, J.; Singh, J.P.; Kaur, A.; Singh, N. Phenolic compounds in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) peel and their health-promoting activities. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2273–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albishi, T.; John, J.A.; Al-Khalifa, A.S.; Shahidi, F. Phenolic content and antioxidant activities of selected potato varieties and their processing by-products. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Weshahy, A.; Rao, A.V. Isolation and characterization of functional components from peel samples of six potatoes varieties growing in Ontario. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, K.B.; Chandran, J.; Dhanya, R.; Krishna, P.; Jayamurthy, P.; Nisha, P. A comparative evaluation of antioxidant and antidiabetic potential of peel from young and matured potato. Food Biosci. 2015, 9, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sabally, K.; Kubow, S.; Donnelly, D.J.; Gariepy, Y.; Orsat, V.; Raghavan, G.S. Microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic antioxidants from potato peels. Molecules 2011, 16, 2218–22132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohdaly, A.A.A.; Sarhan, M.A.; Smetanska, I.; Mahmoud, A. Antioxidant properties of various solvent extracts of potato peel, sugar beet pulp and sesame cake. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Esch, G.J. Toxicology of tert-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ). Food Chem. Toxicol. 1986, 24, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xiong, X.; He, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Analysism occurrence, toxicity and environmental health risks of synthetic phenolic antioxidants: A review. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samotyja, U. Potato peel as a sustainable resource of natural antioxidants for the food industry. Potato Res. 2019, 62, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Lin, A.H.-M.; Han, Q.; Xu, Q. Evaluation of Direct Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Potato Peels. Processes 2020, 8, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, P.P.; Das, P.; Badwaik, L.S. Ultrasound treated potato peel and sweet lime pomace based biopolymer film development. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 36, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez Maldonado, A.F.; Mudge, E.; Gänzle, M.G.; Schieber, A. Extraction and fractionation of phenolic acids and glycoalkaloids from potato peels using acidified water/ethanol-based solvents. Food Res. Int. 2014, 65, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.G.; Xu, H.Y.; Ma, Q.; Cao, Y.; Ma, J.N.; Ma, C.M. Isolation, identification and quantification of unsaturated fatty acids, amides, phenolic compounds and glycoalkaloids from potato peel. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2425–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade Lima, M.; Andreou, R.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Chatzifragkou, A. Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Potato (Solanum tuberosum) Peels. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galhano dos Santos, R.; Ventura, P.; Bordado, J.C.; Mateus, M.M. Valorizing potato peel waste: An overview of the latest publications. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2016, 15, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wang, S.; Rakita, M.; Wang, Y.; Han, Q.; Xu, Q. Effect of ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds on the characteristics of walnut shells. Food Nutr. Sci. 2018, 9, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacotet-Navarro, M.; Rombaut, N.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Danguien, M.; Bily, A.; Chemat, F. Ultrasound versus microwave as green processes for extraction of rosmarinic, carnosic and ursolic acids from rosemary. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 27, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, B.; Tiwari, B.K.; Hossain, M.B.; Brunton, N.P.; Rai, D.K. Recent advances on application of ultrasound and pulsed electric field technologies in the extraction of bioactives from agro-industrial by-products. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Fernandez, J.S.; Seker, A.; Davaritouchaee, M.; Gu, X.; Chen, S. Recovering Valuable Bioactive Compounds from Potato Peels with Sequential Hydrothermal Extraction. Waste Biomass Valor. 2021, 12, 1465–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Riaz, S.; Sameen, A.; Naumovski, N.; Iqbal, M.W.; Rehman, A.; Mehany, T.; Zeng, X.-A.; Manzoor, M.F. The Disposition of Bioactive Compounds from Fruit Waste, Their Extraction, and Analysis Using Novel Technologies: A Review. Processes 2022, 10, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.M.K.; Akanbi, T.O.; Kirkman, T.; Nguyen, M.H.; Vuong, Q.V. Recovery of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidants from Coffee Pulp (Coffea canephora) Waste Using Ultrasound and Microwave-Assisted Extraction. Processes 2022, 10, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirok, N.T.; Yıkmış, S. Combined Effect of Ultrasound and Microwave Power in Tangerine Juice Processing: Bioactive Compounds, Amino Acids, Minerals, and Pathogens. Processes 2022, 10, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaberrieta, I.; Mellinas, C.; Jiménez, A.; Garrigós, M.C. Recovery of Antioxidants from Tomato Seed Industrial Wastes by Microwave-Assisted and Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction. Foods 2022, 11, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, M. An Empirical Model for the Description of Moisture Sorption Curves. J. Food Sci. 1988, 53, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramov, O.V. High-Intensity Ultrasonics Theory and Industrial Applications; Gordon & Breach: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Xu, C.L.; Han, Q. Effect of ultrasonic vibration on unmixed zone formation. Scripta Mater. 2006, 55, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q. Ultrasonic Processing of Materials. Metall. Mater. Trans B 2015, 46, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rakita, M.; Han, Q. Influence of pressure field in melts on the primary nucleation in solidification processing. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2017, 48, 2232–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameter | DUAE | IUAE | CSE (60 Min) | CSE (6 Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1, min/(mg GAE/g dry wt.) | 0.0483 | 0.0459 | 0.1985 | 14.249 |
| k2, 1/(mg GAE/g dry wt.) | 0.107 | 0.1136 | 0.1696 | 0.1166 |
| q0, (mg GAE/g dry wt.)/min | 20.70 | 21.79 | 5.04 | 0.07 |
| CP, mg GAE/g dry wt. | 9.346 | 8.803 | 5.896 | 8.576 |
| R2 | 0.9999 | 0.9989 | 0.9985 | 0.9928 |
| CMax, mg GAE/g dry wt. | 9.30 | 9.09 | 5.86 | 9.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Q.; Wang, S.; Milliron, H.; Han, Q. The Efficacy of Phenolic Compound Extraction from Potato Peel Waste. Processes 2022, 10, 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112326
Xu Q, Wang S, Milliron H, Han Q. The Efficacy of Phenolic Compound Extraction from Potato Peel Waste. Processes. 2022; 10(11):2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112326
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Qin, Shusheng Wang, Heather Milliron, and Qingyou Han. 2022. "The Efficacy of Phenolic Compound Extraction from Potato Peel Waste" Processes 10, no. 11: 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112326
APA StyleXu, Q., Wang, S., Milliron, H., & Han, Q. (2022). The Efficacy of Phenolic Compound Extraction from Potato Peel Waste. Processes, 10(11), 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112326