Application of the EGSB-CMBR Process to High-Concentration Organic Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Water Volumes and Water Quality
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Inoculating Sludge and Starting Method
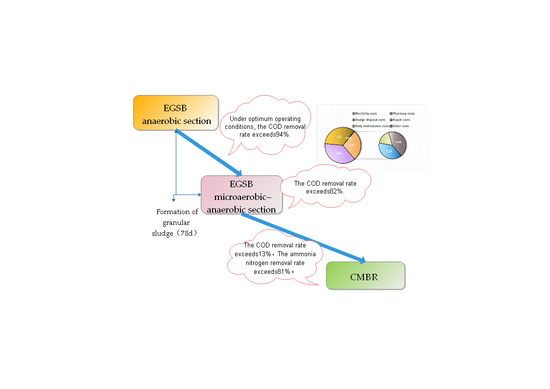
2.4. Process Flow Diagrams
2.4.1. EGSB
2.4.2. CMBR
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Operational Effect of the EGSB Reactor in the Commissioning Stage
3.2. Formation of Granular Sludge
3.3. CMBR
3.4. Operation Phase
4. Operation Cost Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, B.; Chen, Y. Research progress of high concentration organic wastewater treatment technology. Chem. Manag. 2021, 9, 40–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Koga, Y.; Rouse, J.D.; Furukawa, K.J. Trace elements enhance biofilm formation in UASB reactor for solo simple molecule wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9296–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Y. Fast start-up of expanded granular sludge bed (EGSB) reactor using stored Anammox sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z. Partial nitrification coupled with anammox in a biofilter reactor (BR) of large height-to-diameter ratio for treatment of wastewater with low C/N. Process. Biochem. 2021, 104, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Li, J.; Meng, J.; Li, J.; Avinash, K.J.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of reflux ratio on the anaerobic sludge and microbial social behaviors in an expanded granular sludge bed reactor: From the perspective of acyl-homoserine lactones-mediated quorum sensing. Bioresour. Technol 2021, 337, 125360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdi, M.; Garcia, J.L. Comparison between the anaerobic filter and anaerobic contact process for fermented olive mill wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol 1991, 38, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Ward, A.J.; Ambye, J.M.; Møller, H.B. Pilot-Scale anaerobic digestion of by-product liquid (brown juice) from grass protein extraction using an un-heated anaerobic filter. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 146, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Zhang, H. Optimization of sensing performance in an integrated dual sensors system combining microbial fuel cells and up-flow anaerobic sludge bed reactor. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.H.; Luo, G.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Li, A. Substrate competition and microbial function in sulfate-reducing internal circulation anaerobic reactor in the presence of nitrate. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granatto, C.F.; Grosseli, G.M.; Sakamoto, I.K.; Fadini, P.S.; Varesche, M.B. Influence of cosubstrate and hydraulic retention time on the removal of drugs and hygiene products in sanitary sewage in an anaerobic Expanded Granular Sludge Bed reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, C.; Shen, J.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Wang, K.; Zuo, J. Performance and microbial community of an expanded granular sludge bed reactor in the treatment of cephalosporin wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, A.D.; Silva, E.L. Hydrogen production from sugarcane juice in expanded granular sludge bed reactors under mesophilic conditions: The role of homoacetogenesis and lactic acid production. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 138, 111586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Huo, J. Process characteristics and operational performance of anaerobic granular sludge expansion bed (EGSB). Ind. Water Wastewater 1999, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Tian, K.; Xie, P.; Ren, X.; Li, Y.; Kou, Y.; Chon, K.; Hwang, M.H.; Ko, M.H. Insights into the minimization of excess sludge production in micro-aerobic reactors coupled with a membrane bioreactor: Characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fida, Z.; Price, W.E.; Pramanik, B.K.; Dhar, B.R.; Kumar, M.; Jiang, G.; Hai, F.I. Reduction of excess sludge production by membrane bioreactor coupled with anoxic side-stream reactors. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 28, 111919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Long, F.; Zheng, B. A pilot studied on the treatment of low concentration organic wastewater using biofilm process. Environ. Sci. Res. 2007, 2, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, M.B.; Zhang, Z. Ceramic membrane technology for water and wastewater treatment: A critical review of performance, full-scale applications, membrane fouling and prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Fan, X. Application of flat plate ceramic membrane MBR process in rural wastewater treatment. China Water Supply Drain. 2021, 37, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Di, S.W. Potassium dichromate method for the determination of COD in wastewater. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2017, 15, 113–114. [Google Scholar]
- State Environmental Protection Administration. Methods of Analysis for Water and Wastewater Monitoring, 3rd ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 154–169. [Google Scholar]
