Production of High-Value Proteins under Stringent Cost Constraints—The Case of Hollow Fiber Technology for Cell Culture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cells
2.3. HF Bioreactor Setup
2.4. Continuous Cell Culture in HF Bioreactor
2.5. Batch Culture in Cell Culture Dishes
2.6. Glucose and L-Lactic Acid Measurements and Calculations
2.7. Quantification of mAbs
2.8. Estimation of Scale-Up Production and Cost
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of Cell Culture in the HF Bioreactor
3.2. Quantification of Antibody Production
3.3. Effect of Cell Number in the Inoculum
3.4. Cell Culture in Tissue Culture Plate Operated in Batch Mode
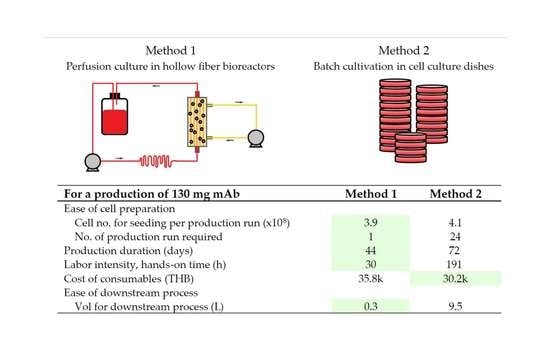
3.5. Scale-up Estimation and Cost Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lv, Z. A brief review of monoclonal antibody technology and its representative applications in immunoassays. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2018, 39, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, D.M.; Jones, S.D.; Levine, H.L. The therapeutic monoclonal antibody market. MAbs 2015, 7, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, L.R.; Trudel, L.; Lipman, N. Small-Scale Monoclonal Antibody Production in Vitro: Methods and Resources. Lab Anim. 1999, 28, 38–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jyothilekshmi, I.; Jayaprakash, N.S. Trends in Monoclonal Antibody Production Using Various Bioreactor Syst. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, E.; Kumar, A. Upstream processes in antibody production: Evaluation of critical parameters. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 46–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewar, V.; Voet, P.; Denamur, F.; Smal, J. Industrial implementation of in vitro production of monoclonal antibodies. ILAR J. 2005, 46, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griffiths, J.B. Animal cell culture processes--batch or continuous? J. Biotechnol. 1992, 22, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, A.; Koch, S.; Valley, U.; Emmrich, F.; Marx, U. Membrane-based cell culture systems--an alternative to in vivo production of monoclonal antibodies. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1999, 101, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Knazek, R.A.; Gullino, P.M.; Kohler, P.O.; Dedrick, R.L. Cell culture on artificial capillaries: An approach to tissue growth in vitro. Science 1972, 178, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitford, W.G.; Cadwell, J.J. Interest in hollow-fiber perfusion bioreactors is growing. BioProcess Int. 2009, 7, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Cadwell, J.J. New developments in hollow-fiber cell culture. Am. Biotechnol. Lab. 2004, 22, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Eghbali, H.; Nava, M.M.; Mohebbi-Kalhori, D.; Raimondi, M.T. Hollow fiber bioreactor technology for tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2016, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valdés, R.; González, M.; Geada, D. Assessment of a Protein-Free Medium Performance in Different Cell Culture Vessels using Mouse Hybridomas to Produce Monoclonal Antibodies. Pharm. Anal. Acta 2012, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gramer, M.J.; Britton, T.L. Selection and isolation of cells for optimal growth in hollow fiber bioreactors. Hybridoma 2000, 19, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowrey, D.; Murphy, S.; Goffe, R.A. A comparison of monoclonal antibody productivity in different hollow fiber bioreactors. J. Biotechnol. 1994, 36, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altshuler, G.L.; Dziewulski, D.M.; Sowek, J.A.; Belfort, G. Continuous hybridoma growth and monoclonal antibody production in hollow fiber reactors-separators. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1986, 28, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.H.; Liu, Y.X.; Kumari, M.; Wu, W.C. Multivariate analysis of metabolic parameters and optimization of antibody production using high cell density hybridoma in hollow fiber bioreactors. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, R.; Gonzalez, M.; González, Y.; Gómez, H.; García, J.; Alvarez, T.; Gómez, L.; Gavilondo, J. Production of an anti-HBsAg mouse IgG-2b κ monoclonal antibody in hollow fiber bioreactors using different cell culture media and operation modes. Biotecnol. Apl. 2005, 22, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Lowrey, D.; Murphy, S.; Goffe, R.A. The effect of intracapillary media feed protocols on hollow fiber cell culture. Biotechnol. Lett. 1993, 15, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramer, M.J.; Poeschl, D.M.; Conroy, M.J.; Hammer, B.E. Effect of harvesting protocol on performance of a hollow fiber bioreactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1999, 65, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, R.; Tamayo, A.; González, M.; Padilla, S.; Geada, D.; Ferro, W.; Milá, L.; Gómez, L.; Alemán, R.; Leyva, A. Production of a monoclonal antibody by ascites, hollow fiber system, and transgenic plants for vaccine production using CB. Hep-1 mAb as a study case. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2012, 17, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.E.; Costa, A.R.; Henriques, M.; Azeredo, J.; Oliveira, R. Technological progresses in monoclonal antibody production systems. Biotechnol. Prog. 2010, 26, 332–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Vijayasankaran, N.; Shen, A.Y.; Kiss, R.; Amanullah, A. Cell culture processes for monoclonal antibody production. MAbs 2010, 2, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komolpis, K.; Udomchokmongkol, C.; Phutong, S.; Palaga, T. Comparative production of a monoclonal antibody specific for enrofloxacin in a stirred-tank bioreactor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2010, 16, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyildiz-Tamis, D.; Nalbantsoy, A.; Elibol, M.; Deliloglu-Gurhan, S.I. Effect of Operating Conditions in Production of Diagnostic Salmonella Enteritidis O-Antigen-Specific Monoclonal Antibody in Different Bioreactor Systems. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.-J.; Ohashi, R.; Hamel, J.-F.P. Perfusion Culture of Hybridoma Cells for Hyperproduction of IgG2a Monoclonal Antibody in a Wave Bioreactor-Perfusion Culture System. Biotechnol. Prog. 2007, 23, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsang, S.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Galaev, I.Y.; Rakshit, S.K.; Holmdahl, R.; Mattiasson, B.; Kumar, A. Monoclonal antibody production using a new supermacroporous cryogel bioreactor. Biotechnol. Prog. 2007, 23, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermasvuori, R.; Hurme, M. Economic comparison of diagnostic antibody production in perfusion stirred tank and in hollow fiber bioreactor processes. Biotechnol. Prog. 2011, 27, 1588–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, U.; Embleton, M.J.; Fischer, R.; Gruber, F.P.; Hansson, U.; Heuer, J.; de Leeuw, W.A.; Logtenberg, T.; Merz, W.; Portetelle, D.; et al. Monoclonal Antibody Production. Altern. Lab. Anim. 1997, 25, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, A.; Paleari, R.; Leone, D.; Ivaldi, G. The relevance of hemoglobin F measurement in the diagnosis of thalassemias and related hemoglobinopathies. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 42, 1797–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pata, S.; Khummuang, S.; Pornprasert, S.; Tatu, T.; Kasinrerk, W. A simple and highly sensitive ELISA for screening of the alpha-thalassemia-1 Southeast Asian-type deletion. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2014, 35, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitford, W.; Cadwell, J.J. The potential application of hollow fiber bioreactors to large-scale production. BioPharm Int. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Omasa, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Nishikawa, T.; Shioya, S.; Suga, K.-I.; Uemura, S.-I.; Kitani, Y.; Imamura, Y. Enhancement of antibody production by growth factor addition in perfusion and hollow-fiber culture systems. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1995, 48, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Bioreactor System | Culture Volume | Culture Duration (Days) | mAb Concentration (mg/L) | Space-Time Yield, STY 1 (mg/L/day) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HF bioreactor | 12 mL ECS | 60–90 | 280–1200 | 144–236 | [6] |
| 32 | 1349–4456 | 209–866 | [13] | ||
| 60 mL ECS x 2 cartridge | 90–120 | 340–500 | 53–54 | [6] | |
| 27 | 1960 ± 250 | 2778 | [21] | ||
| Stirred tank bioreactor with cell retention device | 1.2 L | 15 | 73.6 | 61.4 | [24] |
| 2 L | 12 | 70.0 | 20.6 ± 0.8 | [25] | |
| Wave bioreactor | 1 L | 12 | 463.6 | 33.10 | [26] |
| Polymeric cryogel bioreactor | 10 mL bed volume | 55 | 130 | 287–325 | [27] |
| Parameters | Unnormalized | Normalized * (per Million Cells) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run 1 | Run 2 | Run 1 | Run 2 | |
| GUR, average (mg/h) | 1.2 | 5.3 | 0.112 | 0.105 |
| LPR, average (mg/h) | 0.55 | 1.1 | 0.050 | 0.022 |
| Total yield (mg) | 1.6 | 5.9 | 0.15 | 0.12 |
| Performance Indicators 1 | HF Bioreactor (15.5 mL ECS Volume) | Culture Dish (10 cm Dish) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| M2 | L3 | ||
| Antibody production phase | |||
| Number of runs (run) | 1 | 24 | 33 |
| Number of culture units (unit) | 2 | 950 | 1314 |
| Production time (days) | 44 | 72 | 132 |
| Hands-on time (h) | 30 | 191 | 263 |
| Full-time equivalent | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Serum media (L) | 0.3 | 9.5 | 13.1 |
| Base media (L) | 19.6 | - | - |
| Cost of consumables (THB) | 35.3 k | 18.2 k | 25.2 k |
| Seed culture preparation phase | |||
| Number of cells for seeding (×108) | 3.9 | 99.1 | 18.0 |
| Number of cells for seeding, per run (×108) | 3.9 | 4.1 | 0.54 |
| Preparation time (days) 2 | 8 | 9 | 6 |
| Serum media (L) | 0.3 | 6.2 | 1.3 |
| Cost of consumables (THB) | 0.5 k | 12.0 k | 2.6 k |
| Downstream process | |||
| Volume for the downstream process (L) | 0.3 | 9.5 | 13.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tantakitti, F.; Pata, S.; Laopajon, W.; Kasinrerk, W.; Hidalgo-Bastida, A. Production of High-Value Proteins under Stringent Cost Constraints—The Case of Hollow Fiber Technology for Cell Culture. Processes 2023, 11, 889. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030889
Tantakitti F, Pata S, Laopajon W, Kasinrerk W, Hidalgo-Bastida A. Production of High-Value Proteins under Stringent Cost Constraints—The Case of Hollow Fiber Technology for Cell Culture. Processes. 2023; 11(3):889. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030889
Chicago/Turabian StyleTantakitti, Faifan, Supansa Pata, Witida Laopajon, Watchara Kasinrerk, and Araida Hidalgo-Bastida. 2023. "Production of High-Value Proteins under Stringent Cost Constraints—The Case of Hollow Fiber Technology for Cell Culture" Processes 11, no. 3: 889. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030889
APA StyleTantakitti, F., Pata, S., Laopajon, W., Kasinrerk, W., & Hidalgo-Bastida, A. (2023). Production of High-Value Proteins under Stringent Cost Constraints—The Case of Hollow Fiber Technology for Cell Culture. Processes, 11(3), 889. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030889