- Long, P.; Yang, C.; Pu, W.; Yang, J.; Bai, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, G.; Li, C. Cultivation and Characteristics of Aerobic Granular Sludge in SFBR. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, W. Treatment of high-concentration wastewater from an oil and gas field via a paired sequencing batch and ceramic membrane reactor. Int. J. Environ. Res. Pub. Health 2020, 17, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Zheng, L.; Ye, C.; Zhou, Z.; Baosen, N.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H. Unveiling organic loading shock-resistant mechanism in a pilot-scale moving bed biofilm reactor-assisted dual-anaerobic-anoxic/oxic system for effective municipal wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol 2022, 347, 126339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fariaa, C.V.; Souzab, D.F.; Pontesb, T.M.; Amaralc, M.C.; Fonsecaa, F.V. Strategies of anaerobic sludge granulation in an EGSB reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, P. New technology for the treatment of molasses alcoholic wastewater. Guanghou Environ. Sci. 2006, 3, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Li, S. Kinetic Competition between Methanogenic and Sulfate-reducing Bacteria in Anaerobic Mixed Cultures I. A model and experimental approach for kinetic presumptions. J. Zhongshan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2003, 42, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Bai, J. Mechanism of high contaminant removal performance in the expanded granular sludge blanket (EGSB) reactor involved with granular activated carbon for low-strength wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Ma, H.; Kong, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y. Bulking and floatation of the anammox-HAP granule caused by low phosphate concentration in the anammox reactor of expanded granular sludge bed (EGSB). Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárecnas-Ruiz, C.D.; Carrillo-Reyes, J.; Arellano-García, L.; Celis, L.B.; Alatriste-Mondragón, F.; Elías, R.F. Pretreatment and upward liquid velocity effects over granulation in hydrogen-producing EGSB reactors. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 107, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Jiang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, W. Resource recovery from liquid digestate on swine wastewater by an ultrafiltration membrane bioreactor (UF-MBR) and reverse osmosis (RO) process. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| pH | COD (mg/L) | NH4+-N (mg/L) | Suspended Solids (SS) (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet | 4.74–6.88 | 65,000–80,000 | 200–400 | 2290–3440 |
| Effluent | 6-9 | 300 | 50 | 200 |
| Time | Average Particle Size/ mm | Sludge State | The Rising Flow Rate of Liquid in the Reactor (m/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Start | 0.392 | Flocculent | 1 |
| 14 days | 0.436 | Flocculent (small amounts of fine particles) | 1 |
| 43 days | 0.668 | Partially granulated sludge | 2 |
| 86 days | 1.556 | Uniform granular sludge | 3 |
| 120 days | 1.542 | Uniform granular sludge | 3 |
| pH | COD (mg/L) | NH4+-N (mg/L) | SS (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGSB anaerobic section | 6.42 | 16,800 | – | 2020 |
| EGSB microscopic section | 6.37 | 941 | 178.33 | 241 |
| CMBR | 7.59 | 162 | 33.79 | 143 |
| Total discharge | 7.55 | 141 | 33.03 | 83 |
| Project | Details | Fees (RMB 10,000/Year) | Cost per Ton of Water (CNY/Ton) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electricity costs | Electricity Tariff (0.75 CNY/kwh) | 4.25 | 4.66 |
| Pharmacy costs | Potassium dihydrogen phosphate, urea, sodium bicarbonate, microbial promoter (added as appropriate for the operation) Other agents (flocculant polyacrylamide, coagulant polymeric aluminum chloride, ferric chloride, etc. used in sludge dewatering machines) | 3.83 | 4.2 |
| Repair costs | Discounted at 2.2% of the original value of fixing assets | 1.21 | 1.33 |
| Daily maintenance costs | Routine maintenance of fixed assets, including maintenance of automatic control systems, a strong inspection of dosage instruments, preventive testing of electrical equipment, and the cost of materials used for some routine repairs. At 1% of the original value of fixed assets | 0.55 | 0.60 |
| Depreciation costs | Set useful life of 20 years, the residual value of assets at 10% | 2.475 | 2.71 |
| Sludge disposal costs | Costs for sludge discharge, sludge dewatering, sludge compaction, off-site transport, and environmentally sound landfill disposal during reactor operation | 560 | 0.08 |
| Other costs | For example, the water treatment process is used to flush various types of structures, membrane modules, treatment equipment water consumption, reactor operation, commissioning and routine maintenance of sewage, sludge test fee, greening costs, etc. | 1 | 1.48 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Jin, Y. Application of the EGSB-CMBR Process to High-Concentration Organic Wastewater Treatment. Processes 2022, 10, 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10051039
Zhang X, Wang D, Jin Y. Application of the EGSB-CMBR Process to High-Concentration Organic Wastewater Treatment. Processes. 2022; 10(5):1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10051039
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xuli, Dunqiu Wang, and Yue Jin. 2022. "Application of the EGSB-CMBR Process to High-Concentration Organic Wastewater Treatment" Processes 10, no. 5: 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10051039
APA StyleZhang, X., Wang, D., & Jin, Y. (2022). Application of the EGSB-CMBR Process to High-Concentration Organic Wastewater Treatment. Processes, 10(5), 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10051039